AP Psychology Semester 1 Final Study Guide
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
Neurons
The basic building blocks of the nervous system that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals.
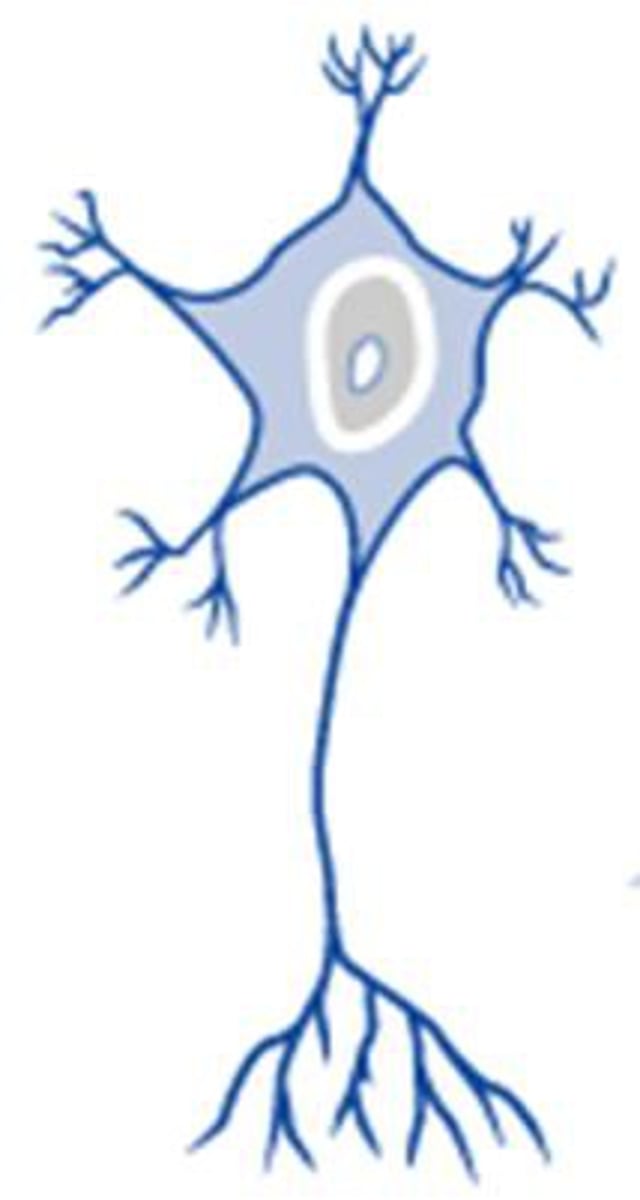
What does the cell body do?
process information and is in charge of the go-no-go
What are dendrites?
receives signals from other neurons, conducts impulses TOWARD the body of a neuron
What is the mylein sheath?
a fatty layer that covers the axon to insulate it from interference, therefore enabling messages to transferred faster
Synapse
The junction between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals.
what model does the synapse use with the neurotrasmitters?
The Lock and Key model
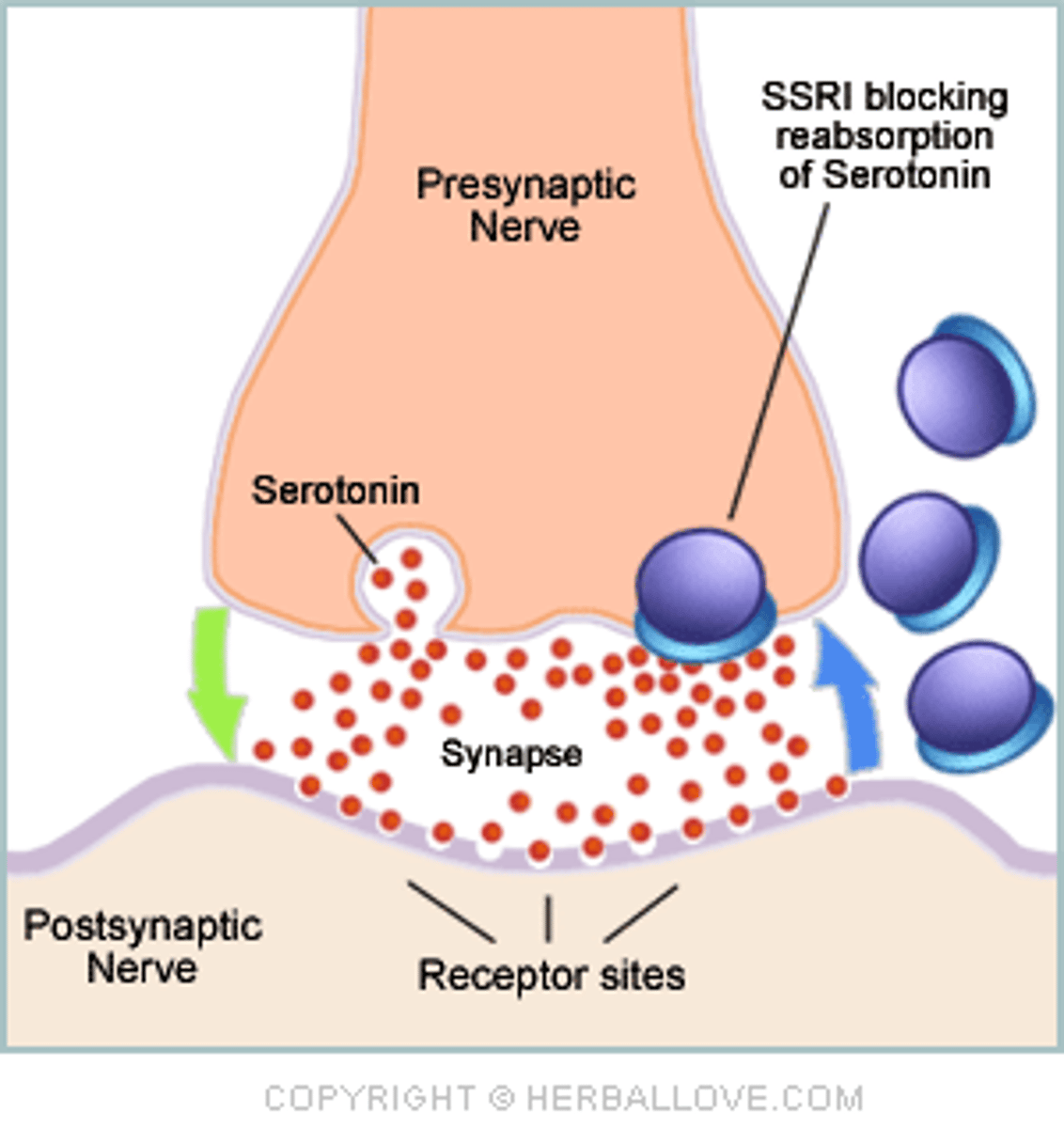
What is reputake?
