IMSE311 (LEC) - FINALS: BASIC IMMUNOLOGIC PROCEDURES
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
A medical science dealing with blood serum especially in regard to its immunological reactions and properties.
Serology
TRUE OR FALSE
Yellow tops may be used in serological tests.
FALSE
If a blood is delayed for less than 72 hours, what should be done to preserve the specimen?
Refrigerate it
If a blood is delayed for more than 72 hours, what should be done to preserve the specimen?
Freeze at -72°C
TRUE OR FALSE
In preparing the specimen for serological tests, whole blood can be refrigerated.
FALSE - only the serum can be refrigerated.
This refers to preparation of blood specimen by transferring the serum into a compatible secondary container.
Aliquot
Name at least 3 agents for erroneous results
Icteric Sample
Turbid Samples
Bacterial Contamination
Chyle
Contamination with alkali or acid
Incorrect time of collection
If the serum is highly turbid and testing is necessary, troubleshooting should be performed by ______ the lipids to minimize analytical interference.
Precipitating
Considered as the process that destroys complement activity.
Inactivation
known to interfere with the reactions of certain syphilis tests
Complement
In Latex Passive Agglutination Assays, complement activation may interfere by producin a ________ result
A. False Positive
B. False Negative
A.
In Hemagglutination Assays, complement activation may interfere by producin a ________ result
A. False Positive
B. False Negative
B.
How is complement inactivated?
By heating it to 56ºC for 30 minutes
How is complement reinactivated?
By heating it to 56ºC for 10 minutes after more than 4 hours since activation
What are the types of agglutination reaction?
Direct
Indirect
Reverse passive
Agglutination inhibition
Coaggulatination
The process whereby specific antigens (e.g., red blood cells) aggregate to form larger visible clumps.
Agglutination
Antibodies that induce agglutination reaction are often called ______
Agglutinins
Warm-reacting antibody
A. IgG
B. IgM
A
Give particles that can initiate agglutination
Erythrocytes
Bacterial Cells
Inert Carriers such as latex particles
The first step in agglutination, where involves antigen – antibody combination through single antigenic determinants on the particle surface
Sensitization
TRUE OR FALSE
Sensitization is rapid and reversible
TRUE
A step in agglutination considered as the sum of interactions between antibody and multiple antigenic determinants on a particle.
Lattice Formation
In agglutination, this occurs when multiple antibodies bind to different
epitopes on the antigen
Lattice Formation
A type of agglutination that Occurs when antigens are found naturally on a particle.
Direct Agglutination
It is an agglutination reaction involves red blood cells/erythrocytes which
contains antigens that are naturally attached to it.
Hemagglutination
A serum specimen was sent for RF Latex Agglutination. The medical technologist processed it. Upon adding the anti-sera, the medical technologist waited for few seconds. A smooth milky suspension was seen. What is the result?
NEGATIVE for RF
A type of agglutination reaction which employs particles that are coated with antigens not normally found on their surfaces.
Passive or Indirect Agglutination
Particles which Are inexpensive, are relatively stable, and are not subject to cross-reactivity with other antibodies.
Latex Particles
In indirect agglutination assays, these serve as ccariers for the antigen
Latex particles
Immunoglobulin which is capable of adsorption when added to the surface of polystyrene latex particles.
IgG
In this type of agglutination reaction, antibody rather than antigen is
attached to a carrier particle
Reverse Passive Agglutination
With any agglutination reactions, patients with a positive _______ may cause a false positive results as it reacts with any IgG antibody.
Rheumatoid Factor
In reverse passive agglutination, which is coated in the latex particles?
Antibodies
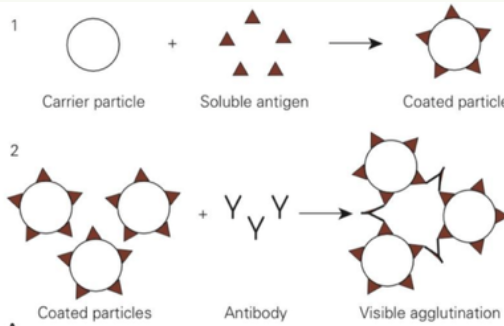
Which type of agglutination reaction is depicted in the image?
Passive/Indirect agglutination since carrier particle is coated with a soluble antigen.
