3rd Quarter Vocabulary - Earth Science - 7th Grade
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

52 Terms

Solution
A mixture where one substance is completely dissolved in another.
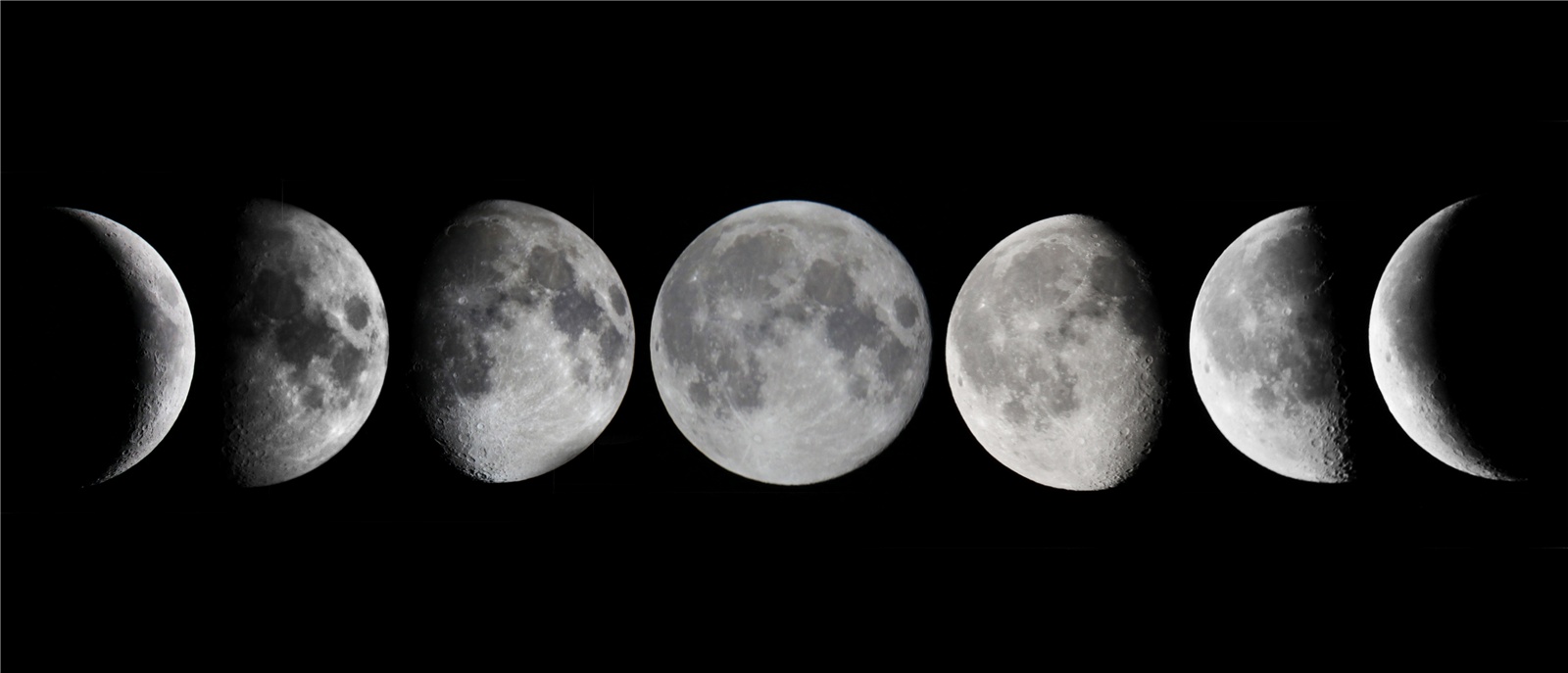

Lunar Phases
The different shapes of the Moon we see during the month.

Waxing
When the Moon looks like it’s getting bigger.

Waning
When the Moon looks like it’s getting smaller.

Gibbous
When the Moon looks more than half full, but not completely full.
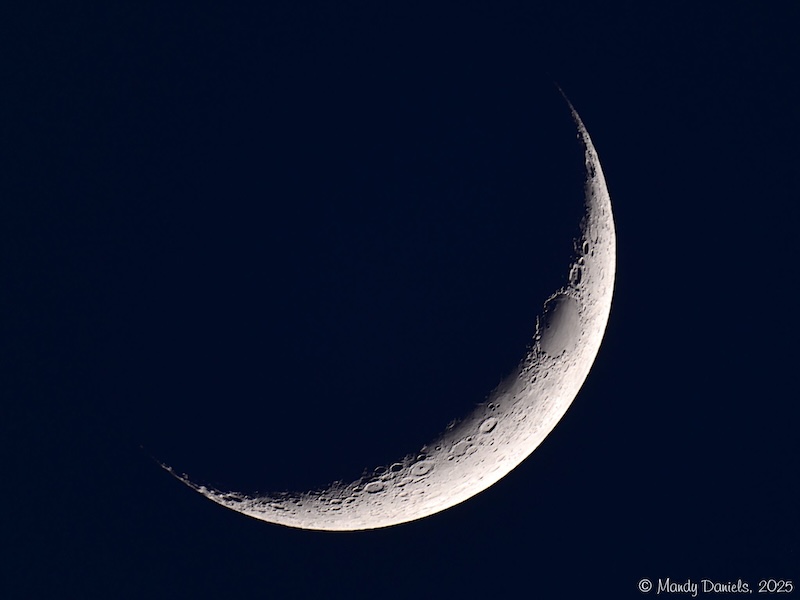

Crescent
When the Moon looks like a tiny sliver, it is less than half full.