Reputake involves the neurotransmitter being pumped back into the neuron that released it, in order to clear the synapse.
What does the term plasticity mean?
The brian's ability to change and adapt as a result of an experience.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that transmit signals across the synapse from one neuron to another.
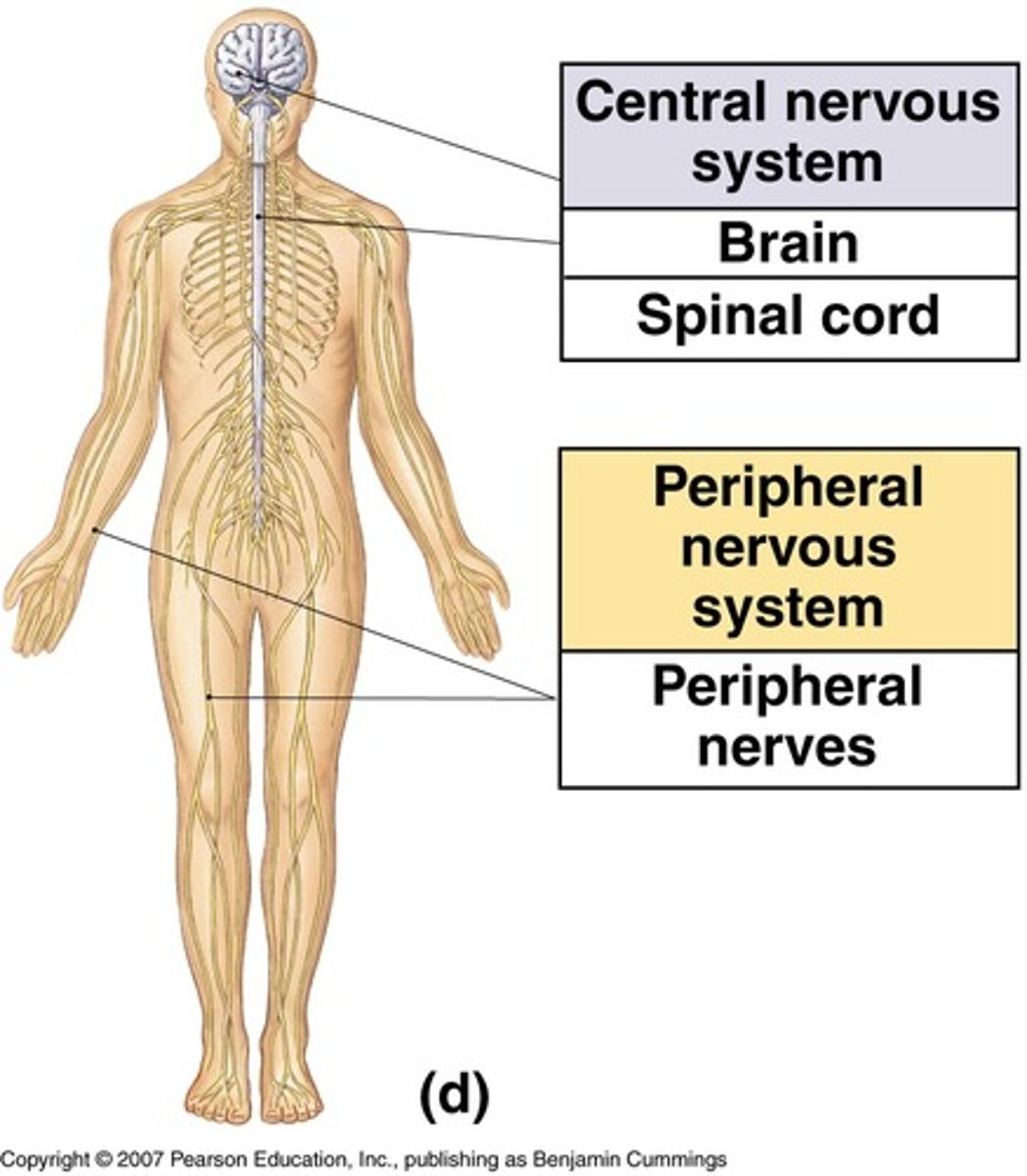
Central Nervous System
The part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