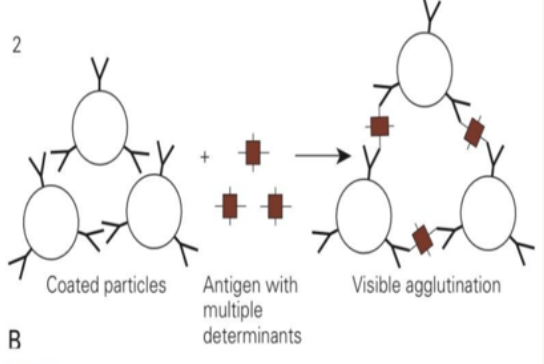
Which type of agglutination reaction is depicted in the immage?
Reverse Passive Agglutination since antibodies coat the coated particles, as seen in the image.
This type of agglutination reaction is based on competition between particulate and soluble antigens for limited antibody-combining sites
Agglutination Inhibitions
What is the positive indication of an agglutination inihibition reaction?
A. Presence of agglutination
B. Lack of agglutination
B
MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE:
In agglutination inhibition reaction, the positive indicator of reaction is the lack of agglutination.
Particulate antigens are small and monovalent. Hence, when added to the sample along with the antibody reagent, no visible lattice formation occurs.
A. Statement 1 is true
B. Statement 2 is true
C. Both statements are true
D. Both statements are false
A
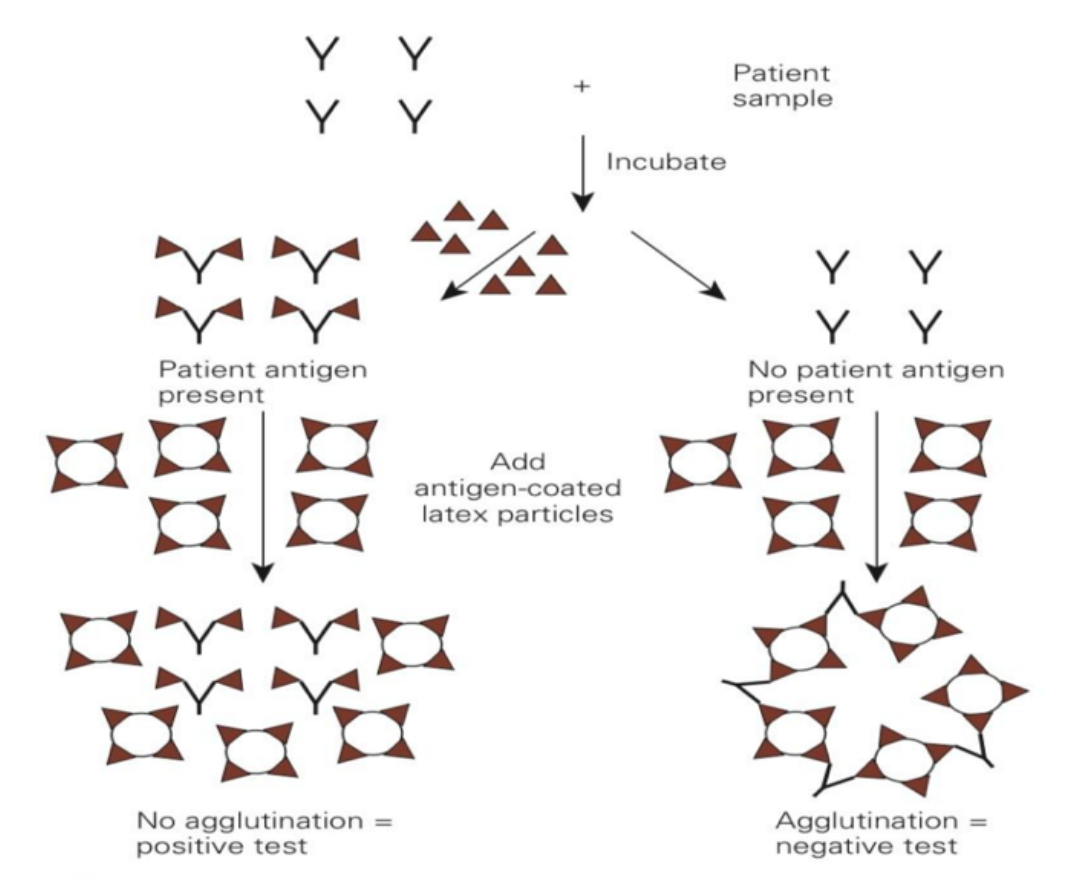
Which agglutination reaction is depicted in the photo?
