Unit 1: Generators, Motors, and Transformers - Key Terms and Definitions
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What do generators do?
- converts mechanical energy to electrical energy
- uses Faraday's discovery: moving lines of flux in relationship to a conductor
What is a simple generator?
- composed of conductor & magnets
- conductor is a rotating armature, set between opposing magnetic poles
- when the armature is rotated by a strong mechanical force, the generator produces energy
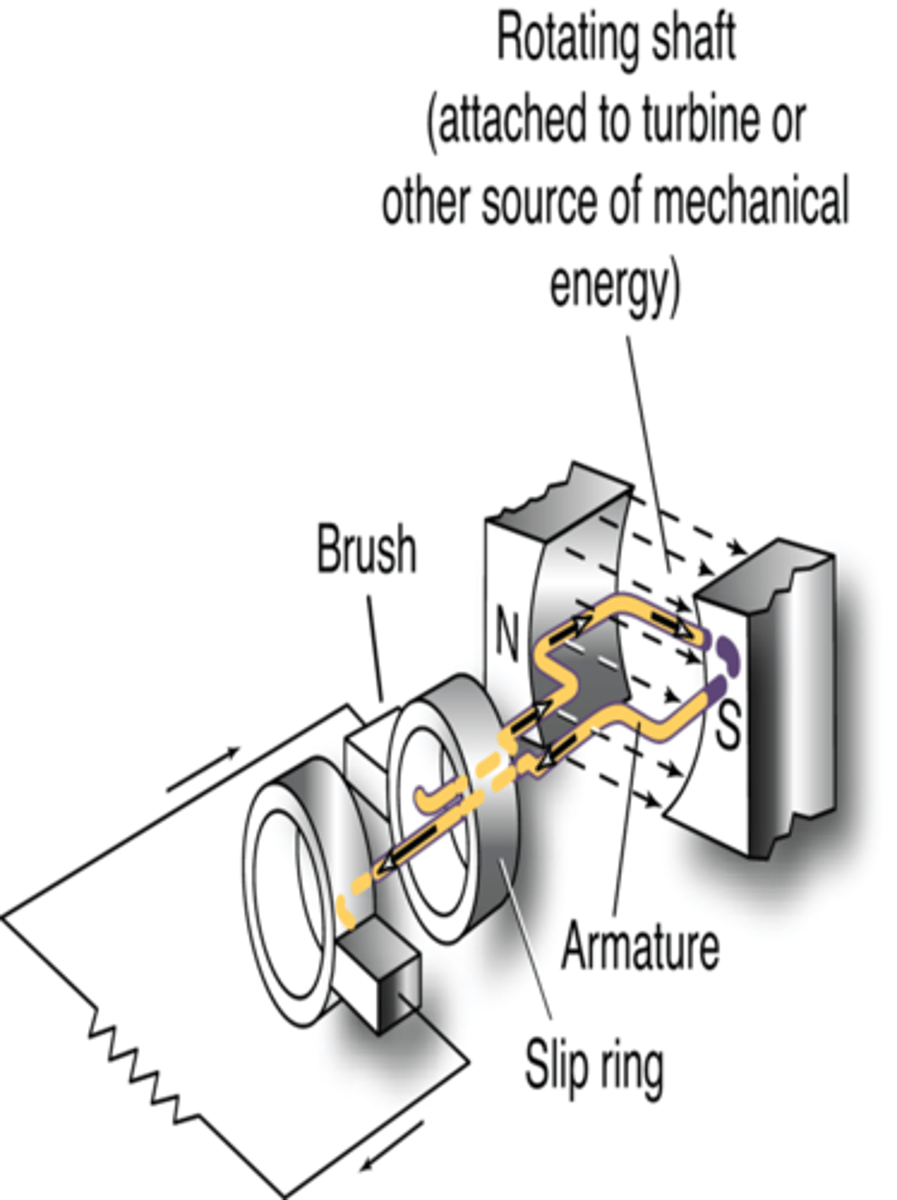
What are used to convey the electrical current from the armature to the circuit?
a set of slip rings & brushes
What is the purpose of the slip rings & brushes?
