L8 Osmoregulation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Homeostasis
Internal environment needs to remain constant
Diffusion
solute molecules move from high to low concentration
osmosis
solvent molecules move from low to high soute concentration
Red blood cells in a hypotonic solution
Too low osmolarity, cells will explode
Red blood cells in a hypertonic solution
Too high osmolarity, cells will shrin
Skin properties terrestrial animals
reptiles (birds) and mammals
impentreable (no respiration)
phospholipids/keratin (no evaporation)
osmoregulator
keep internal enivornment constant independently from outside
osmoconformer
internal osmolarity changes with external environment
advantage osmoregulator
changing environment is not harmful
advantage osmoconformer
saves a lot of energy
euryhaline -fish
broad range
stenholaine - fish
small range
osmoregulation is hard for fish because
only 1 cell layer between hypertonic/hypotonic environment and constant internal medium (blood)
fresh water fish: hyperosmotic regulator
hypotonic environment
water enters blood stream (cells explode)
loss of ions
active absorption of NaCl
salt water fish: hypo-osmotic regulator
hypertonic environment
water exists blood stream (cells shrink)
influx of ions
Active secretion of NaCl
marine animals - how to get rid of excess ions
via specialized glands
vetrebrate kidney function
filtration - glomerulus
reabsorption - loop of Henle, only in birds and mammals
secretion - urea
ion pumps in gills; ionocytes/chloride cell
seawater - ion secretion
fresh water - ion uptake
Hormonal effects on gills and gut
Renin/angiotensisn II
vasotocin (vasopressin)
Natriuretic peptide family (ANP)
isotocin (Oxytocin)
cortisol (aldosterone)
salt water ionocyte SW; secretion ions, GH/IGFI, cortisol
Fresh water ionocyte, FW, ion uptake, prolactin/cortisol
Why do we need kidneys
waste secretion (N-groups)
water-salt balance
acid-base regulation
blood pressure control
hormone production
detox and drug handling
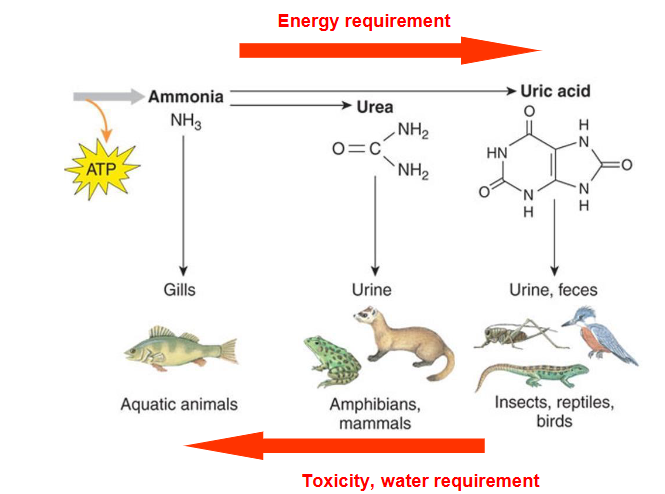
Excretion of nitrogin
→ energy requirement
← toxicity, water requirement
ammonia, gills, aquatic animals (ammonotelic animals)
urea, urine, amphibians, mammals (ureotelic animals)
uric acid, insics, reptiles, birds (Uricotelic animals)
Thermoregulation and osmoregulation
Are correlated
Thermoregulation and osmoregulation are both homeostatic processes in organisms, meaning they help maintain internal stability, but they focus on different aspects of the body’s internal environment.
Longer loop of Henle
more concentrated *hyperosmotic) urine