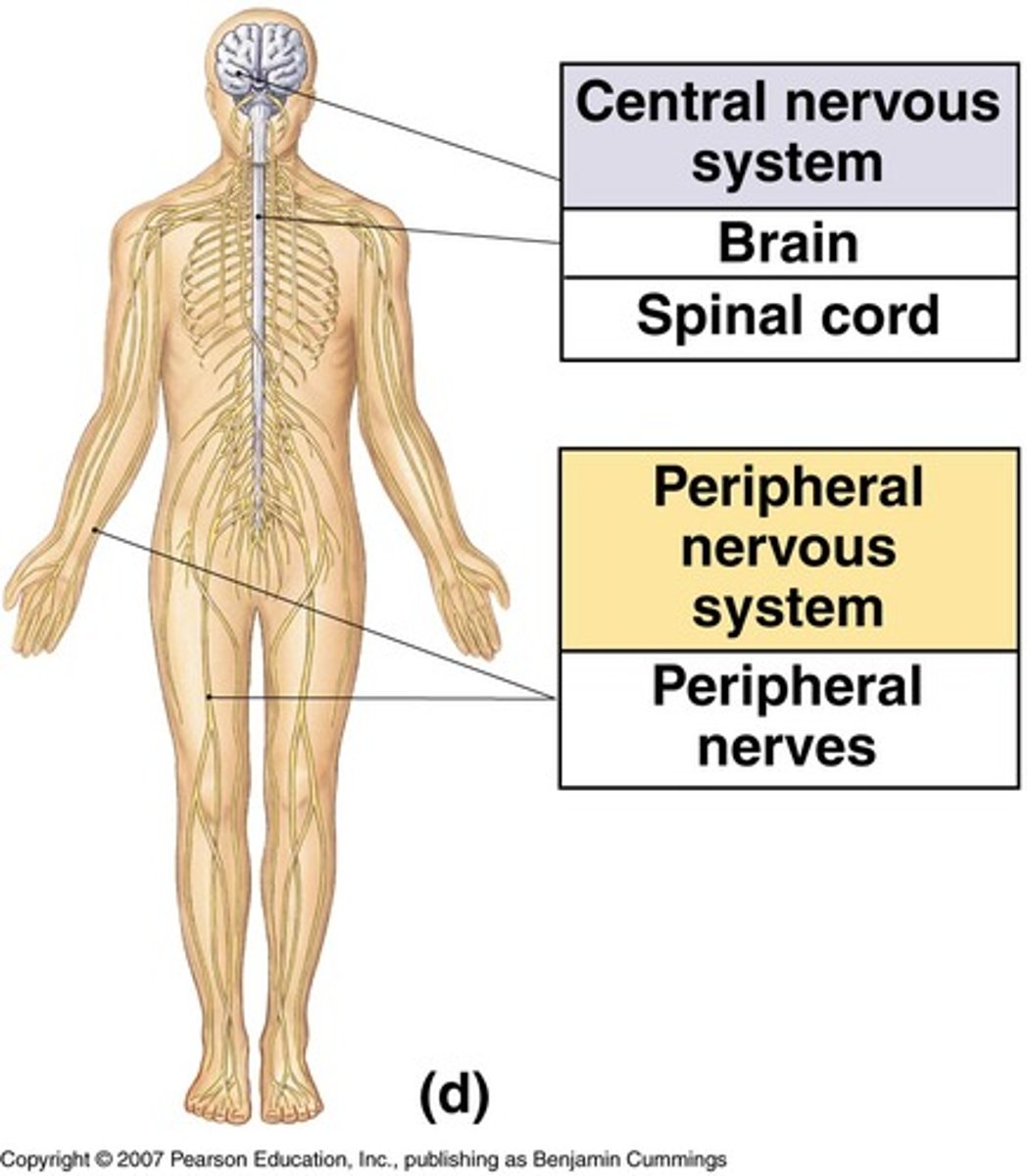
Peripheral Nervous System
The part of the nervous system outside the central nervous system, including sensory and motor neurons.
Somatic Nervous System
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
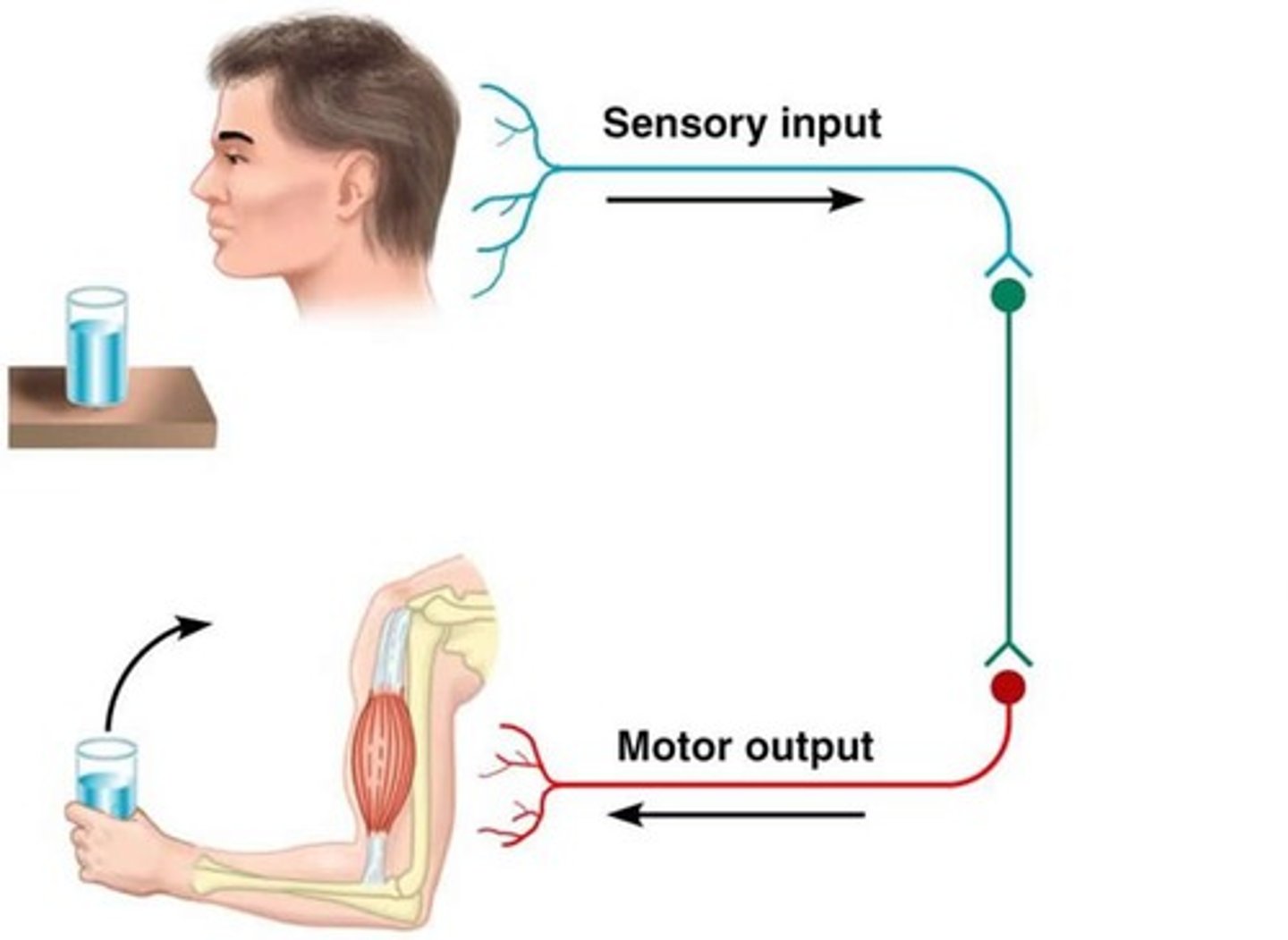
Autonomic Nervous System
The division of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions, such as heartbeat and digestion.