- permits the circuit to remain stationary while the armature rotates without breaking the electrical contact between them
- allows electrons to flow without interruption
- each slip ring connects to one end of the armature wire
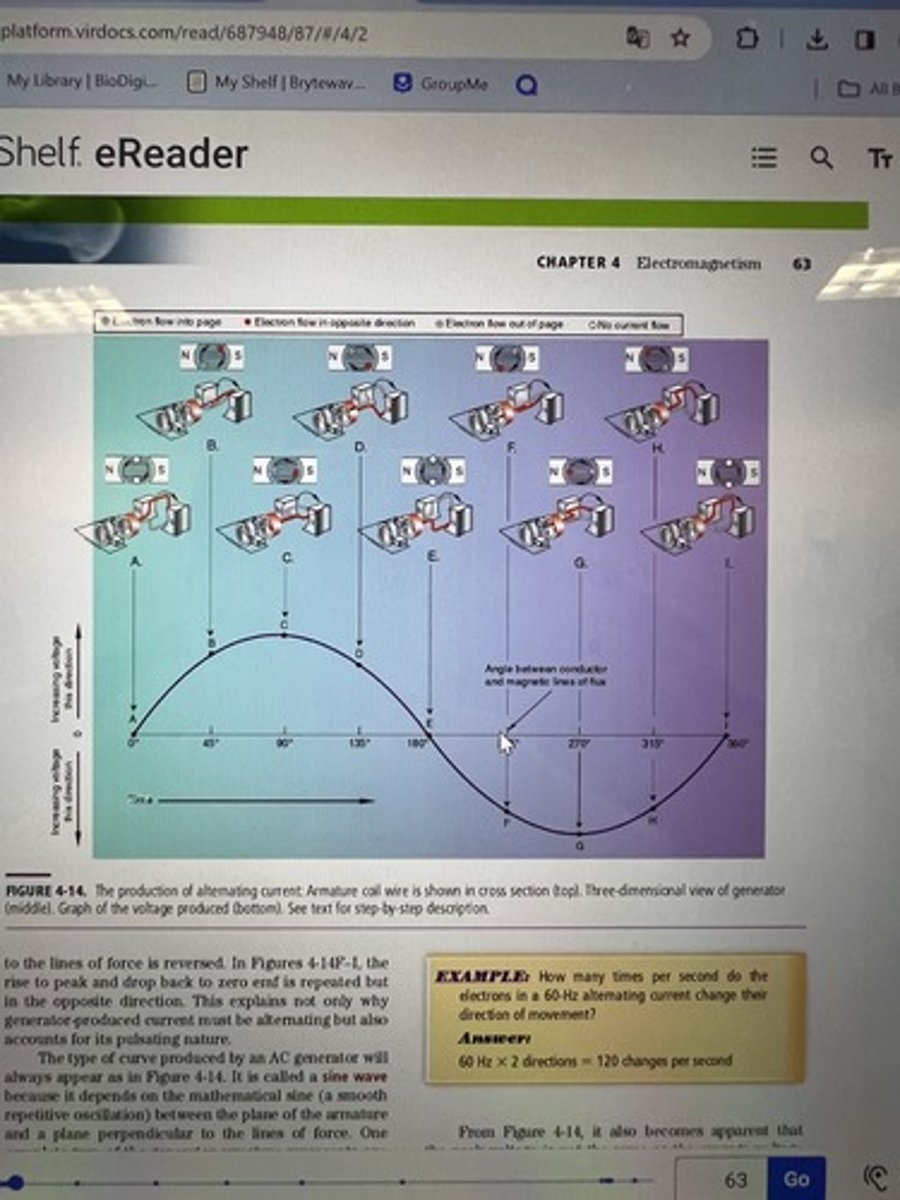
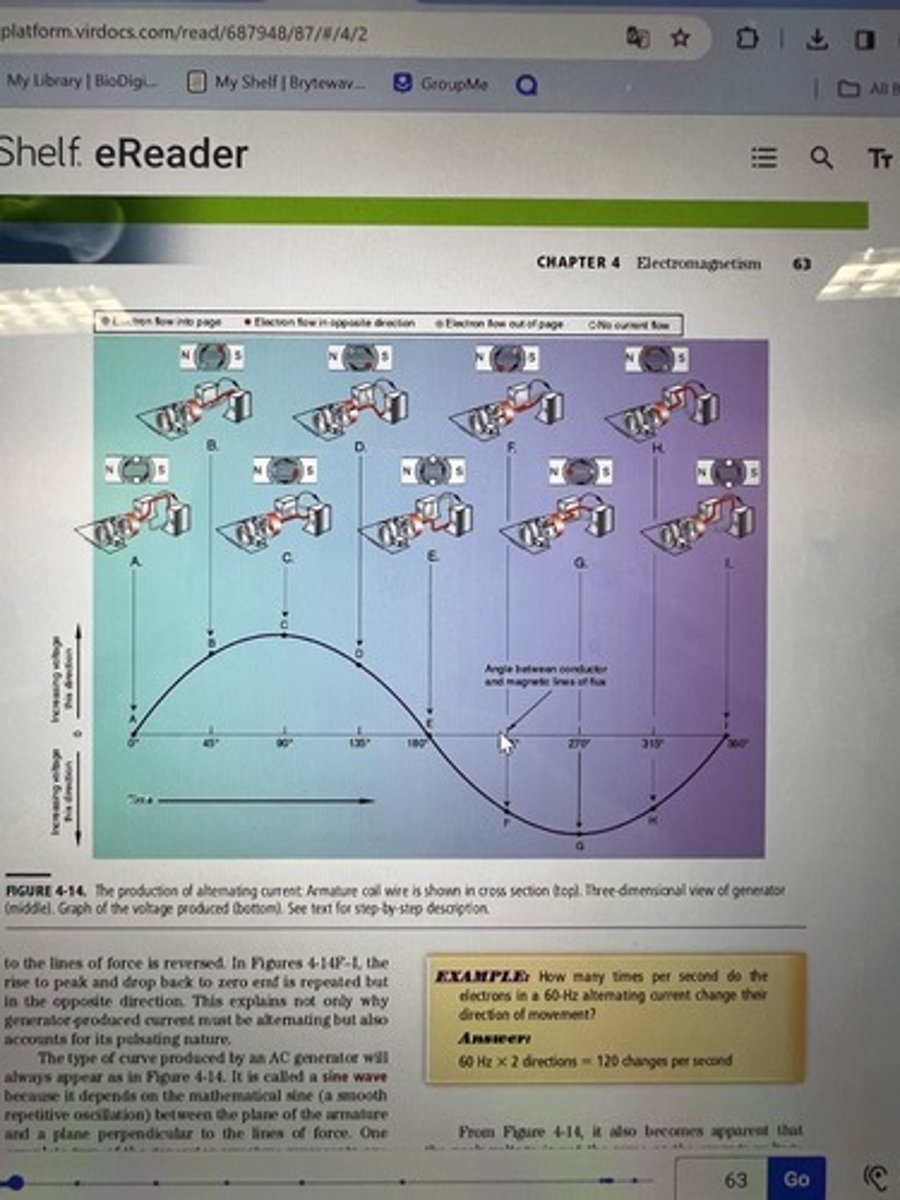
What is the significance of figure 4-14?
- armature coil wire is shown in cross-section at the top
- armature coil wire is shown three dimensionally in the middle
- the graph at the bottom represents the voltage produced
* know that it is an alternating current and creates a sine wave
What is the frequency of a sine wave determined by?
cycles per second
What is the unit of frequency?
hertz (Hz)
True or false:
the peak voltage is the same as the average voltage
false
What are root mean square values used for?
amperage & voltage
* in x-ray kilovoltage settings are representative of peak voltage, not average or rms values
What is a direct current generator made by?
exchanging of the slip rings for a commutator ring
What is a commutator ring?
single ring that is divided in half, with each half connected to one end of the armature wire
How is the sine wave different for direct current?
- armature still turns the same way, but the commutator routes the current differently
- the commutator ring has changed the brush with which it is contact
- has same effects as switching the existing connections on the armature wires
How is direct current produced?
commutator rings reverse the connections, keeping the current in the circuit flowing in the same direction
What is a motor?
- device that is supplied with electrical current to produce mechanical motion
- have same parts as generators & operate on the same principle, but in reverse
- some parts have different names
What is the motor principle?
result of the interaction of magnetic fields when an electrical current is sent along a conductor that is residing in a magnetic field
What allows the conductor to begin moving?
