Pleural Cavity and Lungs
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the parietal pleura?
outer serous membrane that lines the internal thoracic wall, diaphragm and mediastinum
What is the visceral pleura?
inner serous membrane that adheres to the lung surface and follows its fissures
What is the pleural cavity?
potential space between parietal and visceral pleura containing a small amount of serous fluid to reduce friction
What is pleural reflection?
abrupt change in direction where parietal pleura passes from one surface (costal, diaphragmatic, mediastinal) to another
Name the two pleural recesses and there locations
- Costodiaphragmatic recess (lowest part between costal and diaphragmatic pleura)
- Costomediastinal recess (near sternum; between costal and mediastinal pleura)
why is the costodiaphragmatic recess clinically important?
most gravity dependent part of pleural cavity and where excess fluid (pleural effusion) accumulates
- making it ideal for thoracentesis
How do pleura contribute to lung expansion during inspiration?
negative intrapleural pressure and surface tension keep lung adhered to thoracic wall
- as the thoracic cavity expands, lung follows
What happens if pleural integrity is last?
air can enter the pleural cavity, the lungs recoil and collapses due to elastic recoil
What is the primary bronchus?
main airway entering each lung
- right is wider, shorter, and more vertical
What do primary bronchi divide into?
secondary (lobar) bronchi - one for each lobe
What do secondary bronchi divide into?
tertiary (segmental) bronchi
- one for each bronchopulmonary segment
What are the lobes and fissures of the left lung?
two lobes (superior,inferior)
- separated by left oblique fissure; also contains lingula and cardiac notch
What are the Rule of 2s for surface landmarks?
- midclavicular: lung ends rib 6, pleura rib 8
- midaxillary: lung rib 8, pleura rib 10
- scapular: lung rib 10, pleura rib 12
What if the function of the pulmonary arteries?
carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to alveoli for gas exchange
what is the function of the pulmonary veins?
carries oxygenated blood back to left atrium
what arteries supply the lung tissues themselves?
bronchial arteries
- small branches of thoracic aorta
What are the two lymphatic plexuses in the lung?
superficial (beneath visceral pleura)
deep (along bronchi and vessels)
Where do bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes drain into?
tracheobronchial nodes
bronchomediastinal trunks
subclavian vein
What types of nerve fibers make up the pulmonary plexus?
sympathetic (bronchodilation)
parasympathetic (bronchoconstriciton)
visceral sensory afferents
what nerve supplies the parietal pleura?
intercostal nerves (costal and peripheral diaphragmatic pleura)
phrenic nerve (central diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleura)
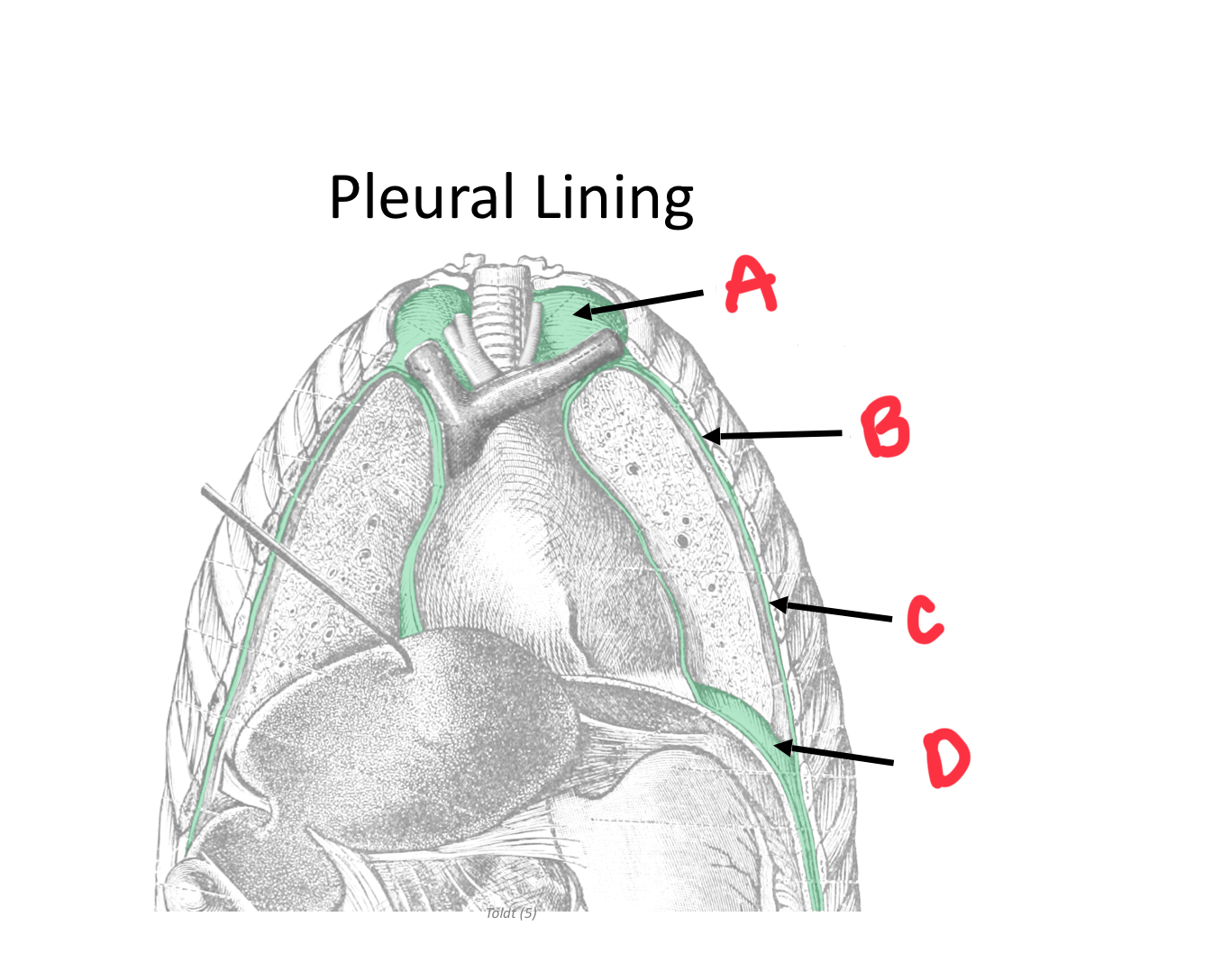
Identify A
Cervical pleura
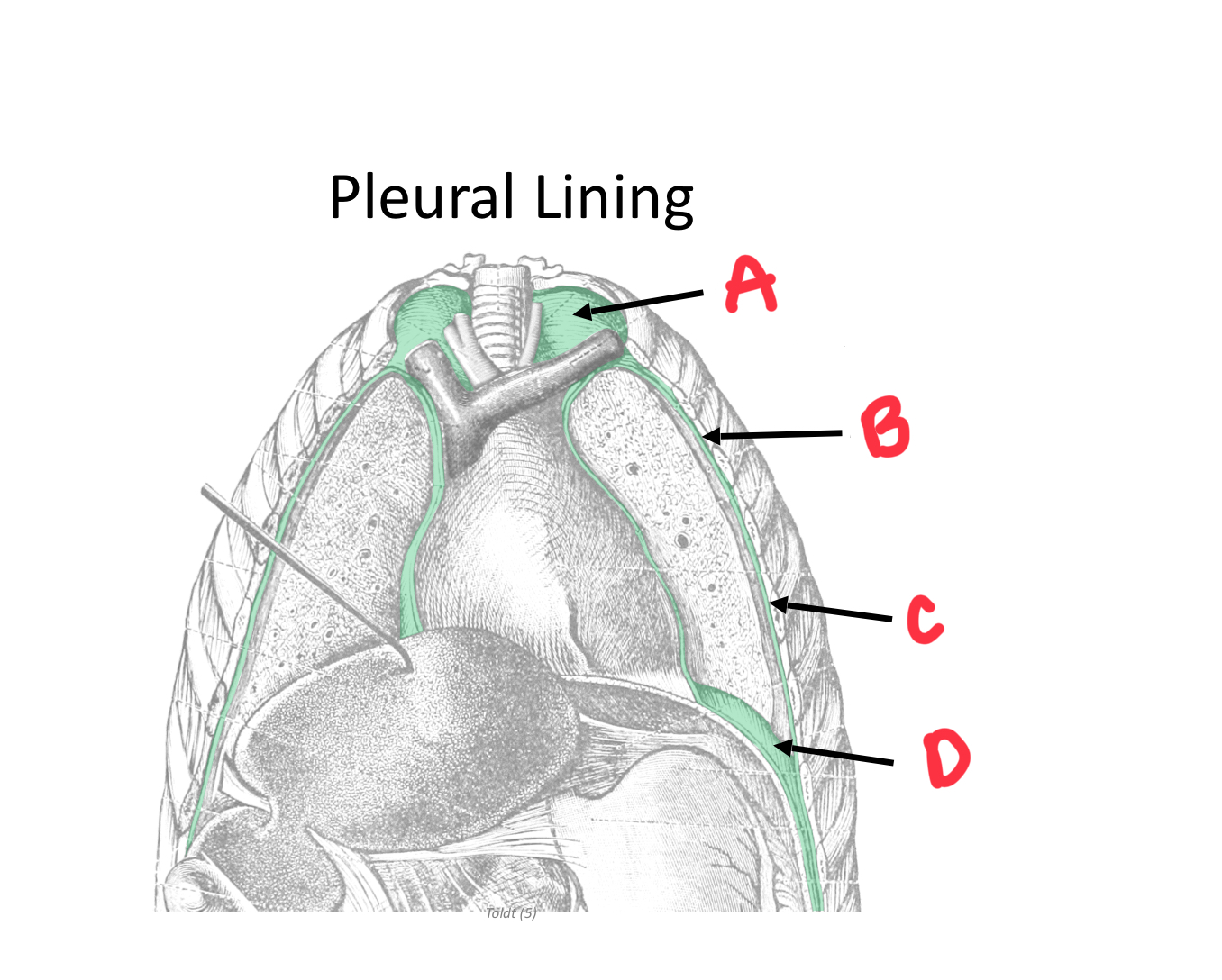
Identify B
Mediastinal pleura
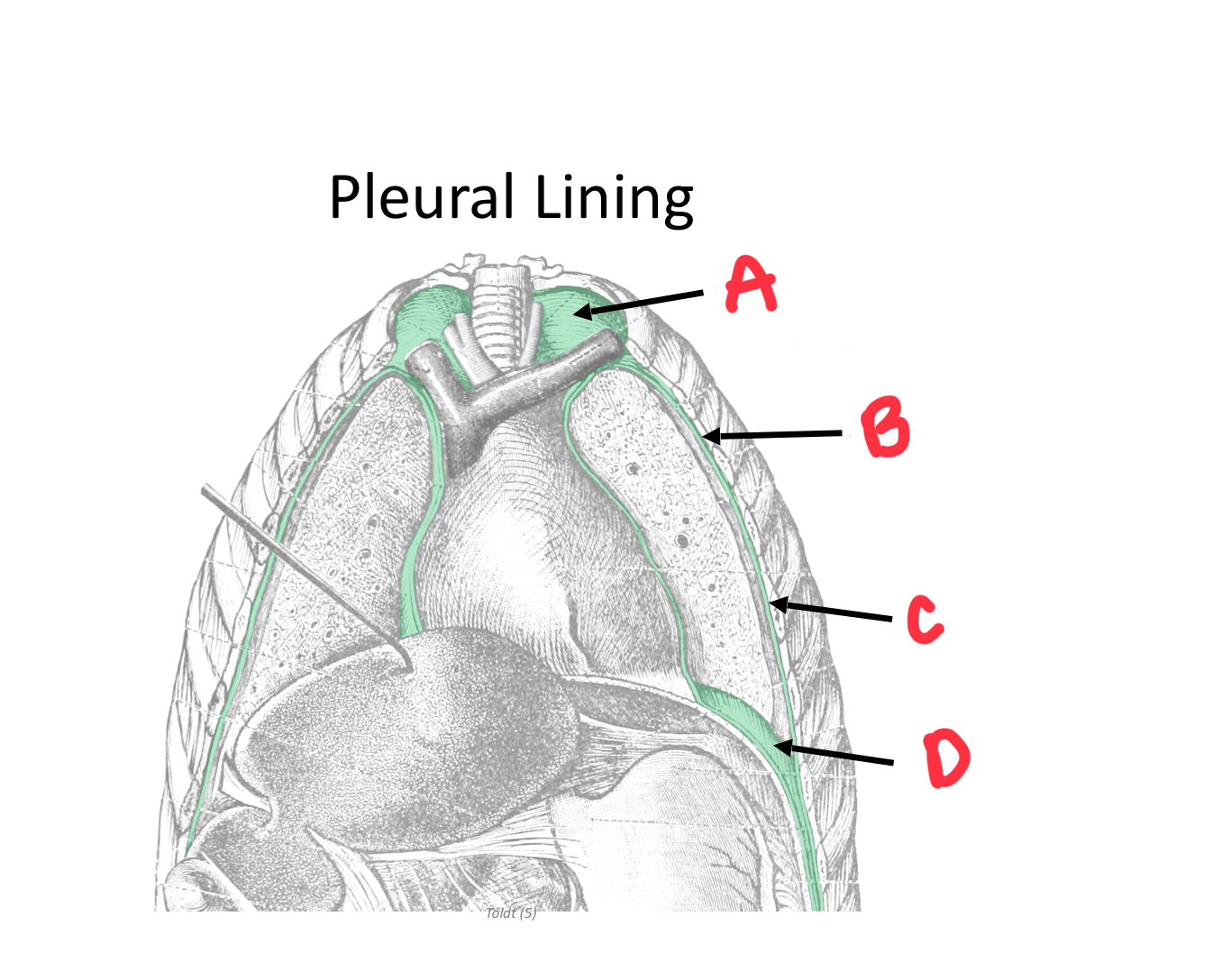
Identify C