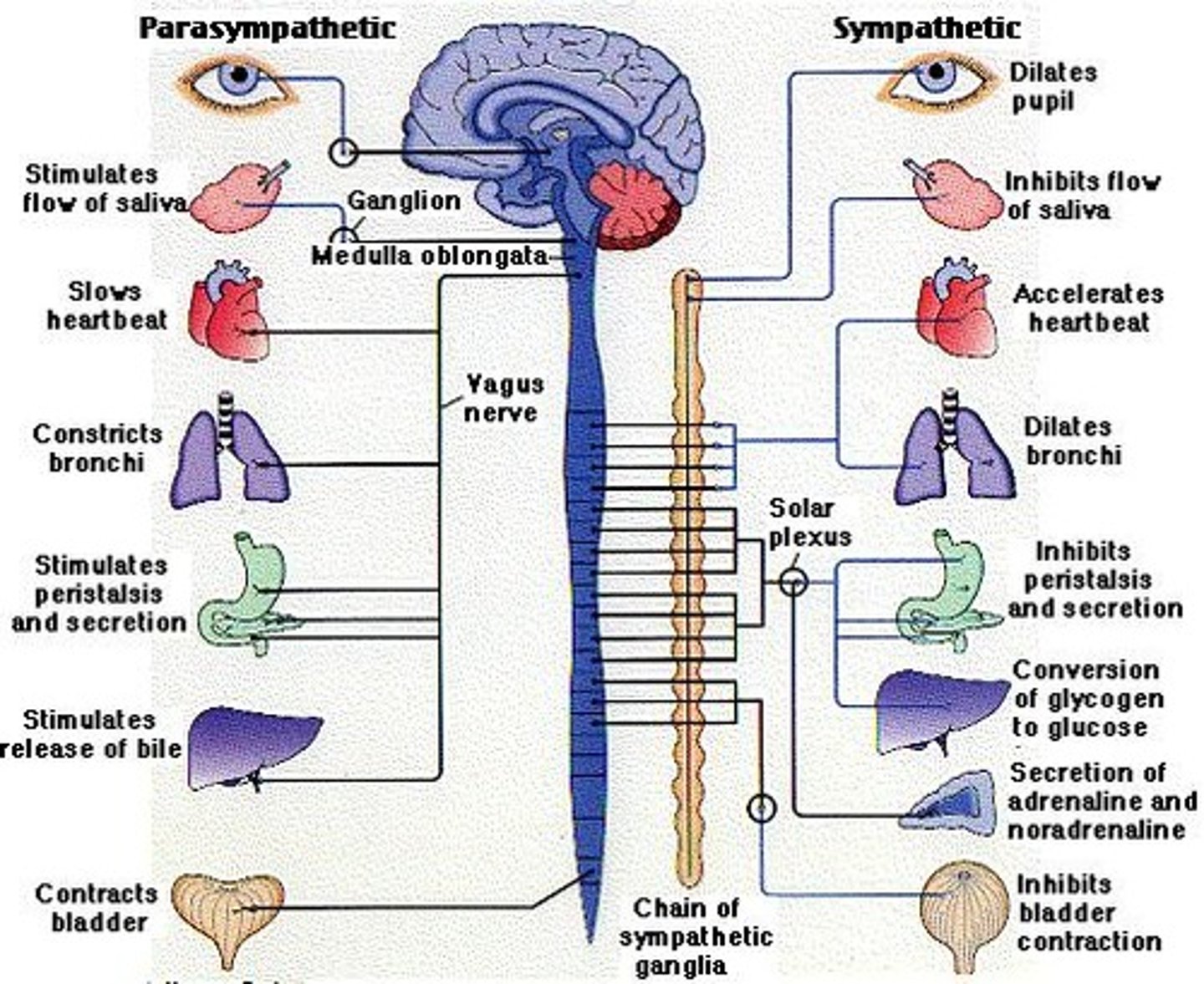
Sympathetic Nervous System
The part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations, often referred to as 'fight or flight.'
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The part of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy and restores the body to a calm and composed state, often referred to as 'rest and digest.'
Interneurons
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system.
Endocrine System
The system of glands that produce hormones to regulate various bodily functions.
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers that control the growth, differentiation, and metabolism of specific target cells
What and where is the pituitary gland?
It is the master gland that controls hormones in the body. It is next to the hypothalamus.
What and where is the thyroid?
The butterfly shaped gland in the neck that controls metabolic processes.
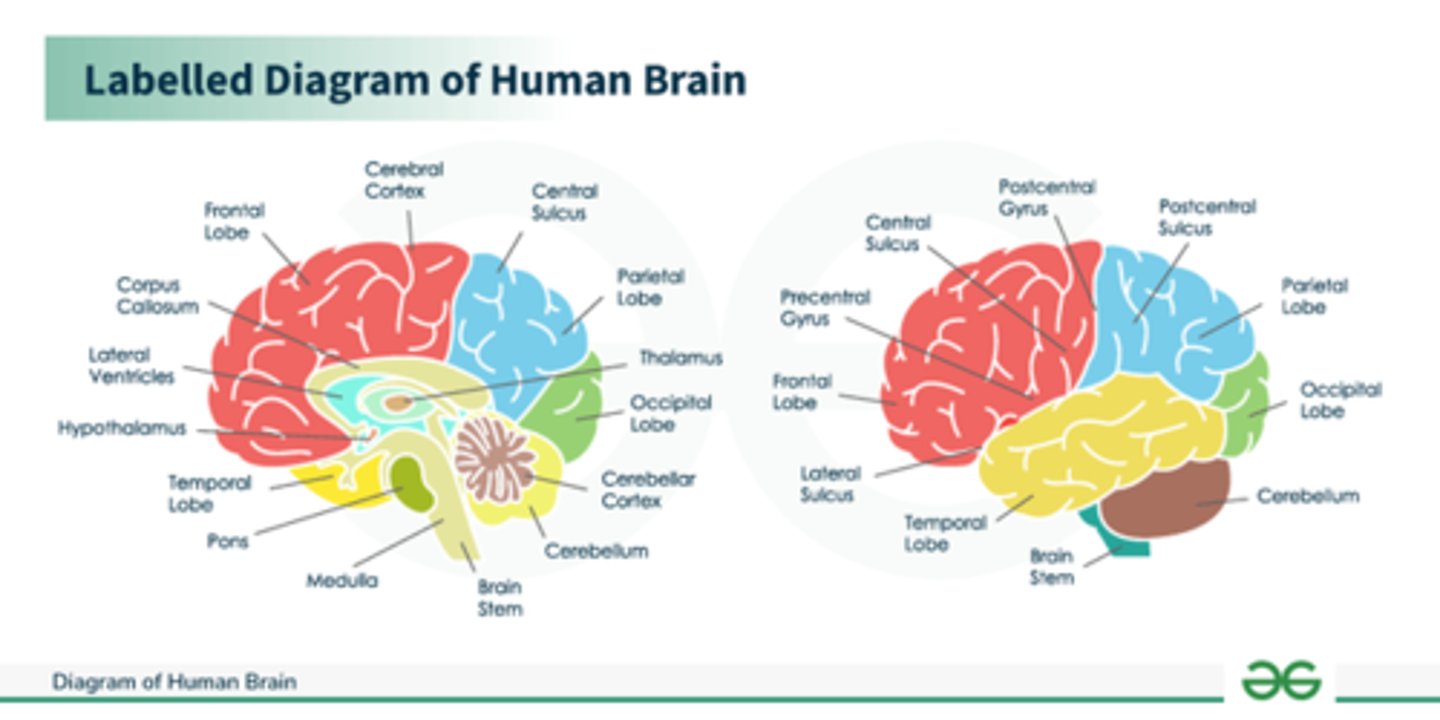
Model of the brain with parts for case questions
Bottom-up Processing
A type of processing that starts with sensory input and builds up to perception.