- as current flows through a conducting coil, a magnetic field is established
- because the coil lies in the lines force of the stationary magnet, the induced lines of forces will be attracted in one direction while at the same time being repelled in the other direction
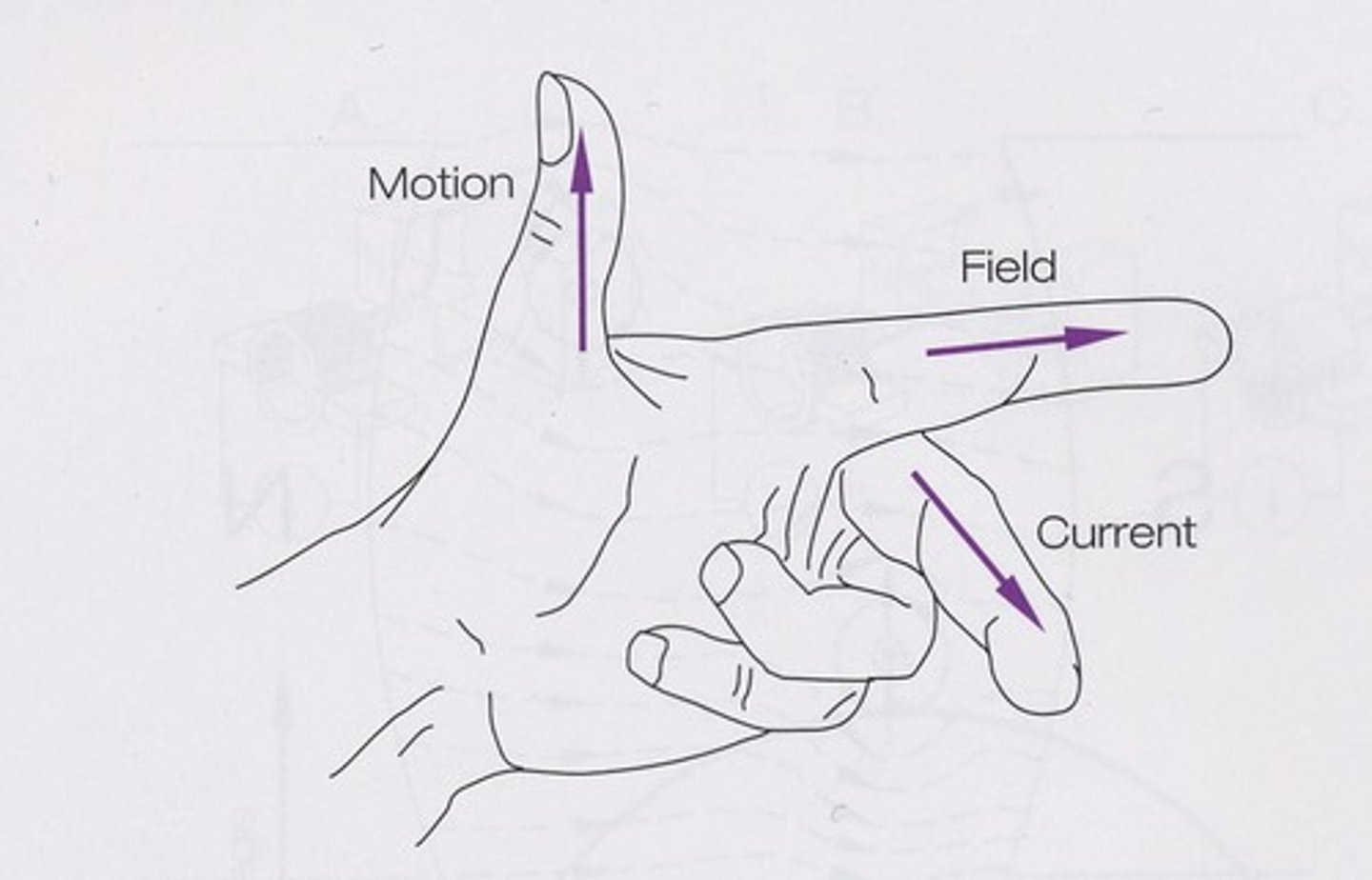
What is Fleming's left-hand motor rule?
- opposite direction of generators
- index finger points in the direction of the magnetic lines of force
- middle finger points in the direction of the conventional current
- thumb indicates direction the conductor will move
CURRENT CREATES MOTION
What do direct current motors use? Alternating current motors?
- commutator rings: DC
- slip rings: AC
What are the 2 main types of alternating current motors?
- synchronous AC motors
- AC induction motors
What are synchronous AC motors?
- have conducting coils that turn at the same speed as the generator armature supplying the current
- useful when a steady speed is necessary
- such as in a timing device
What are AC induction motors?
- use a rotor coil with an exterior magnetic field supplied by several pairs of electromagnets
- it produces a strong magnetic field which increases the power & permits it to run at any desired speed
- x-ray tube uses DC
- rotor in x-ray tubes consists of bars of copper around an iron core that is attached to the x-ray tube anode disk by a shaft
What is used in a AC induction motor instead of commutator or slip rings?
- stator
- stator consists of pairs of stationary magnets arranged around the rotor
- stator is supplied with multiphase current & energized in sequence
What do x-ray tubes use?
- induction motors are used in rotating the anode in x-ray tubes
- the electromagnets have to be outside the vacuum tube to avoid interference with the high voltages
What is the significance in meters? (don't need to know?)
- galvanometers for DC (permanent magnets) to indicate current
- dynamometers for AC (electromagnets)
- when a meter is connected in a series it measures current in amperes & is called an ammeter
- when connected in parallel, it measures potential difference in volts & is called a voltmeter
What is a transformer?
- device that operates on AC to change electricity from a primary voltage to a secondary soruce
Why is a transformer used?
- used to change the magnitude of current & voltage in a circuit
- changes the intensity of alternating voltage & current to a higher or lower value
- change is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary coil as compared to the number of turns in the primary coil
*since a transformer operates on the principle of mutual induction it must have a changing electric current (AC)
What are transformers composed of?
