(2.65-2.69) Heart and Circulatory System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe the flow of blood in the heart.
Pulmonary circuit:
D-O2 blood moves
from right ventricle to the lungs (P. artery),
gets oxidised, and comes back to the left atrium of the heart (P. vein)
Systemic circuit:
O2 blood goes form the left ventricle of the heart
to the rest of the body (aorta)
D-O2 blood from the body goes to the right atrium of the heart (vena cava)
What is the name of the muscle wall that separated the two sides of the heart?
Septum
Which way do veins carry blood?
Towards the heart.
Which way do arteries carry blood?
Away from the heart
What do coronary arteries do?
Supply the cardiac muscle tissue of the heart with oxygenated blood.
What do valves in the heart do?
Prevent blood from flowing backwards.
Describe the path of blood through the heart.
De-oxygenated blood flows from the body through the vena cava and into the right atrium.
The atrium contracts and blood is forced through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
The ventricle contracts and blood is pushed through the semi-lunar valve into the pulmonary artery.
The blood travels to lungs.
Oxygenated blood returns via the pulmonary vein to the left atrium.
The atrium contracts and forces blood through the bi-cuspid valve into the left ventricle.
The ventricle contracts and sends the blood through the semilunar valve and out through the aorta.
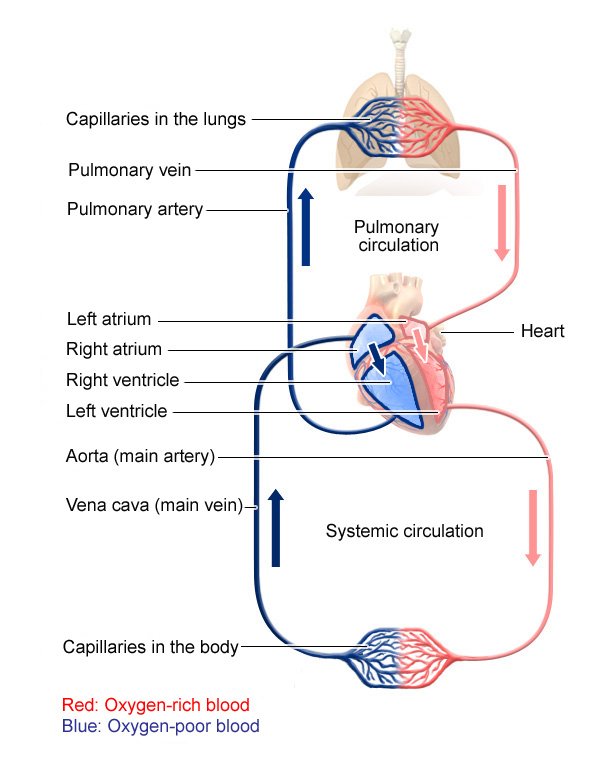
What must you be mindful of about heart diagrams?
The heart is labelled like a chest so the shape is mirrored.
How is a heart rate measured?
Measure the bpm (beats per minute)
What is the role of pacemakers?
They coordinate the contraction of the heart muscle and regulate the heart rate.
How does adrenaline influence heart rate?
It is increased as part of a ‘fight or flight’ response.
How and why does exercise affect heart rate?
During exercise, cells of muscles respire more rapidly to provide energy for muscle contraction.
Increased respiration means increased O2 requirement.
This means heart rate increases to be more frequent and volume of blood pumped out also increases to deliver more O2 and glucose.
What happens in the heart during coronary heart disease?
Layers of fatty material- mainly cholesterol- build up inside coronary arteries.
This means it loses its elasticity and cannot stretch to accommodate the blood being forced through.
This blocked flow of blood means the heart muscles receive a lack of oxygen, leading to heart attacks if it worsens.
What are some risk factors that increase the risk of CHD?
Obesity
High BP
High cholesterol
Smoking
What are the 3 main types of blood vessels?
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
What is an arteriole?
Smaller vessels that branch off from arteries
What is a venule?
Smaller vessels that branch off from veins.
What are the key features of arteries?
carry blood at high pressure away from heart
carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery)
narrow lumen
thick muscular walls
fast blood flow
How is an artery adapted for its function?
Thick walls- withstand high pressure
Narrow lumen- maintain high pressure.
What are the key features of veins?
low pressure blood towards the heart
deoxygenated blood (other than pulmonary vein)
thin walls
large lumen
contain valves
slow blood flow
How is a vein adapted for its function?
large lumen- reduces resistance to blood flow under low pressure
Valves- prevent backflow of blood
What are the key features of capillaries?
carry low pressure blood within tissues
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
one cell thick walls
‘leaky’ walls
slow blood flow
How is a capillary adapted for its function?
thin walls- short diffusion distance
leaky walls- plasma can leak out and form tissue fluid
Describe the circulatory system.
O2 blood is carries from heart towards organs in arteries.
These narrow to arterioles and then capillaries as they pass through the organ.
Respiring cells in the organ use the O2 and veins carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart.