3.2.6 aqueous ions
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
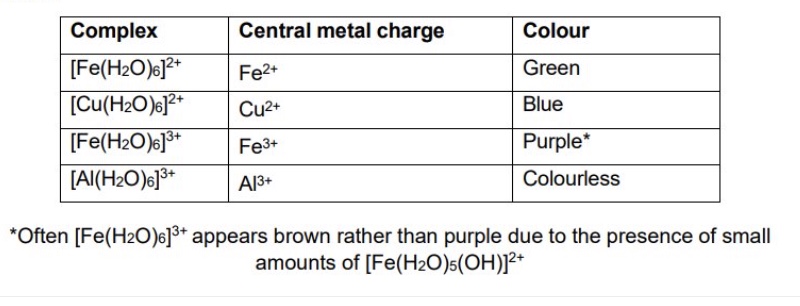
outline what happens if we place a transition metal salt in solution
what is the metal now described as?
it will dissolve to become its ions
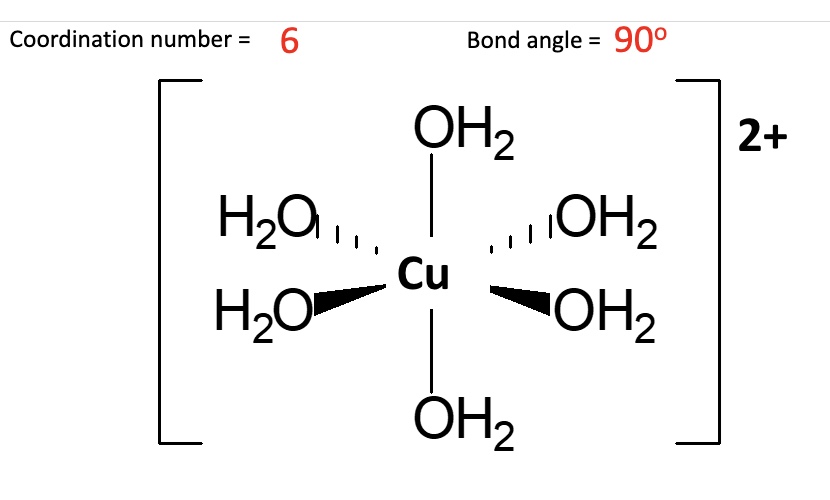
the metal ion is the surrounded by 6 water ligands
its described as a ‘metal aqua ion’ or ‘hexa aqua ion’

give the four metal ions you need to know, along with their complex + colour in water

what is a Bronsted-Lowry acid + base?
acid: proton donor
base: proton acceptor
how can metal aqua ions act as Bronsted-Lowry acids?
if the O-H bond in the water beaks + loses an H⁺ ion
eg give the equation for hexaaqua iron(III) acting as a Bronsted-Lowry acid
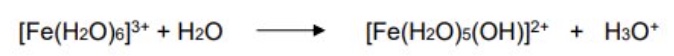
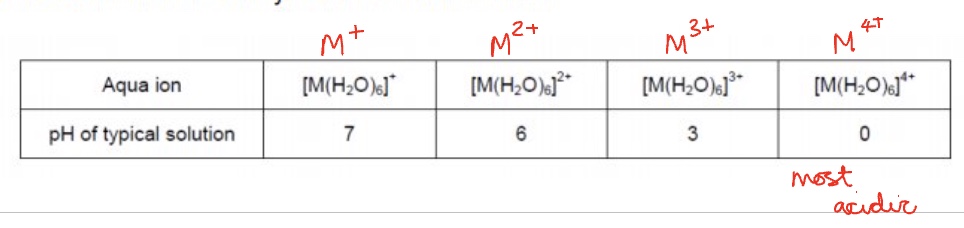
the acidity of complexes will change depending on what?
on the charge on the central metal ion
outline how the acidity of complexes changes due to charge on central metal ion
the higher the charge, the higher the charge density
so the more polarised the O-H bond so the more H⁺ ions you will find in the solution
descibe the other way of describing acids + bases in chemistry