- 2 coils of wire placed near one another, but without electrical connection
- if current is supplied to one coil, the lines of force that are induced will pass through the other coil & induce flow of electrons
*primary coil: supplied with current
*secondary coil: induced with current
What causes the induced current to be different in the secondary coil?
the number of turns of wire in the primary coil is designed to be different from the number of turns of wire in the secondary
What are the 3 important transformers in the x-ray circuit?
- step-up transformer
- step-down transformer
- autotransformer
What is a step-up transformer?
- uses alternating current
*when voltage is increased from primary coil to secondary coil it increases voltage while decreasing amperage
- number of turns in the secondary coil is greater than the number of turns in the primary coil
- used to raise the incoming-line voltage to the kilovoltage range necessary for x-ray production
- operates on mutual induction
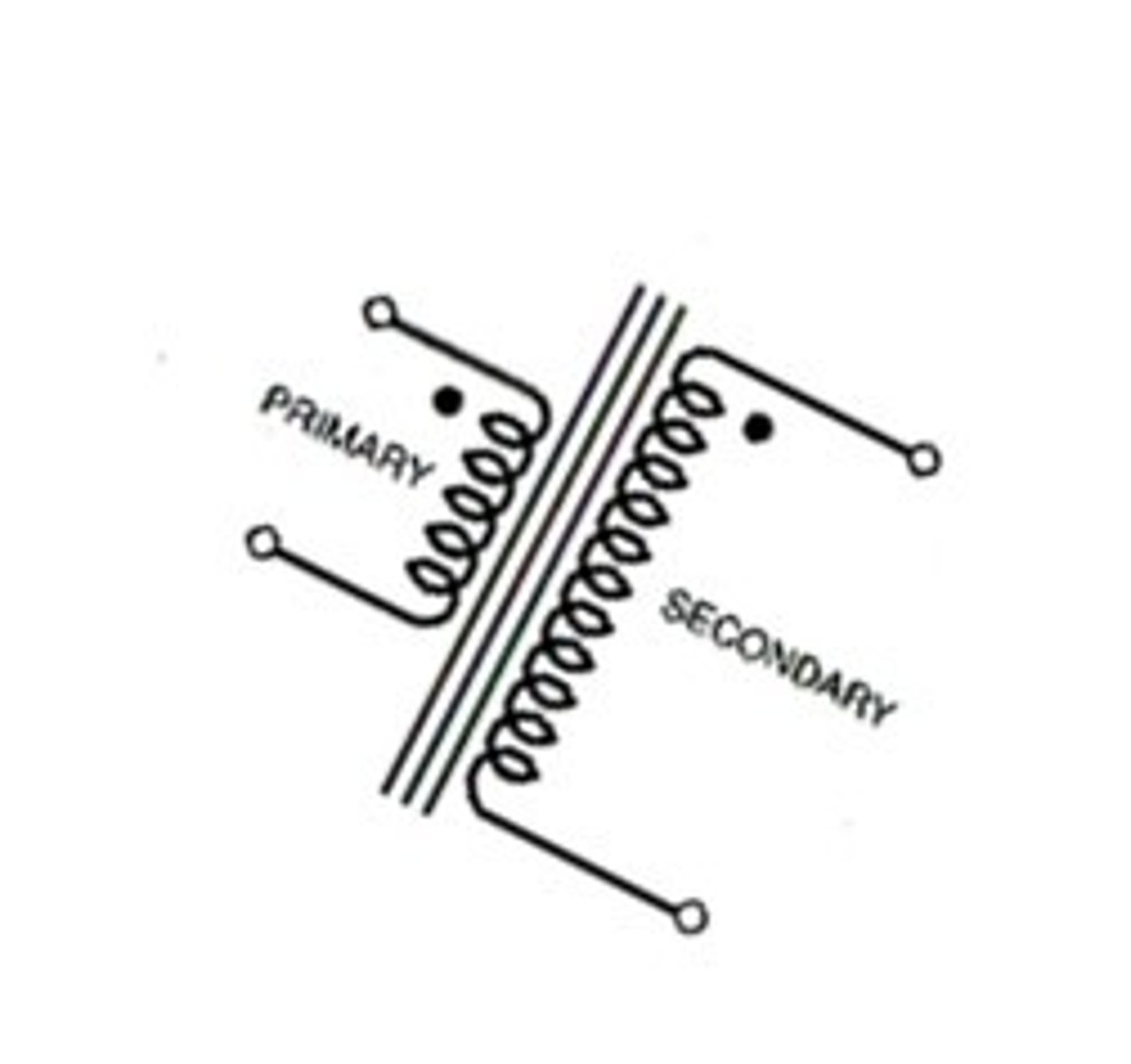
What is a step-down transformer?
