Temperature and Heat - PH2105
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Absolute temperature scale
scale, such as Kelvin, with a zero point that is absolute zero
Absolute zero
temperature at which the average kinetic energy of molecules is zero
Calorimeter
container that prevents heat transfer in or out
Calorimetry
study of heat transfer inside a container impervious to hear
Coefficient of linear expansion (alpha)
material property that gives the change in length, per unit
length, per 1 degree celsius change in temperature; a constant used in the calculation of linear expansion; the coefficient of linear expansion depends to some degree on the temperature of the material
Coefficient of volume expansion (beta)
similar to (alpha) but gives the change in volume, per unit volume, per change in temperature
Conduction
heat transfer through stationary matter by physical contact
Convection
heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of fluid
Critical point
for a given substance, the combination of temperature and pressure above which the liquid and gas phases are indistinguishable
Critical pressure
pressure at the critical point
Critical temperature
temperature at the critical
point
Emissivity
measure of how well an object radiates
Greenhouse effect
warming of the earth that is due
to gases such as carbon dioxide and methane that absorb infrared radiation from Earth's surface and reradiate it in all directions, thus sending some of it back toward Earth
Heat
energy transferred solely due to a temperature difference
Heat of fusion
Energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the solid phase to the liquid phase, or released when the substance changes from a liquid to solid
Heat of sublimation
energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the solid phase to the vapor phase
Heat of vaporisation
energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the liquid phase to the vapor phase
Heat transfer
movement of energy from one place or material to another as a result of a difference in temperature
Latent heat coefficient
general term for the heats of fusion, vaporization, and sublimation
Mechanical equivalent of heat
work needed to produce the same effects as heat transfer
Net rate of heat transfer by radiation
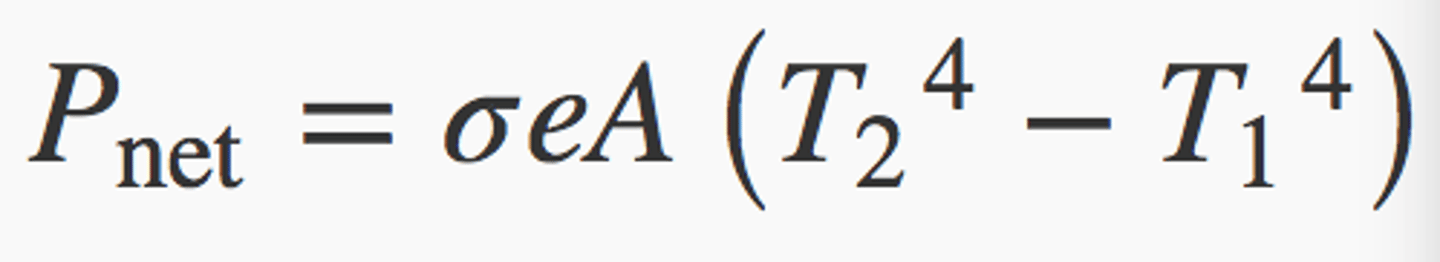
Phase diagram
graph of pressure vs. temperature of a particular substance, showing at which pressures and temperatures the phases of the substance occur
Radiation
energy transferred by electromagnetic waves directly as a result of a temperature difference
Rate of conductive heat transfer
rate of heat transfer from one material to another
Specific heat
amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of a substance by
1.00dC; also called "specific heat capacity"
Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation
is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, A is the surface area of the object, T is the absolute temperature, and e is the emissivity
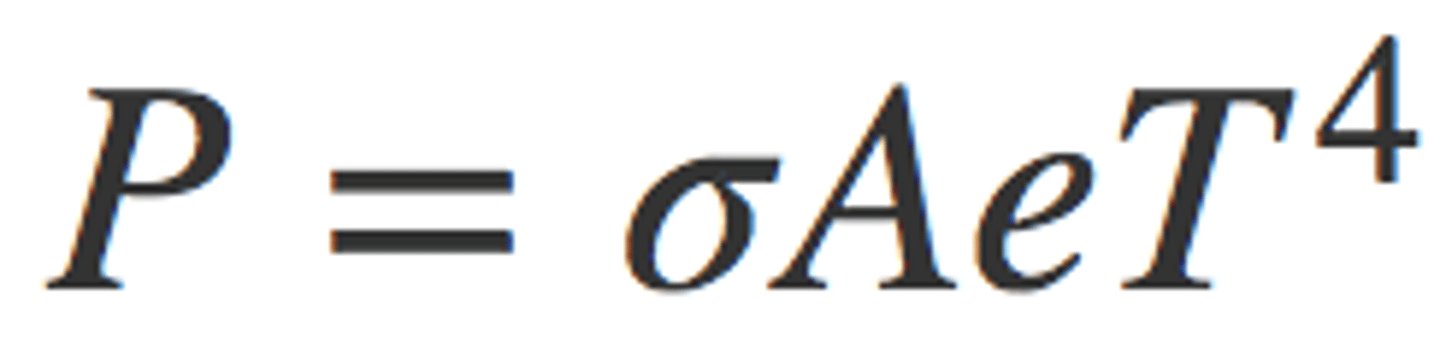
Sublimation
phase change from solid to gas
Temperature
quantity measured by a thermometer, which reflects the mechanical energy of molecules in a system
Thermal conductivity
property of a material
describing its ability to conduct heat
Thermal equilibrium
condition in which heat no longer flows between two objects that are in contact; the two objects have the same temperature
Thermal expansion
change in size or volume of an
object with change in temperature
Thermal stress
Stress caused by thermal expansion of contraction
Triple point
pressure and temperature at which a
substance exists in equilibrium as a solid, liquid,
and gas
Vapor
gas at a temperature below the boiling temperature
Vapor pressure
pressure at which a gas coexists with its solid or liquid phase
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
law that states that
if two objects are in thermal equilibrium, and a third object is in thermal equilibrium with one of those objects, it is also in thermal equilibrium with the other object