Tide
The rise and fall of the ocean caused by the Moon’s gravity.
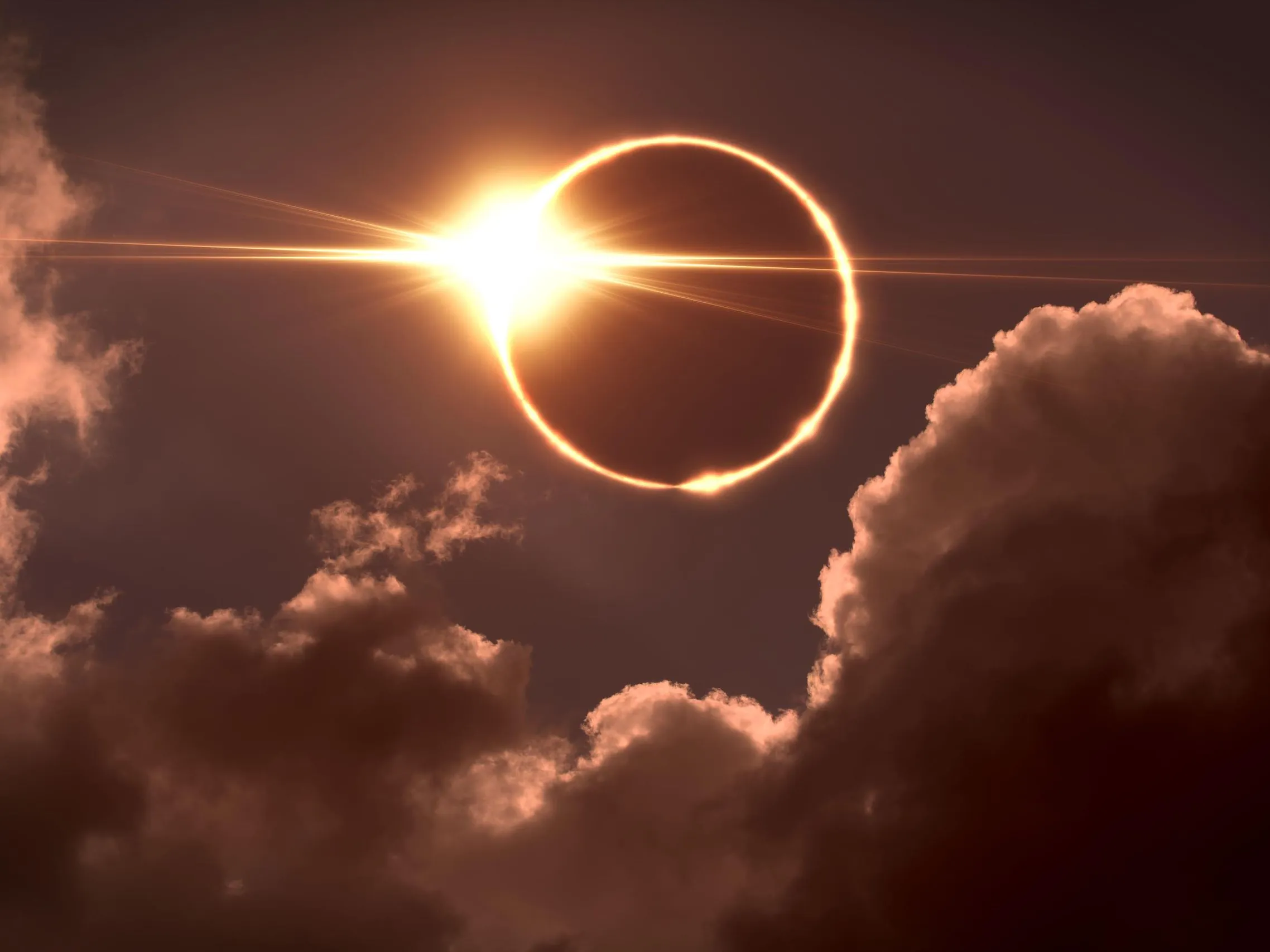

Eclipse
When one object in space blocks the light from another.
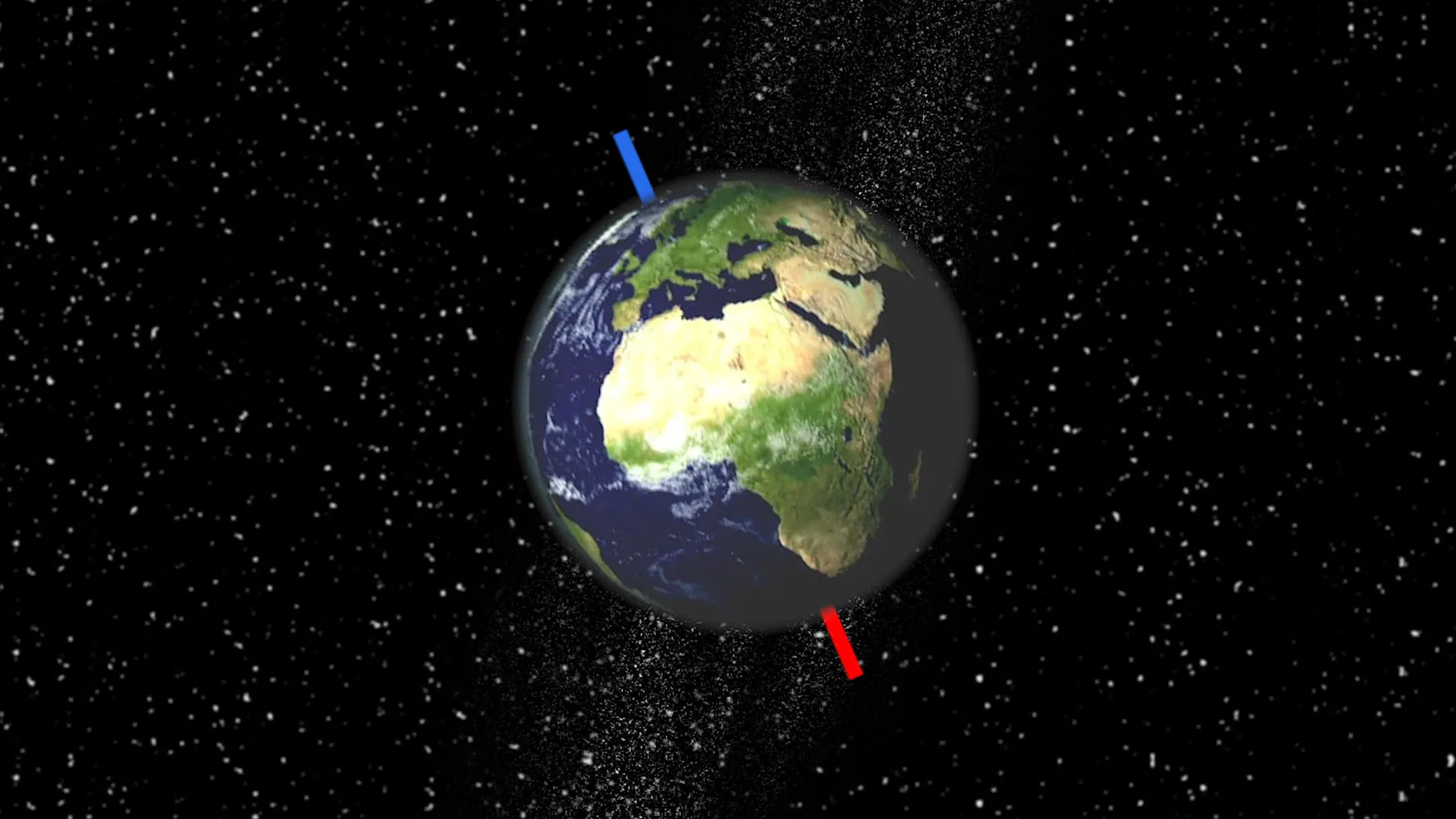
Earth's Tilt
The way Earth leans on its side, causing the seasons.