Top-down Processing
A type of processing that starts with the brain and uses prior knowledge to interpret sensory information.

Signal Detection Theory (Threshold)
A theory that explains how we detect signals amidst noise, considering both sensitivity and decision criteria.
Weber's law gives the exact percentage values of the different senses.
what is the process of priming?
the process of giving hints of themes or sounds to then elicit a wanted response from a person.
Sensory Adaptation
The process by which our sensitivity to unchanging stimuli decreases over time.
What is the difference between vision and sight?
Vision is the clarity in which an object can be seen. Sight is the process of seeing and processing in the brain.
What are the basic parts of the eye?
Cornea, iris, lens, pupil, retina, fovea, optic nerve, rods, and cones.

How does sight work?
the eye detects light energy and transmits information about intensity, color, and shape to the brain
What are the basic parts of the ear?
Pinna, Ear canal, ear drum, middle ear, and inner ear.
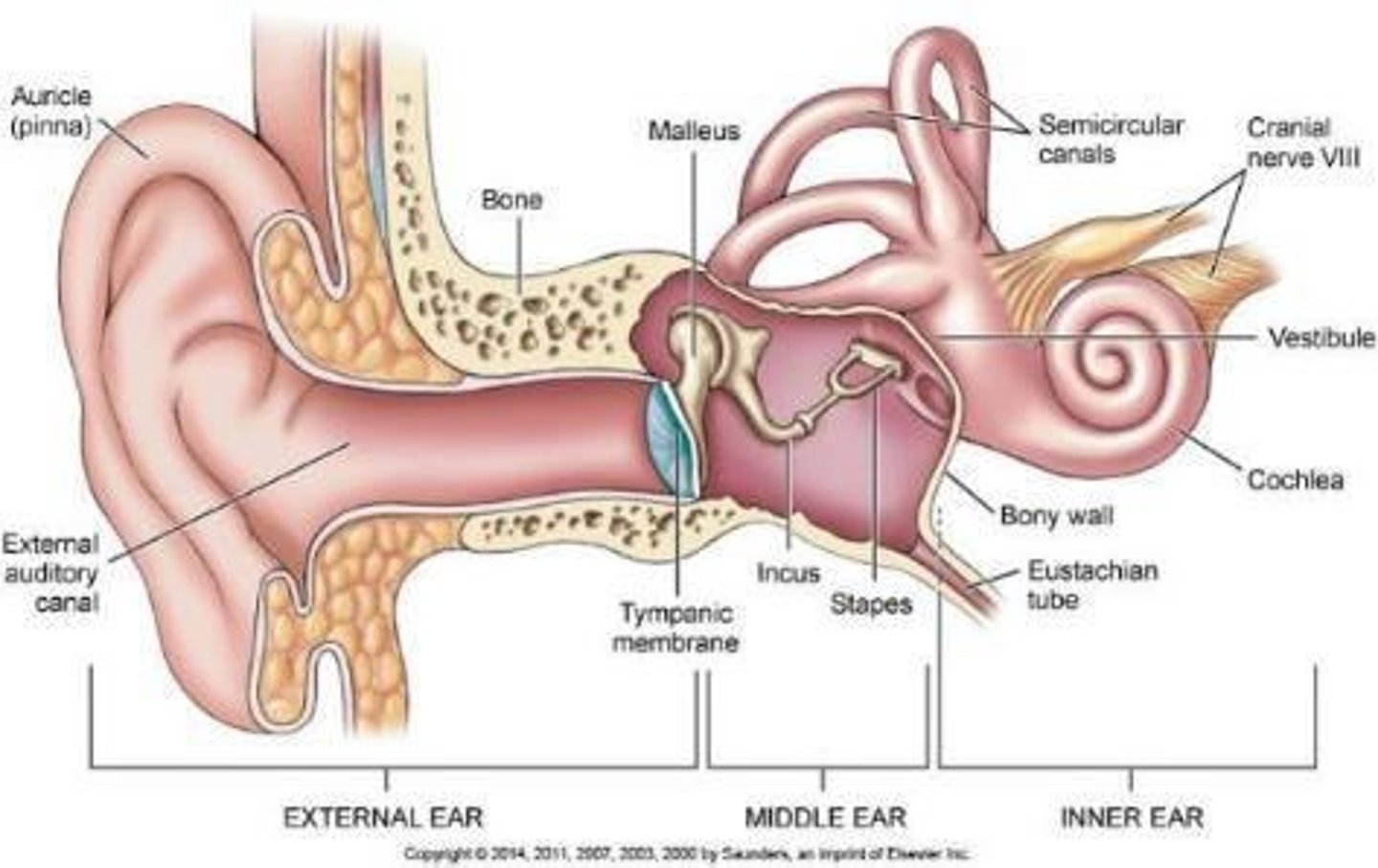
How does hearing work?
1. moving air molecules enter the ear and cause the eardrum to vibrate
2. vibrations in the hammer, anvil, and stirrup are transmitted to the cochlea in the inner ear
3. converted to signals that the brain interprets as sounds through the auditory nerve (this connects to the medulla oblongata)
How do touch and pain relate?
When you are touched by something and it is picked up by the nociceptors, the signal is converted to pain.