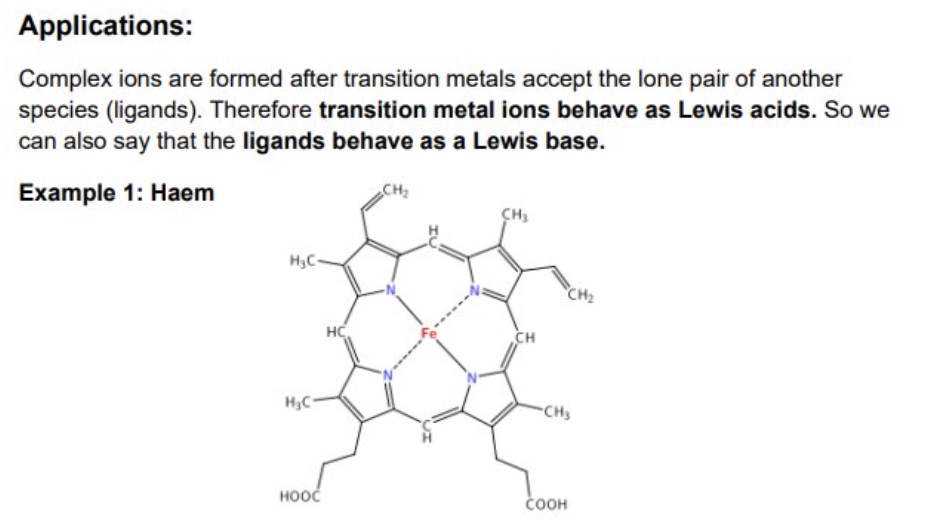
give the Lewis acid and base for haem

acid base reactions of the metal ions follow…
the same essential structure
what do all charged species form + why?
they are all soluble in water + so form solutions
what will happen if the product of a reaction is neutral?
then it will be insoluble in water + come out of the solution forming a precipitate
if you add small amounts of OH- (base) to the M²⁺ (Fe²⁺, Cu²⁺), what will happen?
give the general symbol equation for this reaction
the neutral hydroxide product is insoluble + so will form a precipitate

why will small amounts of ammonia behave in the same way as OH- ions?
as they are also bases + so will remove protons from water molecules + form NH₄⁺ as a product
give the general equation when small amounts of ammonia is added to a M²⁺ (Fe²⁺, Cu²⁺)
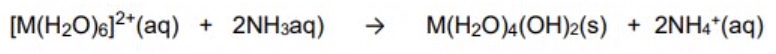
what will happen when you add small amounts of OH- to the M³⁺ (Fe³⁺, Al³⁺)?
give the general equation for this reaction
the OH- will remove protons from the aqua ion structure
this product is in effect [M(OH)₃] which is uncharged + therefore forms a precipitate
![<ul><li><p>the OH- will remove protons from the aqua ion structure </p></li><li><p>this product is in effect [M(OH)₃] which is uncharged + therefore forms a precipitate </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b19c7e0d-caf7-45fa-9166-7ddba87b4a53.jpg)
give the general equation when small amounts of ammonia are added to the M³⁺ (Fe³⁺, Al³⁺)
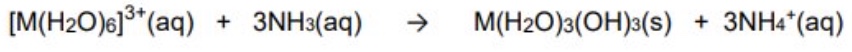
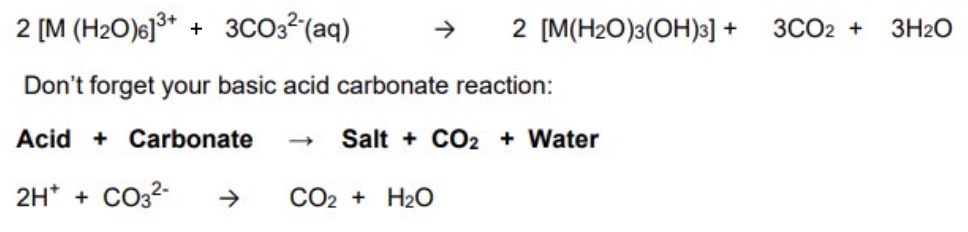
what can carbonate ions do to the M³⁺ complex aqua ions? explain why
they can remove their protons in the same way as OH- and NH₃
this is because M³⁺ complexes have a high acidity due to their high charge/size ratio so carry out acid base reactions with CO₃²⁻ ions
protons are lost from water, forming a neutral precipitate
what happens when carbonate ions react with M²⁺ complexes?
the carbonate ion cannot remove the protons from the M²⁺ as it is a weaker acid + instead forms a carbonate
typically the M²⁺ ions will form …… but the M³⁺ ions will form the….. when carbonate ions are added
carbonate complexes
acid base precipitate
give the general equation for the M²⁺ reactions with the carbonate ions (Fe²⁺, Cu²⁺)
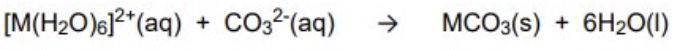
give the general equations, including the basic acid carbonate reaction, when carbonate ions are added to the M³⁺ (Fe³⁺, Al³⁺)
what does amphoteric mean?
acts as both an acid and a base
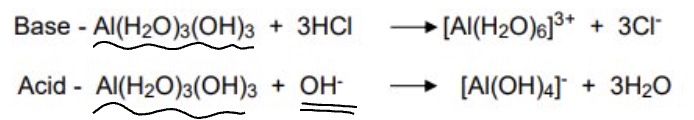
what metal ion is amphtoteric?
Al³⁺
give 2 reactions to show how aluminium acts as a base + acid
what could we replace the water ligands with?
with another neutral ligand such as ammonia
how can water ligands be replaced by ammonia?
the water ligands are roughly the same size as ammonia ligands + they are both neutral so the water ligands can be replaced by excess ammonia
give the overall equation for the substitution of the water ligands in the hexaaqua copper (II) complex with ammonia

