lenses 10l
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
convex lenses
converge
f’ (secondary focus) is on the left side, principal f is on the right side
IN: parallel to pa OUT: through princiapl f
IN: through secondary f OUT: parallel to pa
IN and OUT through optical centre
concave lenses
diverge
principal f is on the left side, secondary is on right (where light seems to not focus)
IN: parallel to Pa, OUT: as if it had come through princiap f
IN: appears to pass through F’, OUT: parallel to PA
IN and OUT through optical centre.
sign convenctions if do, di, ho, hi, f, and m are postivite
do - always
di - real image, on the opposite side of the lens
ho - always
hi - upright
f - converging, convex
m - upright / virtual
if do di ho hi f m are negative
do - never
di - virtual (same side of lens)
ho - never
hi - inverted
f - divering, concave
m - inverted / real
where is the digital sensor in a camera on a ray diagram
between princiapl f and 2f, closer to 2f
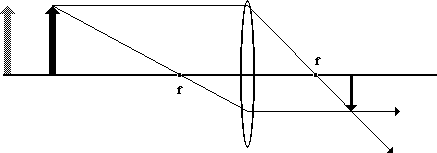
as the object moves closer to the lens, what happens to the height of the image? why? do cameras produce real or virtual images?
it will get bigger, so di gets smaller and the do gets better (inversely related)
produce real images bc because the light rays physically converge on the sensor or film to form the image.
This real image is inverted, but post-processing makes it appear upright for viewing.
The object distance gets smaller because the object is physically moving closer to the lens.
The image distance gets larger because the lens needs to move farther from the sensor to keep the image in focus.
Cameras have a fixed sensor position, so they adjust focus by moving the lens. When focusing on a nearby object, the lens is shifted farther from the sensor to ensure the light rays converge correctly on the sensor plane.
At the same time, the magnification increases, making the image larger on the sensor.
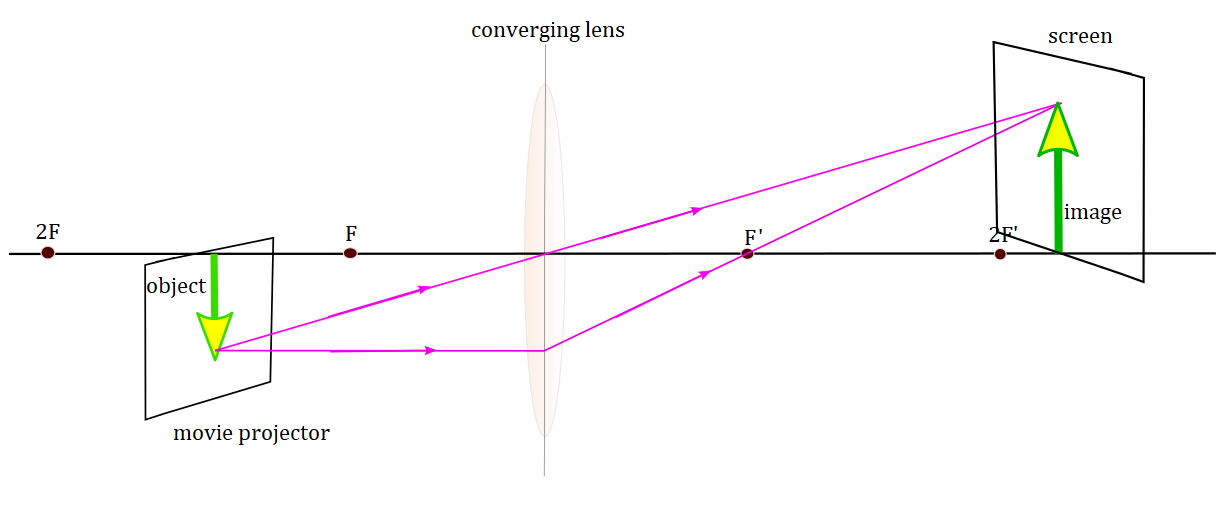
differences and similarties between cameras n projecters
sim - converging, real images that are inverted
differences - projecter is larger, inverted real image of a small object; the object (the film strip) lies between F ʹ and 2F ʹ, and the image is located beyond 2F.
