Arterial circulatory system anatomy
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Tunica intima, media, and adventicia
What are the 3 layers of vessels
Tunica intima
What is the innermost layer of vessels consisting of endothelial cells
Tunica media
What layer of vessels is made up of smooth muscle cells
Tunica adventitia
What layer of vessel is consisting of connective tissue, nerve fibres and small vessel capillaries
Tunica media
What layer of vessels is the thickest
Tunica adventitia
What lay of vessels does vasa vasorum originate in
Small vessel capillaries
What are vasa vasorum
Endothelial lining
What is 1
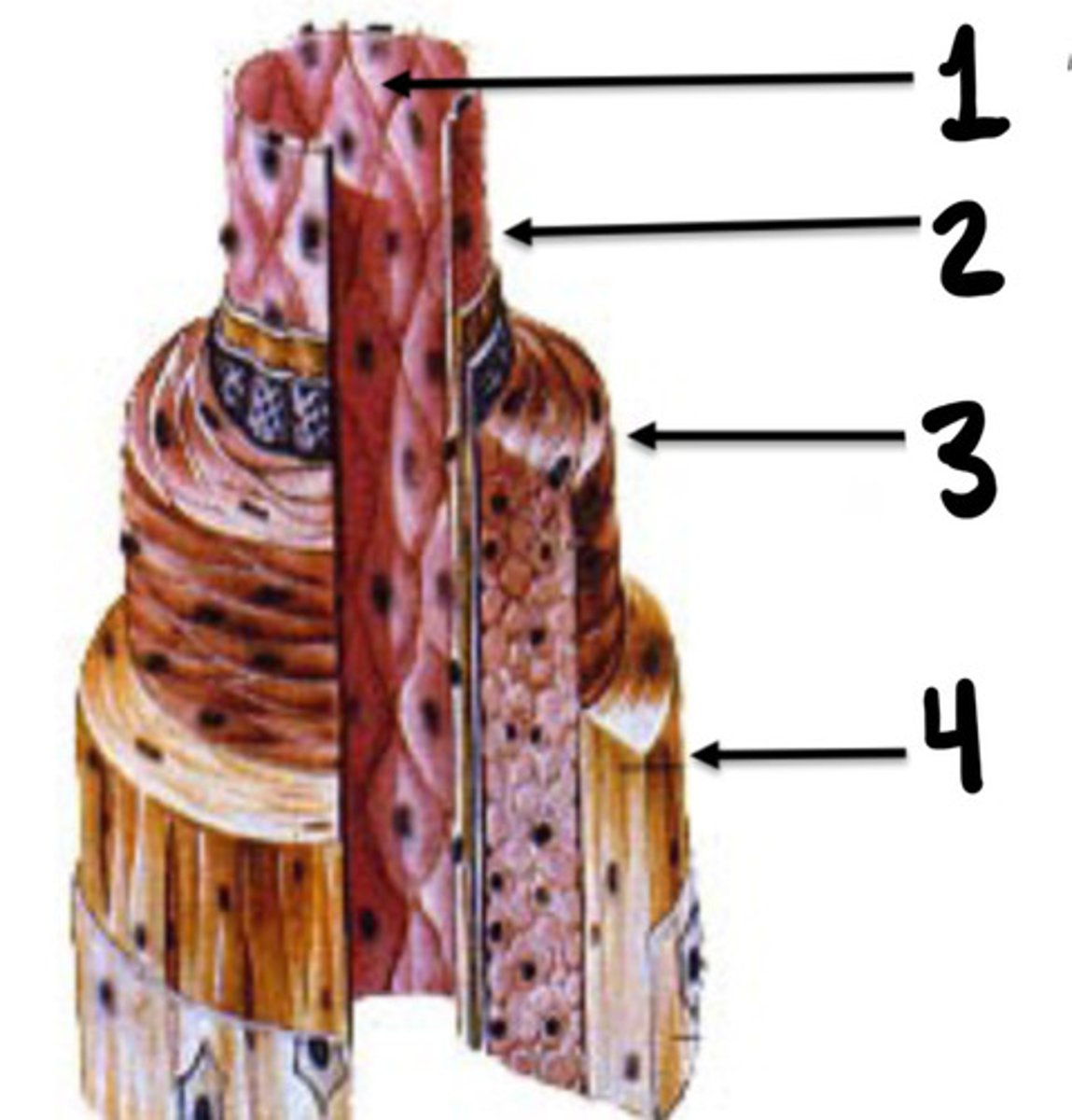
Intima
What is 2
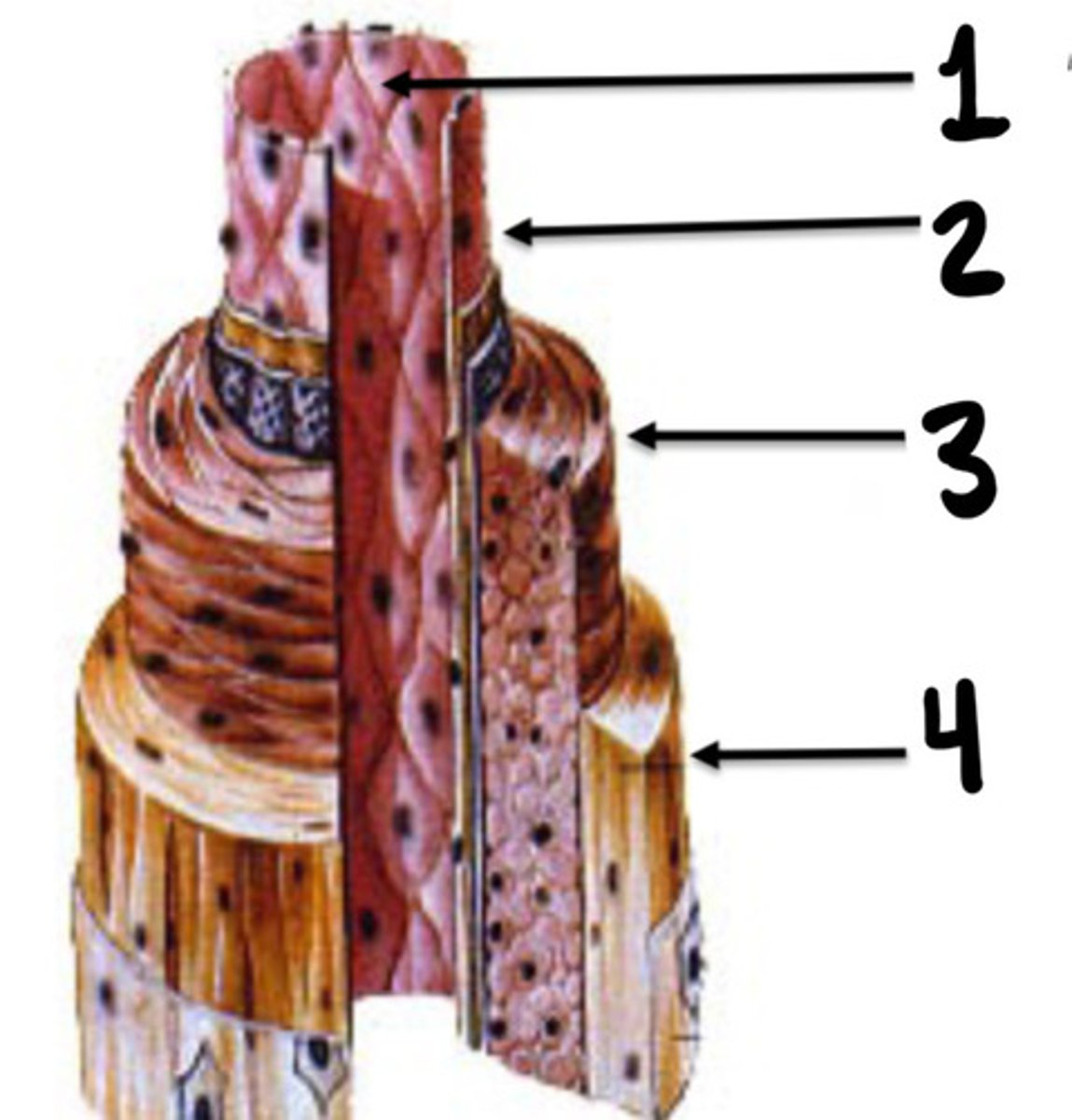
Media
What is 3
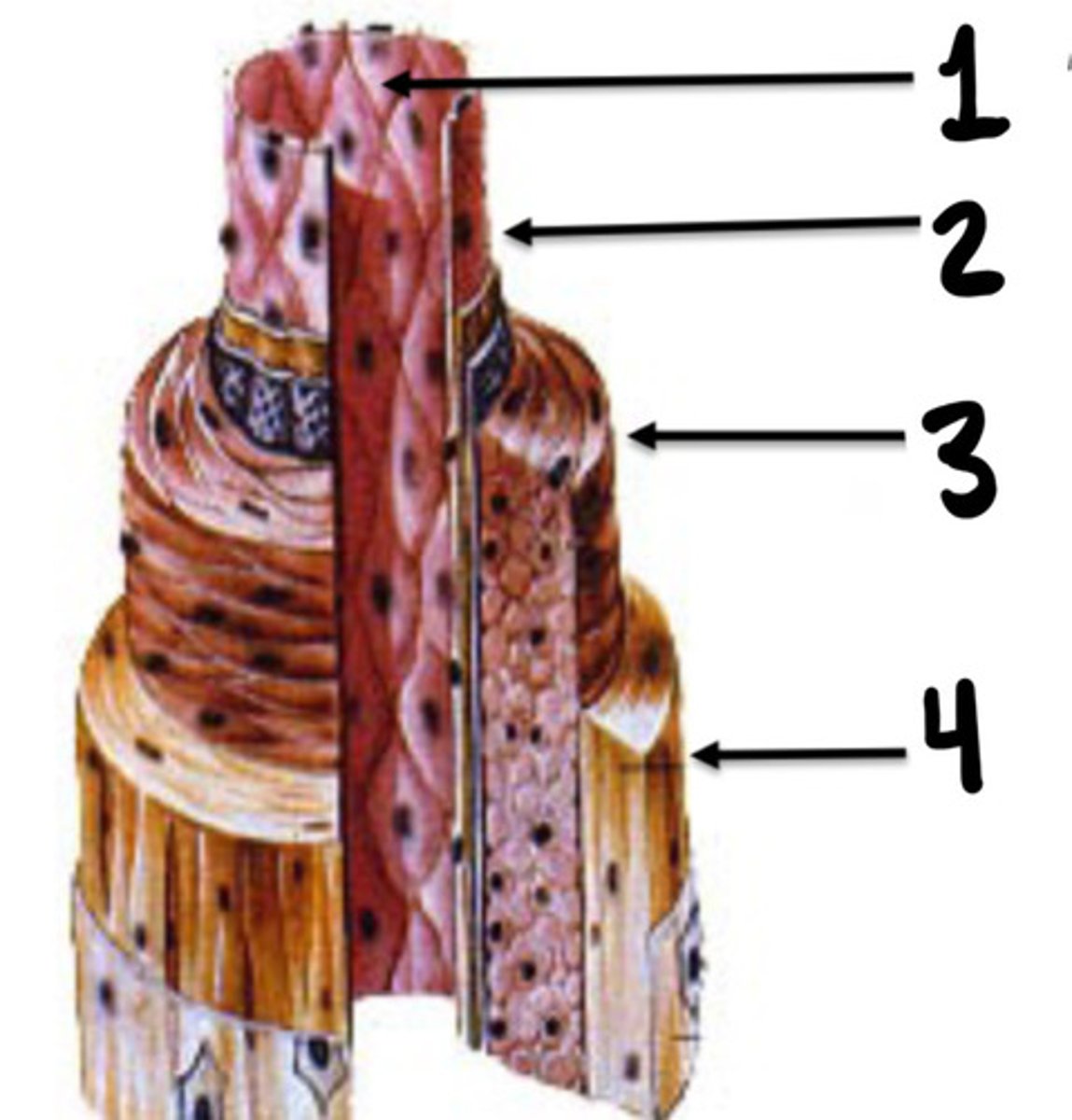
Adventicia
What is 4
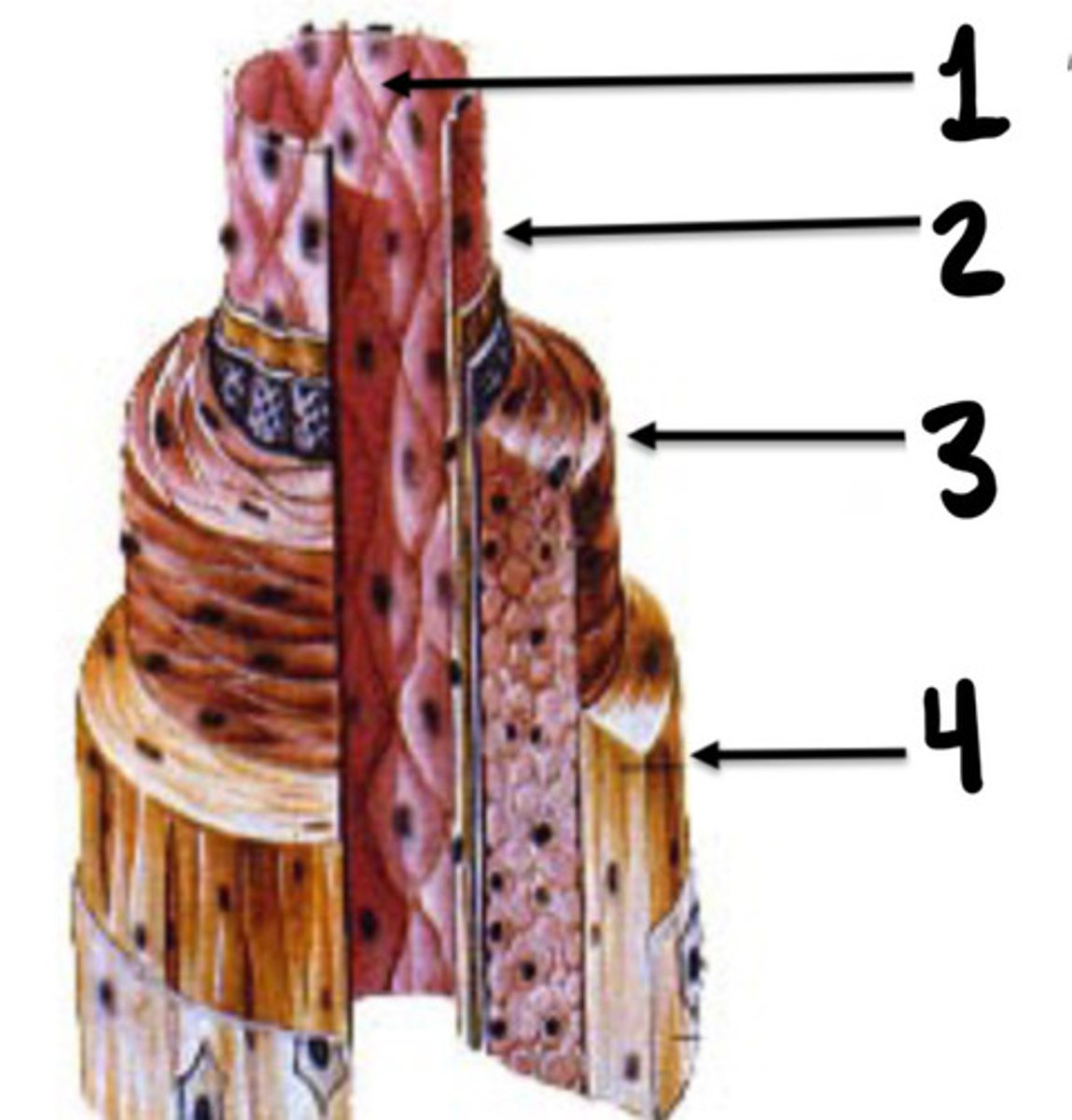
Stopcocks
Arterioles are the ___________ of the vascular system
Resistance
The arterioles are the main providers of ___________ to blood flow within the vascular system
All arteries except the aorta and major branches
What does small and medium sized arteries include
True
T/F: small and medium sized arteries are more elastic and fibrous than arterioles
Aorta and its largest branches
What does large elastic arteries include
Large amount of elastic fibres and less smooth muscle cells
Describe the composition of the walls of large arteries (aorta and its branches)
Size
What are arteries classified according to
Four
How many vessels supplies the brain
2 ICA's and 2 vertebral arteries
What 4 arteries supply the brain
Brachiocephalic, LT cca, and LT subclavian (arteries coming off the aortic arch)
What supplies the central nervous system
Brachiocephalic, LT CCA, LT subclavian
What are the 3 branches of the aortic arch
Slightly posterior from the arch to the right side of the neck
Describe the path of the Brachiocephalic artery
Innominate artery
What is another term for the Brachiocephalic artery
Rt CCA and rt subclavian artery
What does the innominate artery branch into
Upper border of the right sternoclavicular junction
Where does the Brachiocephalic artery branch into the RT CCA and RT Subclavian artery
Left sternoclavicular joint
What does the LT CCA pass underneath after ascending from the aortic arch
False
T/F: the common carotid arteries have a lot of branches coming off them as they travel toward the brain
Internal and external carotid arteries
what does the common carotid artery split into?
