Pre-Calc final
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
1
New cards
Function Notation
A way to name and evaluate functions
2
New cards
Difference Quotient
F(x+h)-f(x)
—————, h=0
h
—————, h=0
h
3
New cards
Point Slope form
Y-y1=m(x-x1)
4
New cards
Slope Intercept form
Y=mx+b
5
New cards
Slope
Rate of change
6
New cards
“b” in y=mx+b
Y intercept
7
New cards
Slope of a horizontal line
Slope=0
8
New cards
Standard form
Ax+by=C
9
New cards
Input variables
Domain
10
New cards
X-coordinate of the point where a line crosses the horizontal axis
X-intercept
11
New cards
Slopes of perpendicular lines
Slopes are negative reciprocals
12
New cards
Point where two lines intersect
Solution to a system of equations
13
New cards
Reciprocal
Multiplicative inverse
14
New cards
Slope of a vertical line
The slope is undefined
15
New cards
Output variables
Range
16
New cards
General form
Ax+By+C=0
17
New cards
Piecewise function
A function defined b two r more equations over a specified domain
18
New cards
Vertical line test
Way to tell if a graph is a function visually
19
New cards
Equation to find slope
M=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
20
New cards
Domain explanation
Domain is the furthest x value to the left and right
21
New cards
Range explanation
Highest and lowest y values
22
New cards
Polynomial function the 0 degree is what kind of function
Constant function
23
New cards
Polynomial function the 1st degree is what kind of function
Linear function
24
New cards
Polynomial function the 3rd degree is what kind of function
Cubic function
25
New cards
what does “n” represent in the leading coefficient test
The degree of the function
26
New cards
How does the graph behave when “n” is odd and the leading coefficient is positive
Falls to the left and rises to the right
27
New cards
How does the graph behave when “n” is even and leading coefficient is positive
Rises to the left and rises to the right
28
New cards
How does the graph behave when “n” is odd and leading coefficient is negative
Rises to the left and falls to the right
29
New cards
How does the graph behave when “n” is even and leading coefficient is negative
Falls to the left and falls to the right
30
New cards
Asymptotes
Lines that a graph of a function approaches but never touches
31
New cards
N(x) represents
The numerator
32
New cards
D(x) represents
The denominator
33
New cards
Asymptotes effect the graphs
End behavior
34
New cards
If the degree of the numerator N(x) is less than the degree of the denominator D(x) the graph has a horizontal asymptote at
Y=0
35
New cards
If the degree of the numerator N(x) is equal to the degree of the denominator D(x) the graph of “f” has a horizontal asymptote at where “a” and “b” are the leading coefficients of N(x) and D(x) respectively
Y=a/b
36
New cards
If the degree of the numerator N(x) is greater than the degree of the denominator D(x) the graph of “f” has
No horizontal asymptote
37
New cards
Multiplicity
When one answer is worth three for example X^3=0 is x=0 three times
38
New cards
The imaginary unit
“i”
39
New cards
quadratic formula
\
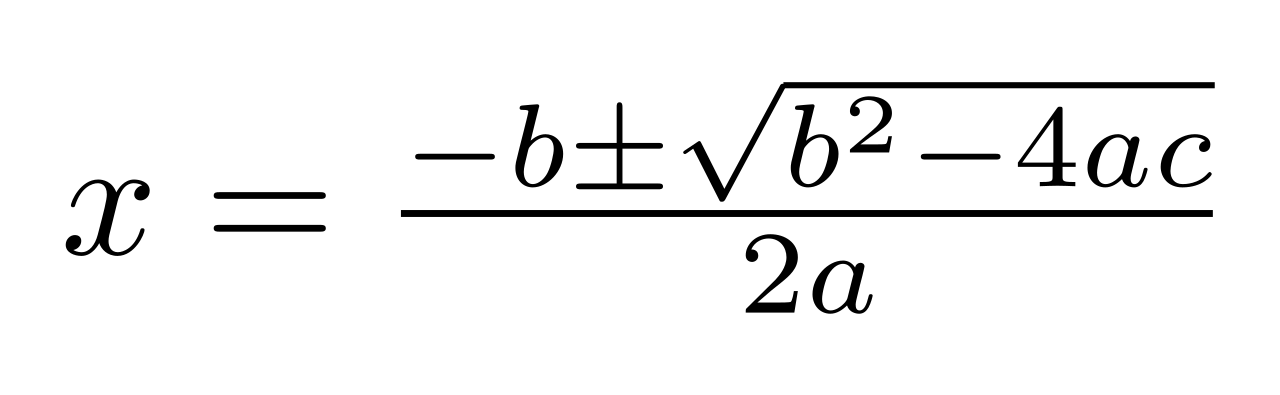
40
New cards
Vertex form of parabolas
Y=a(x-h)^2+k
41
New cards
what does “h” in vertex form represent
X coordinate of the vertex
42
New cards
What does the “k” in vertex form represent
Y coordinate of the vertex
43
New cards
formula to find the vertex of a parabola
X= -b/2a
44
New cards
Axis of symmetry on a parabola
The point that divides the graph into two halves
45
New cards
Formula used when compounding a certain amount of time (ex. A year)
A=P(1+r/n)^nt
46
New cards
“N” value when compounded annually
1
47
New cards
“N” value when compounded semiannually
2
48
New cards
“N” value when compounded quarterly
4
49
New cards
“N” value when compounded bimonthly
6
50
New cards
“N” value when compounded monthly
12
51
New cards
“N” value when compounded semimonthly
24
52
New cards
