Health Management Information System, HIS Lec! L6 Midterms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Health management information system
______ _______ _______ _____
As defined by the World Health Organization (2004), a Health Management Information System (HMIS) is an information system specially designed to assist in the management and planning of health programs, as opposed to delivery of care
HMIS is one of the six building blocks essential for health system strengthening. It is a data collection system specifically designed to support planning, management, and decision-making in health facilities and organizations
World health organization (2004)
Health Management Information System
As defined by the _____ ______ ______ ____, a Health Management Information System (HMIS) is an information system specially designed to assist in the management and planning of health programs, as opposed to delivery of care
HMIS is one of the six building blocks essential for health system strengthening. It is a data collection system specifically designed to support planning, management, and decision-making in health facilities and organizations
management
Health Management Information System
As defined by the World Health Organization (2004), a Health Management Information System (HMIS) is an information system specially designed to assist in the ______ and planning of health programs, as opposed to delivery of care
HMIS is one of the six building blocks essential for health system strengthening. It is a data collection system specifically designed to support planning, management, and decision-making in health facilities and organizations
Health
Information System Venn Diagram
H- ______
Clinical studies assist in the understanding of medical terminology, clinical procedures, and database processes
S- Information System
The ability to analyze systems and to design and implement advanced computer applications make the transfer of patient information efficient and effective
M- Management
Management principles enhanced by finance, law, and planning help administer the health care enterprise
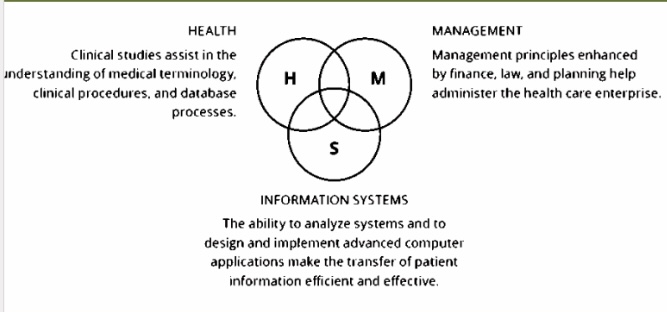
Management
Information System Venn Diagram
H- Health
Clinical studies assist in the understanding of medical terminology, clinical procedures, and database processes
S- Information System
The ability to analyze systems and to design and implement advanced computer applications make the transfer of patient information efficient and effective
M- ________
Management principles enhanced by finance, law, and planning help administer the health care enterprise
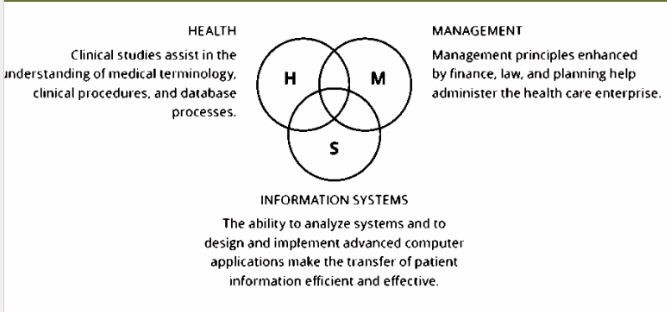
Ministry of Health (2010)
According to the _____ ___ ______ ____, HMIS was developed within the framework of the following concepts:
The information collected is relevant to the policies and goals of the healthcare institution, and to the responsibilities of the health professionals at the level of collection
The information collected is functional; It is to be used immediately for management and should not wait for feedback from higher levels
Information collected is integrated; there is one set of forms and no duplication of reporting
The information is collected on a routine basis from every health unit
Relevant
According to the Ministry of Health (2010), HMIS was developed within the framework of the following concepts:
The information collected is ______ to the policies and goals of the healthcare institution, and to the responsibilities of the health professionals at the level of collection
The information collected is functional; It is to be used immediately for management and should not wait for feedback from higher levels
Information collected is integrated; there is one set of forms and no duplication of reporting
The information is collected on a routine basis from every health unit
Functional
