Bio Quiz 2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz 2 - Spermatogenis - Oogenesis - Errors during Meiosis - Mendelian Genetics - Monohybrid Crosses - Dihybrid Crosses - missing last lesson will
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Gametogenesis
gamete formation
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
meiosis takes place in testes
begins with diploid sell called a spermatogonium
Oosgenesis
production of eggs
meiosis takes place in the ovaries
begins with a diploid cell called an oogonium
Ogonia reproduces by mitosis, then begin meiosis but stops at purchase 1 till meiosis 1 continues for the cell each month beginning at puberty. Creating an unequal division of cytoplasm (a polar body and a visible egg)
Gamete formation in animals
Meiosis in mammals differs drastically between males & females
two types of ____________ in humans
Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis
Spermatogonium (pl: Spermatogonia)
a diploid that starts spermatogenesis
_____________ reproduces by mitosis and resulting cells undergo meiosis
1 _____________ produces 4 sperm
Oogonium (pl: Oogonia)
a diploid cell that starts oogenesis
_________ reproduces by mitosis, then begins meiosis but stops at prophase 1
Polar Body
created during oogenesis and will eventually degenerate
Major differences between Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis
cytokinesis is unequal among daughter cells during __________
at birth, the ovaries contain all the cells it will ever have that will develop into eggs
sperm continue to develop by meiosis throughout the male reproductive years
__________ has a long resting period after prophase 1 until hormones activate them
Why is cytokinesis is unequal during oogenesis
ensures only one zygote is formed during fertilization
more nutrients given to 1 egg to ensure survival or zygote
more than one zygote means nutrients are divided (increases chance of health complications)
400,000 - 500,000 eggs
all the cells in the ovaries that will ever develop into eggs
only 400 will mature and become eggs
each egg will complete division process upon puberty one at a time
Fraternal Twins
When more than 1 egg is released and both are fertilized (diff DNA)
Identical Twins
A single zygote divides into two separate bodies (genetically identical)
Importance of Meiosis
provides a vast amount of genetic variation
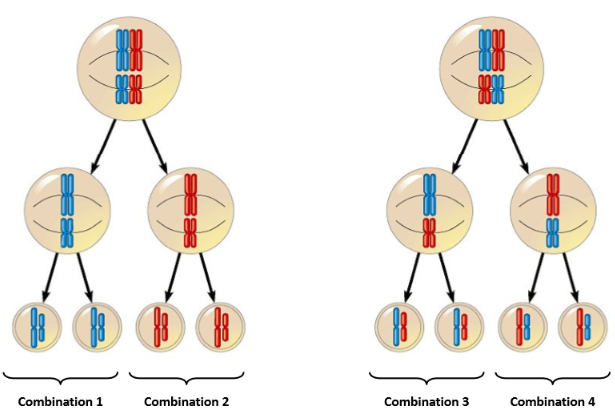
Independent Assortment
How pairs orient themselves in Metaphase1 and Metaphase2 will determine their variance (diff combos of chromosomes). In Anaphase1 homologs pairs independently separate, in Anaphase2 sister chromatids independently separate.
2n
2n
number of genetically distinct gametes that can be produced from a diploid cell during independent assortment
n = number of chromosome pairs
In humans 223 = 8,388,608
Crossing Over
In prophase1 chromosomes exchange DNA by ________ each other
occurs in several points along non-sister chromatids
result: chromosomes have genes form maternal & paternal origin
bonds holding DNA together are broken & reformed (might not reform correctly)
Errors Cause by Changes in Chromosome Structure
Deletion, Duplication, Inversion & Translocation
Deletion
a piece of the chromosome deleted/lost
missing gene = info form making vital proteins missing
can be caused by: viruses, irradiation, chemicals
Cri du Chat Syndrome
example of deletion
rare genetic disorder due to missing part of chromosome 5 symptoms include unusual facial features
Prader-Willi Syndrome
deletion in chromosome 15
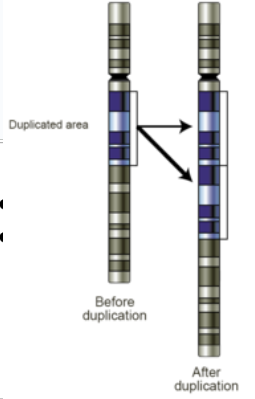
Duplication
a section of a chromosome appears two or more times in a row, some repeats are okay but too many can affect the function of the gene
Fragile X Syndrome
example of duplication when a singe nucleotide sequence (CCG) repeats on the X chromosome

Inversion
a certain gene segment becomes free from its chromosome momentarily before being reinserted in the reverse order. Changes the position and order of chromosome genes and can alter gene activity.
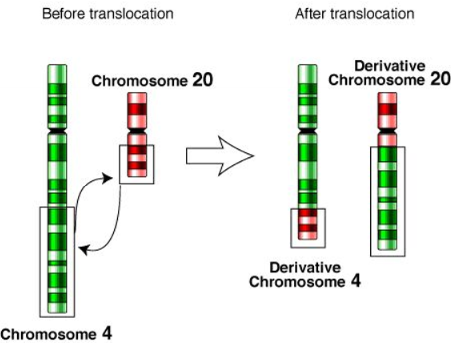
Translocation
part of one chromosome changes places with another part of the same chromosome pr with part of another, non-homologous chromosome.
