Biology Unit 9 - Evolution
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
the process of change which causes offspring (descendants) to differ from their ancestors
Evolution
what explains how new species form?
evolution
a group of organisms that can reproduce and have fertile offspring
Species
In 1809, Jean-Baptiste LaMarck started to think about evolution. What did he say?
he said fossils of extinct animals resemble animals living today
What is LaMarcks’s theory called? What does it mean?
The Theory of Acquired Characteristics
This means that traits that are acquired during your lifetime are passed onto future generations
According to this theory, all giraffes once had short necks. They had to stretch their necks to reach high branches. What are the two major problems with this theory?
Can’t stretch organs
Can’t pass on acquired traits
Scientists study ______ to learn more about how evolution works.
Fossils
hard parts of animals that lived in the past
Fossils
What body parts would make the best fossils?
bones
Claws
Teeth
What are the two ways that evolution may happen?
Catastrophism (catastrophes)
Gradualism (gradually)
What are examples of catastrophism (catastrophes)?
Natural disasters:
floods and volcanoes
happen that cause entire species to go extinct
What is gradualism (gradually)?
Slow processes that cause organisms to evolve over a long period of time
In 1831 Charles Darwin traveled on a ship called ___ ______ for an around the world journey. He stopped in the _________ _______ for observations.
HMS Beagle
Galapagos Islands
What did Darwin notice on the islands?
All of these animals that were never seen anywhere before
variation
differences between members of a population
variation
Variation includes physical differences (____,____) and non-physical differences (_____ _____, ______ __ _______)
color and size
foods eaten, number of offspring
Darwin said these ______ allow them to survive in a changing environment.
Adaptions
Wheee do we see more variation?
Domesticated animals (pets) or wild animals?
Domesticated animals (pets)
humans choose what traits we want our pets to have and breed accordingly
artificial selection
must be able to passed on
heritable
T or F
In nature, the environment determines which traits are favorable - not humans
True
Who created The Theory of Natural Selection?
Charles Darwin
individuals that have beneficial adaptations are more likely to mate and pass on those traits
Natural selection
Darwin argued that there are not enough resources for every organism in a ______. The ones that have the _______ adaptations will survive, and then pass them on.
Population
Favorable
How many parts are there to the theory of natural selection?
4
What are the first two parts to the theory of natural selection?
There is variation (differences) in every population
Some of this variation is good and some is bad
What are the 3rd and 4th parts to the theory of natural population?
Not all young produced in each generation will survive
many will die as a result of disease, starvation, or predators
Individuals that survive and reproduce are those with the favorable variations
being able to better survive and reproduce than other members of their population
Fitness
the study of fossils or extinct organisms
paleontology
someone who studies fossils
paleontologist
Fossils of fish have been found in places where no water exists today - this is evidence of what?
Pangea
What is a difference and more evidence of Pangea between African and Asian elephants?
Found on different continents
the study of how living things are distributed around the world
Biogeography
the study of embryos (unborn babies) and how they form
embryology
the body structure of a living thing
anatomy
What two themes of anatomy did Darwin notice?
Homologous and analogous
structures that are SAME in structure but different species and have different functions and form the SAME ancestors
evidence that they all evolved from a common ancestor
Homologous structures
similar functions, but mot similar in origin
Analogous structures
inherited structures that are reduced in size and unused
Vestigial structures
Why is genetic variation very important in population?
The more variation in a population, the better the population’s chances for survival
Which penguin would do better if it’s a brutal cold winter?
Short, fat penguins stay warmer
combines alleles of all the individuals in a population and stores genetic variation
gene pool
is the measure of how common an allele is in a population
allele frequency
random change in the DNA
mutation
different ways mom’s and dad’s chromosomes can match up
recombination
In a population, traits are usually arranged by a what?
Normal distribution
means most fall in the middle
sometimes called a bell-shaped curve
Normal distribution
How many ways are there that distribution can change?
