Brain structure and the Neuron parts
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
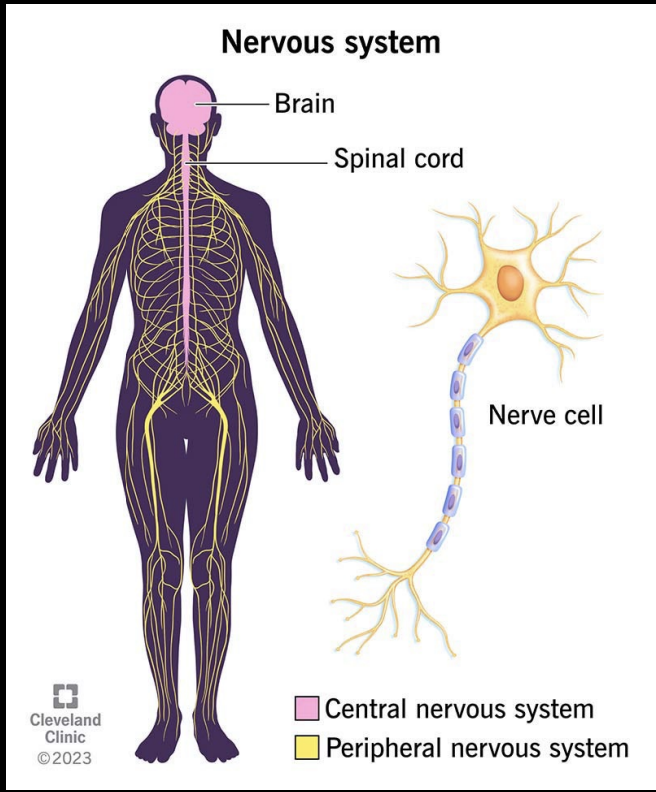
Organization of Human Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
ALL the nerves that exit the brain and spinal cord, carrying sensory and motor messages to and from the other parts of the body
Neurons
Cells that make up the brain and the nervous systme
Adult brain 100 billion neurons
10^15 synapses
Representation by Neural Firing
Definition of the mind: The mind creates representations of the world so we can achieve goals
Principle of Neural Representation: All experiences are based on representations in the person’s nervous system
How the brain relates to mind
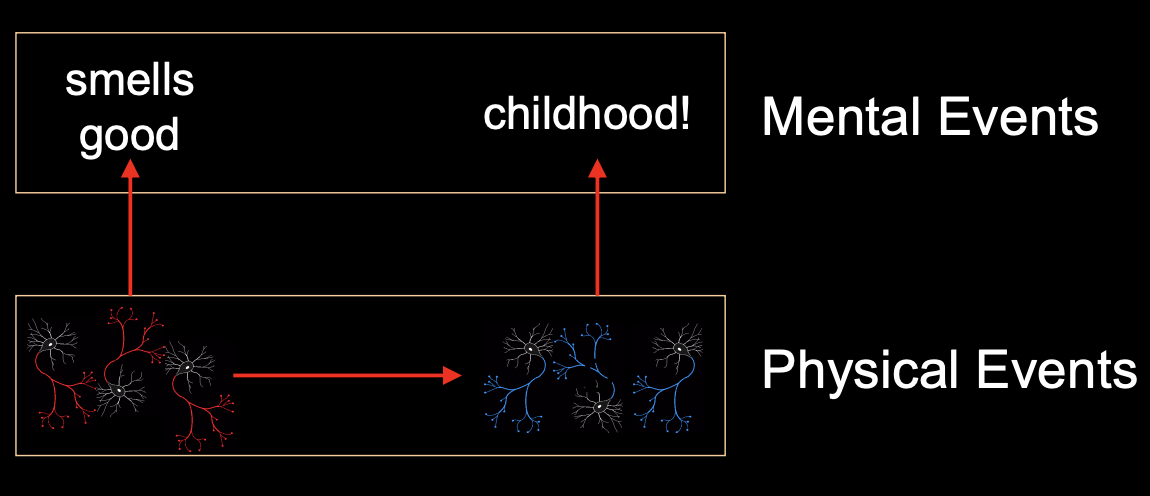
“Brain cells fire in patters”
One neuron getting active is referring to a message being transmitted to another neuron
- Sequences
“A pattern corresponds to a thought. One pattern causes another pattern”
The minds is what the brain does!