Revolution
One full trip around something, like Earth going around the Sun.
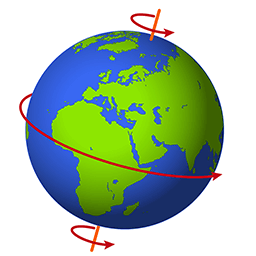
Rotation
When something spins, like Earth turning on its axis.
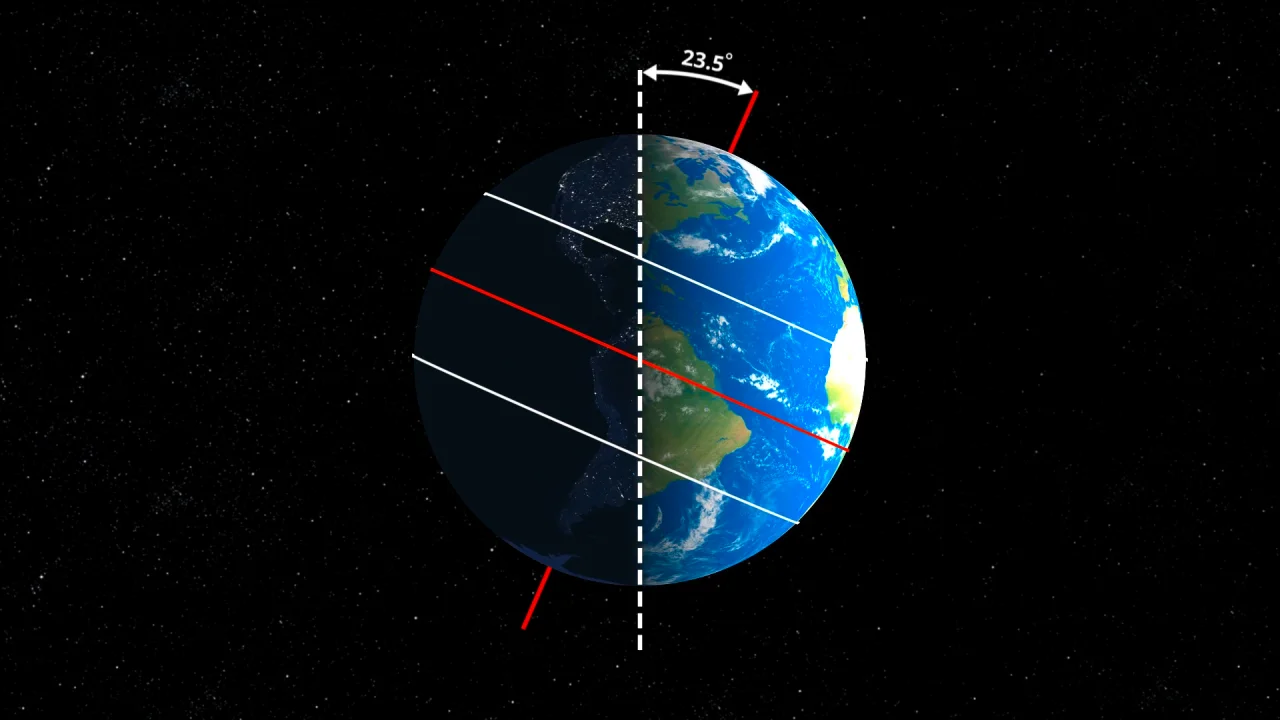
Axis
The imaginary line Earth spins around.
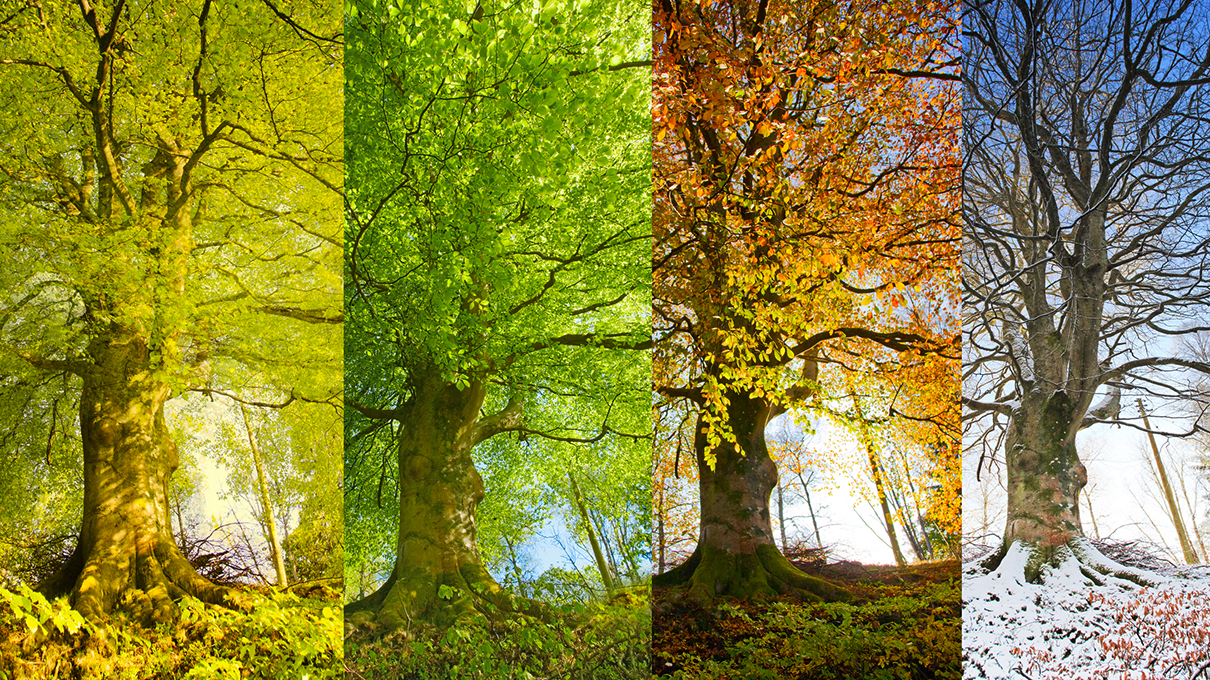

Seasons
The four parts of the year caused by Earth’s tilt.
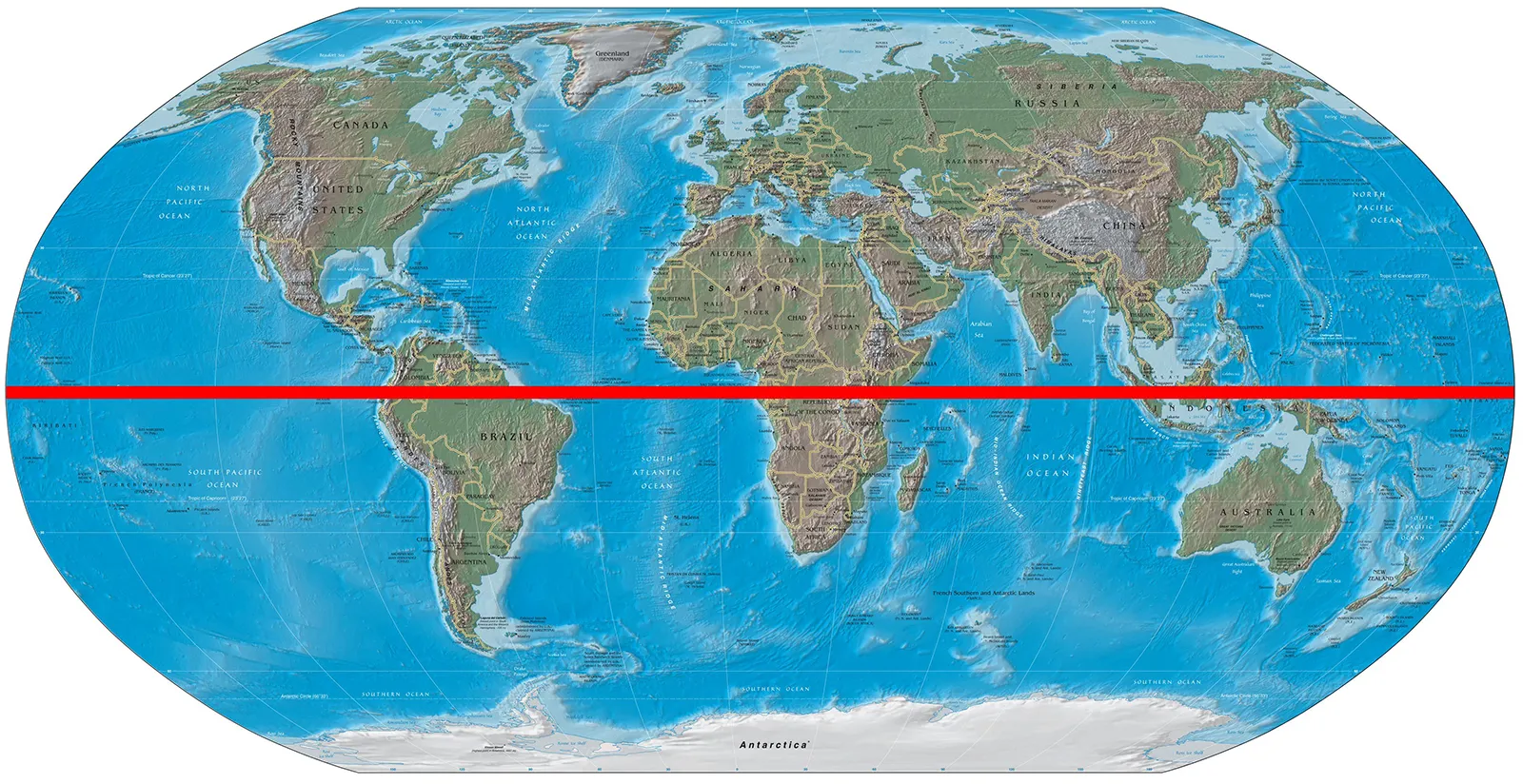
Equator
The imaginary line around the middle of Earth.

