Lecture 7: Cutaneous & Subcutaneous Fungal Infections
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Tinea/Pityriasis Versicolor
Malassezia
Lipid-dependent, dimorphic fungus, of normal skin microbiota
Yeast and pseudohyphae – “spaghetti-meatballs” appearance
Superficial fungal infection
Not contagious
Transforms from yeast cells to pathogenic mycelial form
Macules, patches, and thin plaques can be hypo-, hyperpigmented or erythematous
Fine scale often present
Lesions small but frequently coalesce
Adolescents & adults – upper trunk and proximal upper extremities
Children likely to involve face
UV: fluoresce yellow to yellow-green
Dermatophytosis
Cutaneous mycosis
Filamentous fungi capable of superficial infection
Metabolize & subsist on keratin – skin, hair, & nails
Keratinase - invasion of cytokeratin-containing tissues
Mannan glycoproteins in cell wall = adhesin; inhibit action of macrophages
Produces microconidia and macroconidia on Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA)
MAIN Infective form/stage – arthrospores – fragmented hyphae
Disseminate from one host to another
Person to person + fomite transmission
Can survive in the environment (fomite)
Arthrospores adhere by fibrils to keratinocytes and germinate
Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LCB) stain
Tinea Corporis
Trichophyton rubrum
Infection of trunk, neck, arms, and legs OR body surfaces other than the feet, groin, face, scalp, or beard hair
Direct skin contact with infected individual, animal, fomites or secondary spread from other dermatophyte infection sites
Begins as pruritic, circular or oval, erythematous or hyperpigmented, scaling patch or plaque
Spreads centrifugally
Center clearing follows, with an active, advancing, raised border remains
Ring-shaped plaque → ringworm
Multiple plaques may coalesce
Pustules occasionally appear
Extensive tinea corporis → underlying immune disorder (e.g. diabetes; HIV)
Tinea Pedis
Athlete’s Foot
Infection of the skin on the foot
Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale (mentagrophytes), & Epidermophyton floccosum
Direct skin contact with causative microbe, by walking barefoot in locker rooms or swimming pool facilities
Usually occurs – adolescents and adults; rare prior to puberty
Most often medial foot; possible underlying erythema
Can occur in association with onychomycosis, tinea cruris, or tinea manuum – same fungus
Interdigital tinea pedis
Pruritic erosion or scales b/n toes (esp. 3rd or 4th digital spaces)
Associated fissure may cause pain
Possible source for bacterial infection → cellulitis
Hyperkeratotic tinea pedis
Diffuse, hyperkeratotic eruption of souls and medial/lateral surfaces of feet
Variable underlying erythema
Vesiculobullous (inflammatory) tinea pedis
Pruritic, sometimes painful, vesicular/bullous eruption
Tinea Cruris
Jock Itch- Dermatophyte infection crural fold
Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton interdigitale (mentagrophytes), & Epidermophyton floccosum
Often spread from concomitant tinea pedis
More common in males than females
Begins w/ erythematous or hyperpigmented patch, proximal medial thigh
Infections spreads centrifugally, w/ partial central clearing & slightly elevated, erythematous or hyperpigmented, sharply demarcated border
Infection may spread to perineum & perianal areas, into gluteal cleft, or onto buttocks
Males - scrotum not or slightly affected
Tinea Capitis
Infection of of the scalp and hair
Pruritic, scaling areas of hair loss
Trichophyton and Microsporum
Trichophyton tonsurans – primary in US
Direct contact of scalp w/ dermatophyte from another infected (carrier) human or animal or fomite
Children, prepubertal – most likely
Adults: Colonization by commensal yeast – Malassezia (Pityrosporum)
Progresses from stratum corneum down into follicle then hair
Endothrix
arthroconidia found w/in hair shaft
Trichophyton tonsurans
Patches of alopecia w/ black dots
black dots due to distal ends of hairs broken at surface
alopecia areas
Ectothrix
arthroconidia primarily surround outside hair shaft
Microsporum canis
Scaly patches with alopecia
Patches few to several cm
enlarge centrifugally wks to months