Materialism
Mind and brain have a casual relationship
“A pattern corresponds to a thought. One pattern causes another pattern”
Explanations of Behavior
Physiological
describe mechanisms that produce behaviors
Activity of the cells of the nervous system
experience is the product of a nervous system made up of an enormous number of discrete cells
What are discrete cells?
They are just neurons, individual nerve cells, the fundamental structural and functional units that communicate through electrical and chemical signals
Shoulder vs hand squeeze demonstrations
Shoulder is closer to the spine, faster nerve signaling to brain (Rozin and Jonides, 1977)
Three types of Neurons
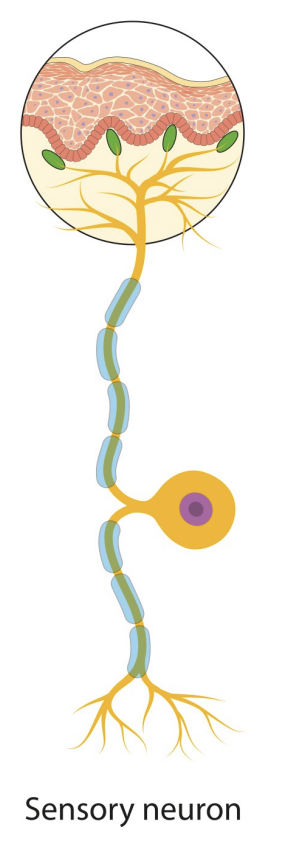
Sensory neuron (afferent neuron)
Interneuron
Motor neuron (efferent neuron)
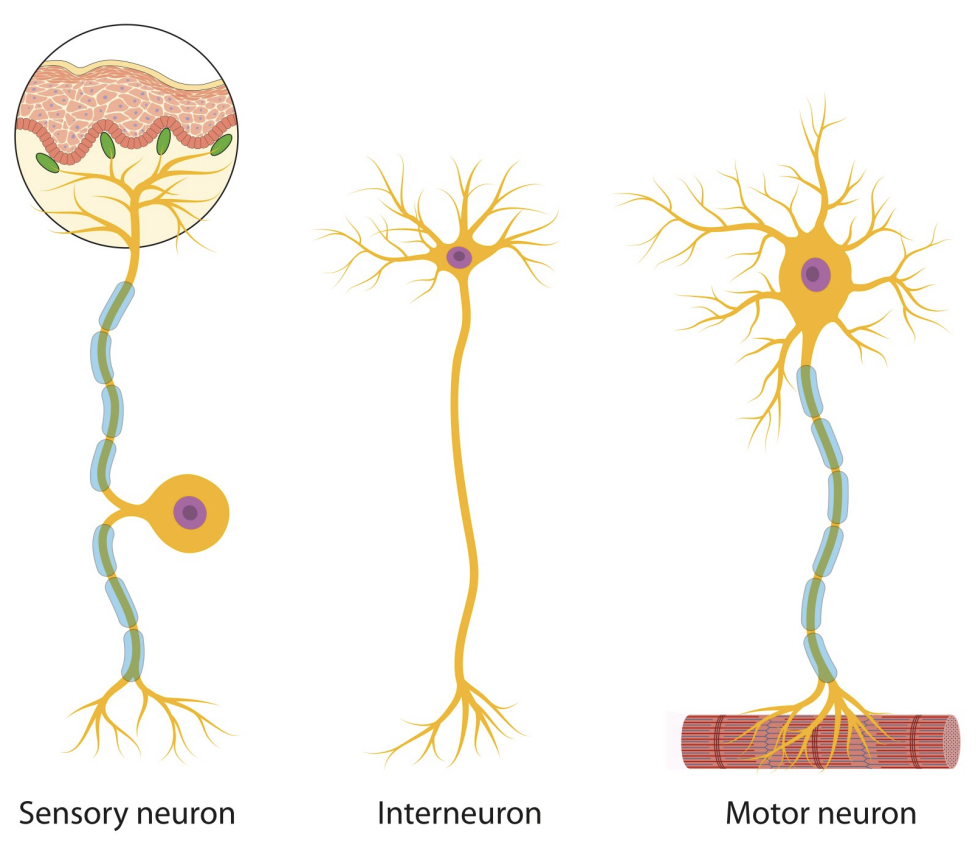
Sensory neuron (afferent neuron)
Neuron that detects changes in the external or internal environment