Indirect/Direct Rays
Direct rays hit Earth straight on (warmer); indirect rays hit at an angle (cooler).

Ecosystem
A community of living and nonliving things that work together.
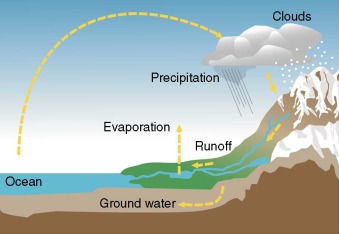
Hydrologic Cycle
The movement of water through the air, land, and sea.

Precipitation
Water that falls from the sky as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
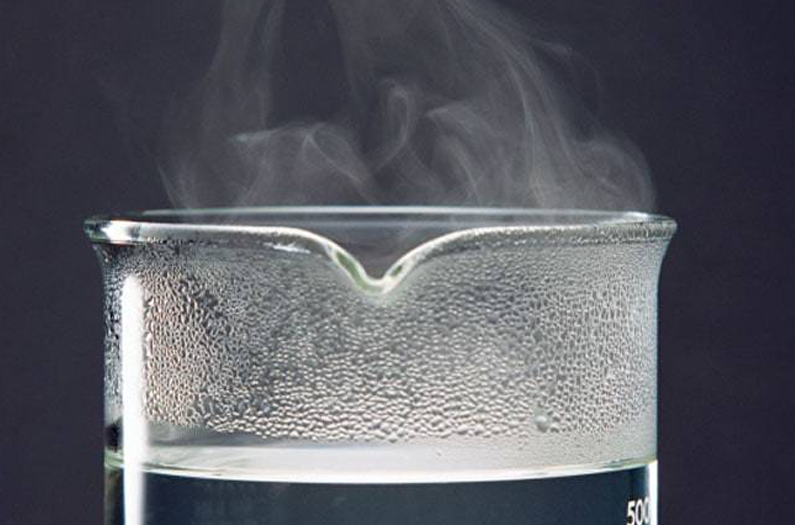

Evaporation
When water turns into vapor and rises into the air.

Condensation
When water vapor cools and forms clouds.

Run-off
Water that flows over the ground into rivers and lakes.
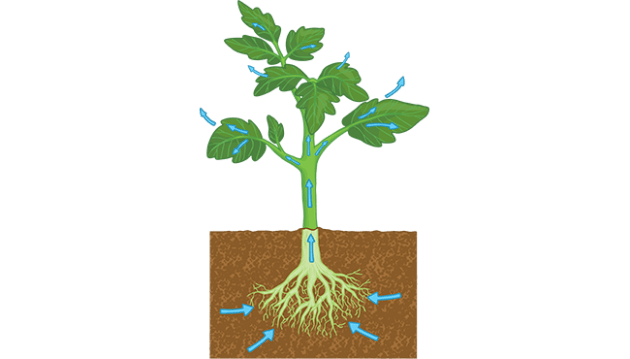
Transpiration
When plants release water vapor into the air.
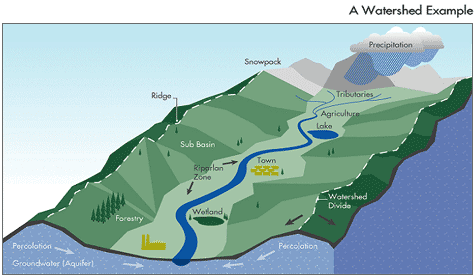
Watershed
An area of land where all the water drains to the same place.

Solar Energy
Energy that comes from the Sun.
Divide
A high area of land that separates two watersheds.