- when voltage is decreased from primary to secondary
- the number of turns in the secondary is less than the number of turns in the primary coil
- used to decrease the incoming-line voltage to the 6 to 12 volt & 3 to 5 ampere range used to heat the x-ray tube filament
- operates on mutual induction
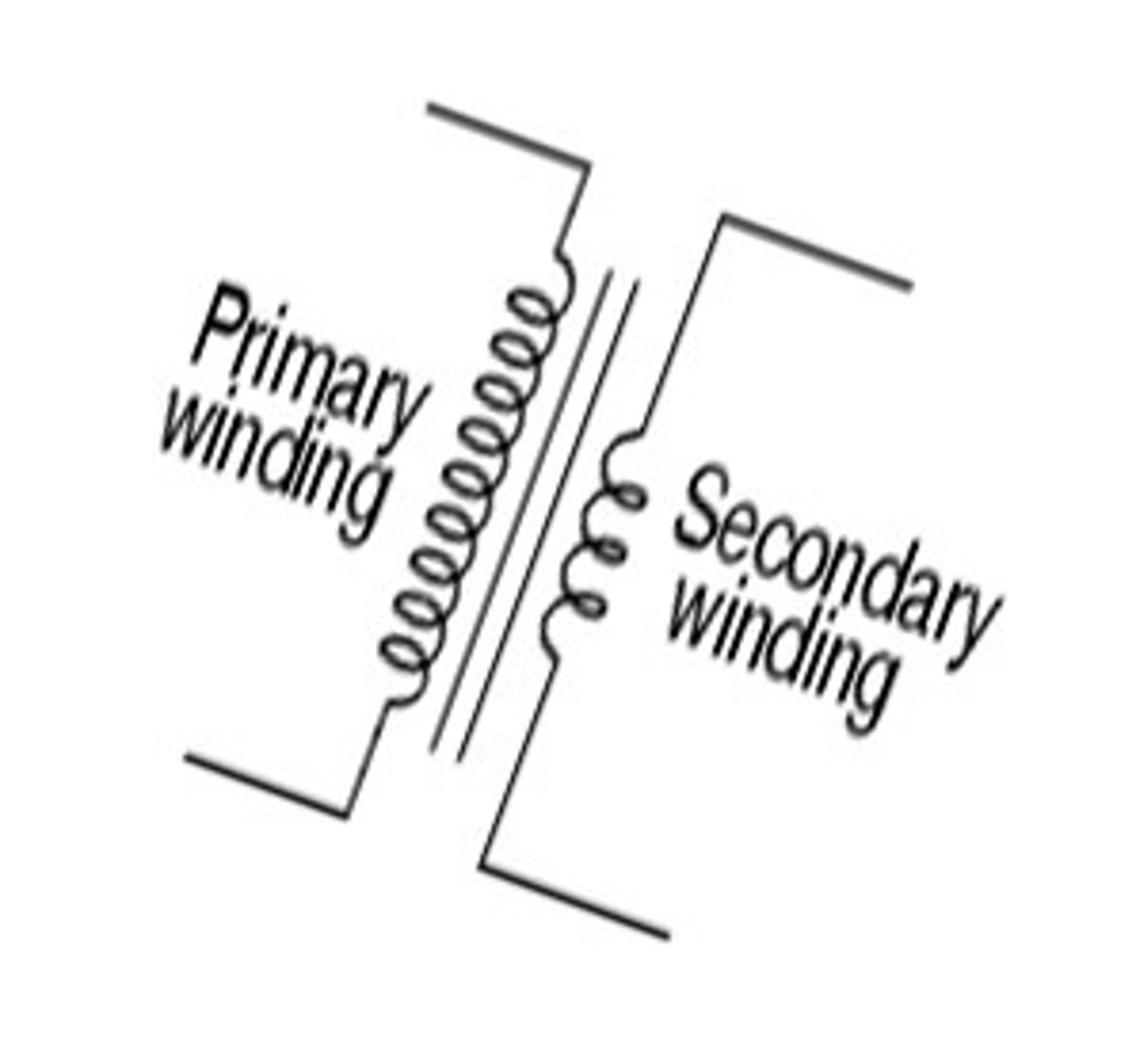
What is an autotransformer?