camera - produce a smaller, inverted, real image of a large object; the object is beyond 2Fʹ (to focus properly), and the real image is located between F and 2F in the camera body
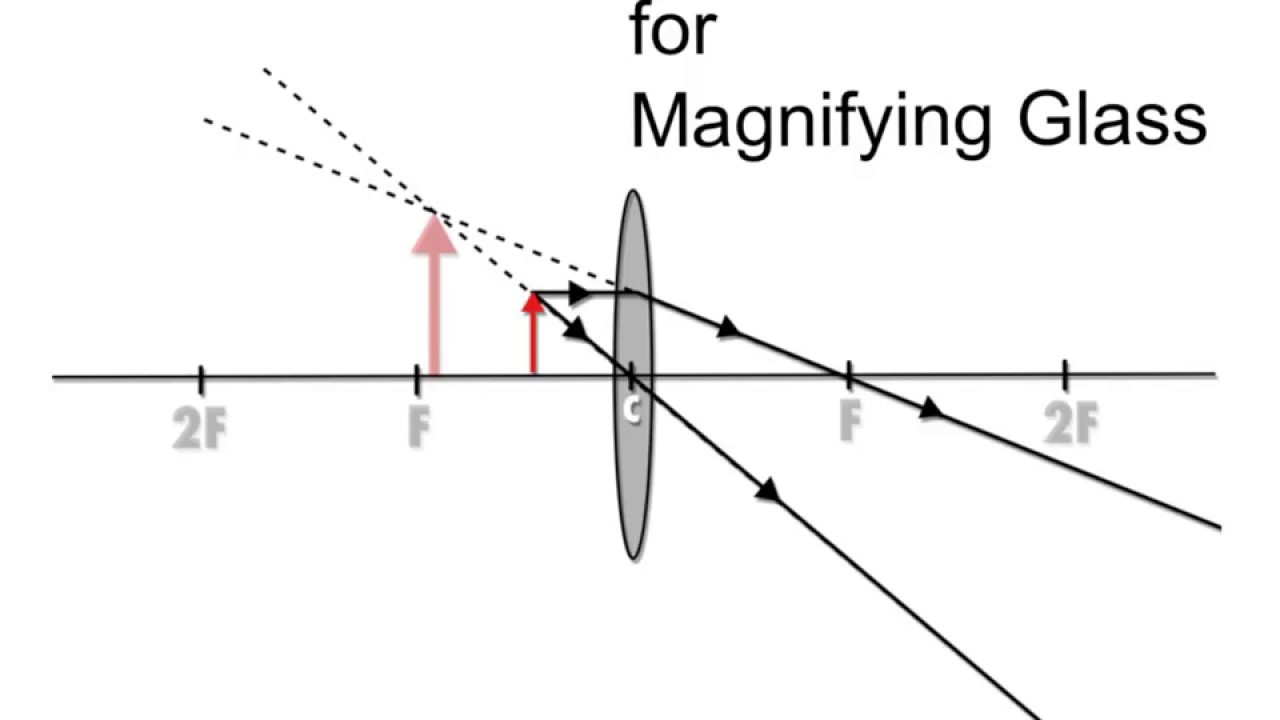
magnifying glass
A magnifying glass, or simple microscope, is a converging lens in
the object is located between the lens and Fʹ.
A larger, upright, virtual image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
similarites between a projecter and a magnifying glass and differences
sim - converging lens, produce a larger imagie
projecter -
the obkect (film strip) is between f’ and 2f’,
will produce an inverted real image
image will be produce beyond 2f and its inverted on the screen
magnifying glass -
object between lens and f’
will produce uprigt and virtual image on the same side as the object and
its upright when viewed through lens
for a camera to foucs on a second object further back, shoudld the lens move towards the object or backwards (further into the camera)
further into the camera
The lens needs to move backwards (closer to the sensor) to focus the image correctly.
The image distance decreases as the object distance increases.
This adjustment ensures that the light rays from the object still converge properly on the camera sensor, maintaining a sharp image.
what type of images can cameras use to caputre images
most of the time, real images
old school will alwasy have real images
digutal sensors can make it upright
why can we only focus on 1 point in a camera
because the lens focuses light rays to converge at a single point on the sensor.
Light rays from other distances will not focus properly, causing those objects to appear blurry.
The depth of field allows for a small range of objects to appear somewhat in focus, but only one specific point can be sharply focused at a time.
The point of the lens is to focus light, so it can only focus on one object at a time
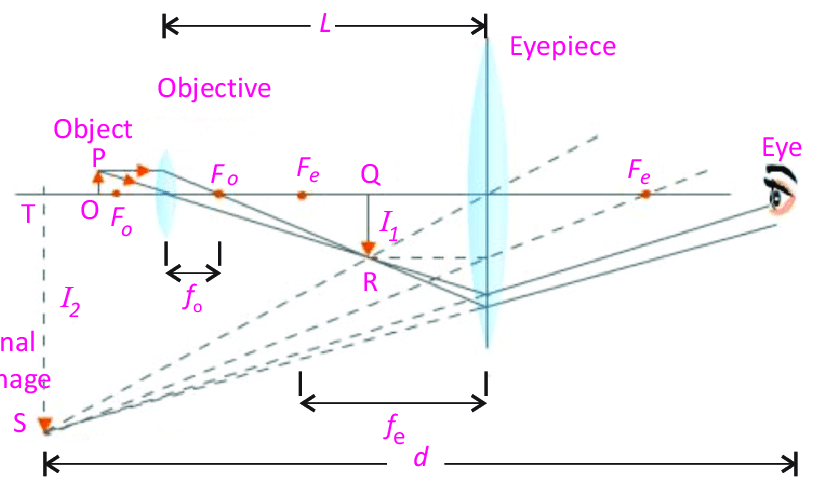
why would the objective lens and the eyepiece lens reversed in a compound microscope not work? why not?
bc it would prevent the microscope from forming a clear magnifed image, you need to create a real image first… the lens postion doesn’t matter tho.
the image formed would be out of focus or inverted,
and the lenses would not perform their intended roles properly in terms of magnification and image formation.
what type of image is produce by each len in a compound microscope? how do u calculate the magnication of an image using a cm?
objective lens is real
eyepiece lens is virtual
multiply the 2 M values
Why would the film strip in a movie projector never be located beyond 2F'?Where is the film strip actually located? Why?
If the film strip is beyond 2F’, the projected image will be too small and upside down.
The film strip is located between F′ and 2F′ to create a large, inverted image that can be projected clearly onto a screen.
why are projecters viewed upright
The projector lens creates a real, inverted image of the film. The film itself produces an upside-down image, and when the light passes through the lens, it also inverts it.
However, the screen acts like a mirror of sorts and reflects the image as it is projected onto it.
Since we are viewing the image from a distance (as viewers sitting in the theater), the inverted image on the screen appears upright to us.