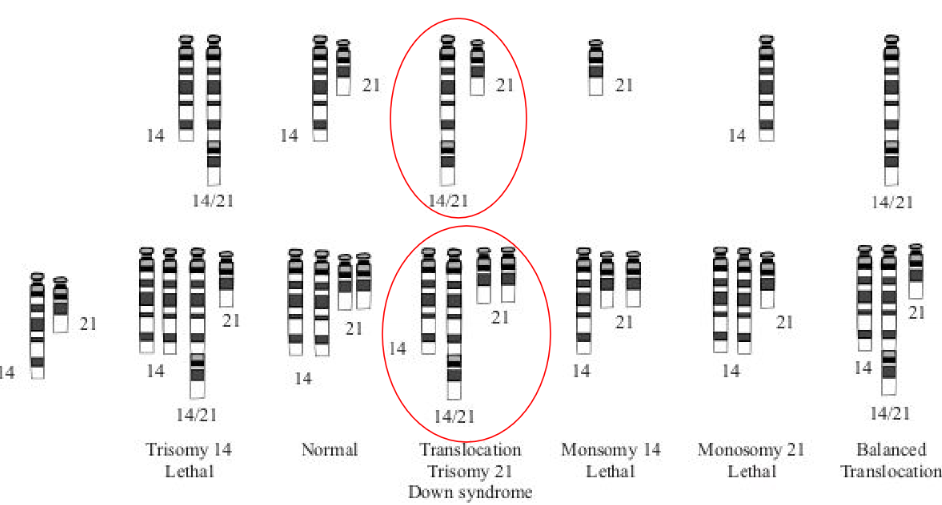
Translocation Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21 Down Syndrome)
_______________ can be caused by a translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21. Only form of this syndrome that can sometimes be inherited from a parent.
Errors Caused by Changes in Chromosome Number
Non-disjunction
When homologous chromosomes don’t separate during meiosis. Can be during Anaphase1 or Anaphase 2 (sister chromatids don’t separation)
result: one sell has too many chromosomes and one has too little
Down Syndrome as Trisomy
Instead of 46 chromosome, a person with _________ has 47. An additional chromosome is added to the 21st pair.
Trisomy
3 chromosomes
Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Austrian monk who studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants and developed the laws of inheritance. Work wasn’t recognized until the turn of the 20th century.
1856-1863, cultivated and tested some 28,000 pea plants and found that the plants' offspring retained traits of the parents
Called the “Father of Genetics"
Particulate Inheritance
Mendel stated that physical traits are inherited as “particles” not knowing the the “particles” were actually DNA
Trait
any characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring (based on two genes, one from mom & one from dad)
Heredity
passing of traits from parent to offspring
Genetics
study of heredity
monohybrid cross
cross involving a single trait (tracks the inheritance of one trait) and predicts the “probability of the traits that resulting offspring will have
dihybrid cross
cross involving two traits (track inheritance of two traits) and predicts the probability of the traits that the resulting offspring will have.
Alleles
two forms of a gene (dominant & recessive)
Dominant
stronger of two genes expressed in the hybrid; represented by a capital letter (R)
Recessive
gene that shows up less often in a cross; represented by lower case letter (r)
Genotype
gene combo for a trait (ex. RR, Rr, rr)
Phenotype
physical feature resulting from a genotype (ex. red, white)
Homozygous genotype
gene combo involving 2 dominant or 2 recessive genes AKA pure
Heterozygous genotype
gene combo of one dominant & one recessive allele AKA hybrid
Characteristics
determined by genes and environment
Why did Mendel Choose Peas
Can be grown in a small area
Produce lots of offspring
Produce pure plants when allowed to self-pollinate several generations
Can be artificially cross-pollinated
How Mendel Started
produced pure strains by allowing the plants to self-pollinate for several generations
Parental (P1) Generation
the _____________ gen in a breeding experiment
F1 Generation
first-gen offspring’s (first filial gen) from breeding individuals from P1 gen
F2 Generation
second-gen offspring’s (second filial gen) from breeding individuals from F1 gen
3:1
Ratio of Recessive & Dom genes (phenotypic ratio)
What are the results of
RR x rr
R = round
r = wrinkled
Genotype: all Rr
Phenotype: all round
Homozygous dominant x Homozygous recessive
all ofspring’s are heterozygous
Heterozygous x Heterozygous
Offspring:
25% Homozygous dominant RR
50% Heterozygous Rr
25% Homozygous Recessive rr
1:2:1
Genotypic ratio of monohybrid cross
Test Cross
to determine an unknown genotype that is phonetically dominant
if an individual appears phenotypically dom they can be either homozygous dominant or heterozygous
use punnett square to figure out
True-Breeding
Individuals are homozygous (both alleles are the same)
3 Mendelian Laws
law of dominance
law of segregation
law of independent assortment
5 ways of genetic variation
Independent Assortment
Crossing Over
Errors in Chromosome Structure
Errors in Chromosome Splitting (chromosome number)
Errors in DNA replication
Law of Dominance
dominant trait is always expressed
RR x rr = Rr x 4 (only the R trait will be expressed)
Law of Segregation
during the formation of gametes, the two alleles for a single trait separate from each other. Alleles for a trait “recombine” at fertilization, producing the genotype for the trait of the offspring”
Law of Independent assortment
Alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (& offspring) independently of one another.
Occurs when chromosomes line up during metaphase I and metaphase II
Demonstrated in dihybrid crosses
How do we Organize Our Traits?
As per Law of Independent Assortment each pair of alleles segregates independently during gamete formation.
Formula: 2n (n = # of heterozygotes)
What gamete are produced from RrYy?
22 = 4 gametes
RY Ry rY ry
9:3:3:1
Phenotypic ratio for dihybrid crosses