Reservoir
A lake that stores water for people to use.

Tributary
A smaller stream that flows into a larger river.
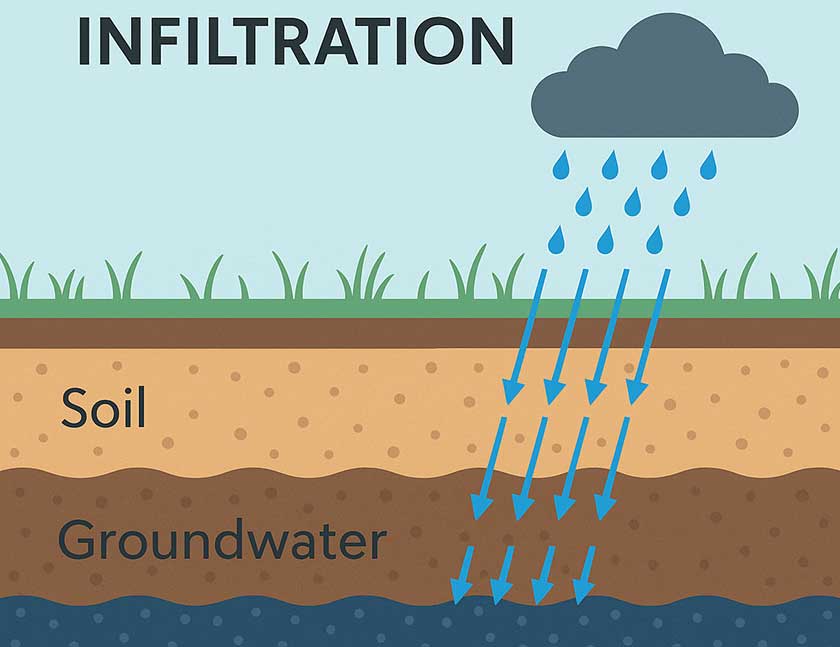
Infiltration
When water soaks into the ground.
Groundwater
Water that fills the spaces under Earth’s surface.

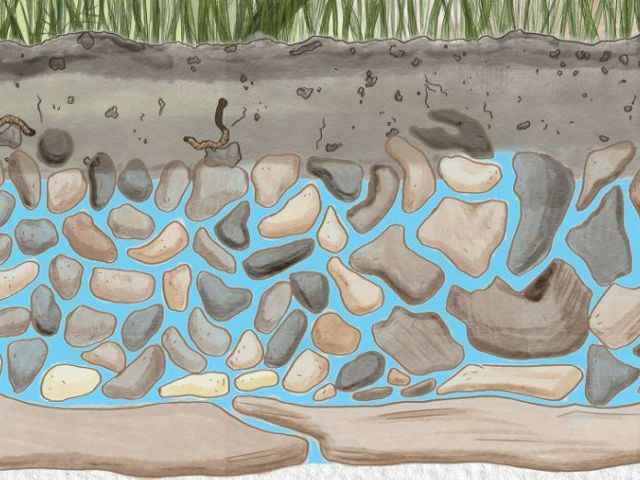
Porosity
How much empty space is in a rock or soil.
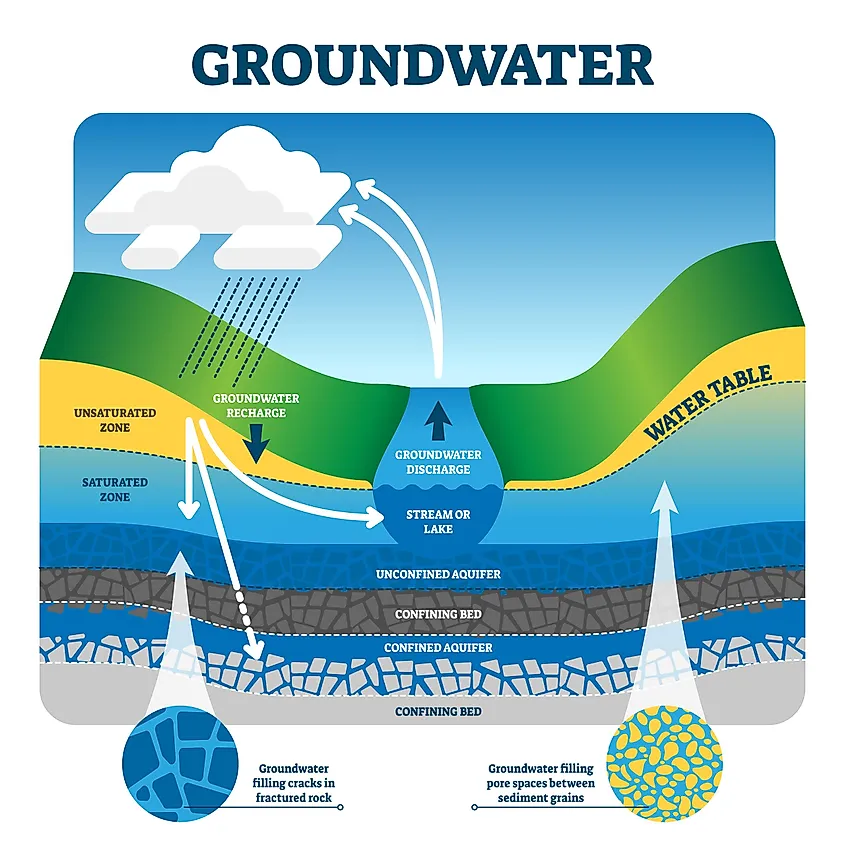
Water Table
The top level of groundwater in the soil.
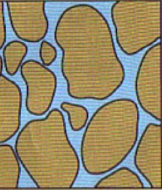
Permeable
Allows water to pass through easily.