Upper border of the thyroid cartilage
Where does the cca divide into internal and external carotids
Aorta
What is 1
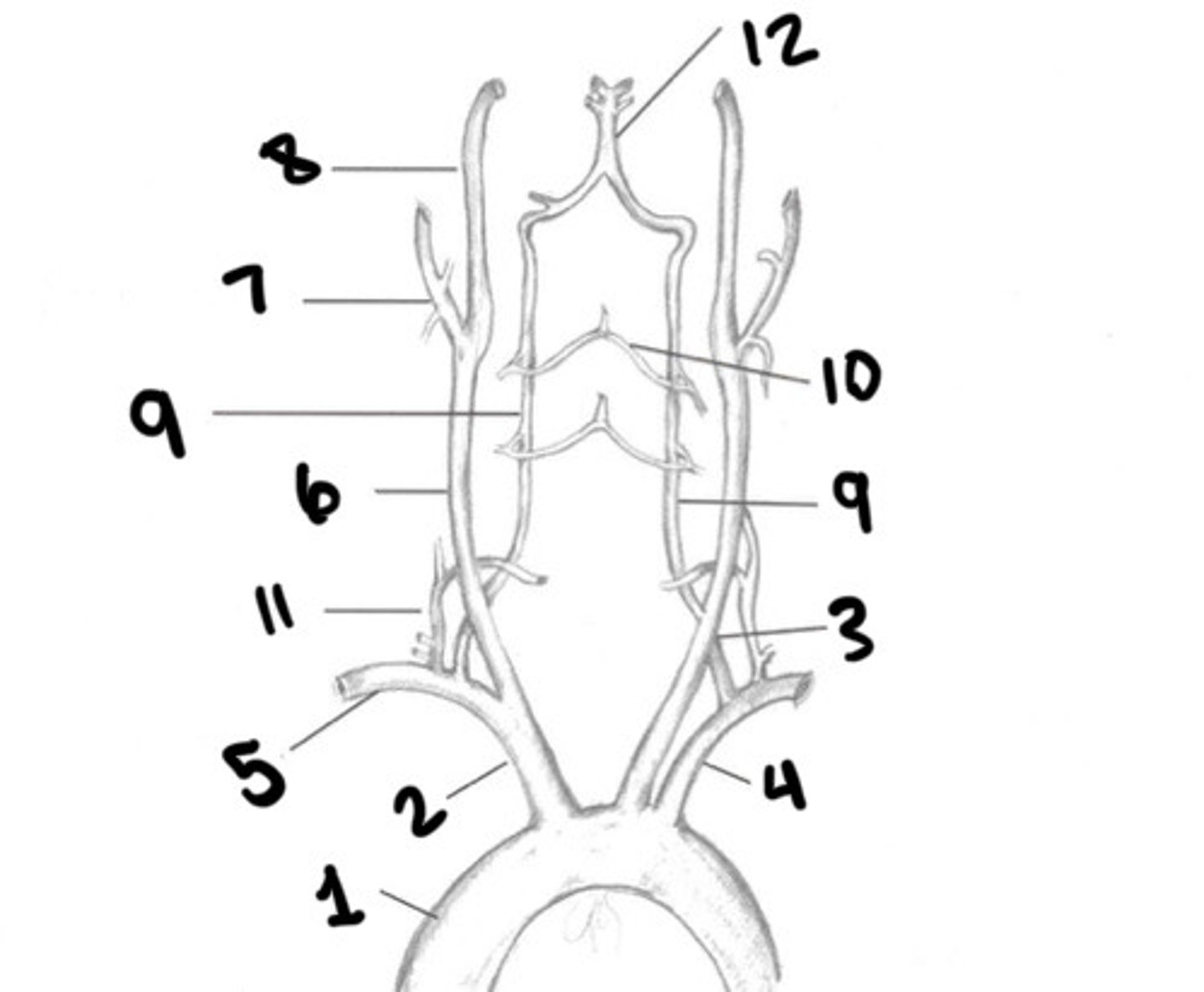
Innominate
What is 2
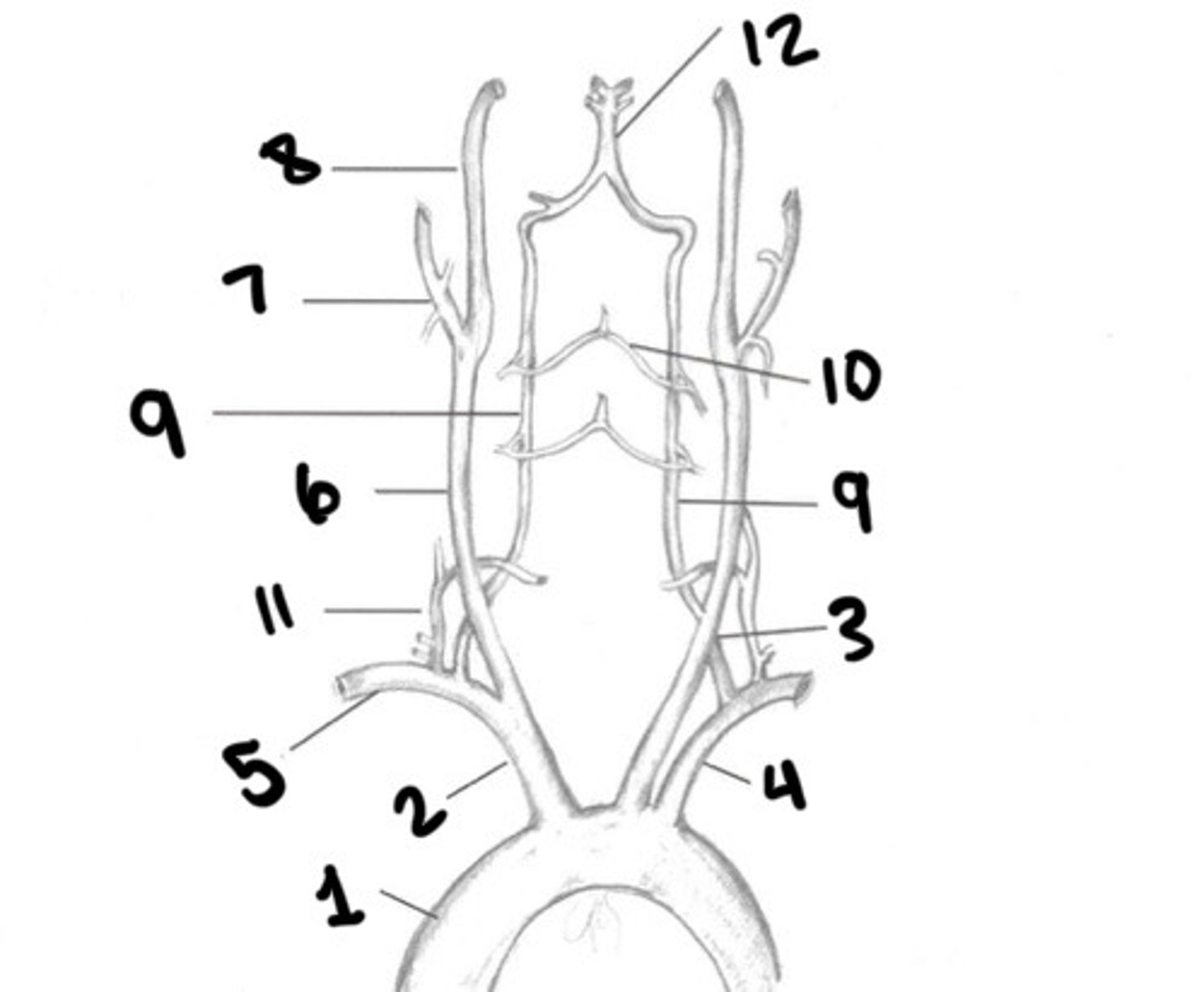
LT CCA
What is 3
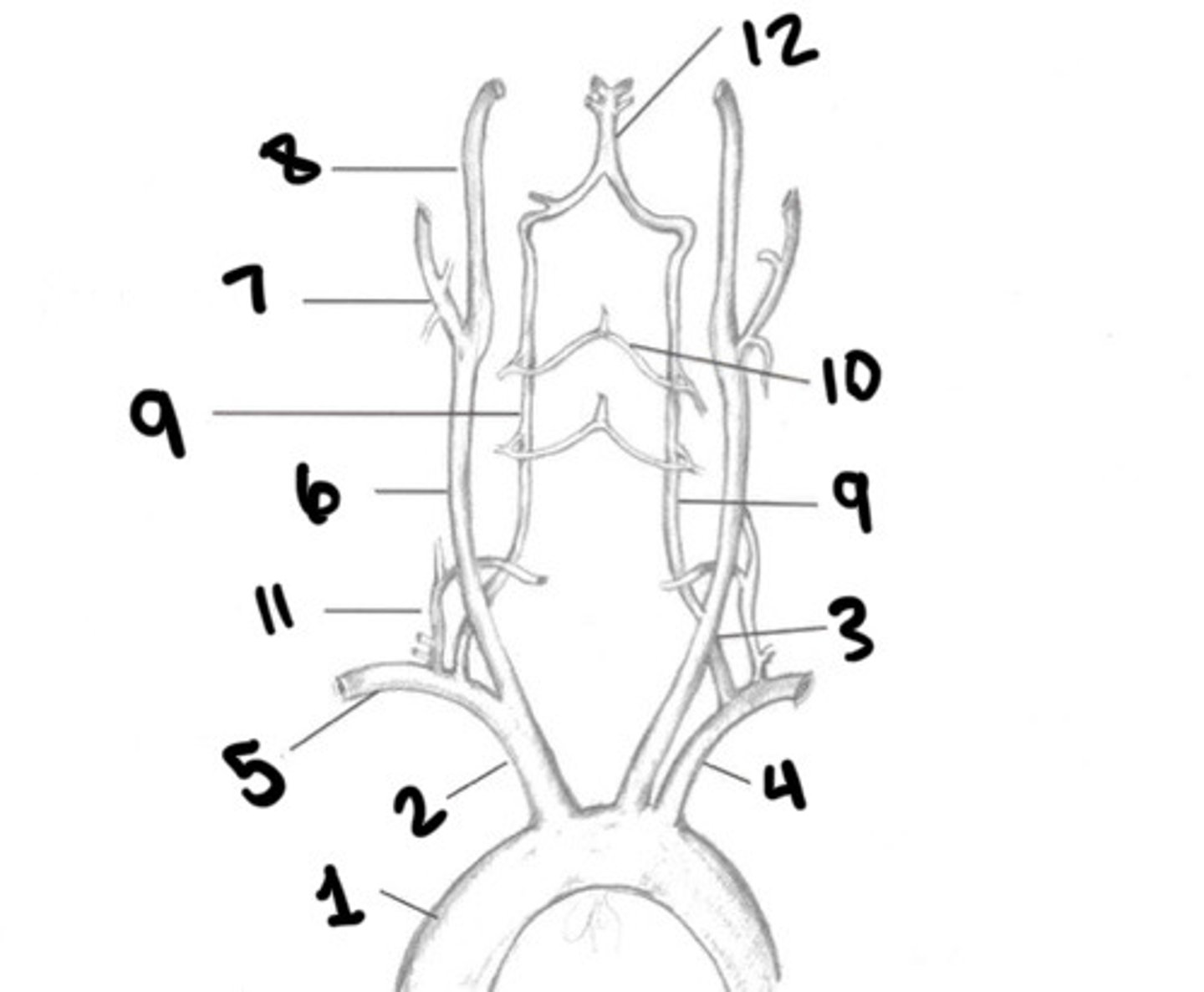
LT subclavian
What is 4