Sends information about these changes to the CNS
Interneuron
Neuron located entirely within the CNS

Motor Neuron (efferent neuron)
Controls the contraction of muscle or the secretions of a gland
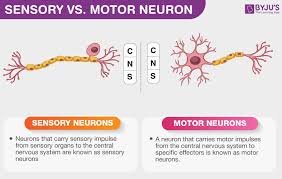
Difference between sensory and motor neuron (AFFERENT) VS (EFFERENT)
The main difference is direction of information flow
Sensory neurons carry signals from the body’s receptors (like eyes, skin, etc) towards the CNS
Motor neurons carry signals away from the CNS to cause a response (like by activating muscles or glands)
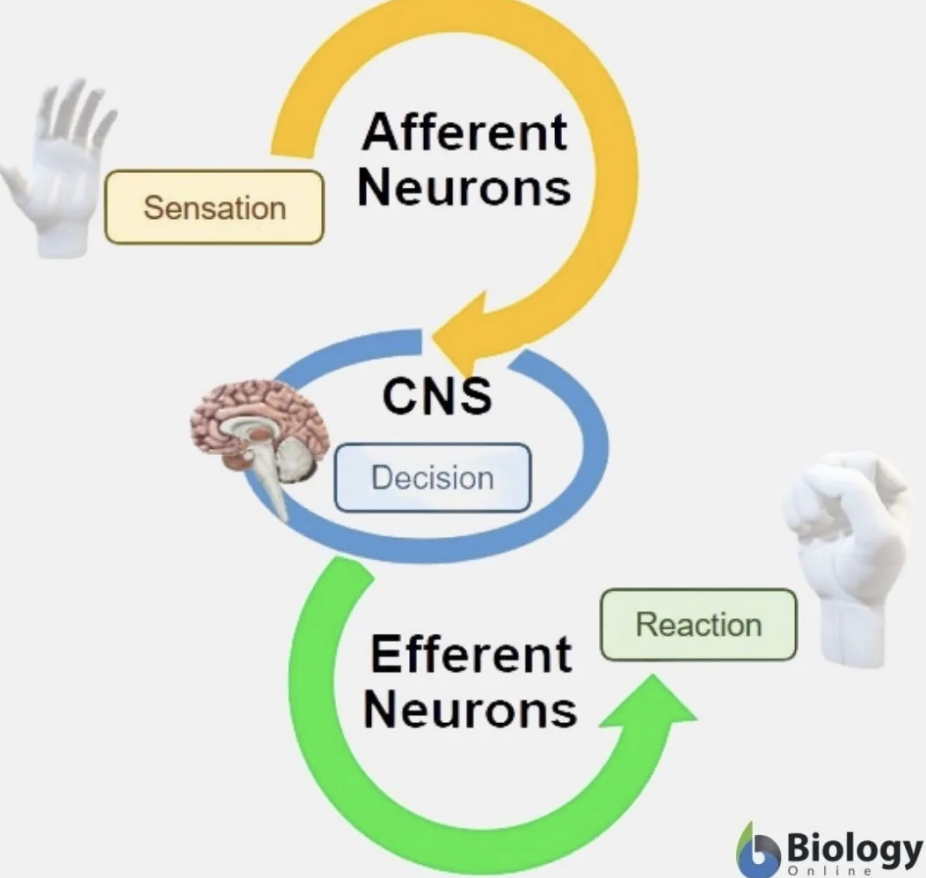
Sensation to Reaction
Sensation (Afferent Neurons) → Decision (CNS) → Reaction (Efferent Neurons)
Dendrite
bushy, branching extensions fo a neurons
Receives messages
Conduct impulses
RECEIVER
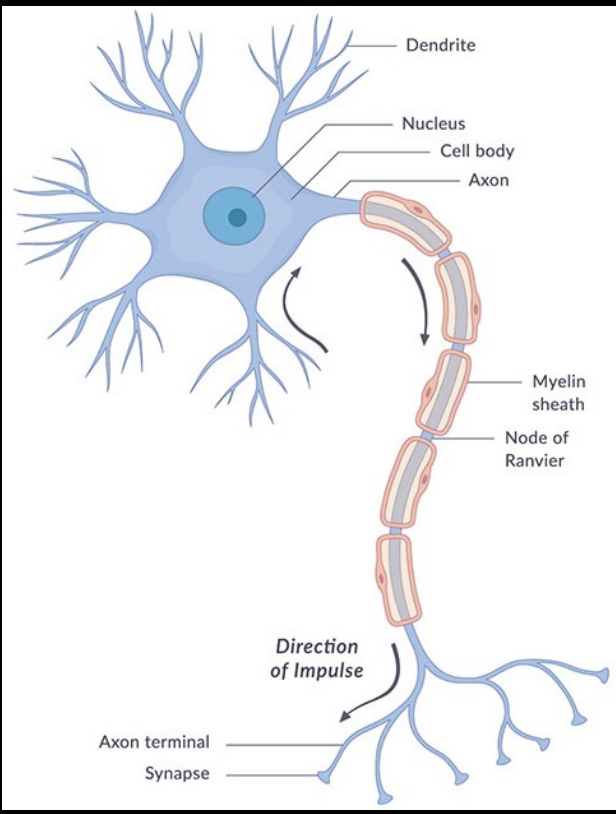
What does the Cell Body/Soma contain?