What are the 5 tastes?
sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
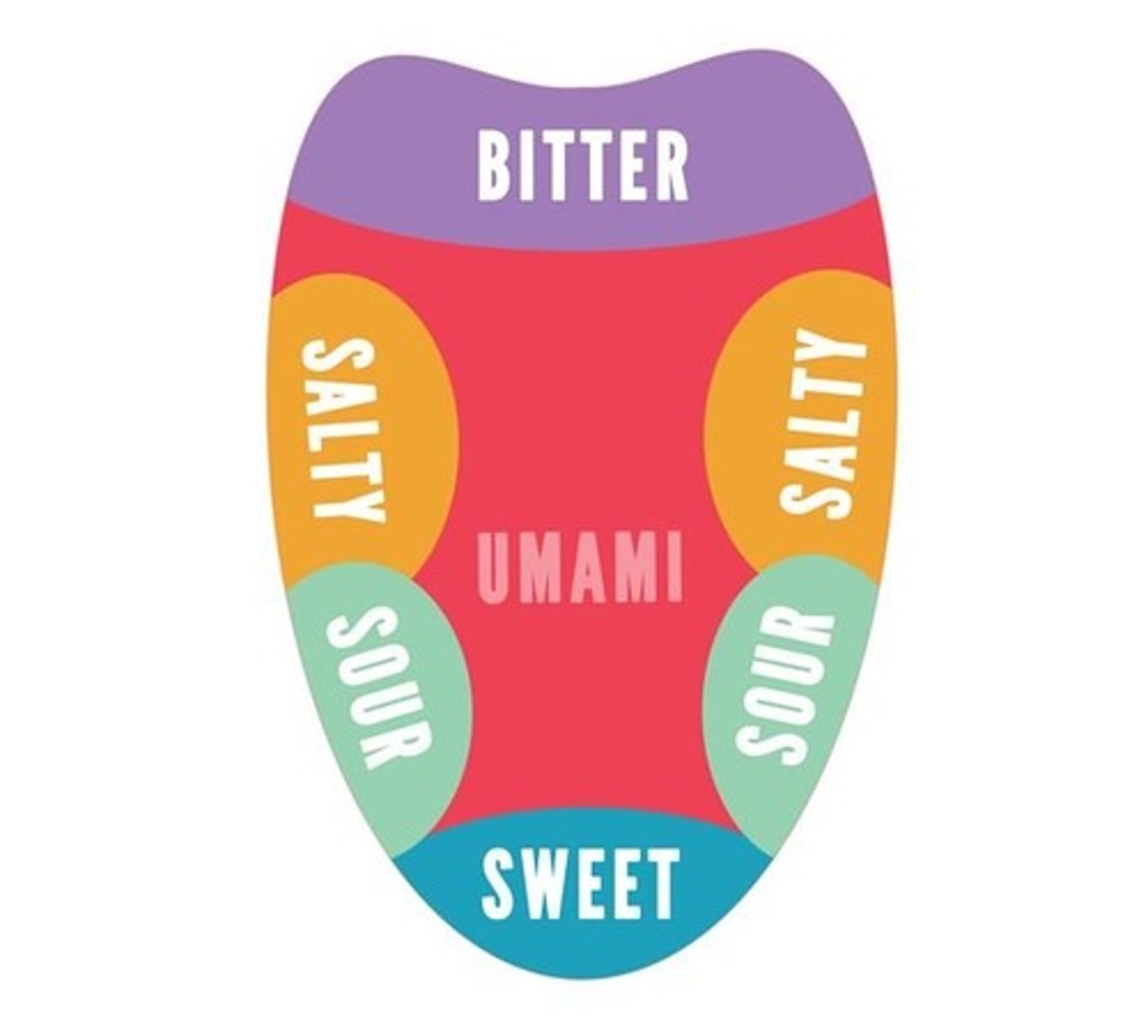
What organ in the body turns food into electrical signals to tell the brain what we are consuming?
Tastebuds
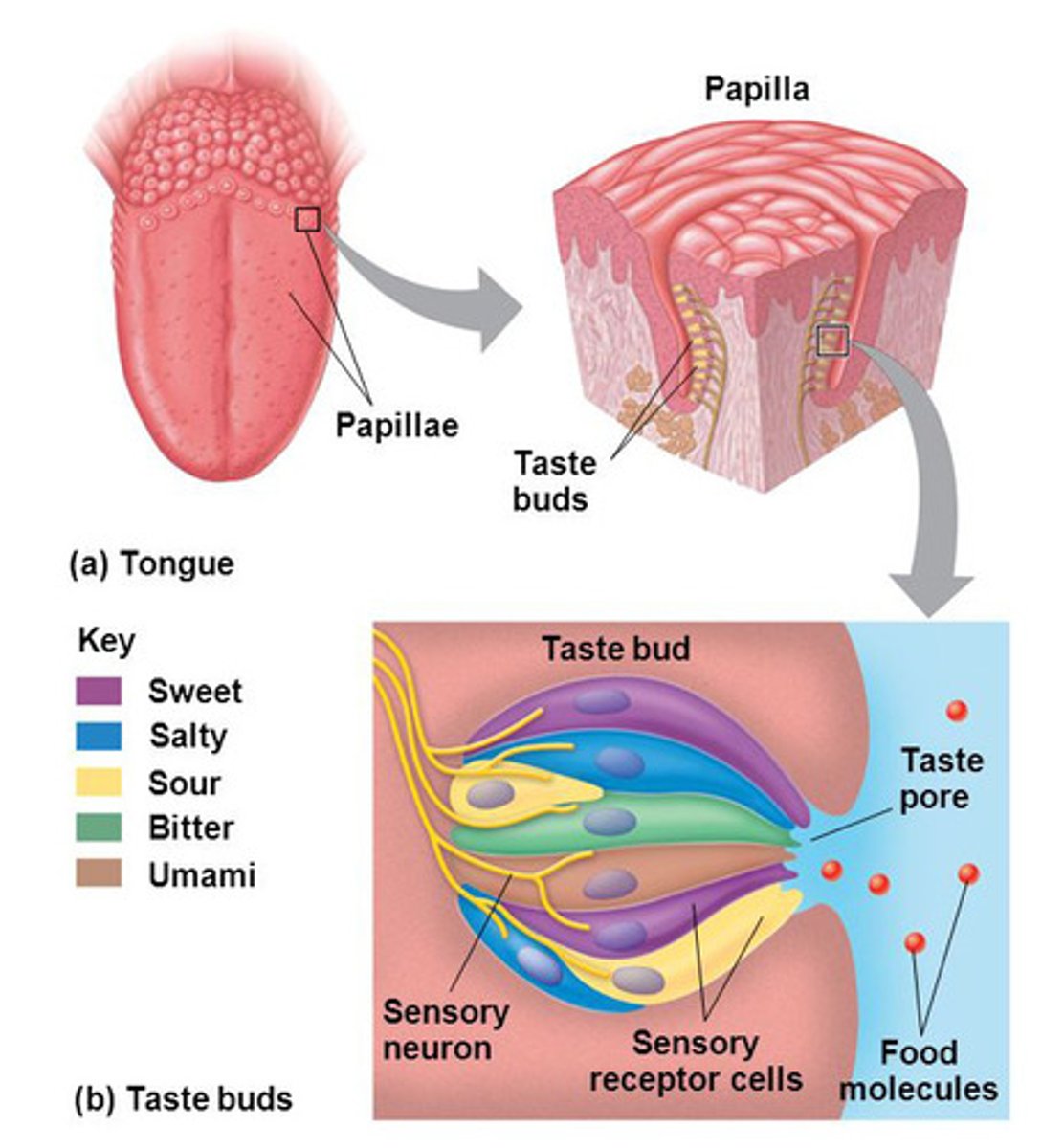
What does smell consist of?