Costal pleura
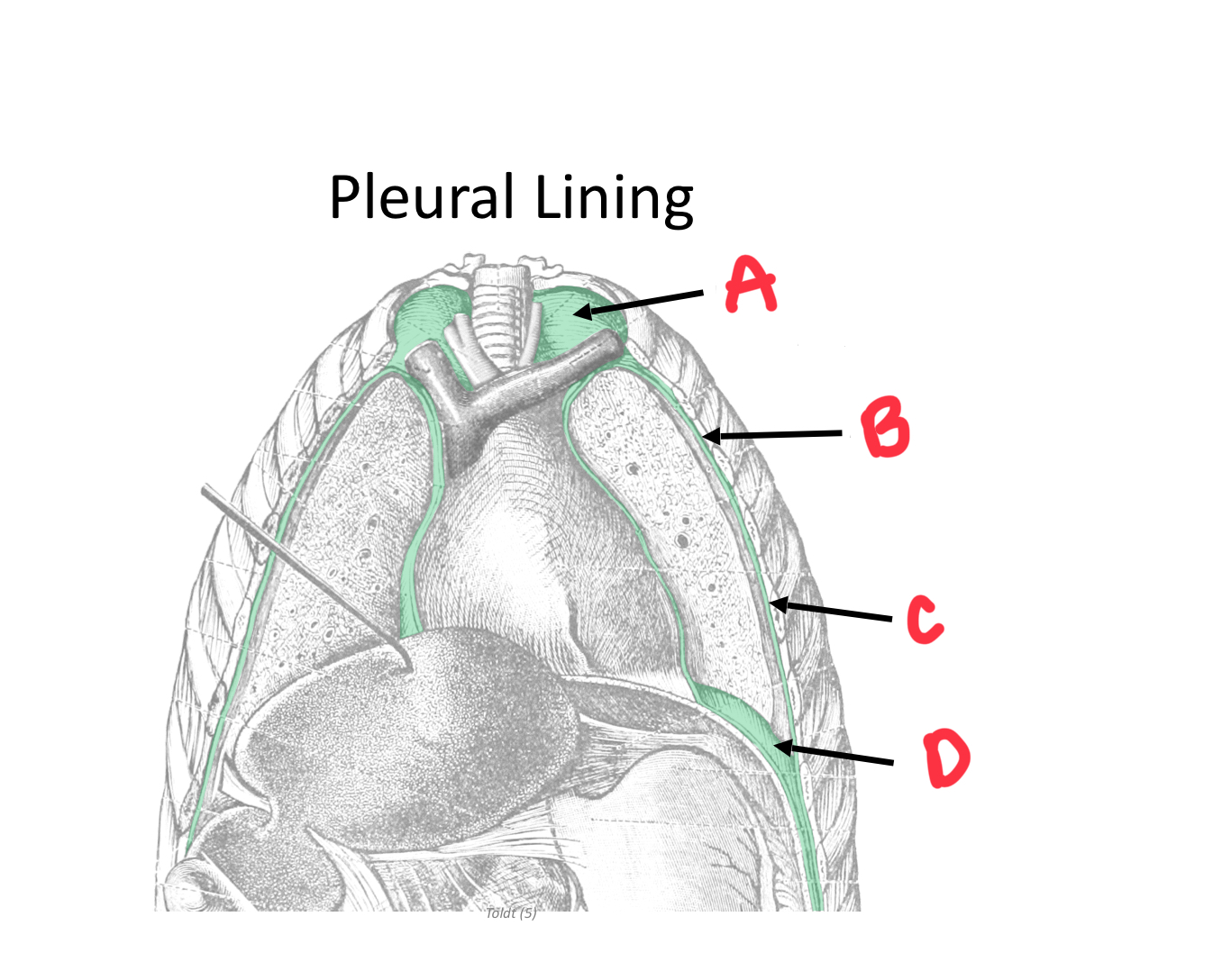
Identify D
Diaphragmatic pleura
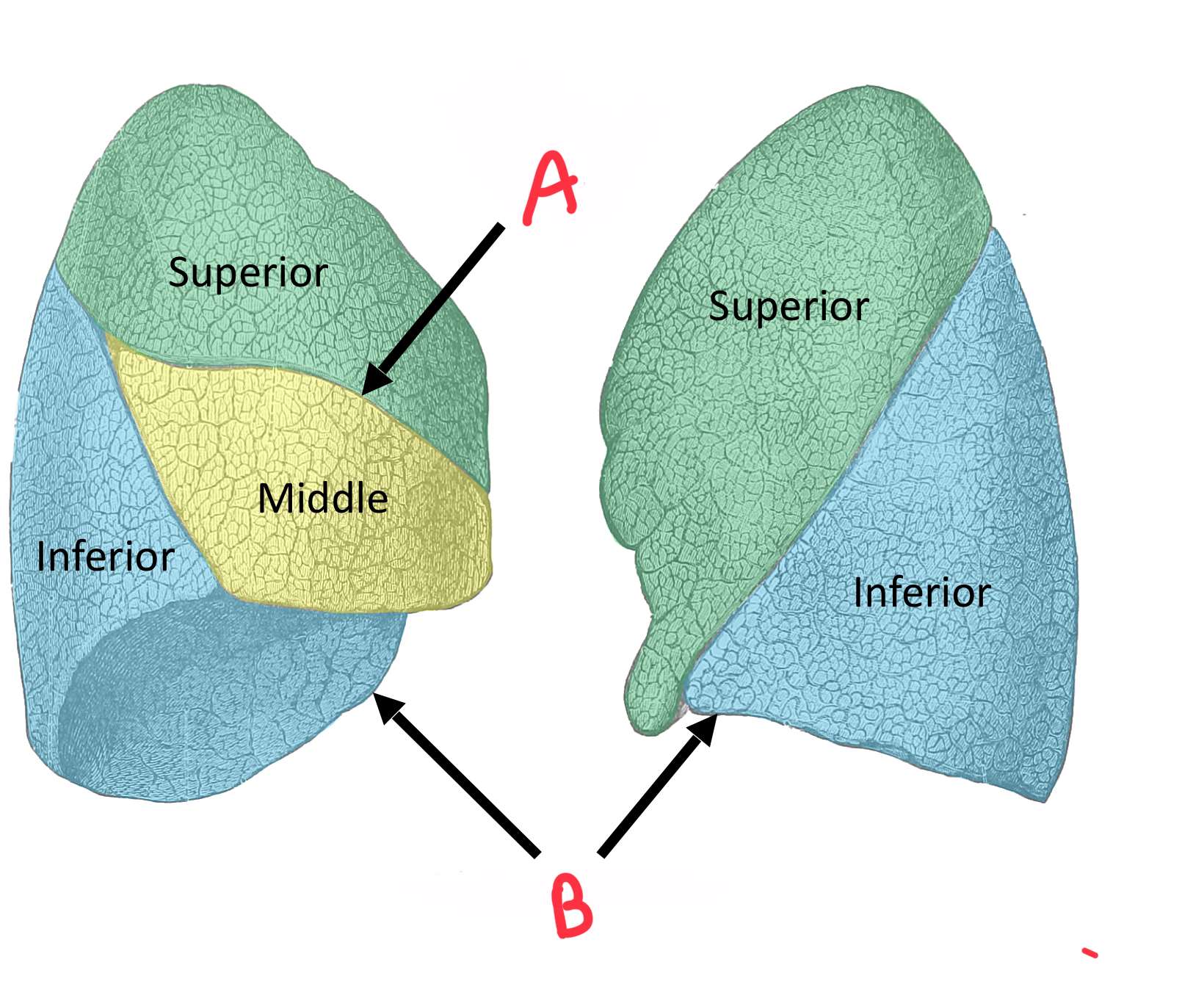
Identify A
Transverse fissure
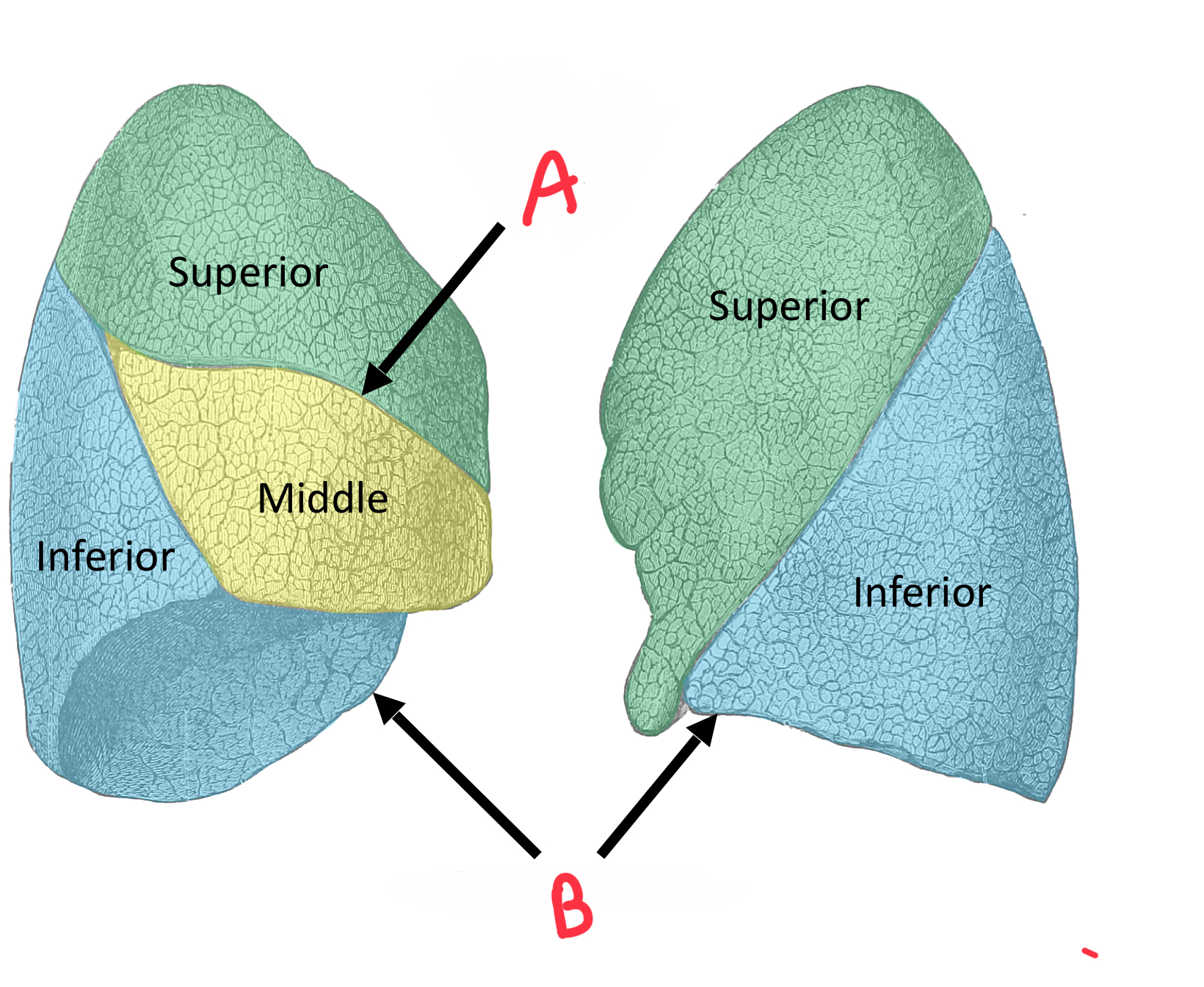
Identify B
Oblique fissure
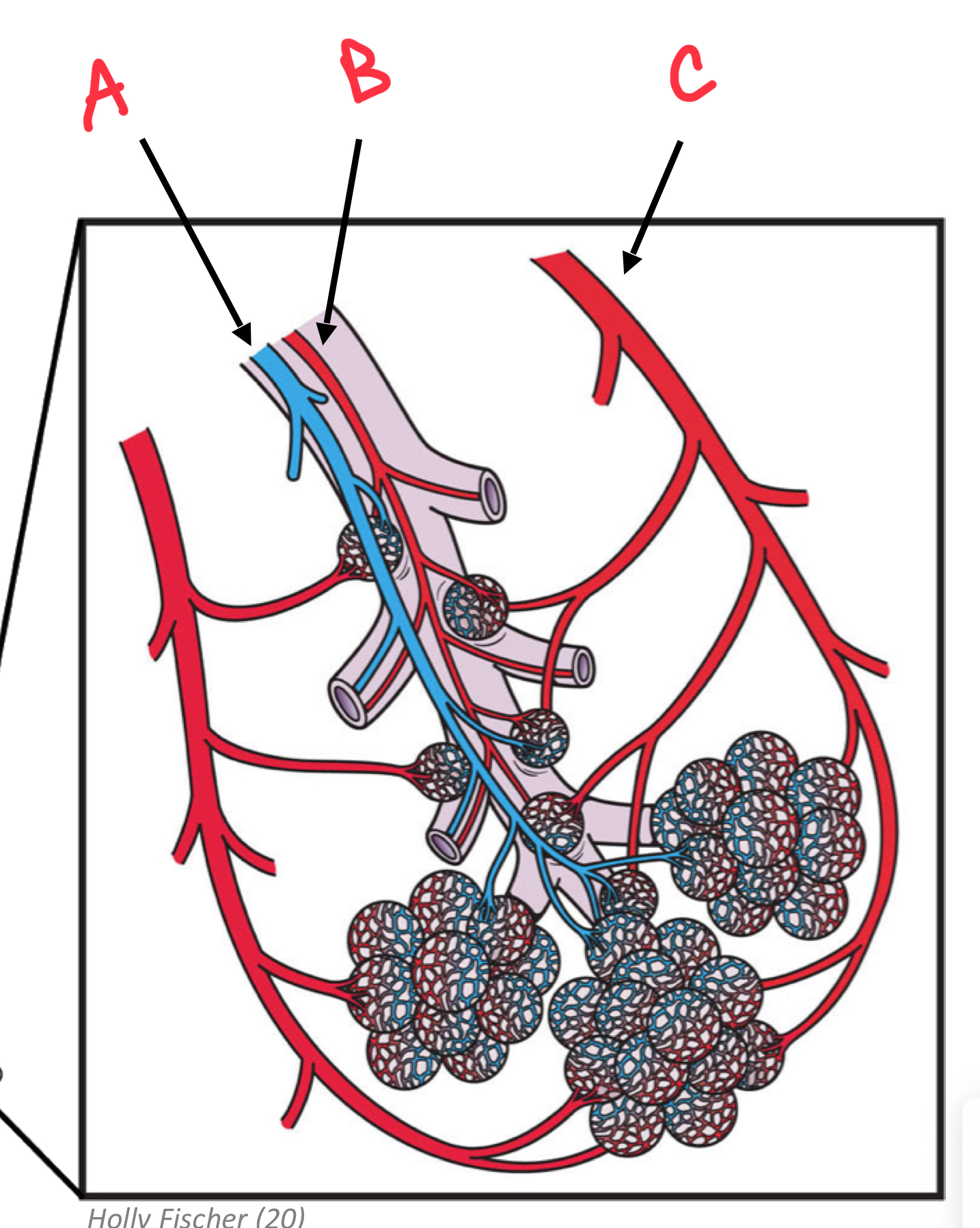
Identify A
Pulmonary Arteriole
Identify B
Bronchial arteriole
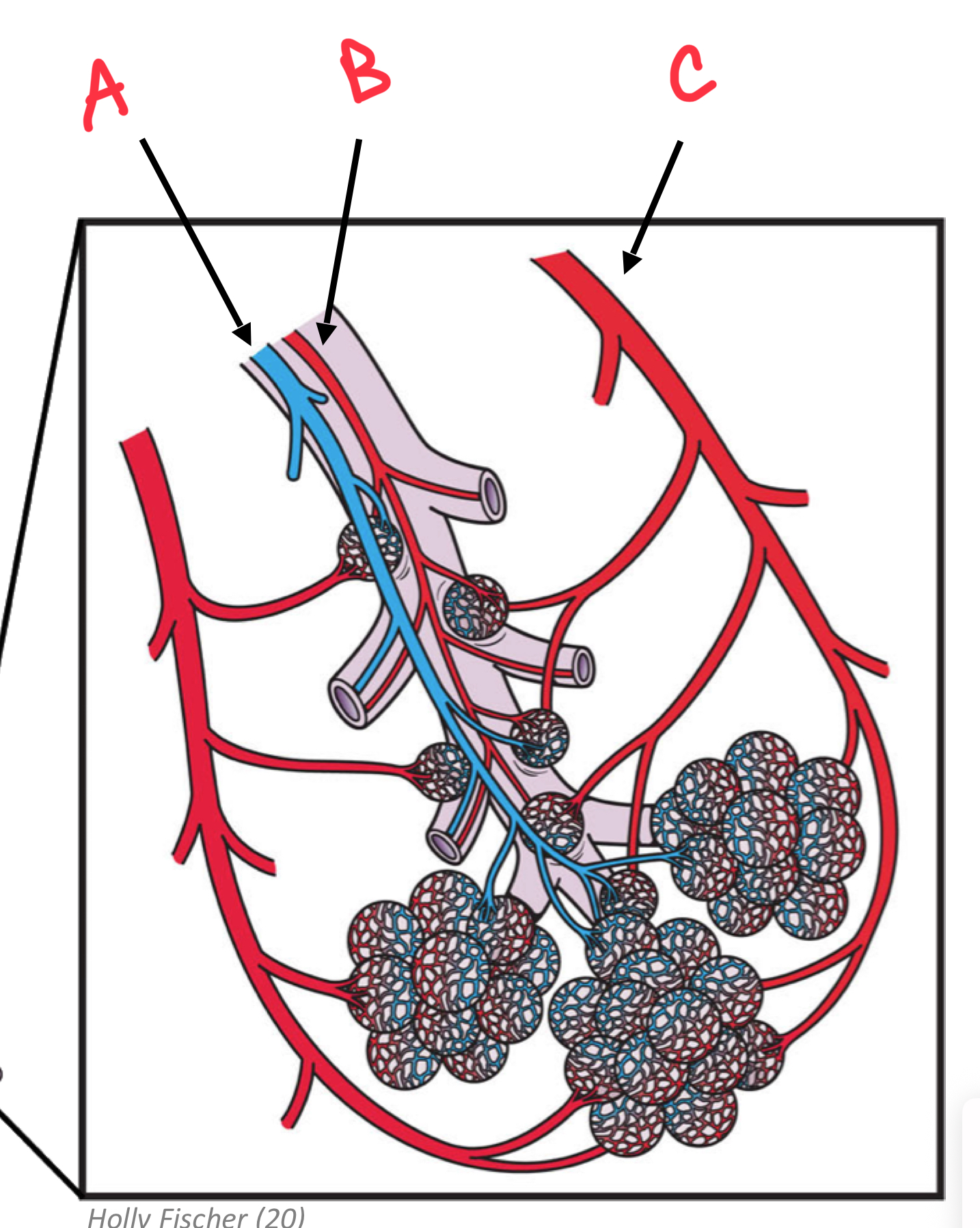
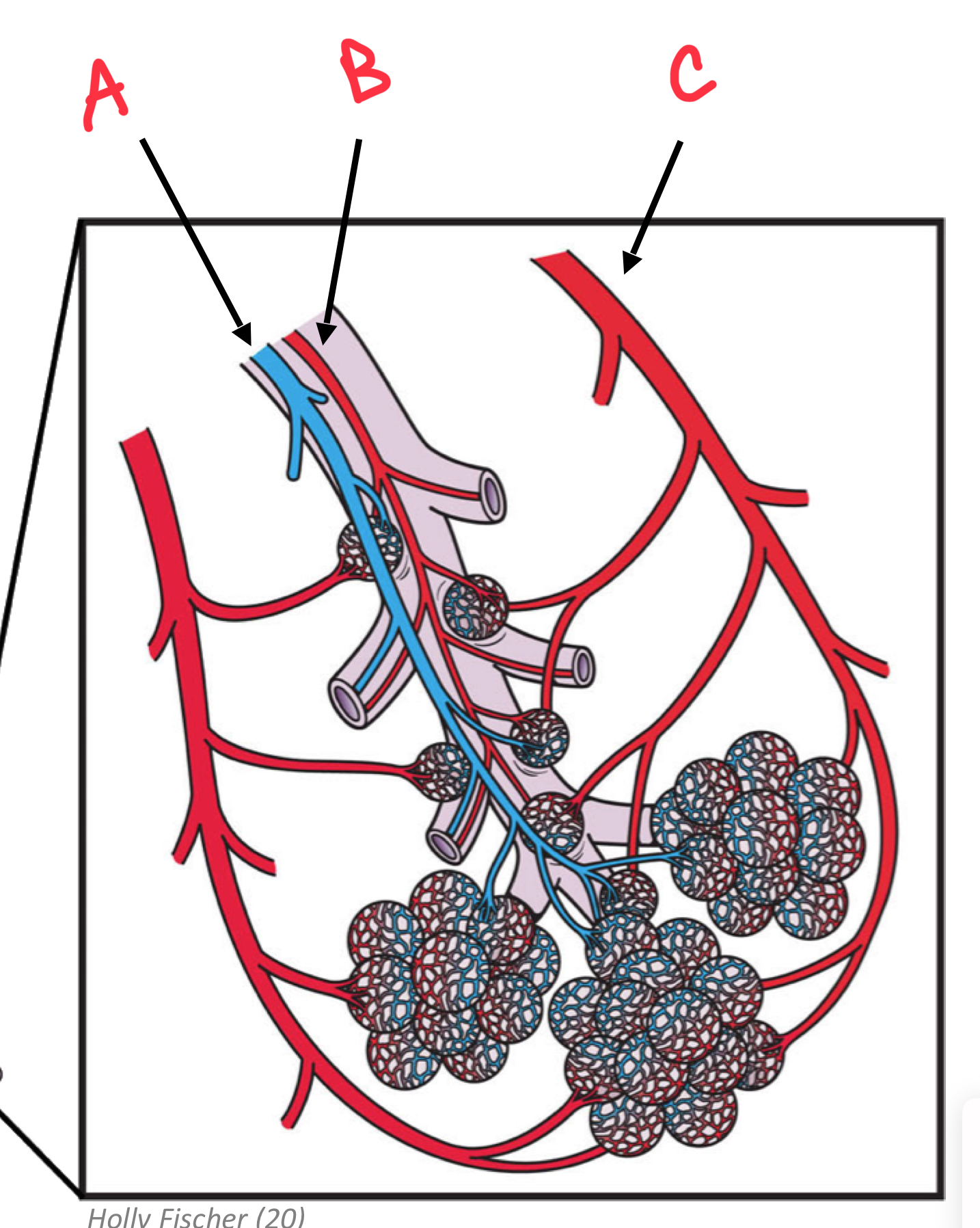
Identify C
Pulmonary Venule