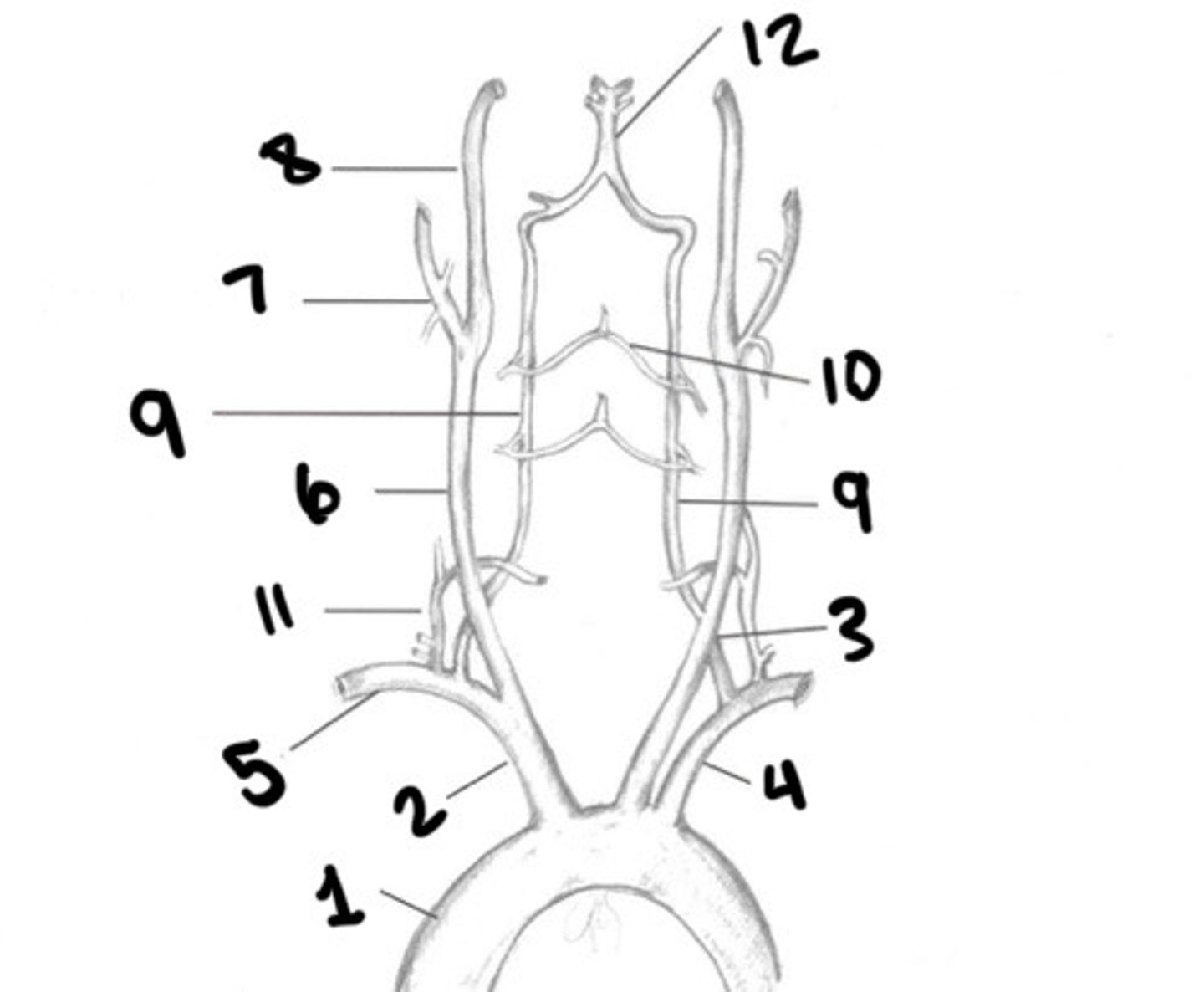
RT subclavian
What is 5
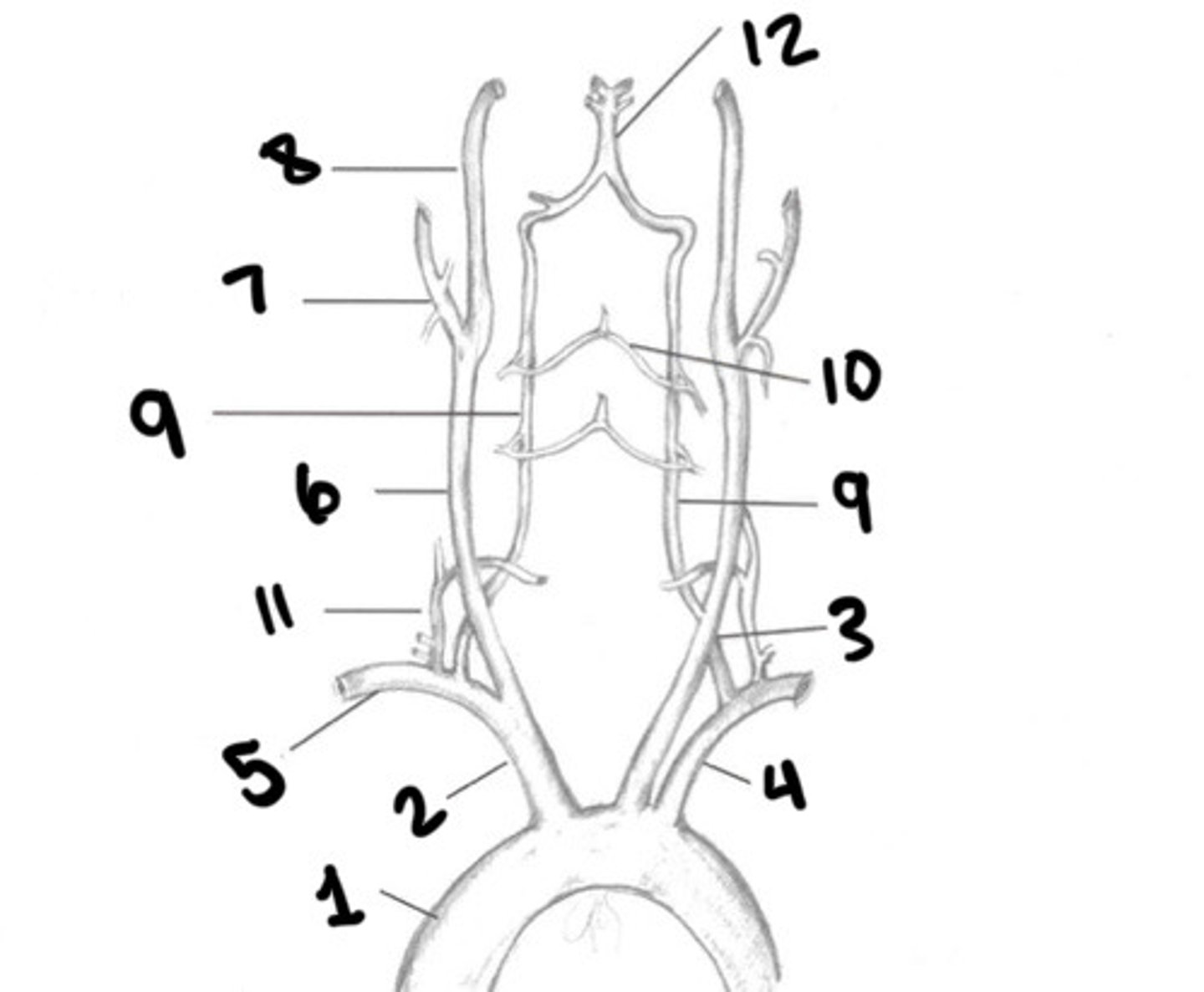
RT CCA
What is 6
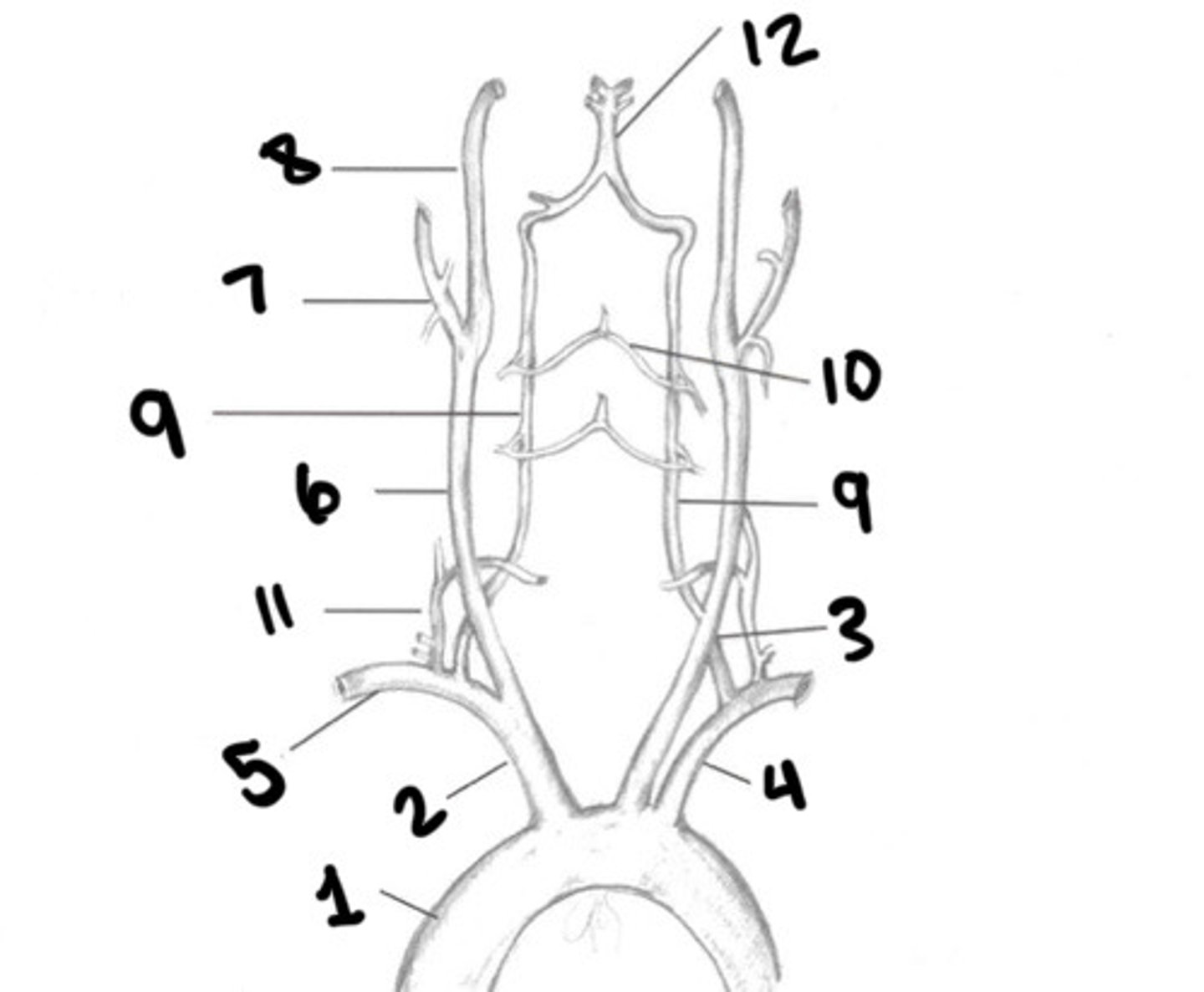
ECA
What is 7
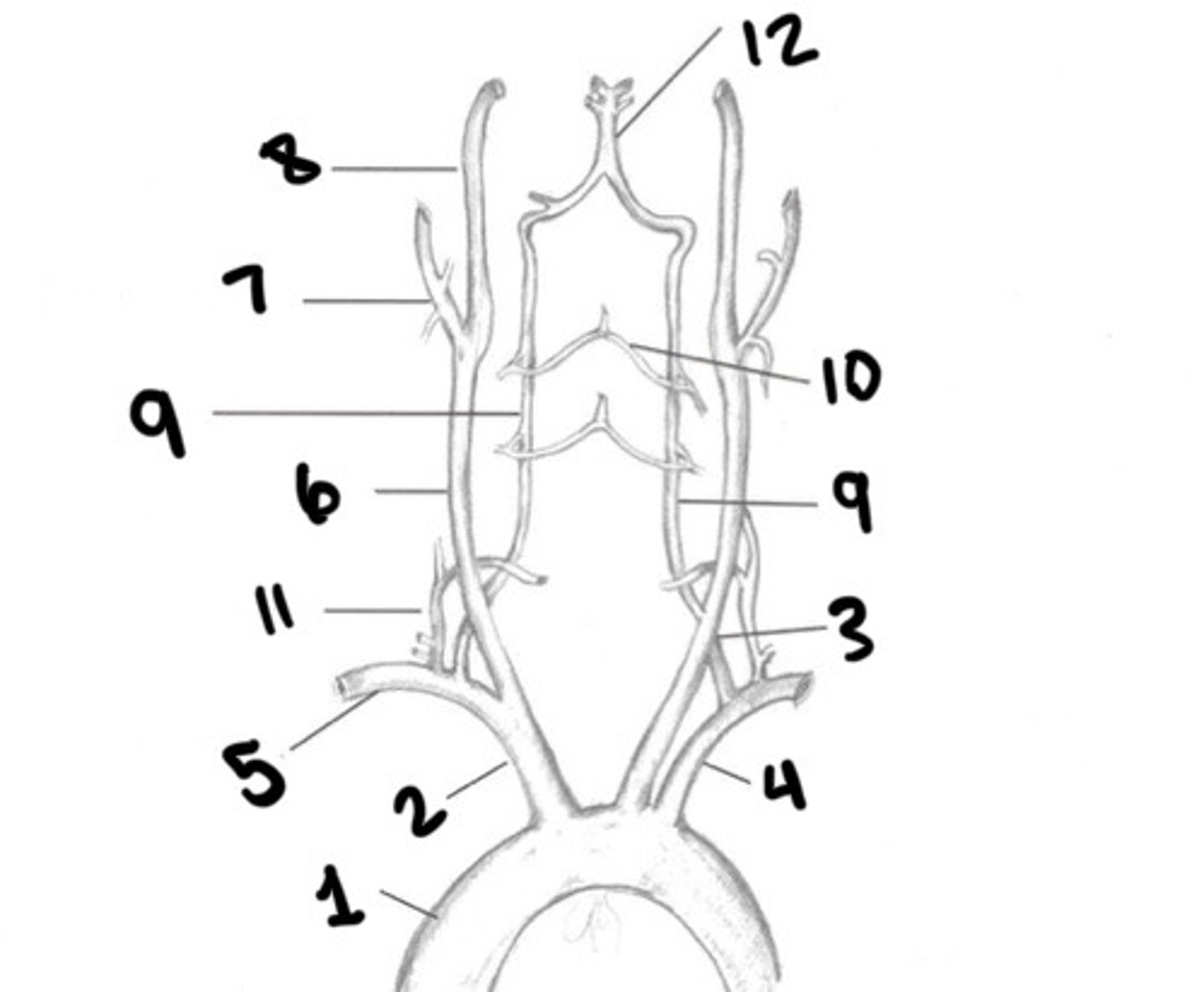
ICA
What is 8
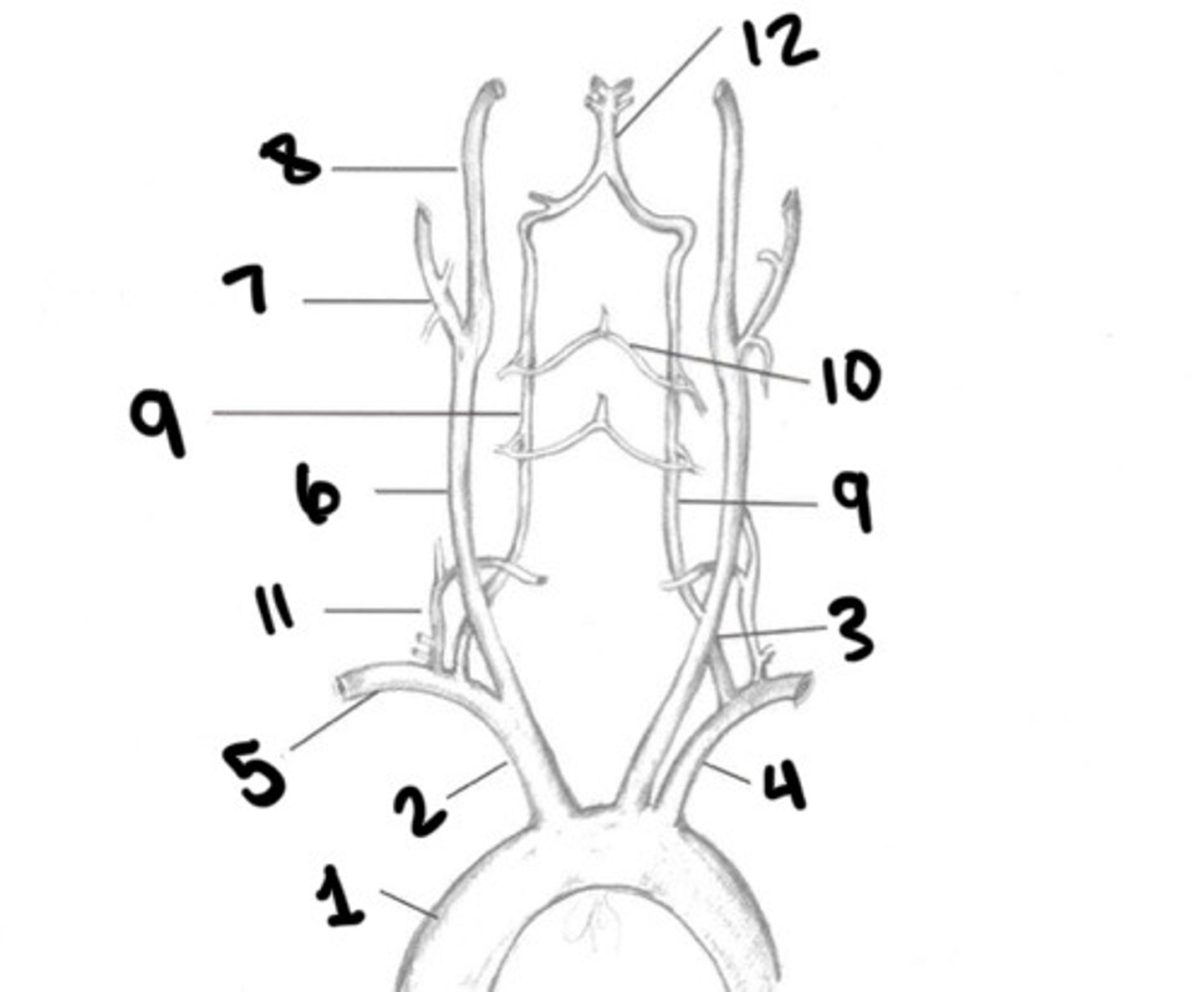
Vertebral arteries