The 350 odor receptors that can detect over 10,000 different scents.
What is kinesthesis?
the system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
What is the body's natural gyroscope/ balance system?
Vestibular system
What is parallel processing?
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions
What is a circadian rhythm?
The biological clock that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and other physiological processes over a 24-hour period.
what controls the circadian rhythm?
The Superchiasmatic Nucleus (SCN).
it also communicates with the hypothalamus, reticular formation, and the pineal gland
Hypnosis
A state of focused attention and heightened suggestibility, often used for therapeutic purposes.
Dual processing
The theory that information is processed by both conscious and unconscious systems in the brain.
Blindsight
A condition in which a person can respond to visual stimuli without consciously perceiving them.
Selective attention
The process of focusing on a particular object in the environment for a certain period while ignoring others.
Inattentional blindness
The failure to notice a fully visible but unexpected object because attention was engaged on another task.
Sleep stages
The different phases of sleep characterized by distinct brain wave patterns, including REM and non-REM sleep.

Sleep disorders
Medical conditions that disrupt normal sleep patterns, including insomnia, sleep apnea, REM Sleep behavior disorder, sleep walking, sleep terrors, and narcolepsy.
Drugs
Substances that alter physiological or psychological processes in the body, often categorized by their effects.
Tolerance
A condition in which a person requires increasingly larger doses of a drug to achieve the same effect.
Addiction
A chronic disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain.
Withdrawal
The physical and mental symptoms that occur after stopping or reducing intake of a substance that one has become dependent on.
Psychological dependence
A condition where a person feels a strong desire or compulsion to use a substance for its psychological effects.
Physical dependence
A state where the body has adapted to a drug, leading to withdrawal symptoms when the drug is not taken.
Stimulants
Substances that increase activity in the central nervous system, leading to increased alertness and energy.
some ex. caffein, nicotine/tobacco, cocaine, meth
Depressants
Substances that reduce the activity of the central nervous system, leading to relaxation and decreased inhibition.
some ex. alcohol, barbiturates, opiates, benzodiazepines
Hallucinogens
Substances that cause perceptual distortions and altered states of consciousness, often leading to hallucinations.
some ex. PCP (angle dust), Ketamine, LSD (acid), Ecstasy, marijuana/THC
Flashbulb Memory
A vivid and detailed memory of an emotionally significant event.
what is the definition of learning?
a relatively enduring change in behavior or thinking that results from our experiences.
what is associative learning?
Understanding that 2 stimulus occur together or in sequence
What is Classical conditioning?
The process of associating two things together to elicit a wanted reaction/response.
Who was Ivan Pavlov?
He was a behavioral psychologist who conditioned dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell.
What is the unconditioned stimulus?
The stimulus that elicits the wanted response.
What is the Unconditioned response?
The natural response to the unconditioned stimulus.
What is the conditioned stimulus?
The selected stimulus that you want to associate with the US.
What is the Conditioned response?
The same/similar thing as the UR, but as a response to the CS.
What is cognitive learning?
mental processes involved in acquiring knowledge and understanding. It includes a range of activities such as thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and memory.
Acquisition
The initial stage of learning where a response is established and gradually strengthened.
Spontaneous recovery
The reappearance of a conditioned response after a period of extinction.
Extinction
The process by which a conditioned response diminishes or disappears when the reinforcement is no longer presented.
Generalization
The tendency to respond similarly to stimuli that resemble the conditioned stimulus.
Discrimination
The ability to distinguish between different stimuli and respond only to the conditioned stimulus.
Operant Conditioning
A learning process through which the strength of a behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment.
Reinforcement
Any event that strengthens or increases the likelihood of a behavior. It can be positive (adding a pleasant stimulus) or negative (removing an unpleasant stimulus).
Shaping
A technique in operant conditioning where successive approximations of a desired behavior are reinforced.
Intermittent vs Continuous Reinforcement
Continuous reinforcement provides a reward after every correct response, while intermittent reinforcement provides rewards after some responses, leading to stronger persistence of behavior.
Punishment
An event that decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, which can be positive (adding an unpleasant stimulus) or negative (removing a pleasant stimulus).
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation comes from within the individual, driven by personal satisfaction, while extrinsic motivation is driven by external rewards or pressures.
Observational learning
Learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others, exemplified by Bandura's Bobo doll experiment, where children imitated aggressive behavior observed in adults.

What is memory?
The mental capacity to encode, store, and retrieve information.
What are the stages of memory?
The stages of memory include encoding, storage, and retrieval.

What is the difference between short-term and long-term memory?
Short-term memory holds information temporarily for immediate use, while long-term memory stores information more permanently for future retrieval.
What is effortful processing?
Effortful processing is the encoding of information that requires attention and conscious effort.
What is flashbulb memory?
Flashbulb memory refers to the vivid and detailed recollection of significant events, often accompanied by strong emotional responses.
What are retrieval cues?
Retrieval cues are stimuli or prompts that help access stored memories.
What is anterograde amnesia?
Anterograde amnesia is the inability to form new memories after the onset of amnesia.