“N” value when compounded bi weekly
26
53
New cards
“N” value when compounded weekly
52
54
New cards
“N” value when compounded daily
365
55
New cards
“N” value when compounded continuously
E
56
New cards
Amplitude
vertical stretch/ compression (height of one wave)
57
New cards
Period
Horizontal stretch/ compression (length of one full cycle of the wave)
58
New cards
Phase Shift
Horizontal shift (determine how far the graph shifts)
59
New cards
Vertical shift
Shifts the graph up and down
60
New cards
2pi/b is h used to find what in a sine graph
The period
61
New cards
When the sine is equal to zero, the close cosecant is ___ and there will be a ____ on the graph
Undefined, asymptote
62
New cards
When the cosine is equal to __the ____ is undefined and there will be an asymptote
Zero, secant
63
New cards
Amplitude in a sine and cosine graph
“A” (first value)
64
New cards
Amplitude in secant, cosecant, and tangent
No amplitude
65
New cards
Formula used to find the period in a tangent graph
Pi/b
66
New cards
Angle
Two rays with the same initial point
67
New cards
Angles that measure between 0 and pi/2 (90) are
Acute
68
New cards
Shared initial point of two rays
Vertex of the angle
69
New cards
Angles that measure between pi/2 (90) and pi (180) are
Obtuse
70
New cards
Two positive angles are said to be _______ if the sum of their angles is pi/2 (90)
Complimentary
71
New cards
Two positive angles are said to be _________ if the sum of their measures is pi (180)
Supplementary
72
New cards
The ____________ is the amount of rotation required to rotate to one side called the ______ to the other side called the _______
Measure of the angle, initial, terminal side
73
New cards
Two angles in standard position that have the same terminal side are said to be _____
Coterminal
74
New cards
To convert degrees to radians multiple degrees by
Piradians/180
75
New cards
To convert radians to degrees multiply radians by
180/piradians
76
New cards
One radian is
The measure of a central angle feta that intercepts an arc *s* equal in length to the radius *r* of the circle
77
New cards
The radian measure of any central angle is
The length of the intercepted arc divided by the circle’s radius
78
New cards
How to find a co-terminal angle
Add or subtract 360 degrees of 2pi
79
New cards
Standard position
1\.) It’s vertex is at the origin of a rectangular coordinate system
2\.) It’s initial side lies along the positive x-axis
2\.) It’s initial side lies along the positive x-axis
80
New cards
Sine=
Y and opposite/hypotenuse
81
New cards
Cosine=
X and adjacent/hypotenuse
82
New cards
Tangent=
Y/x and opposite/adjacent
83
New cards
cosecant=
1/y, hypotenuse/adjacent, 1/sin
84
New cards
Secant=
1/x, hypotenuse/adjacent, 1/cos
85
New cards
cotangent
X/y, adjacent/opposite, 1/tan
86
New cards
On the Unit circle for every 30 degrees you go ___ radians
Pi/6
87
New cards
On the Unit circle for every 45 degrees you go every ____ radians
Pi/4
88
New cards
Y=sin^-1x
\[-pi/2, pi/2\] (Q1 and Q4)
89
New cards
Y=cos^-1x
\[O, pi\] (Q1 and Q2)
90
New cards
Y= tan^-1x
(-pi/2, pi/2) (Q1 and Q4)
91
New cards
Pythagorean Theorem
A^2+B^2=c^2
92
New cards
Angle of elevation
An angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight to an object that is above the horizontal line (Ex. Looking up at a kite)
93
New cards
Angle of depression
The angle formed by a horizontal line and the line of sight to an object that is below the horizontal line (Ex. Lookin down from a building)
94
New cards
Trigonometric Identity
An equation that is true for all values except those for which the expressions on either side of the equal sign are undefined
95
New cards
component form
PQ
96
New cards
Magnitude of PQ
IIPQII= √(x2-x1)^2+(y2-y1)^2
97
New cards
Law of Sines
SinB/b=SinA/a
98
New cards
When do you use law of sines
ASA AAS
99
New cards
Law of consines
a^2=b^2+c^2-2(b)(c)(cosA)
100
New cards
When do you use law of cosines
SAS SSS