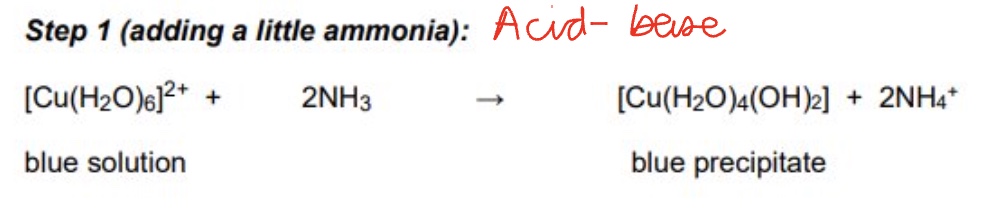
the substitution of water ligands for ammonia in the Cu²⁺ is a two-step process, give step one, including the observations + equation
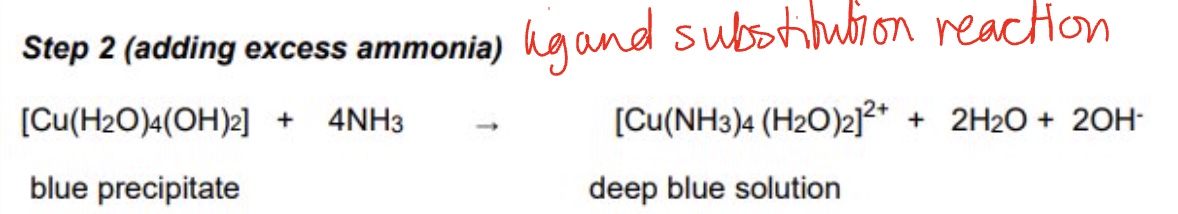
the substitution of water ligands for ammonia in the Cu²⁺ is a two-step process, give step two, including the observations + equation
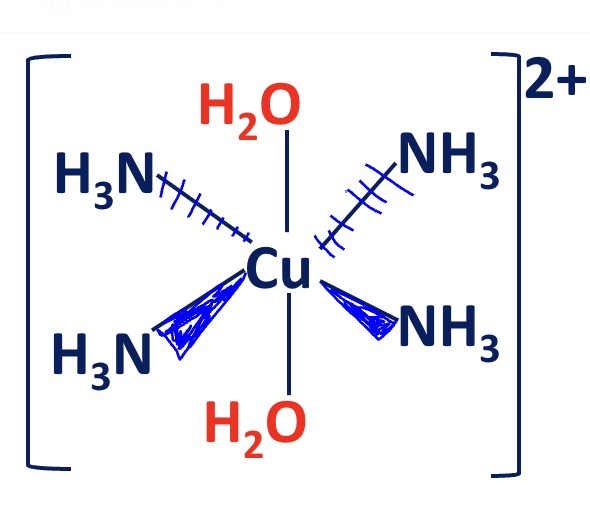
explain the structure of the Cu²⁺ complex formed after the ligand substitution
the structure of the complex ion is slightly distorted as the Cu-O bond is shorter
so the best arrangement is to have the ammonia ligands in. asquare planar arrangement (trans isomer)
for Fe²⁺, give the complex formula + observation for:
a. aqueous ion
b. action of dropwise NaOH
c. action of excess NaOH
d. action of dropwise NH₃
e. action of excess NH₃
f. action of Na₂CO₃

for Cu²⁺, give the complex formula + observation for:
a. aqueous ion
b. action of dropwise NaOH
c. action of excess NaOH
d. action of dropwise NH₃
e. action of excess NH₃
f. action of Na₂CO₃

for Fe³⁺, give the complex formula + observation for:
a. aqueous ion
b. action of dropwise NaOH
c. action of excess NaOH
d. action of dropwise NH₃
e. action of excess NH₃
f. action of Na₂CO₃

for Al³⁺, give the complex formula + observation for:
a. aqueous ion
b. action of dropwise NaOH
c. action of excess NaOH
d. action of dropwise NH₃
e. action of excess NH₃
f. action of Na₂CO₃

give the formula of product produced + observation when Cl- added to Cu²⁺
[CuCl₄]
yellow-green solution
for Ag⁺, give the complex formula + observation for:
a. aqueous ion
b. action of NaOH
c. action of excess NH₃
d. action of Na₂CO₃
e. action of Cl-
a. colourless, [Ag(H₂O)₂]⁺
b. brown ppt, AgOH
c. [Ag(NH₃)₂]⁺ — tollens reagent
d. Ag₂CO₃
e. white ppt, AgCl