What is 9
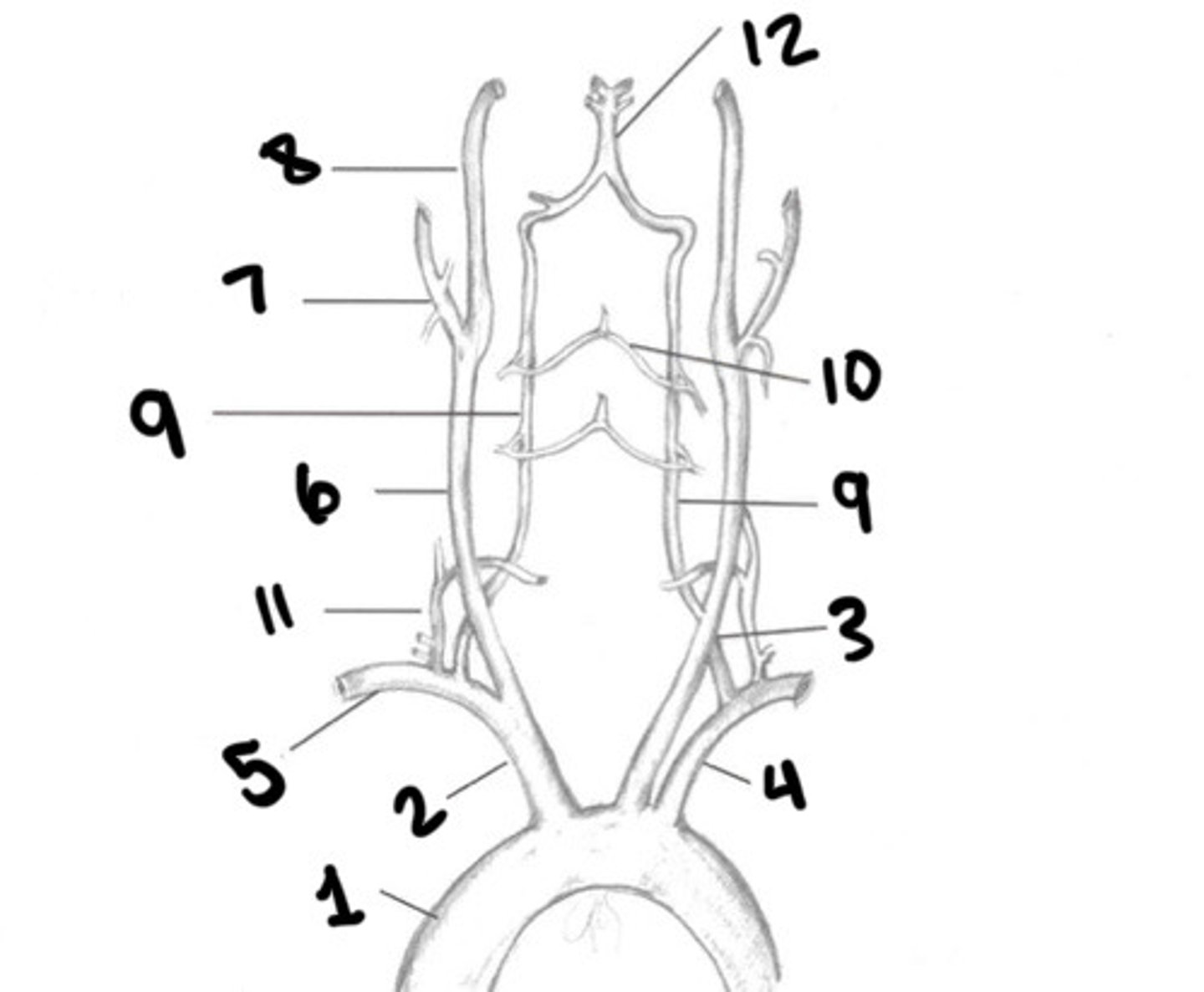
Spinal branches
What is 10
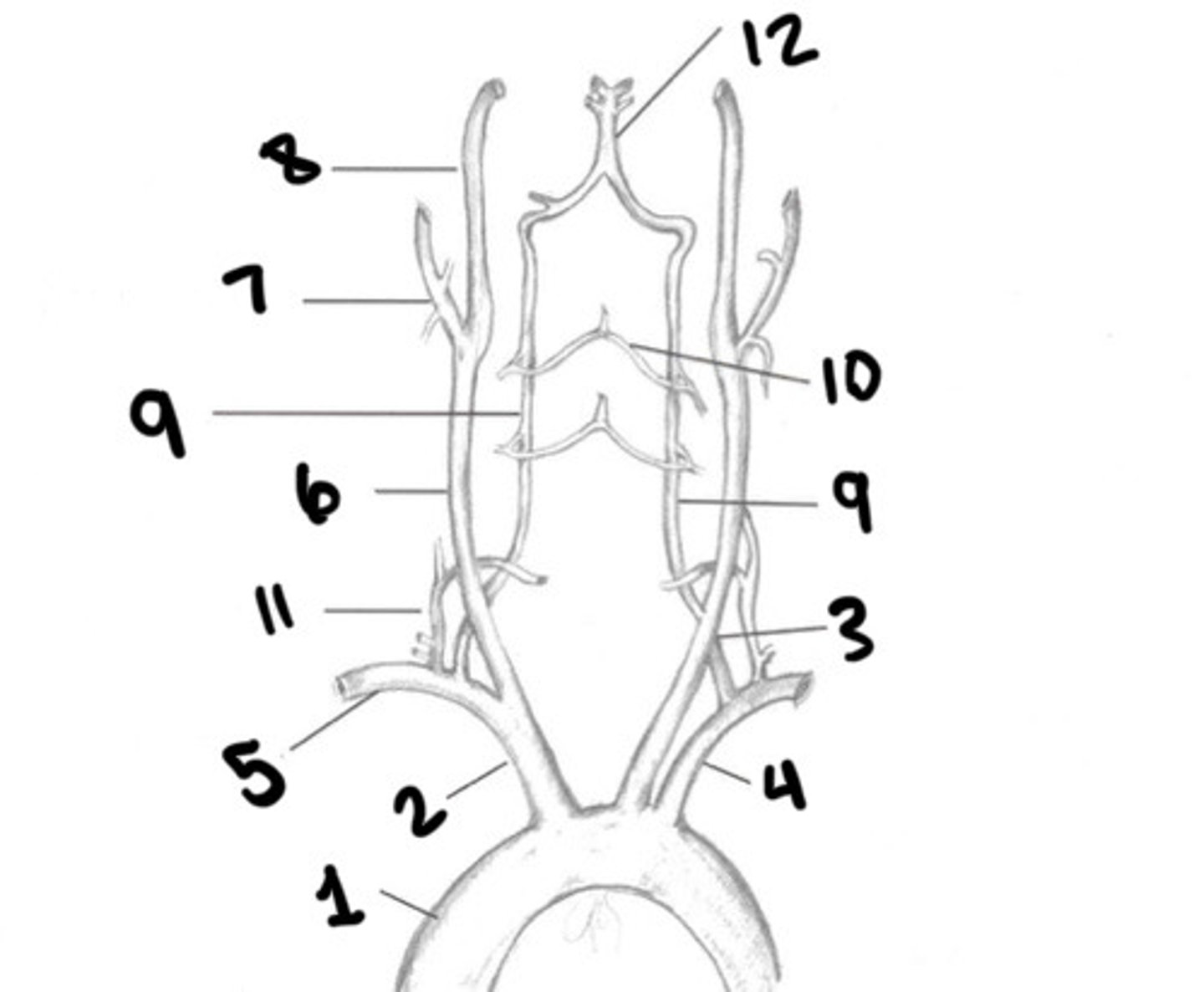
Thryocervical trunk
What is 11
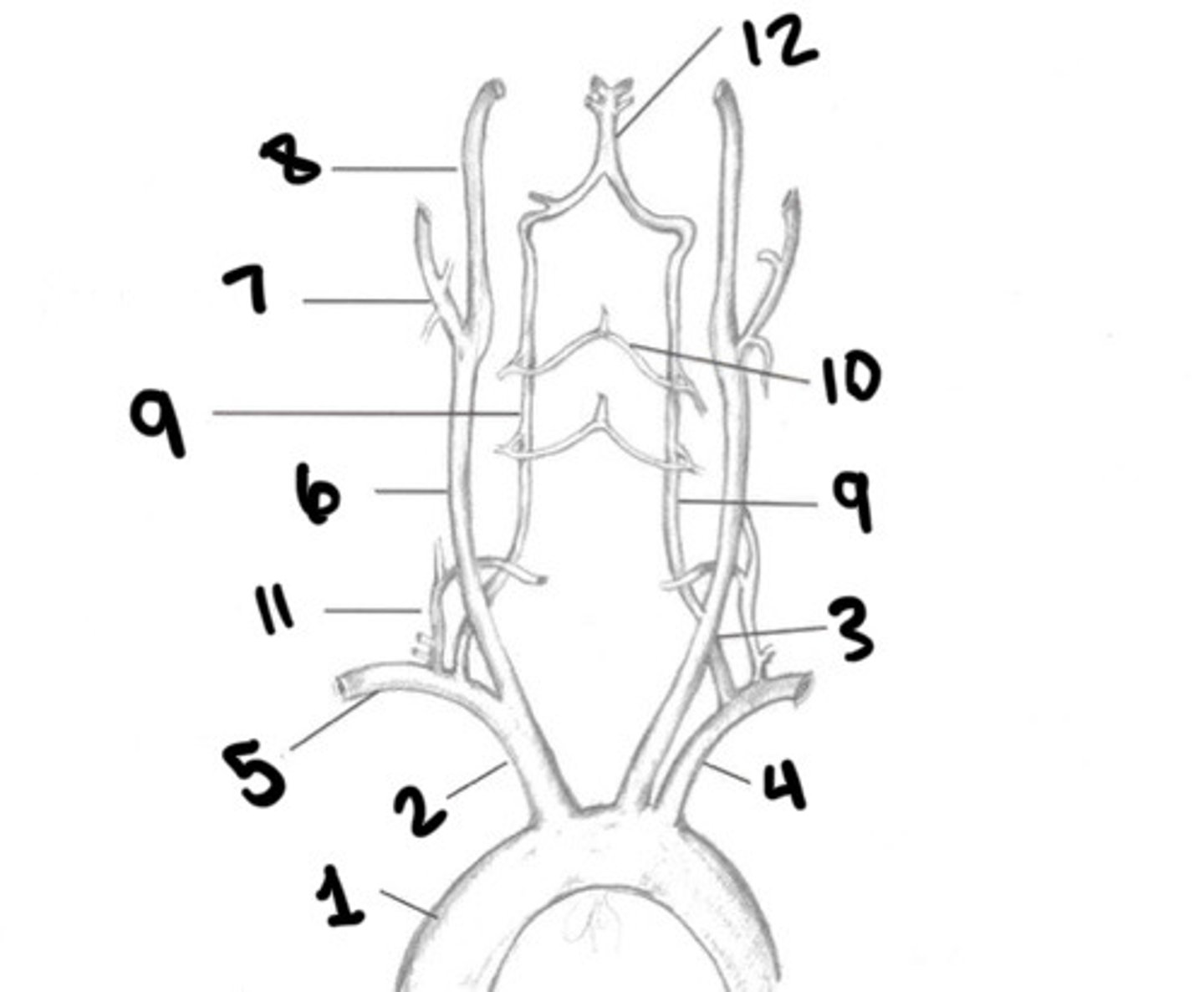
Basilar artery
What is 12
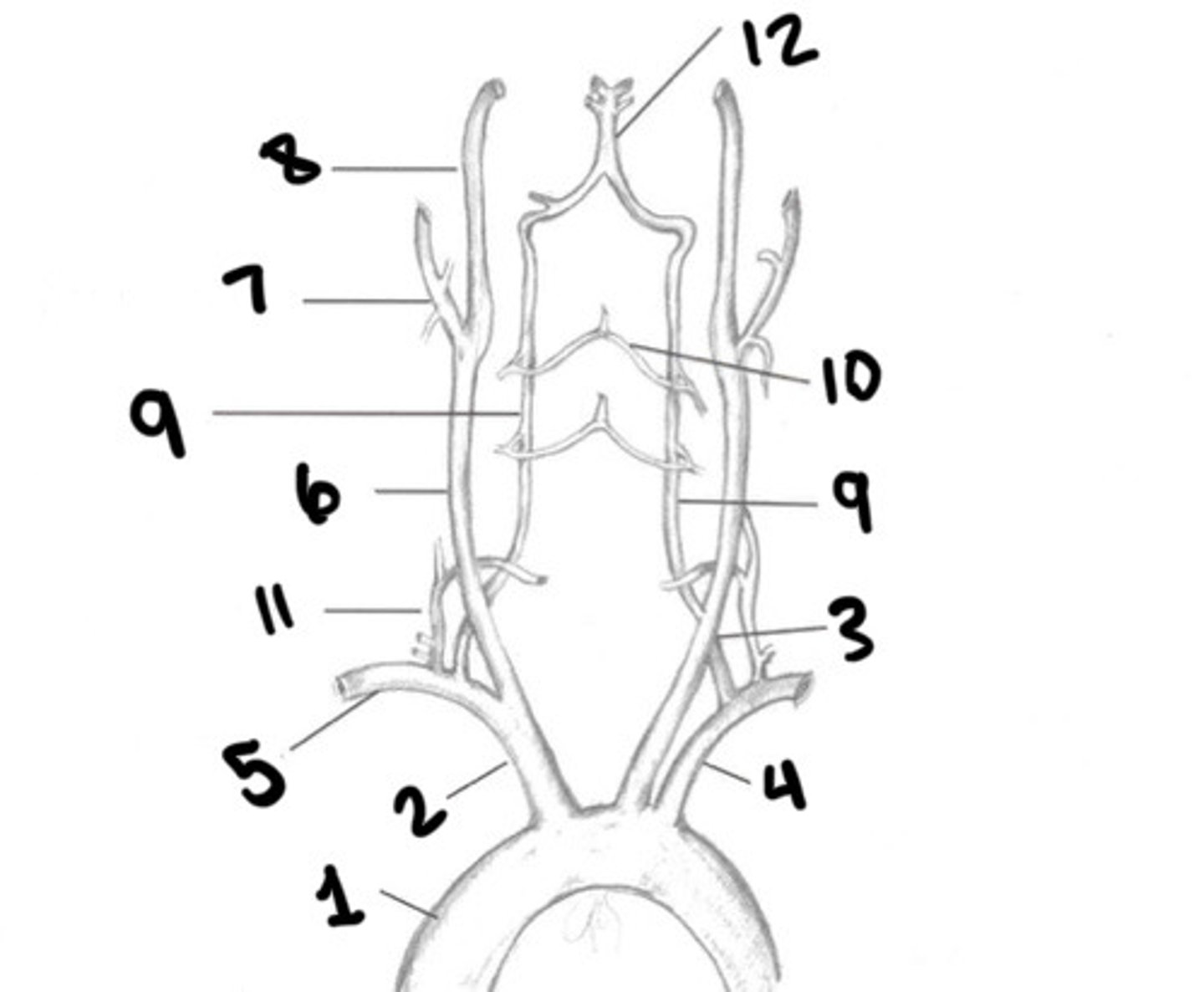
Vessel becomes enlarged, forming carotid bulb
What happens where the CCA splits into the ECA and ICA
In cranium
Where do the ICA's bifurcate
Anterior circulation of the cerebrum
What does the ICAs suppler
True
T/F: the cervical ICA contains no branches
Can be straight or tortuous
Describe the nature of the ICA (is it tortuous or straight?)