Nucleus
DNA of the neuron
other organelles e.g., mitochondria, ribosomes
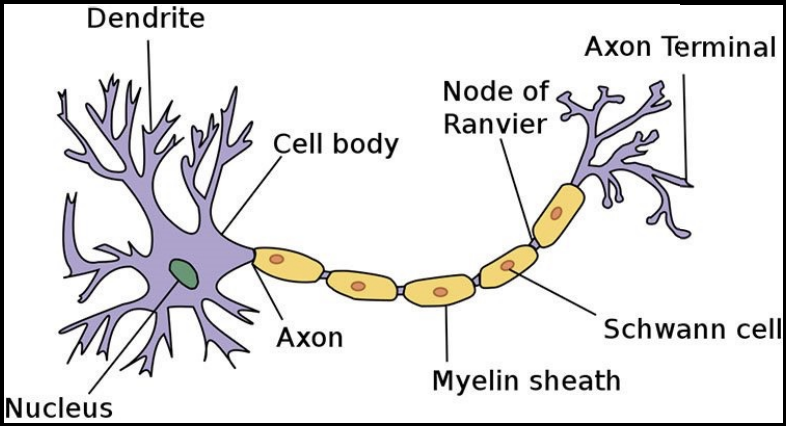
What is the Axon?
Thin fiber of a neuron
The cell’s output structure
Responsible for transmitting nerve impulses
One axon per cell
2 distinct parts
tube-like structure
branches at end that connect to dendrites of other cells
OUTPUT!!!!
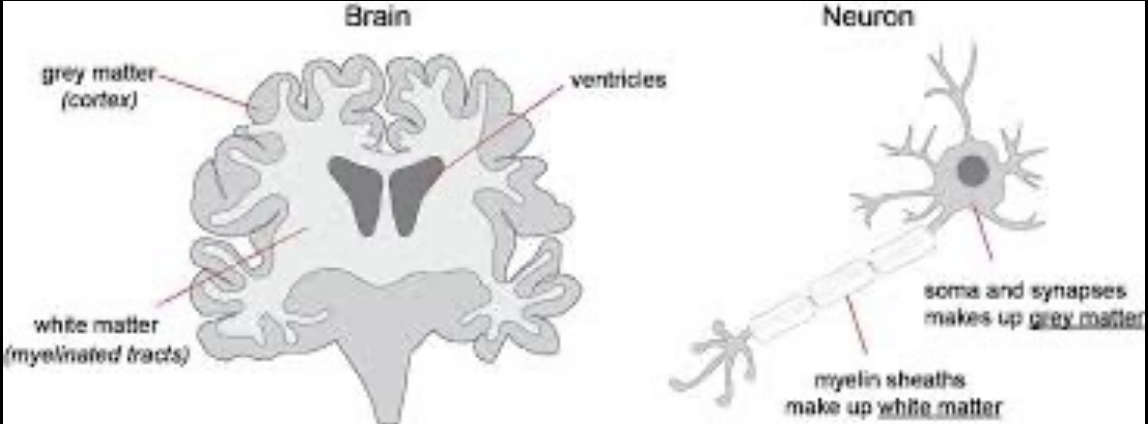
What is the brain made up of?