Impermeable
Does not let water pass through.

Aquifer
An underground layer that holds water.
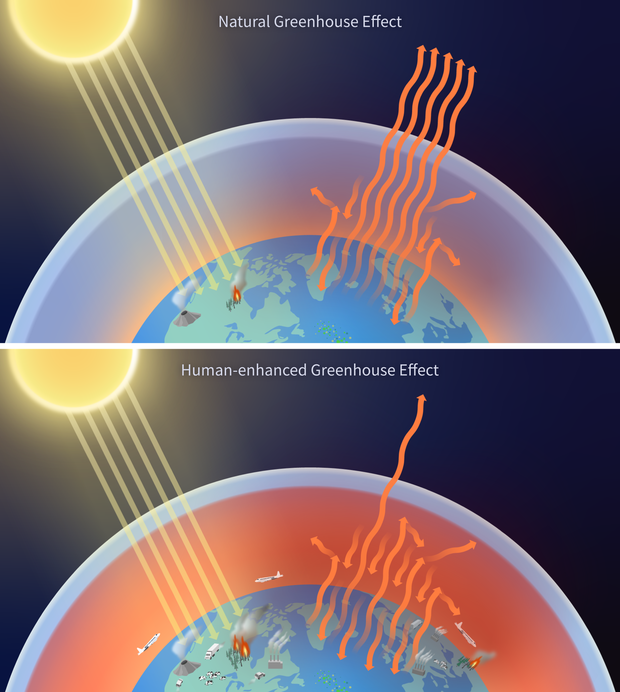
Greenhouse Effect
When Earth’s air traps heat and keeps the planet warm.
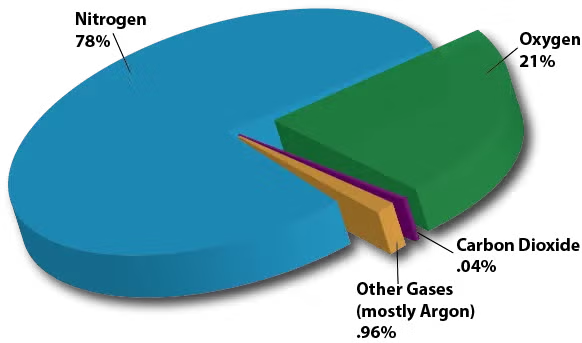
Composition of Air
What air is made of: mostly nitrogen and oxygen.
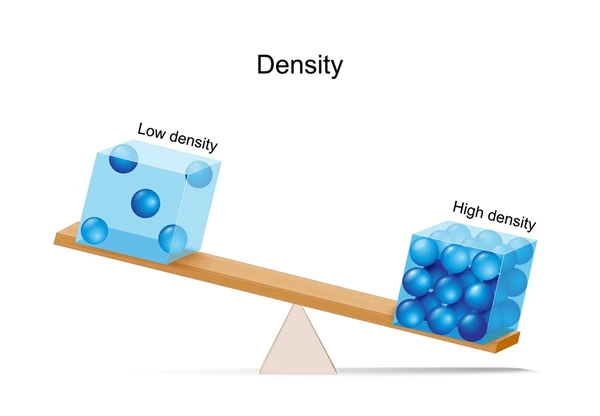
Density
How tightly packed the matter in something is.
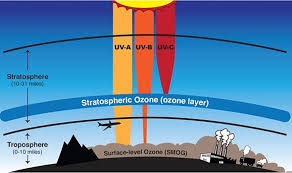
Ozone Layer
The part of the stratosphere that blocks harmful sunlight.

Weather
The day-to-day conditions outside (sunny, rainy, windy, etc.).