Ophthalmic artery
What is the first branch of the ICA
Carotid siphon
Where does the ophthalmic artery arise at the level of
Cavernous and supraclinoid segments of the ICA
What is the carotid siphon
MCA and ACA
What does the ICA bifurcate into in the cranium
Middle cerebral artery
What does MCA stand for
Anterior cerebral artery
What does ACA stand for
CCA
What is 1
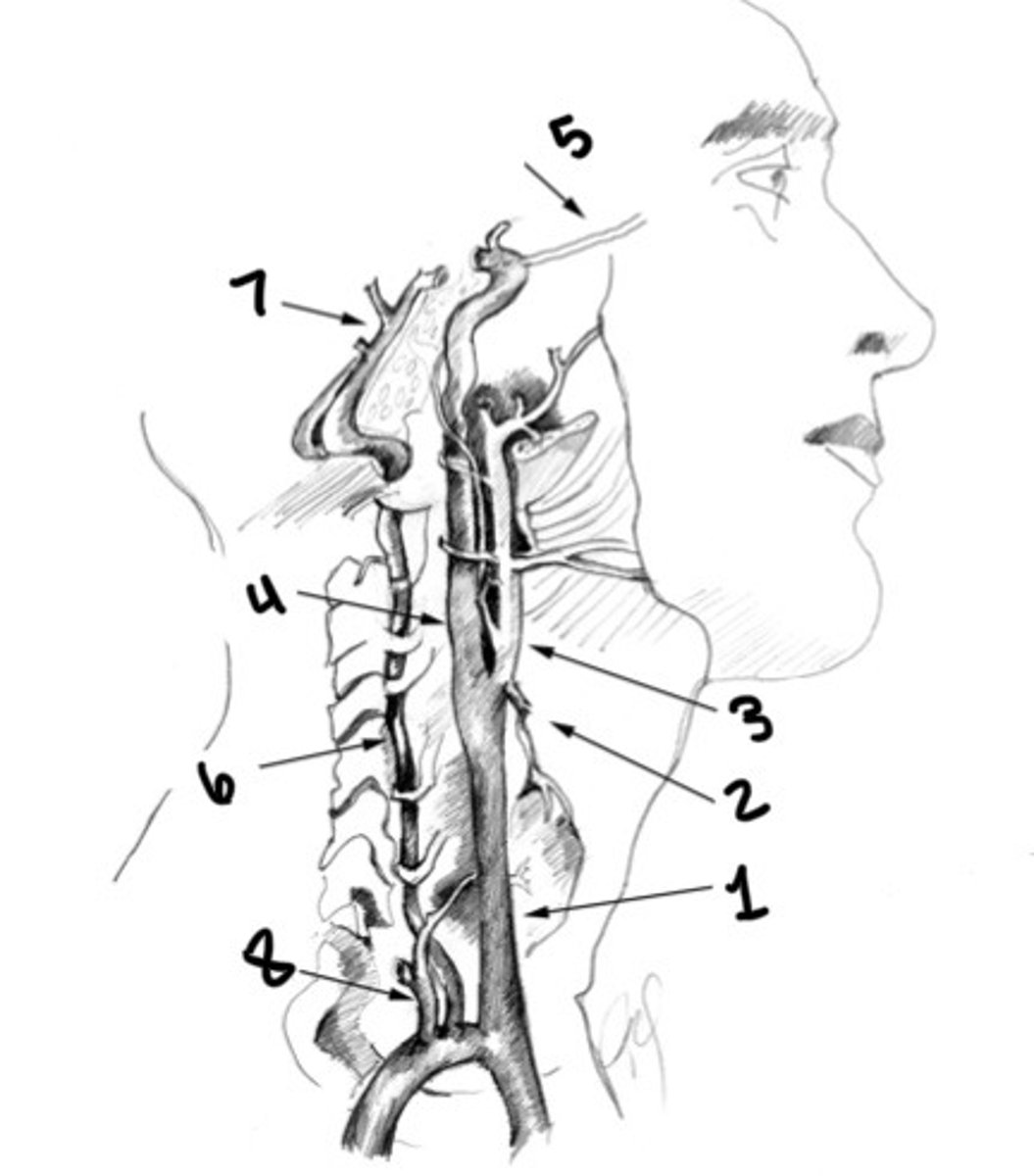
Superior thyroid artery
What is 2
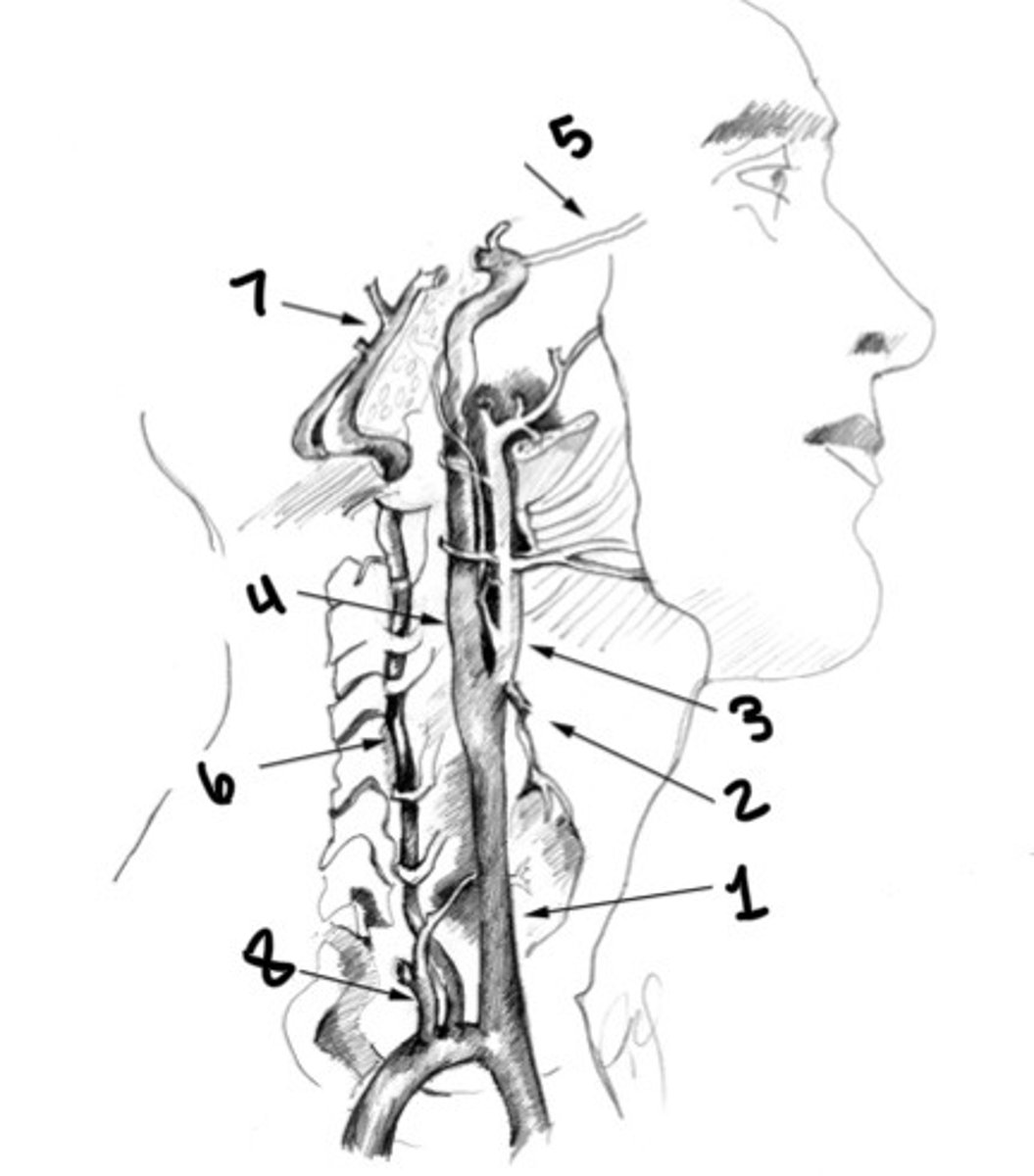
ECA
What is 3
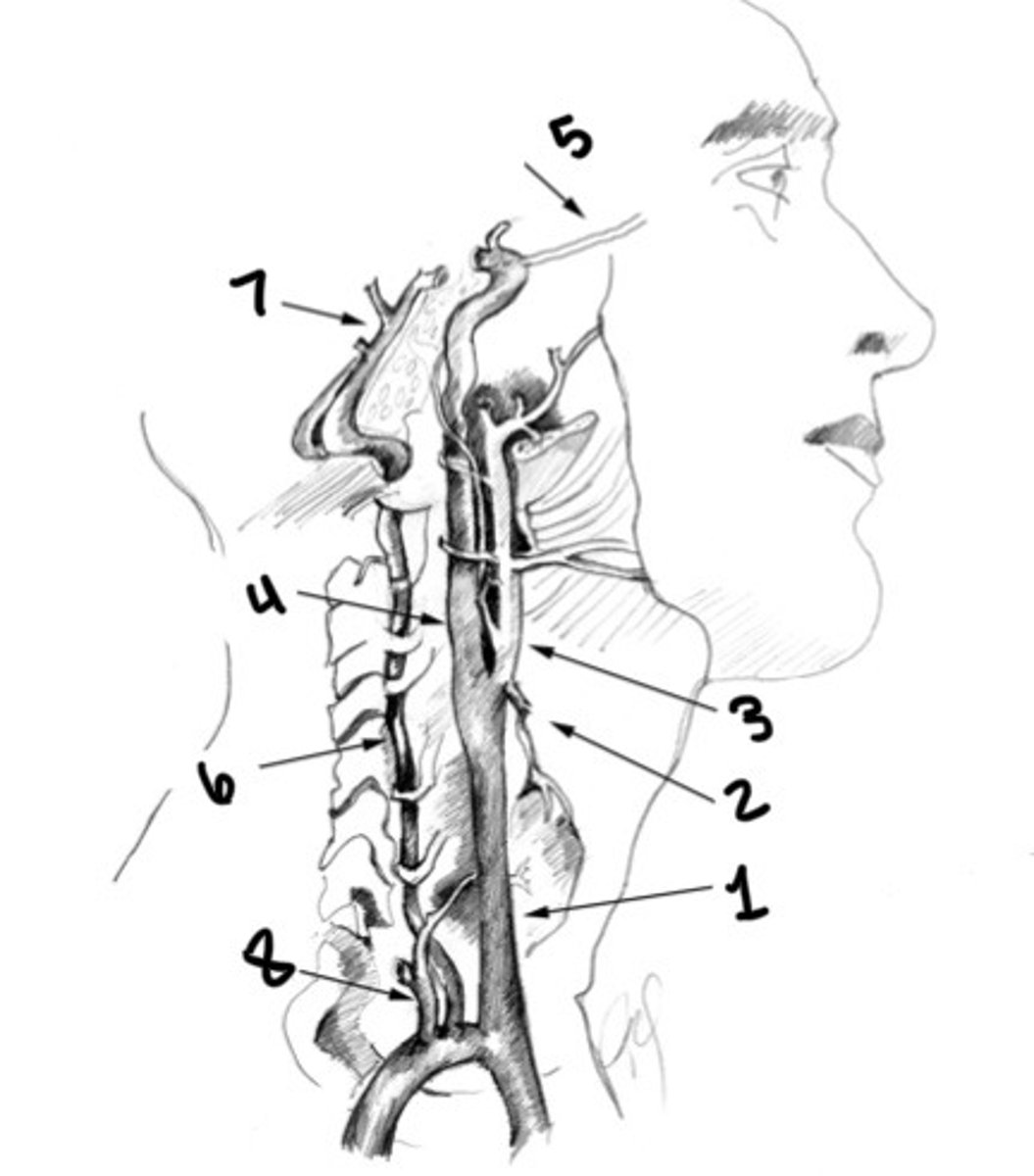
ICA
What is 4
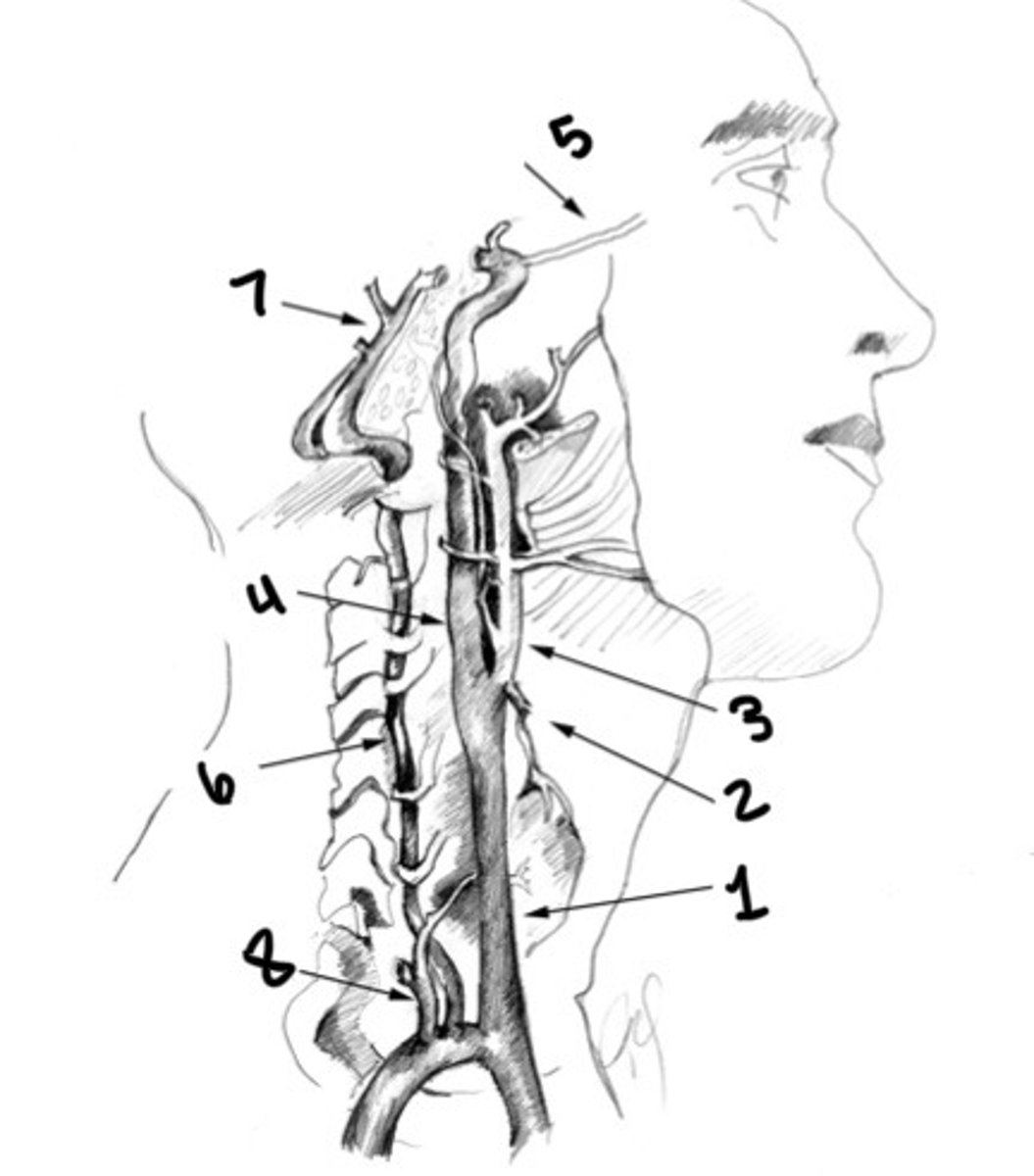
Ophthalmic artery
What is 5
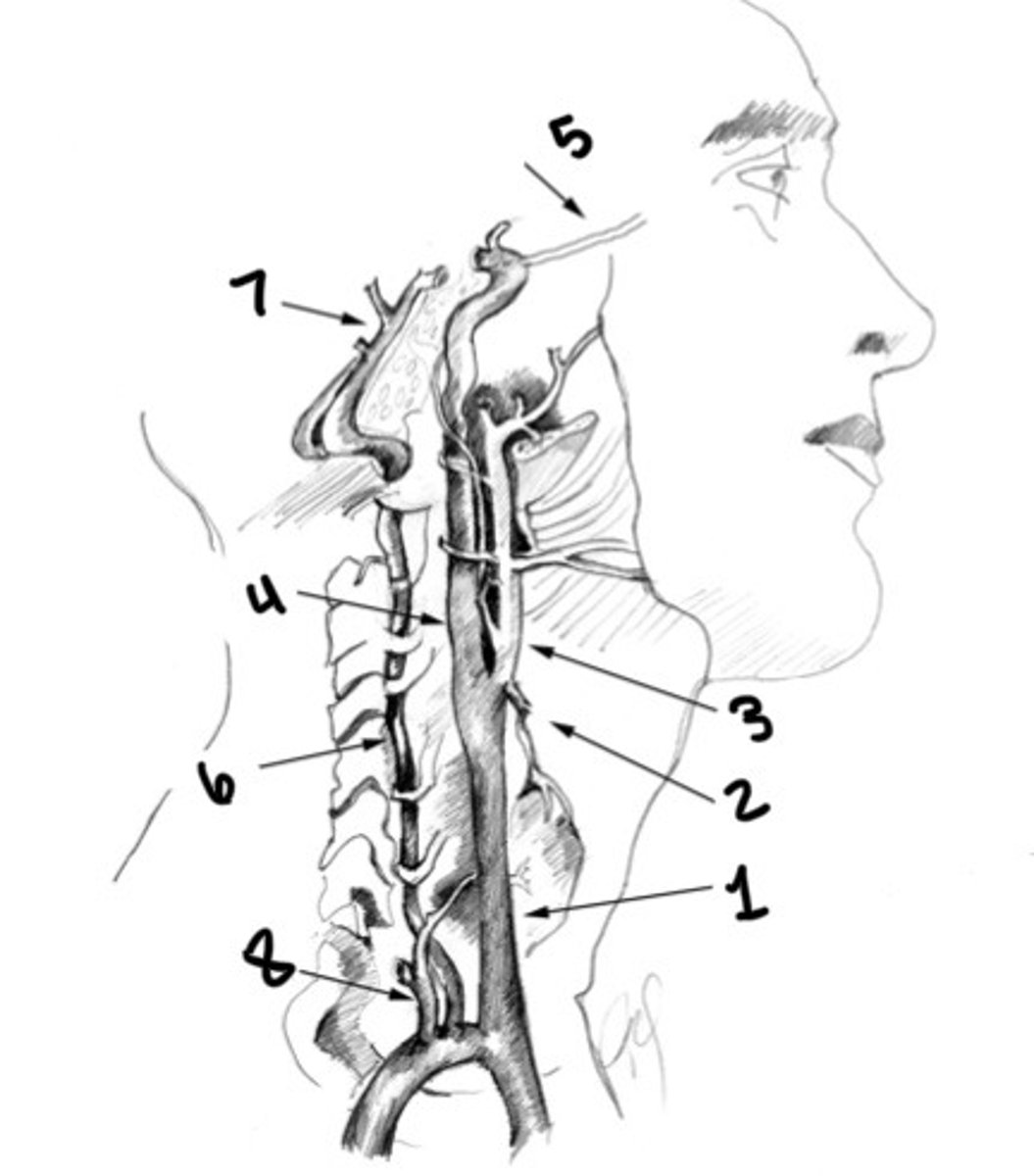
Vertebral artery
What is 6
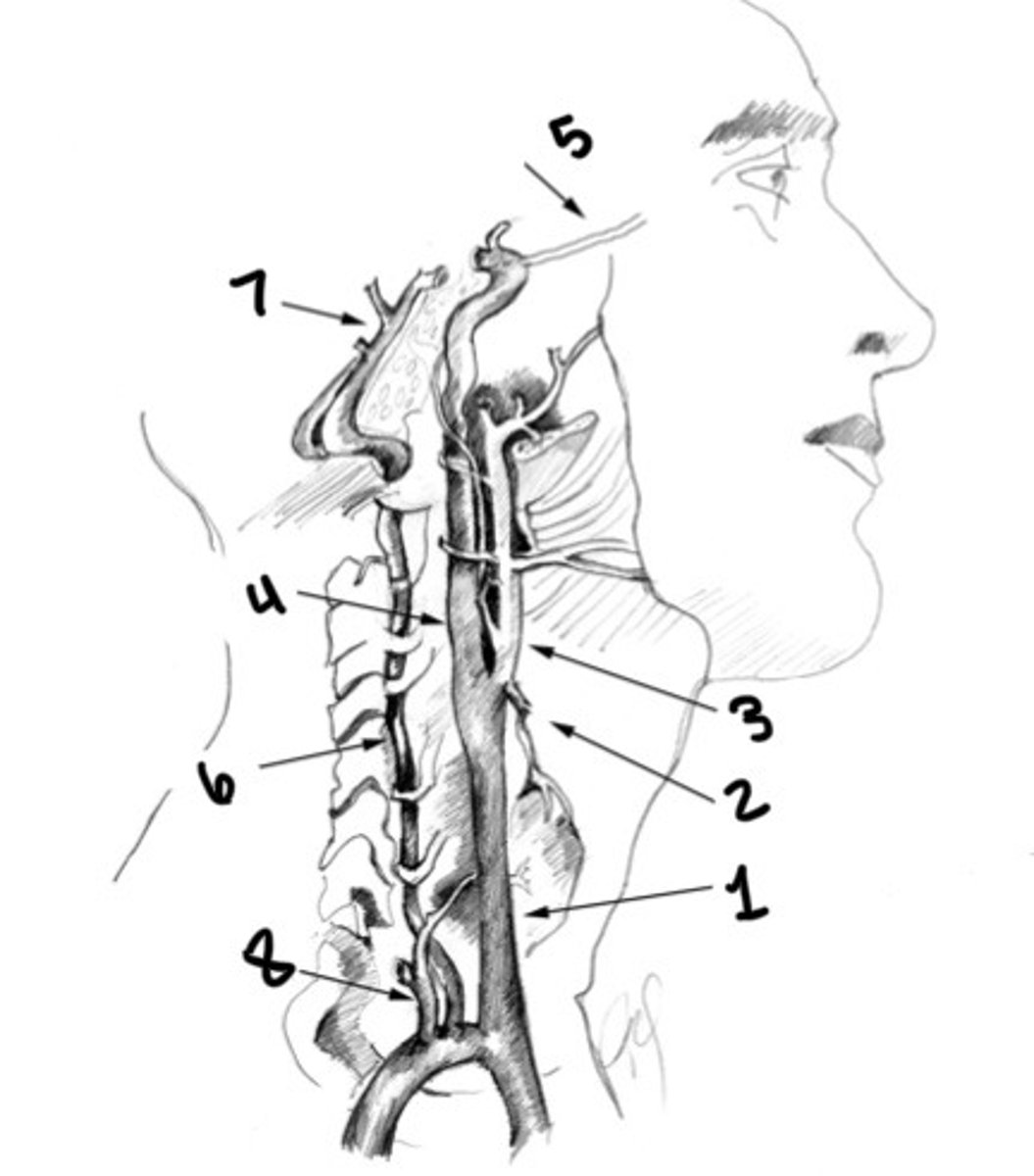
Basilar artery
What is 7
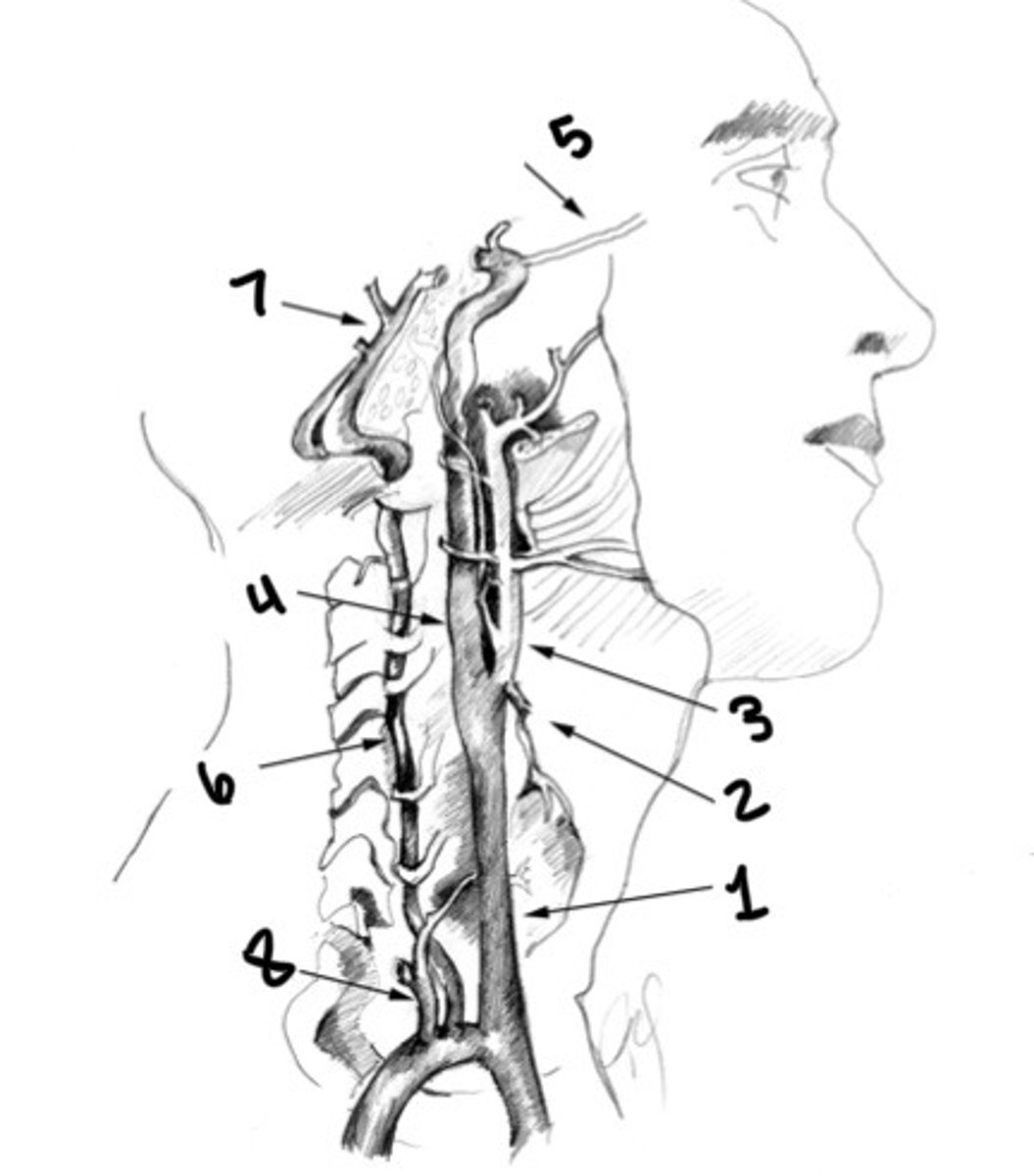
Thyrocervical trunk
What is 8
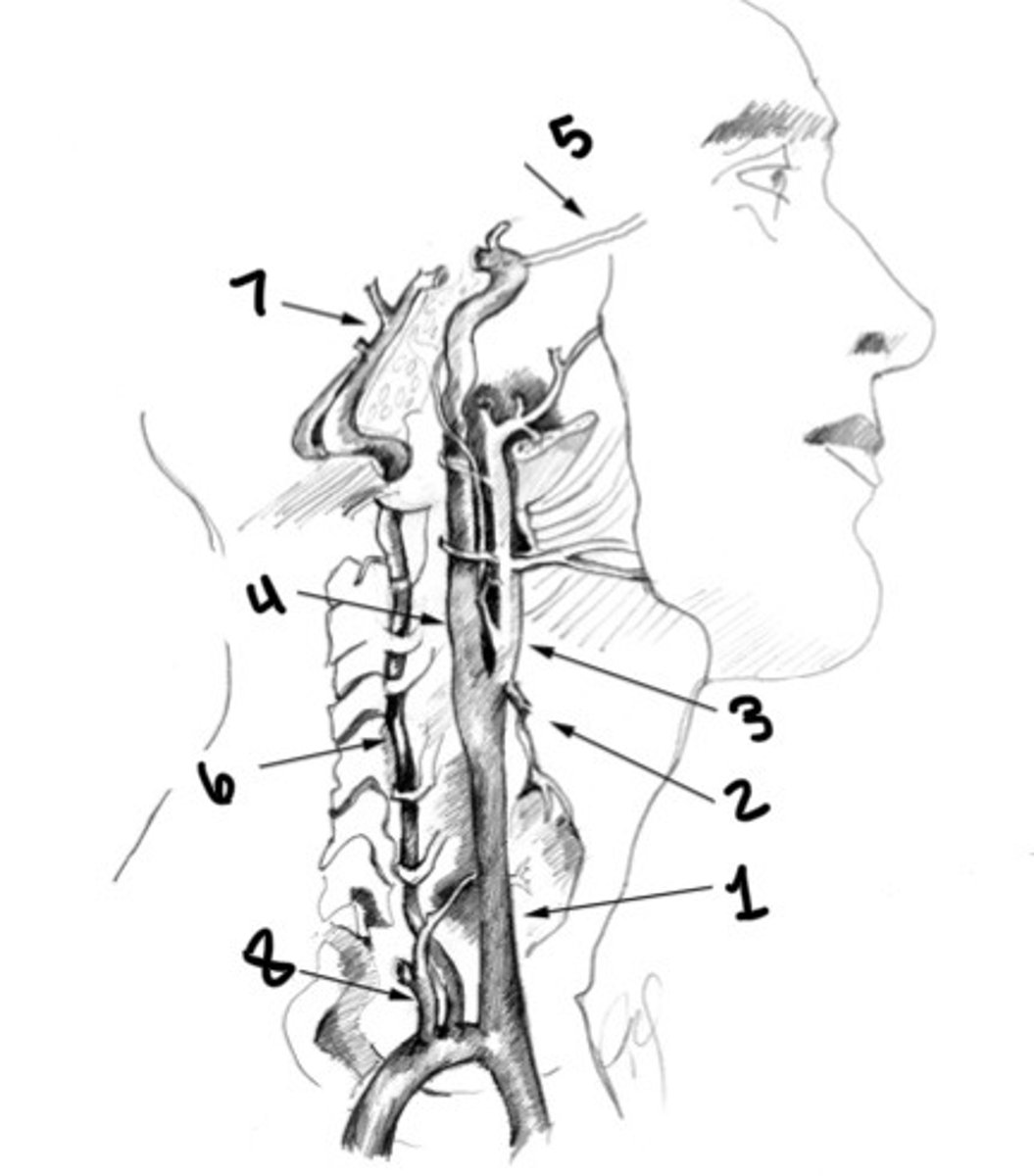
Carotid siphon
Where does the ophthalmic artery arise from
Anterior through the optic canal to the orbit
How does the ophthalmic artery travel
Ophthalmic artery anastomoses with branches of the ECA to create collateral flow
Describe what can happen to the ophthalmic artery when the ICA becomes occluded
Supraorbital artery, frontal artery, nasal artery
List the 3 branches of the ECA that the ophthalmic artery can anastomose with when the ICA becomes excluded