erythema may be present
Kerion
large, pyogenic abscess w/ thick pus oozing from hair follicles & edema
intense immune response
inflammatory plaque w/ pustules, thick crusting, &/or drainage
tenderness & pain
accompanied by secondary bacterial infection
Favus
hyphae and airspaces are found w/in hair shaft
no arthroconidia
T. schoenleinii
formation of scutula – cup-shaped yellow crusts composed of neutrophils, fungi, dried serum, and epidermal cells
unpleasant odor
possible permanent scarring
Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis
chronic fungal infection of toenails or fingernails
Trichophyton rubrum, T. interdigitale, Epidermophyton floccosum, Microsporum
Toenails - DERMATOPHYTE most common
Fingernails YEAST (Candida) most common
More common adults
Direct contact or spread from affected skin
Nail as site of relative immune privilege; lacks effective CMI
Persistence possibly due to biofilm formation → evade host defenses & antifungal therapy
Nail abnormalities – discoloration, subungual hyperkeratosis, onycholysis (painless separation of nail from nail bed); splitting; nail plate destruction
PAS stain
Distal Lateral Subungual Onychomycosis
Nail discoloration & subungual hyperkeratosis
Proximal Subungual Onychomycosis
Whitish discoloration originating under the surface of the proximal nail plate
Total Dystrophic Onychomycosis
Total destruction of nail w/ ridged hyperkeratotic nail bed
Dermatophytosis Diagnosis
Detection of segmented hyphae
PCR
MALDI-TOF – protein profile – requires pure culture
Dermatophytosis Treatment
Topical - most dermatophytosis limited epidermis
Azoles, allylamines (butenafine), ciclopirox, and tolnaftate
Extensive infections:
Oral -Terbinafine, Itraconazole, Griseofulvin
Hepatotoxicity
Azoles
inhibition ergosterol synthesis
Allylamines
inhibits ergosterol synthesis
Hydroxypyridones - Ciclopirox
chelates polyvalent metal ions
inhibition of enzymes
disrupts DNA repair, cell division signals & structures
Echinocandins
inhibit β-glucan synthesis
Pyrimidine - Flucytosine
inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
Griseofulvin
binds to keratin
Polyenes
aggregate with ergosterol
Selenium sulfide/disulfide
reduction in turnover of epidermal cells
Tolnaftate
inhibits squalene epoxidase, an enzyme in production of ergosterol
Butenafine
inhibits ergosterol synthesis
Dermatophytid Reactions
Dermatophytosis Complications
response to fungal antigens
Occur in patients w/ tinea pedis, manuum, corporis, cruris, or capitis
Autoeczematization reactions– secondary, dermatitic eruptions
Occur in association w/ primary, often inflammatory skin disorders
Pruritic, papulovesicular eruptions
Topical steroids & antipruritic agents
Sporotrichosis
Sporothrix schenkii
Thermal Dimorphic Fungus
Thin, septate, branching hyphae; roseate (bouquet-like) arrangement of conidia in Sabouraud dextrose agar at 25° C
Cigar-shaped budding yeast in human tissue & in vitro
Oval and round yeast as well
In vitro medium – Brain Heart Infusion at 37° C
Subacute to chronic infection
Usually cutaneous & subcutaneous tissue
contact with nature- plants and animals
Sporothrix schenkii Virulence Factors
Thermal dimorphism
Adhesins of cell wall:
GP70 – glycoprotein
PRM – peptidorhamnomannan - also immunogenic
Extracellular proteinases: Digestion of host cells for nutrients
Melanin:
Neutralization of ROS & NO
Resistance to antifungals
Biofilm: Resistance to antifungals
Sporotrichosis Clinical Manifestations
Trauma leading to cutaneous inoculations
Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis – healthy individual w/ exposure to fungus
Fixed - Local pustule or ulcer
Lymphocutaneous - Nodules along draining lymphatics
Ascending lymphangitis
Disseminated disease - ONLY immunocompromised host
Sporotrichosis Diagnosis and Treatment
Culture – Gold Standard
Sabouraud dextrose agar @ Room Temp
Confirm with growth on Blood Agar at 37° C
MALDI-TOF identify to species level
Localized infection - Itraconazole
Systemic infection - Amphotericin B
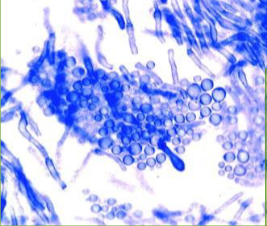
Tinea/Pityriasis Versicolor
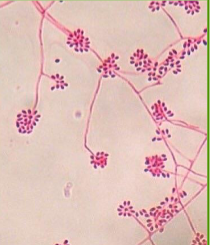
Sporothrix schenkii
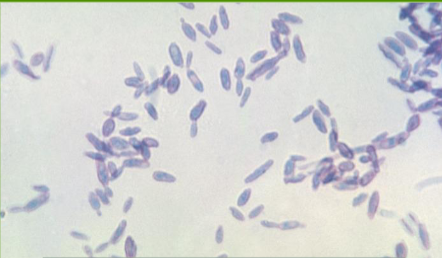
Sporothrix schenkii