Climate
The usual weather in a place over a long time.
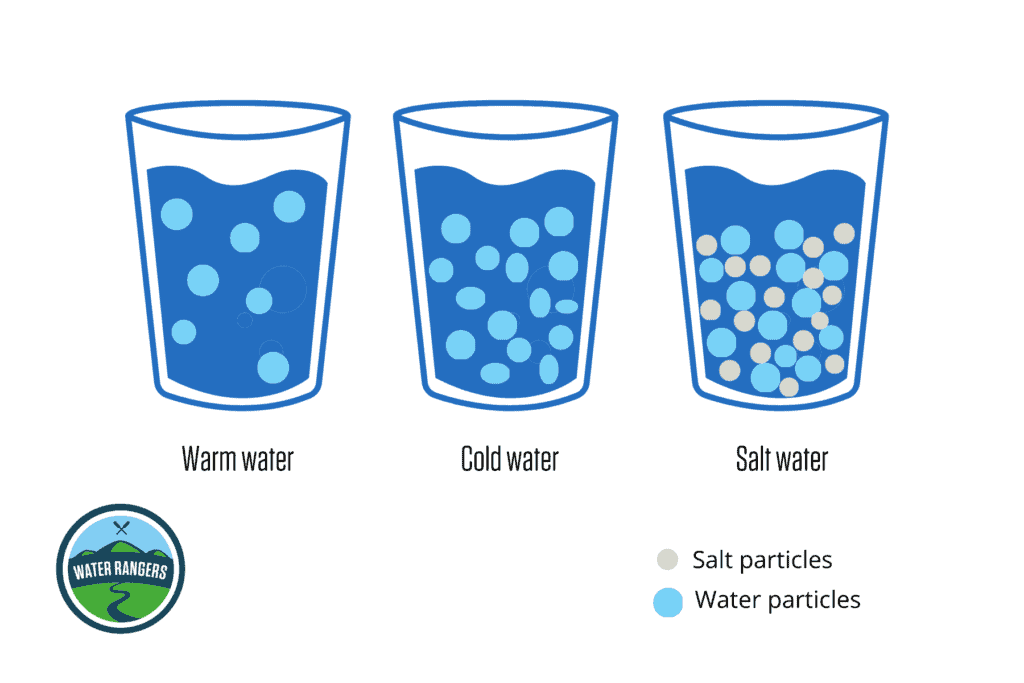
Salinity
How salty the ocean water is.
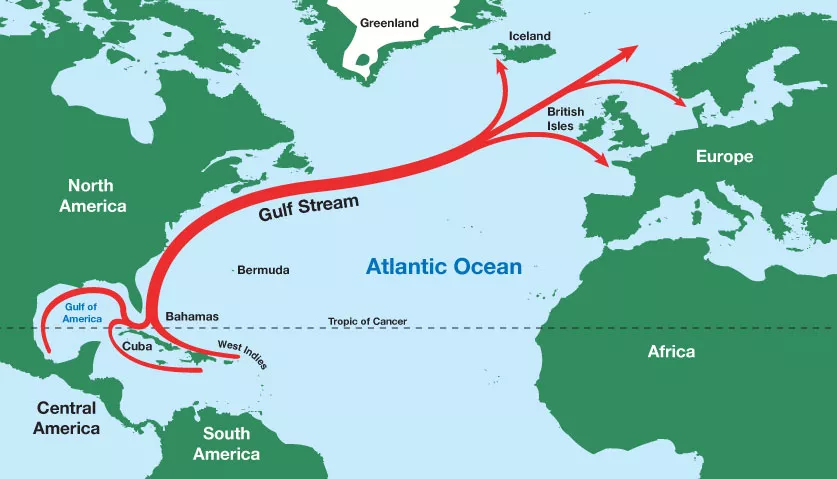
Gulf Stream
A warm ocean current that flows from the Gulf of Mexico across the Atlantic.

Thermal Energy
Energy from heat.
Temperature
How hot or cold something is.

Humidity
How much water vapor is in the air.
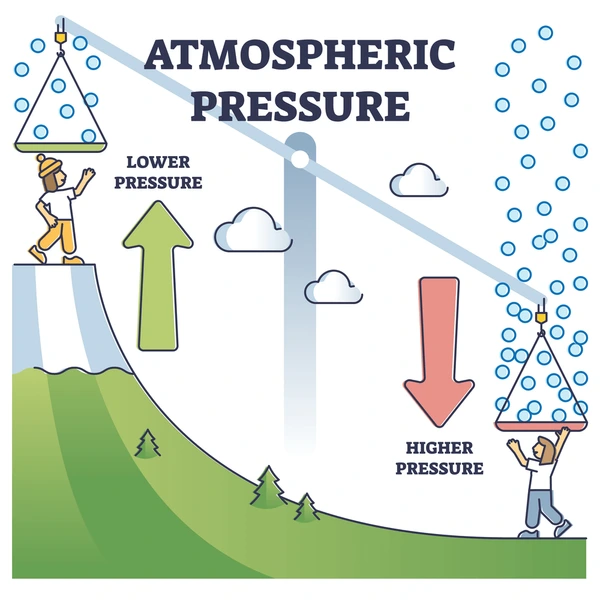
Air Pressure
The weight of air pressing down on Earth.
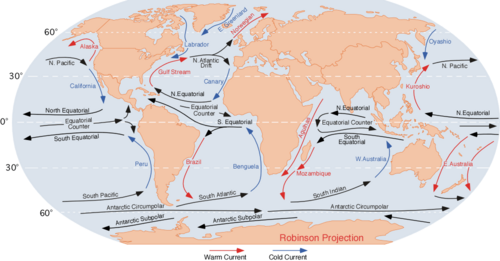
Currents
Flows of air or water moving in one direction.

Catastrophic Event
A very big natural disaster that causes damage.

Climate Change
Big, long-term changes in Earth’s weather patterns.

Fossil Fuel
Energy sources like coal, oil, or gas made from ancient plants and animals.

Energy
The ability to make things move or change.
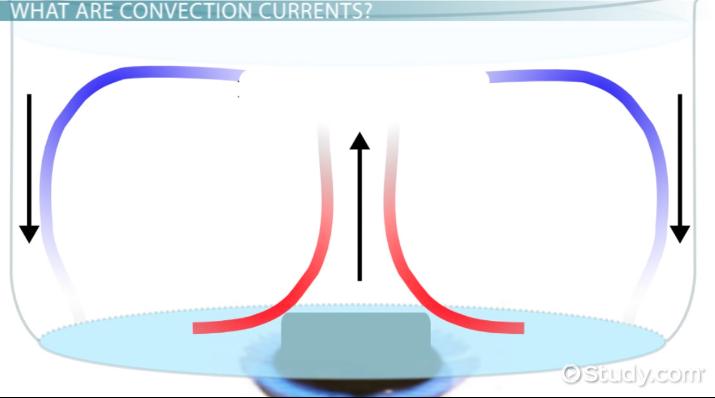
Convection Current
Movement within a fluid caused by differences in heat and density, driving plate motion.