Three
favors phenotypes at an entrance
Ex – peppered moths
•Before the industrial revolution, moths appear lighter in
color
•Tree trunks darkened with pollution and light colored
moths were picked off by birds
•Darker color moths became the new “norm”
directional selection
the middle is favored, the extremes are bad (reduced)
Ex- Birth weight in babies
● If the birth weight of a baby is too low, it will have difficulty
surviving after birth.
● A baby weighing too much would create complications for both
the mother and the child.
● The middle ranges are the optimal birth rate.
stabilizing selection
both extremes are favored, the middle is selected against
Ex – Lazuli birds
•Range in color from dull brown to bright blue
•Bright blue – most aggressive, mate often
•Dull brown – not seen as a threat, left alone, mate
often
Middle colors – selected against
Disruptive selection
A difference in the physical traits of one individual from another in the same group
Variation
The fact that saddle-back tortoises have evolved abnormally long necks is an example of:
Adaptation
While on the ship Darwin:
Found evidence for natural selection
The change in allele frequencies over time.
Evolution
Which of the following ideas proposed by Lamarck was later found to be incorrect?
Acquired characteristics can be inherited
Which of the following ideas is supported by Darwin’s observation of local variation among tortoises in the Galápagos Islands?
a. artificial selection
b. adaptation
c. acquired characteristics
d. tendency towards perfection
Adaptation
The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its specific environment.
Fitness
Natural selection is ______________
Survival of the fittest
Remains of ancient organisms are called _________
Fossils
How does embryology support the Theory of Evolution?
a. It shows that embryos who develop similarly share a
common ancestor
b. It shows that embryos who develop similarly are not
related to one another
c. It shows that organisms have the ability to evolve, or
change, over time.
a. it shows that embryos who develop similarly share a common ancestor
Some organisms that share a common ancestor have features that have different functions, but similar structures. These are known as:
Analogous structures
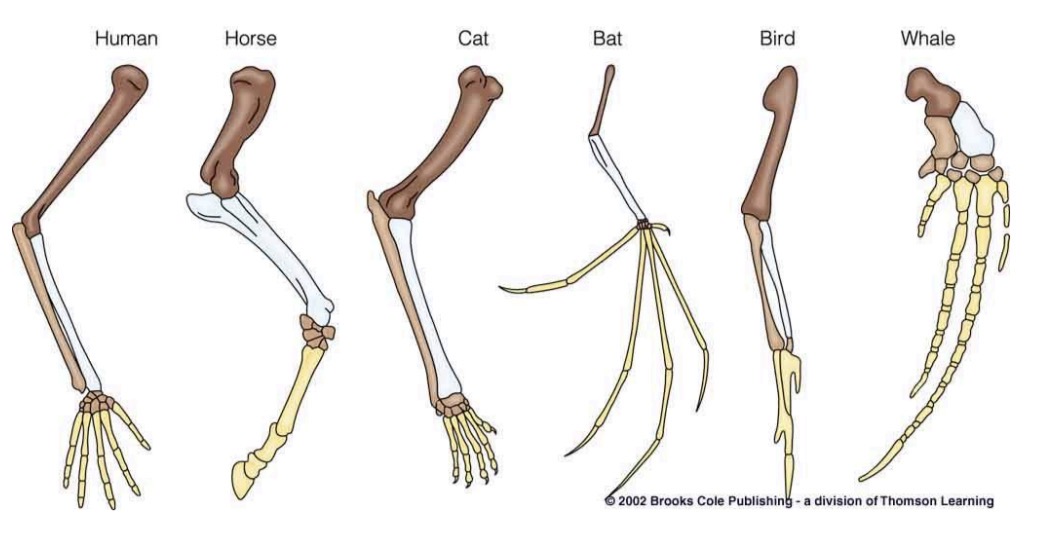
The similarities of the bones in the diagram provide evidence that---
The organisms shown may have developed from a common ancestor
The study of embryos (unborn babies) and how they form
Embryology
A group of organisms that can reproduce and have fertile offspring
Species
Any trait that is able to be passed on
Heritable
body structure of a living thing
Anatomy
Humans choose what traits we want our pets to have and breed accordingly
Artificial selection
The study of how living things are distributed around the world
Biogeography
Differences between members of a population
Variation