- primary & secondary coils are connected in series rather than separating them
- connections are made along a single coil at different points for primary & secondary
- the primary side has a selection of taps available to permit a variable number of turns in primary coil
- secondary side has a selection of taps available to permit a variable number of turns in secondary coil
- when connection to the taps are attached to control buttons, there is an effective means of changing voltage
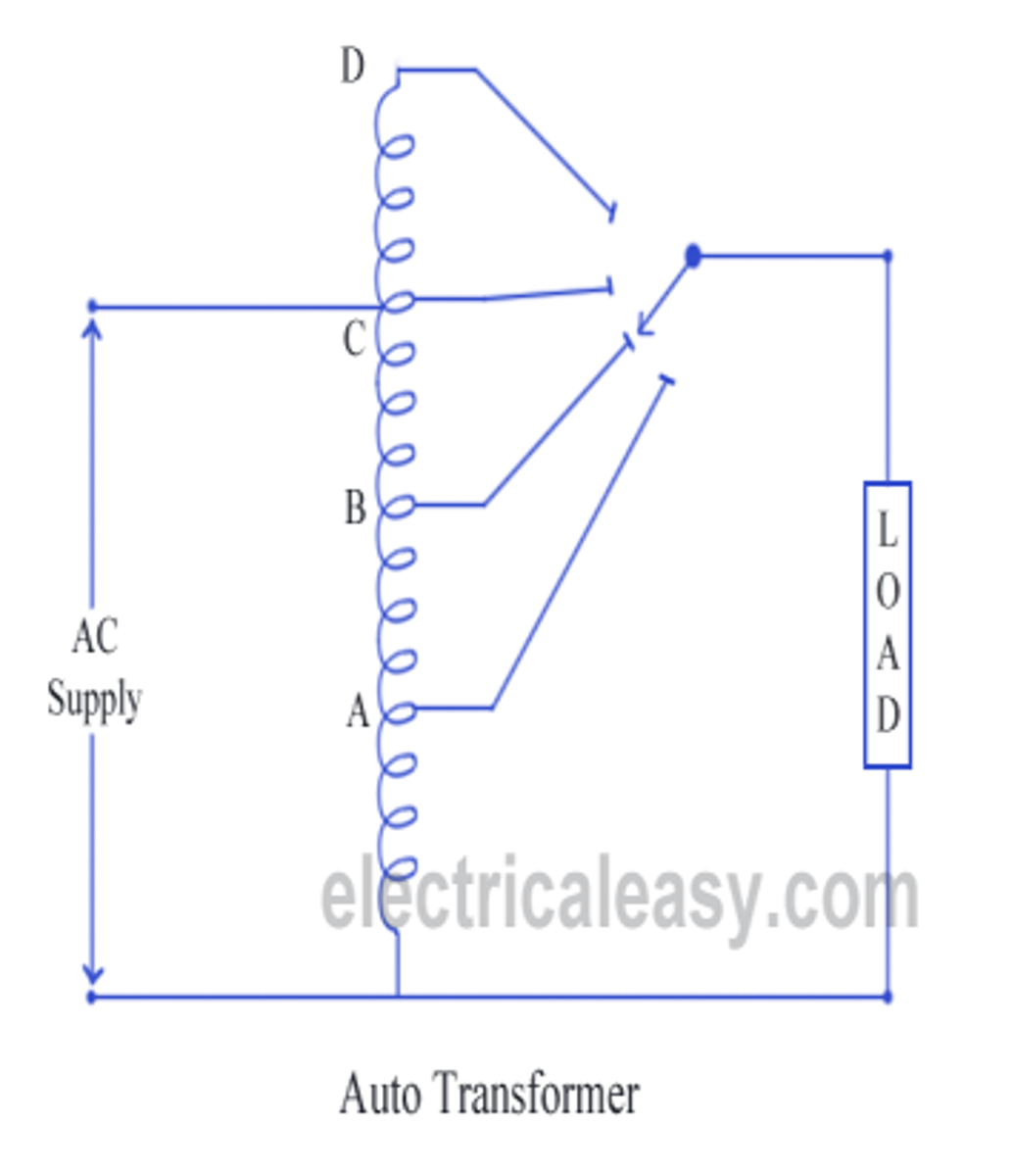
What is significant about an autotransformer?
- supplies a precise voltage to the filament circuit & to the high voltage circuit
- also called variable transformer: can step-up or step-down voltage
- operates on self-induction
- known as the kVp selector
- can increased voltage up to 2x
- determines the amount of voltage sent to the high-voltage, step-up transformer
What are the different types of transformers?