Agglutination Inhibition Reaction
A type of hemagglutination inhibition reaction, which uses erythrocytes as indicator particles.
Hemagglutination Inhibition
In coagglutination reaction, which is used as the inert particle wherein antibody is attached to?
Bacteria
This is the most commonly used bacteria in coagglutination reactions
Staphylococcus aureus
used to demonstrate in vivo attachment of antibody or complement
to an individual’s red blood cells.
Direct Antiglobulin Test
A type of AHG which can serve as an indicator of AHA, HDN and determine the sensitization of erythrocytes during transfusion reactions.
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
This is used to determine the presence of a particular antibody in a patient,
or it can be used to type patient red blood cells for specific blood group
antigens.
Indirect Antiglobulin Test
Determine whether it can cause false positive or false negative reactions in agglutination test
Overcentrifugation
Contaminated glassware, slides or reagents
Inactive reagents
Improper washing of cells
Incorrect incubation time
Cross-reactivity
Saline stored in glass bottles
Postzone phenomenon
Failure to add antiglobulin reagent
Delays in testing procedures
Delays in reading the slides
Heterophile antibody
Autoagglutination
Undercentrifugation
Rheumatoid Factor present in patient’s sample
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
FALSE NEGATIVE
FALSE POSITIVE
involves combining soluble antigen with soluble antibody to produce Insoluble complexes that are visible.
Precipitation
Step in precipitation where first bidning to epitope occurs
A. Avidity
B. Affinity
C. Sensitization
D. Lattice Formation
B.
Is the initial force of attraction that exists between a single Fab site on an antibody molecule and a single epitope
Affinity
In precipitation reactions, this represents the sum of all the attractive forces between an antigen and an antibody.
Avidity
Area where optimum precipitation or agglutination occurs.
Zone of Equivalence
This is where the antibody is excessive, in which antigen combines with only one or two antibody molecules.
Prozone
TRUE OR FALSE
Lattice Formation and Avidity may be achieved with postzone phenomenon. However, sensitization and affinity will occur since antibodies only affect lattice formation and avidity.
A. Statement 1 is true
B. Statement 2 is true
C. Both Statements are true
D. Both statements are false
B.
A serological technique wherein reactants are added to the gel.
Passive Immunodiffusion
Term used to coin as the migration of concentrated solution to a less concentrated solution.
Diffusion
A type of passive immunodiffusion that measures the size of the radius/clear zone.
Radial Immunodiffusion
TRUE OR FALSE
In radial immunodiffusion, the larger the radius of the precipitin ring, the higher the antigen concentration
TRUE
A type of radial immunodiffusion which measures the radius of the precipitin ring at the endpoint, which is when antigen-antibody reaction is complete and the ring stops growing.
Mancin / Endpoint Method
A type of radial immunodiffusion that It measures the radius of the precipitin ring at intervals before reaching the endpoint.
Fahley-McKelvey Method/ Kinetic Method
In Ouchterlony double diffusion, these are measured to observe the reaction between antigen and antibody.
Ouchterlony Double Diffusion
Presence of lines that merge into a curved precipitin line is known as ____
A. Complete identity
B. Partial identity
C. Non-identity
B.
Presence of spur that form between the lines is known as ____
A. Complete identity
B. Partial identity
C. Non-identity
B.
Lines that remain straight and does not form a precipitate is known as ____
A. Complete identity
B. Partial identity
C. Non-identity
C.
A technique that separates molecules according to differences in their electric charge when they are placed in an electric field.
Electrophoresis
This is a double diffusion technique that incorporates electrophoresis current to enhance results/ speed up the separation.
Immunoelectrophoresis
What is the end result of a rocket immunoelectrophoresis?
precipitin line that is conical in shape
A type of electrophoresis, wherein antiserum is applied directly to the gel’s surface after electrophoresis takes place,
Immunofixation Electrophoresis
What is the postive result of a complement fixation test?
A. Presence of Agglutination
B. Presence of Hemolysis
C. No Hemolysis occurs
D. No Agglutination occurs
C.
What is the negative result of a complement fixation test?
A. Presence of Agglutination
B. Presence of Hemolysis
C. No Hemolysis occurs
D. No Agglutination occurs
B.
The formation of downy masses of precipitate that occurs over a narrow
range of antigen concentration.
Flocculation
What is the reagent used in flocculation to form flocs or clumps.
Charcoal