Gray matter, they are cell bodies
White matter, nerve fibers
Myelin sheath
Crucial white fatty casing on axon
Acts as an electrical insulator
Increases the speed of neural signals down the axon
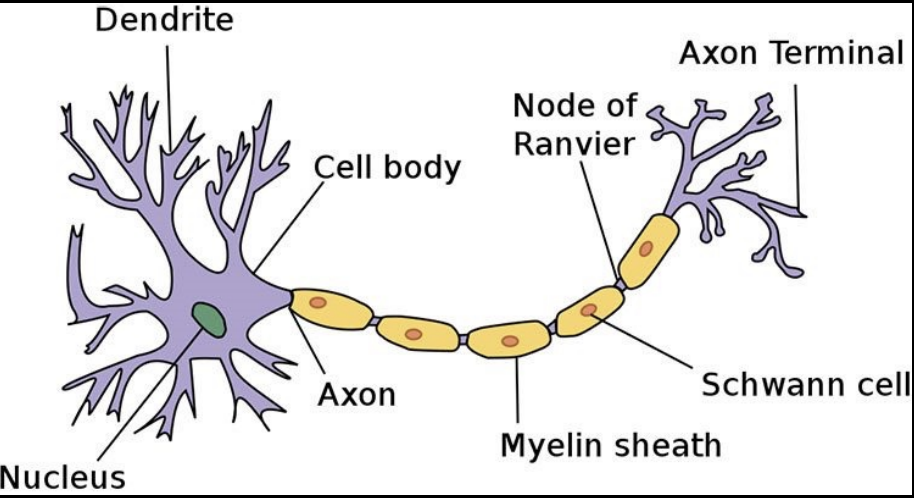
The NEURON
Terminal button
the bud at the end of a branch of an axon
sends information to the next neuron
forms synapses with that neuron
Synapse
junction between the terminal button and the membrane of another neuron
(Vesicle membrane-bound sacs within the axon terminal, neuron store and release neurotransmitters)
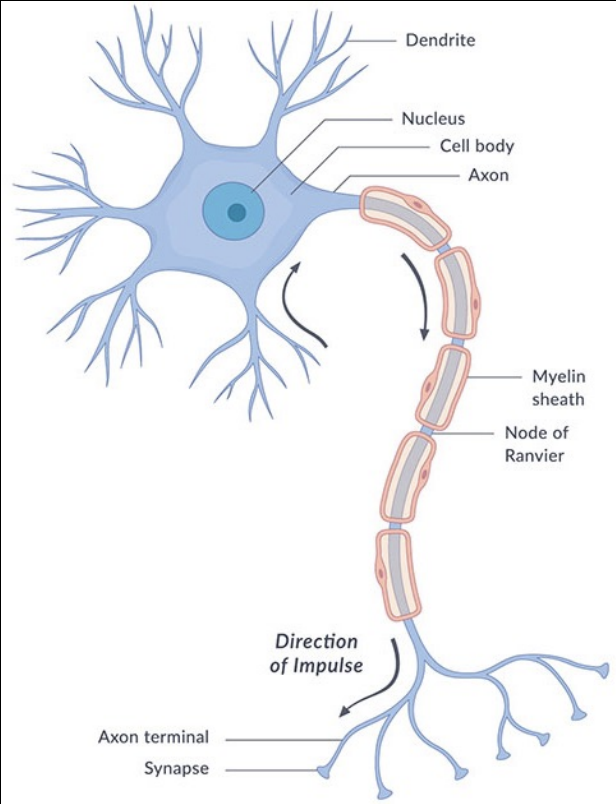
How does a neuron function? (Neuron communication)
Neurons in the CNS
process information
interpret it
send commands to muscles, glands, and organs
Receive and transmit information electrochemically
Neuron Communication (Action potentials)
Action potentials
axons convey info by a combination of electrical and chemical processes
this combo is called ACTION POTENTIAL
signal travels along the axon at a constant strength no matter how far it travels
all-or-none process - it’s either happening or not
influences receiving neuron
What is the communication process?