- air core: 2 coils of wire in proximity
- open core: fill primary & secondary coils with iron core, increases magnetic field
- closed core: close the core on tope & bottom further increases field strength
- shell type: converge both inside & outside lines of force through an iron core
*most common today are laminated core (shell type)
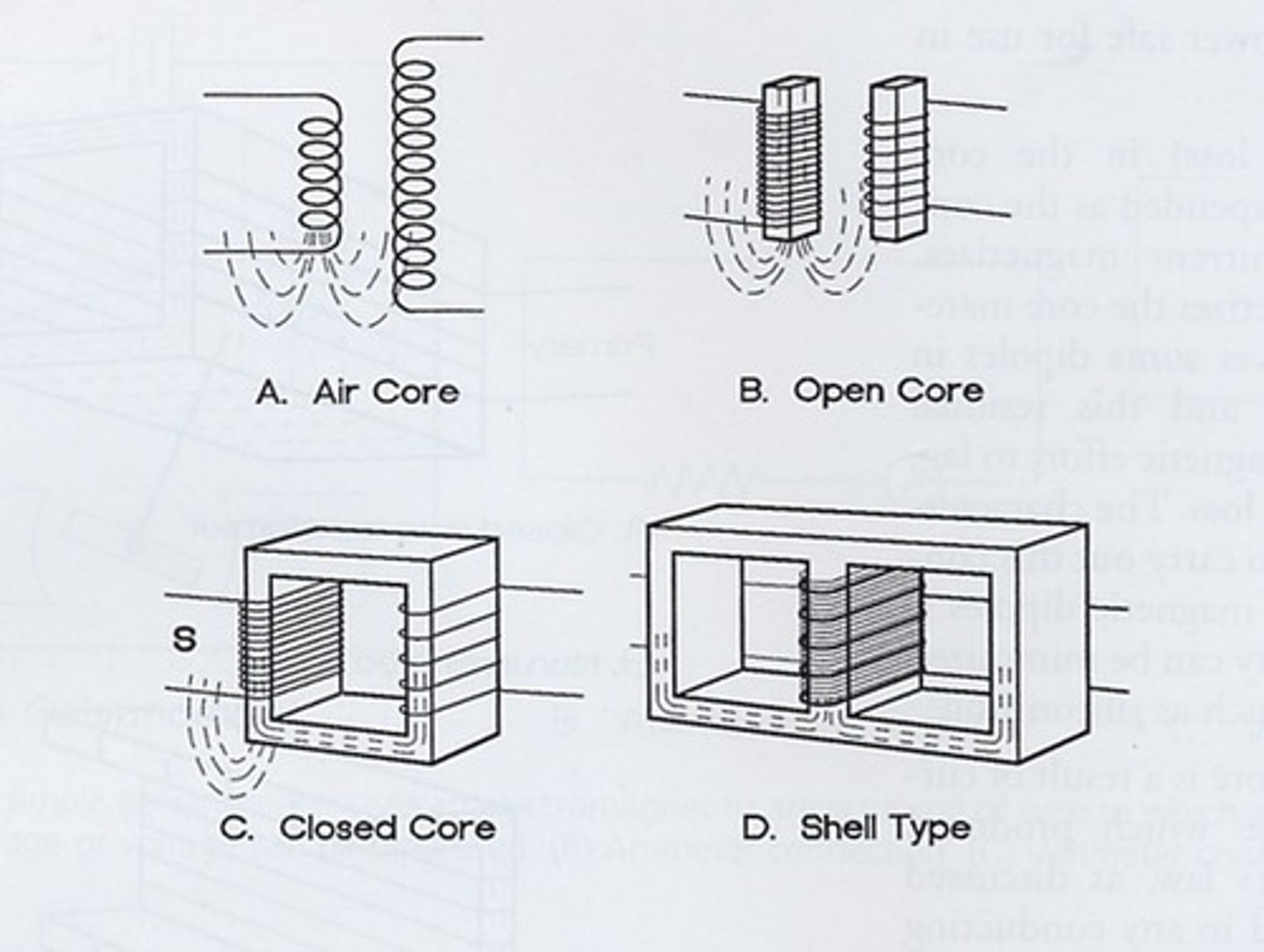
What is the transformer law?
Vs / Vp = Ns / Np
* V: potential difference in volts
* N: number of turns of wire in coil
* P: primary coil
* S: secondary coil
What is transformer efficiency?
the ability of a transformer to avoid power loss, which is usually above 95%
What factors affect how much energy is lost regarding transformer efficiency?
- I2R loss: copper loss, caused by inherent resistance to current flow that is found in all conductors
- hysteresis loss: lagging loss in core, energy is expended as the continually changing AC current magnetizes, demagnetizes & remagnetizes the core material
- eddy current loss: in the core, currents opposing the cause which produced them
* laminating the core reduces eddy current loss
What is a capacitor?
- device for accumulating & storing an electrical charge
- must be charge to be operable
- done by applying DC current
- when discharged, has ability to deliver stored charge in short intervals
- used in mobile x-ray unit
- battery charges
- initiates a burst of high voltage for x-ray exposure