Supraorbital artery
What artery lies over the top of the eyeball and pass through the Supraorbital foramen
Frontal artery
Which artery lies towards the inner aspect of the eye along the top
Nasal artery
Which artery is the most medial branch of the ECA and terminates close to the bridge of the nose
Angular artery
What does the nasal artery become close to the bridge of the nose
Facial artery
Which artery also terminates around the bridge of the nose
Supraorbital artery
Which artery passes through the Supraorbital foramen
False
T/F: the ECA normally supplies blood to the brain
Occlusion
What type of pathology may result in the ECA to abnormally supply blood to the brain
branches of the ECA may anastomose with the ICA or vertebral to provide collateral flow
Describe what would happen to the ECA if there is an occlusion
Ascending pharyngeal, superior thyroid, lingual, external maxillary, occipital, facial, posterior auricular, internal maxillary, transverse facial, superficial temporal arteries
List all of the ECA branches
Those in communication with the ophthalmic artery
Which ECA branches are the most vital to collateral circulation
Posterior circulation to the brain
What does the vertebral artery supply
Transverse foramina of the supper cervical vertebrae
What does the vertebral arteries lie within
Subarachnoid space
What does the vertebral arteries go into anteriorly
Travel cephalic and anteriorly until they join to creat the basilar artery
How does the vertebral arteries travel
Basilar artery
What does the vertebral arteries from with they join
4
How many branches does the basilar artery contain
Pons, anterior and posterior cerebellum
What does the basilar artery feed
Vertebral arteries
What is 1
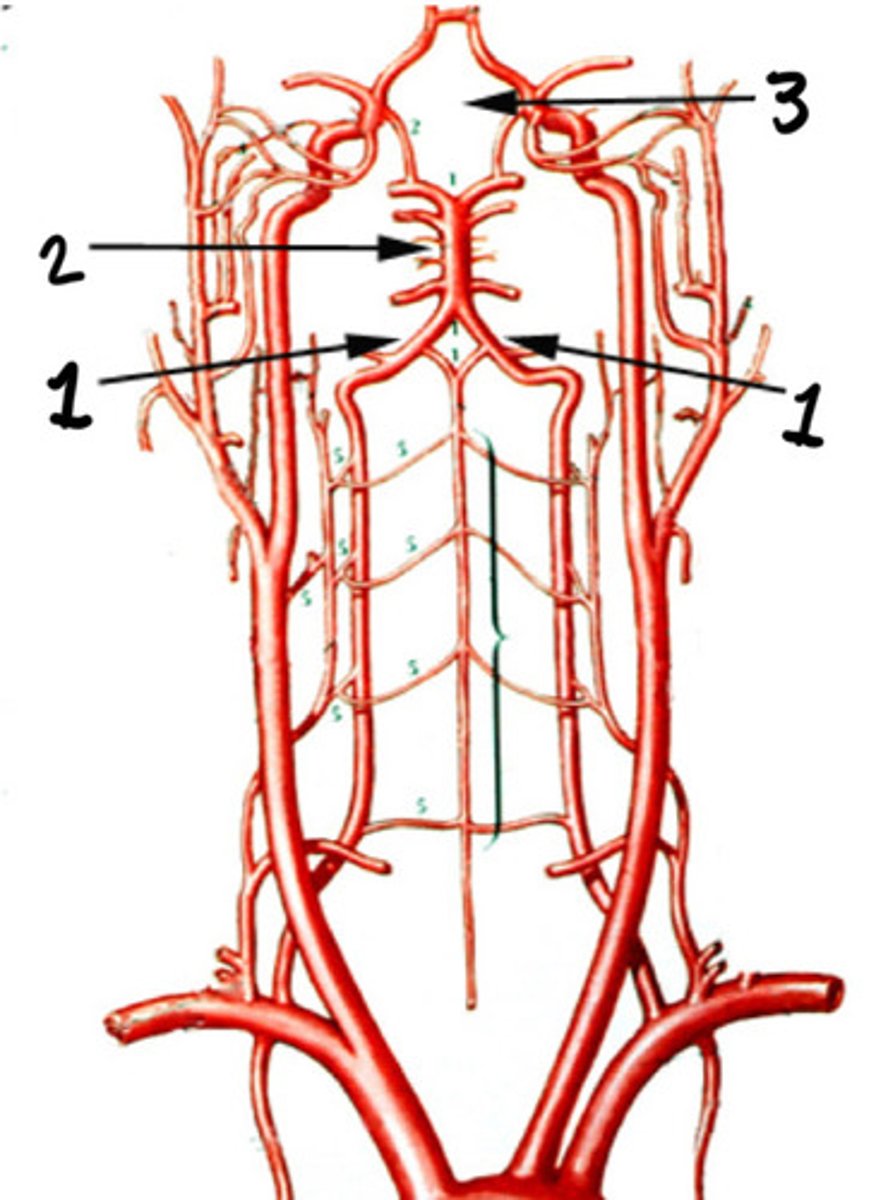
Basilar artery
What is 2
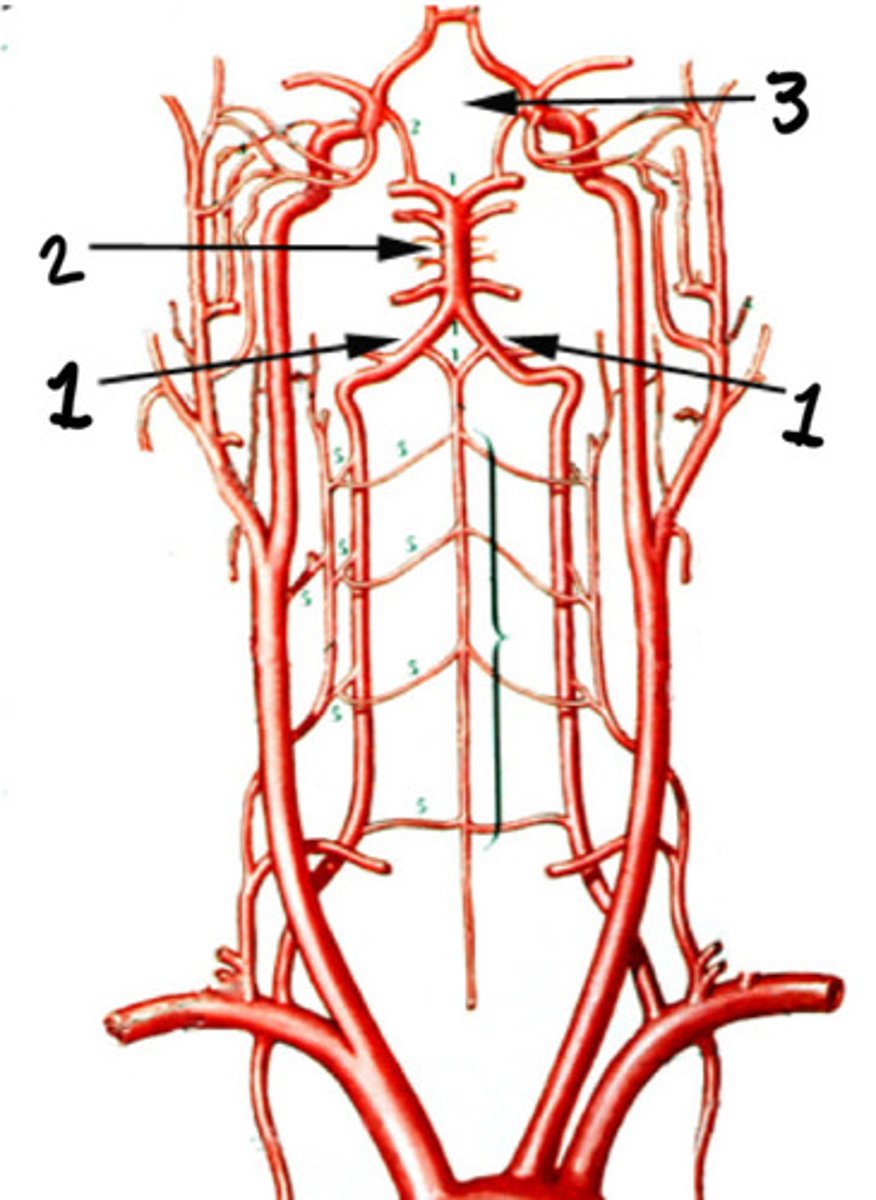
Circle of Willis
What is 3
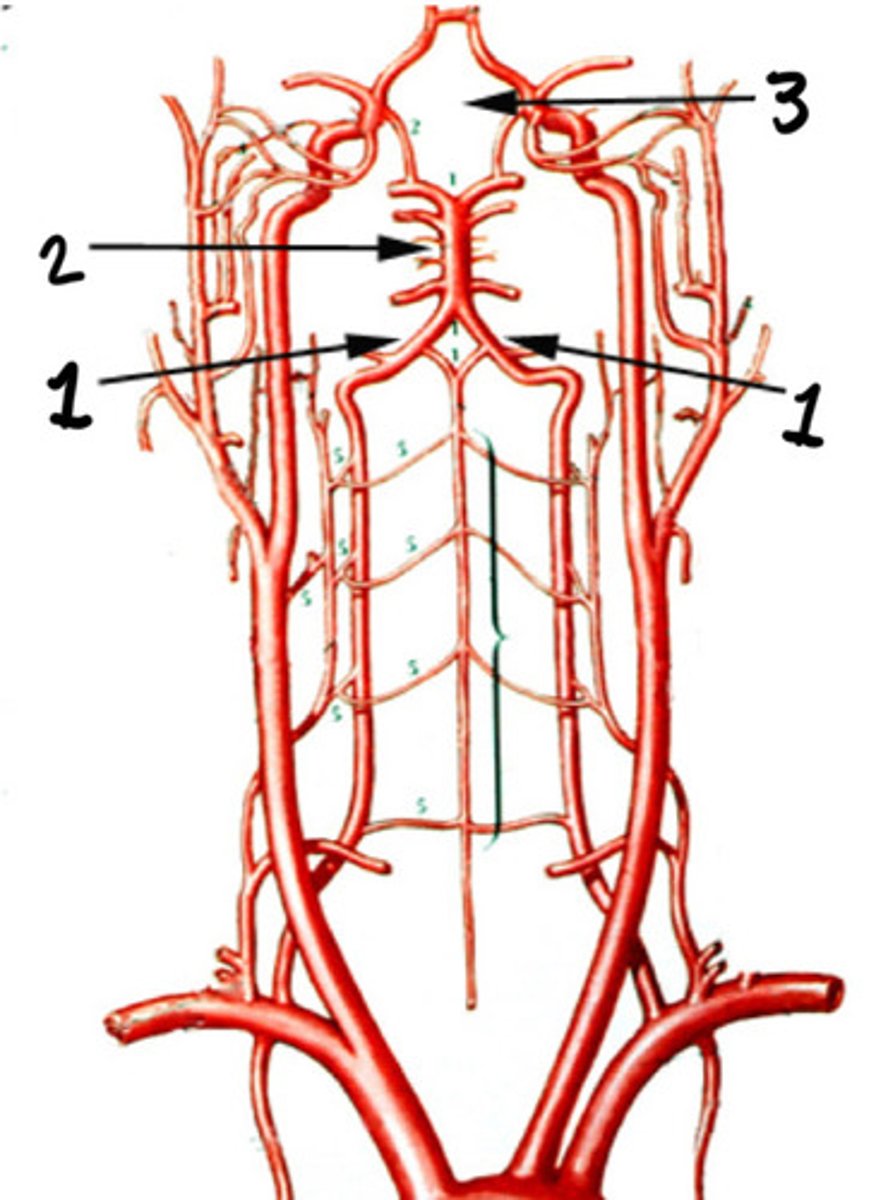
Cerebral branches of the ICAs and the vertebral arteries
What forms the circle of Willis
Base of the brain
Where is the circle of Willis formed
Provide the most important collateral circulation intracranially
What is the significance of the circle of Willis
True
T/F: although the circle of Willis is very important, it is also a frequent site of aneurysm
Anterior and posterior communicating arteries
What are the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries joined together by
ACA
What supplies the majority of blood t the brain
Absence
What does hypoplasia mean
Hypoplasia of one or more of the communicating arteries
What is the most common congenital variations of the circle of Willis