Action potential travels down axon
Causes neurotransmitter to release from axon terminal
Neurotransmitter travels across synapse
Then binds with the receptors on receiving neuron
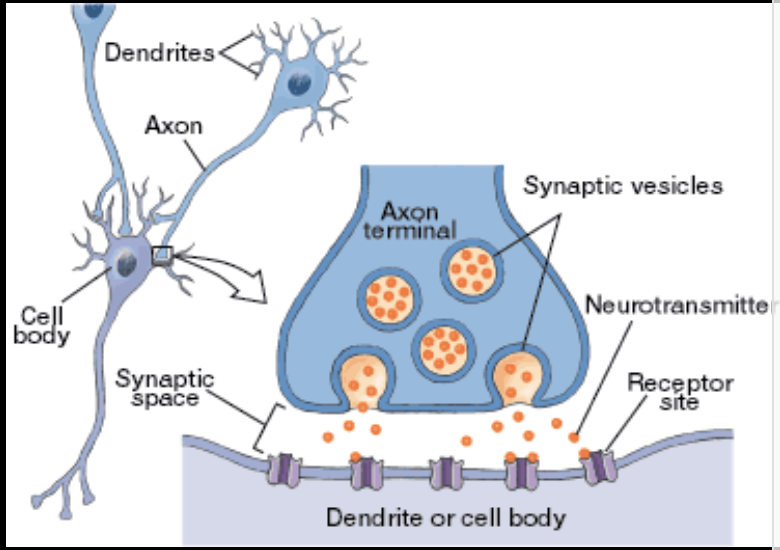
Synaptic Activity
Chemicals released at the synapse excite or inhibit neighboring cells, making action potentials more or less likely
traverse between neurons
… is crucial to brain function
Neurotransmitters
Chemical that’s released by a terminal button
Has an excitatory or inhibitory effect on another neuron
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory
Dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
excess linked with Schizophrenia
Serotonin
affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
too little → depression
Norepinephrine
controls alertness and arousal
too little affects mood negatively
Nerve cell growth
Neurons constantly grow and lose branches to dendrites and axons
this growth is related to new experiences and learning
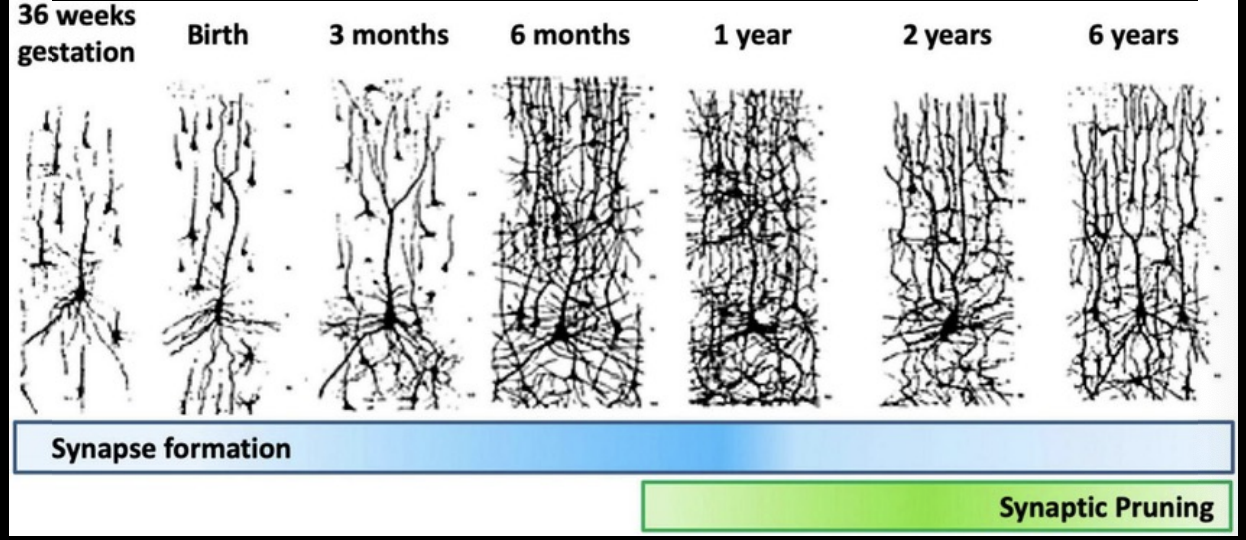
Brain plasticity
Our brain are plastic
Plasticity
brain’s ability to rewire itself
relocating info processing functions to different brain areas and/or neural networks
the stidy of brain plasticity has profound implications on human learning, behavior, and mental health