The process of change which causes offspring (descendants) to differ from their ancestors
Evolution
Inherited structures that are reduced in size and unused (appendix)
Vestigial structures
Theory that says that traits that are acquired during your lifetime are passed on to future generations
Theory if Acquired Characteristics
Slow processes that cause organisms to evolve over a very long period of time
Gradualism
The study of fossils or extinct organisms
Paleontology
Theory that says that Individuals that have the beneficial adaptations are more likely to mate and pass on those traits
Theory of Natural Selection
Structures that are similar in structure but in different species and have different functions (cat and human arm)
Homologous structures
Natural disasters – floods, volcanoes – happen that cause entire species to go extinct
Catastrophism
Structures that are similar function, but not similar in origin (whale and shark fins)
Analogous structures
Someone who studies fossils
Paleontologist
The different ways mom’s and dad’s chromosomes can match up are known as _______________ .
Recombination
SELECT ALL THAT APPLY: Which of the following must be true in order
for organisms to be considered the same species?
a. They must be able to mate
b. They must be able to produce viable offspring
c. They must have structural similarities
d. They must have the same bone structure
b. They must be able to produce viable offspring
c. They must have structural similarities
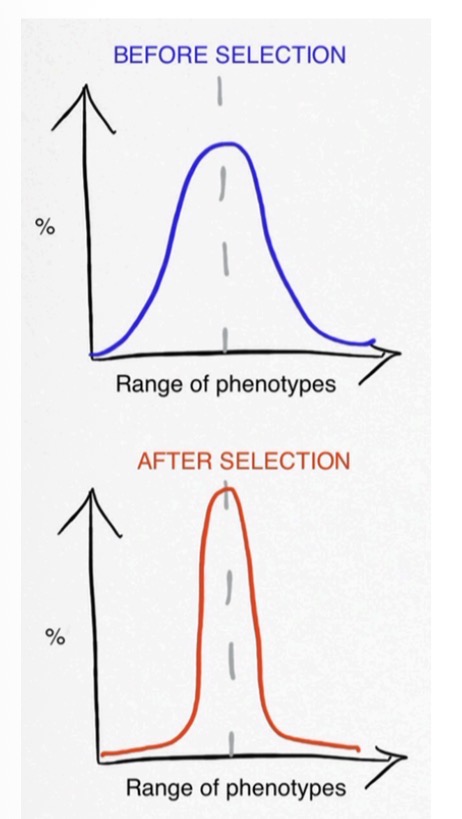
This distribution graph shows
Stabilizing selection
What does the 'p' value represent in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
a. Probability of homozygous recessive genotype
b. Probability of heterozygous genotype
c. Frequency of the dominant allele
d. Frequency of the recessive allele
c. Frequency of the dominant allele
How do you calculate the frequency of heterozygous individuals in a population?
2pq
If 16% of a population is unable to taste a certain chemical due to a recessive allele, what is the frequency of the recessive allele (q)?
0.4
What is the significance of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in studying genetic disorders?
a. It helps in understanding the spread of disorders
b. It predicts the future genetic makeup of populations
c. All of the above
d. It assists in calculating carrier probabilities
c. All of the above
In the Hardy-Weinberg Equation, q2 is the frequency of what?
The dominant genotype
2. A population of 150 individuals has an allele frequency of 0.4 for the dominant allele (B) and a frequency of 0.6 for the recessive allele (b). Use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to determine the frequency of the genotype (bb).
a. 0.09
b. 0.42
c. 0.36
d. 0.72
c. 0.36
Which of the following conditions is necessary for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Large population size