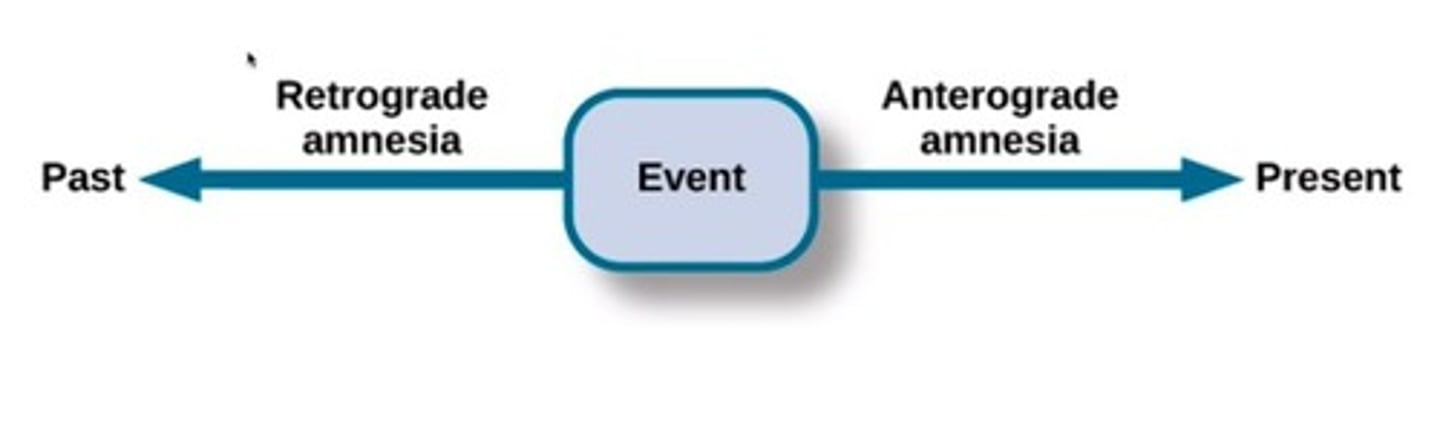
What is retrograde amnesia?
Retrograde amnesia is the loss of memories that were formed before the onset of amnesia.

What is encoding failure?
Encoding failure occurs when information is not properly processed for storage, leading to forgetting.
What is storage decay?
Storage decay refers to the gradual loss of stored information over time.
What is retrieval failure?
Retrieval failure is the inability to access information stored in memory, often due to insufficient retrieval cues. "the tip of my tongue"
Concepts
Mental categories that help organize and interpret information.
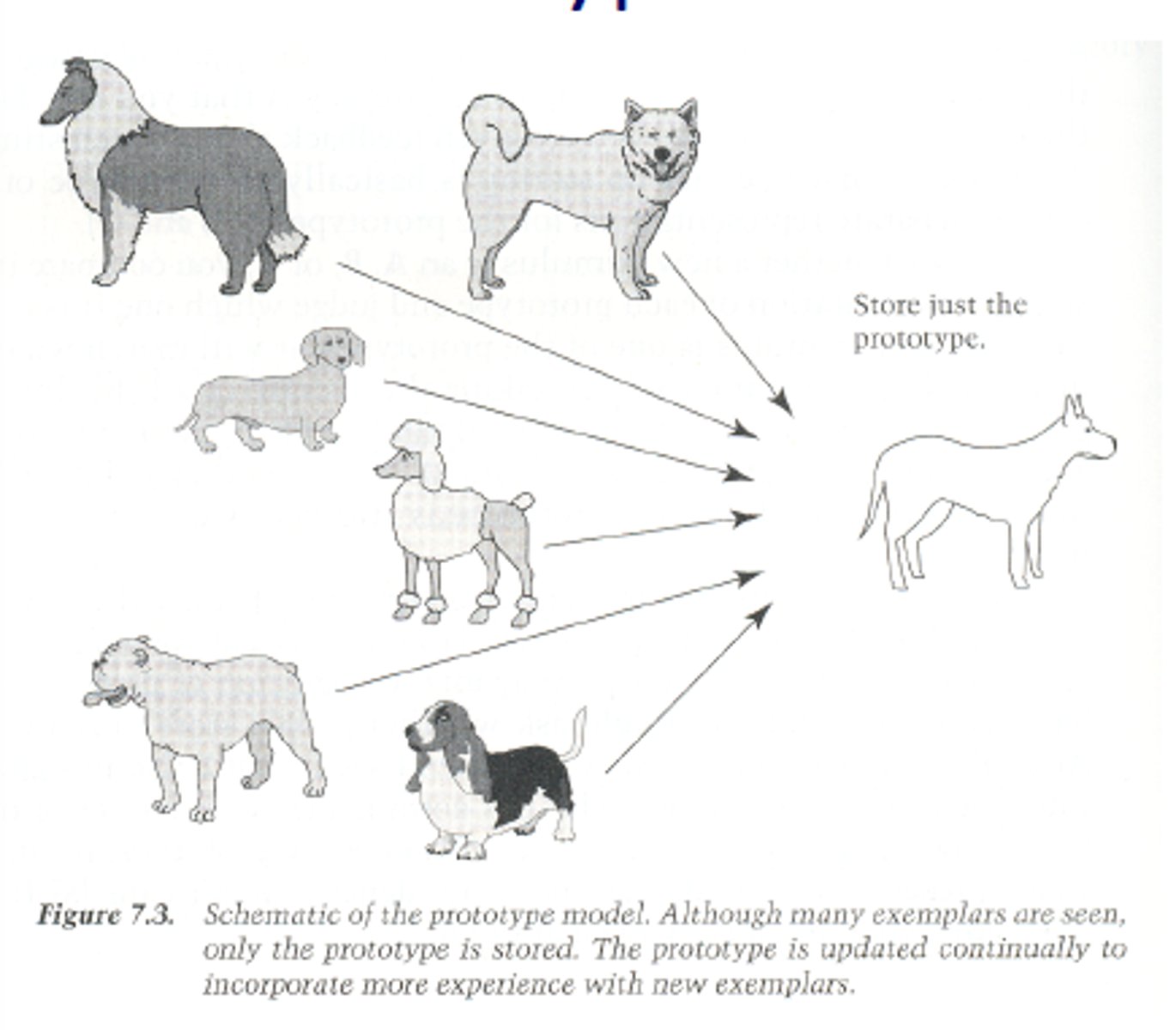
Prototypes
The best or most typical example of a category.
Algorithm
A step-by-step procedure or formula for solving a problem.
Heuristic
A mental shortcut that allows for quick problem-solving and decision-making.
Insight
The sudden realization of a problem's solution.
Availability Heuristic
A mental shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to mind when evaluating a specific topic.
Overconfidence
The tendency to overestimate one's abilities or knowledge.
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information that confirms one's preexisting beliefs.
Belief Perseverance
The phenomenon where people hold on to their beliefs even when faced with contrary evidence.
Creativity
The ability to produce new and valuable ideas or solutions.
Phoneme
The smallest unit of sound in a language that can distinguish meaning.