According to the Ministry of Health (2010), HMIS was developed within the framework of the following concepts:
The information collected is relevant to the policies and goals of the healthcare institution, and to the responsibilities of the health professionals at the level of collection
The information collected is ________; It is to be used immediately for management and should not wait for feedback from higher levels
Information collected is integrated; there is one set of forms and no duplication of reporting
The information is collected on a routine basis from every health unit
Integrated
According to the Ministry of Health (2010), HMIS was developed within the framework of the following concepts:
The information collected is relevant to the policies and goals of the healthcare institution, and to the responsibilities of the health professionals at the level of collection
The information collected is functional; It is to be used immediately for management and should not wait for feedback from higher levels
Information collected is _______; there is one set of forms and no duplication of reporting
The information is collected on a routine basis from every health unit
Collected
According to the Ministry of Health (2010), HMIS was developed within the framework of the following concepts:
The information collected is relevant to the policies and goals of the healthcare institution, and to the responsibilities of the health professionals at the level of collection
The information collected is functional; It is to be used immediately for management and should not wait for feedback from higher levels
Information collected is integrated; there is one set of forms and no duplication of reporting
The information is ______ on a routine basis from every health unit
Complete
The major role of HMIS is to provide quality information to support decision making at all levels of the health care system in any medical institution
A Health Management Information System needs to be:
_____
Consistent
Clear
Simple
Cost-effective
Accessible
Confidential
Consistent
The major role of HMIS is to provide quality information to support decision making at all levels of the health care system in any medical institution
A Health Management Information System needs to be:
Complete
______
Clear
Simple
Cost-effective
Accessible
Confidential
Clear
The major role of HMIS is to provide quality information to support decision making at all levels of the health care system in any medical institution
A Health Management Information System needs to be:
Complete
Consistent
_____
Simple
Cost-effective
Accessible
Confidential
Accessible
The major role of HMIS is to provide quality information to support decision making at all levels of the health care system in any medical institution
A Health Management Information System needs to be:
Complete
Consistent
Clear
Simple
Cost-effective
______
Confidential
Confidential
The major role of HMIS is to provide quality information to support decision making at all levels of the health care system in any medical institution
A Health Management Information System needs to be:
Complete
Consistent
Clear
Simple
Cost-effective
Accessible
______
acquisition, verification
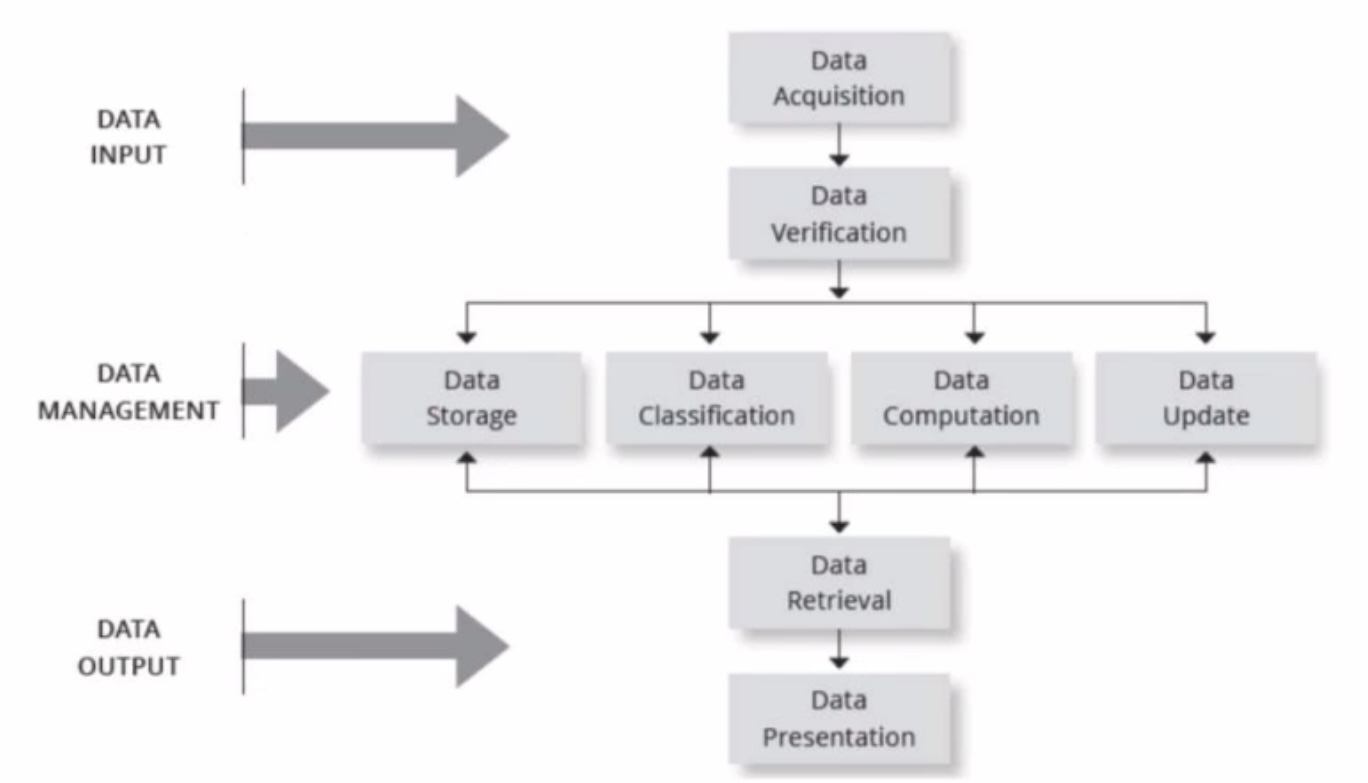
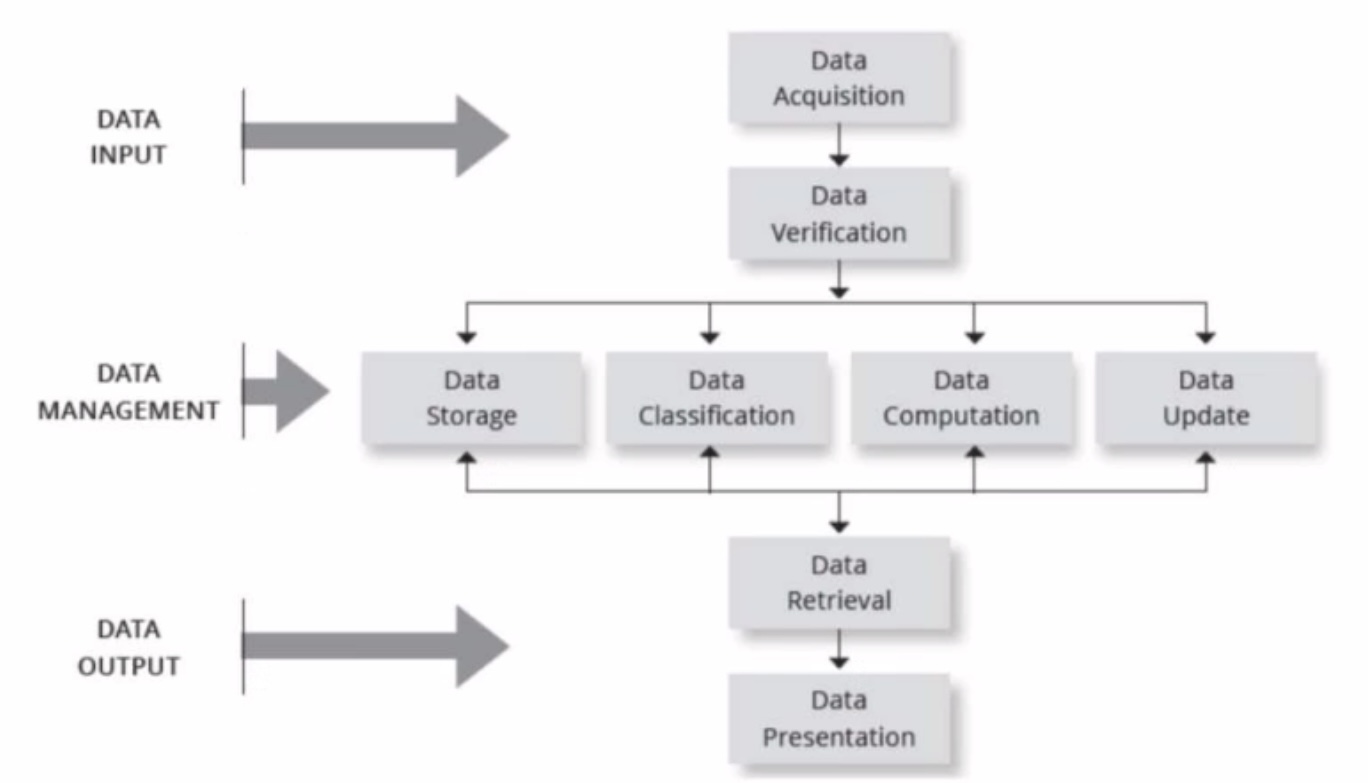
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data ______, Data _______
Data Management —> Data Storage, Data Classification, Data Computation (computations of tests or fees), Data update
Data Output —> Data Retrieval, Data Presentation (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
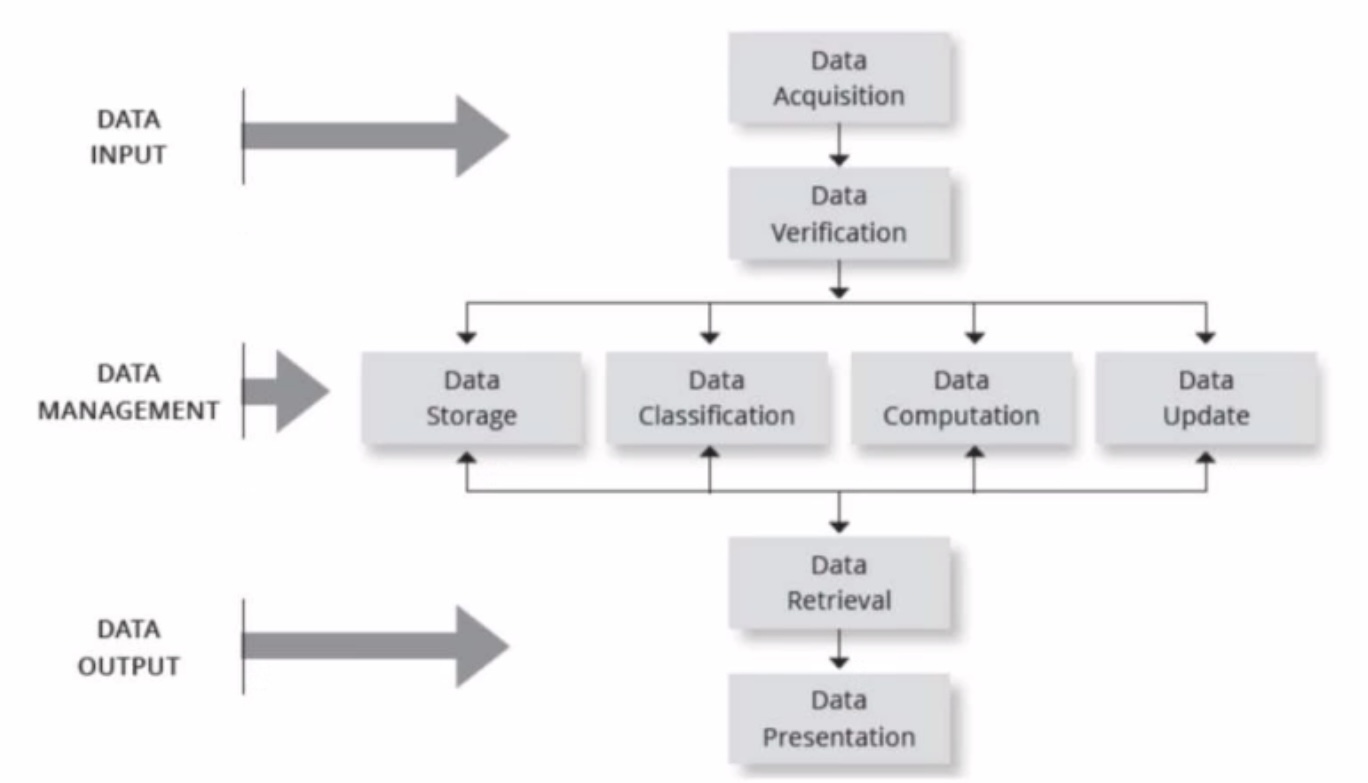
Storage
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data Acquisition, Data Verification
Data Management —> Data ______, Data Classification, Data Computation (computations of tests or fees), Data update
Data Output —> Data Retrieval, Data Presentation (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
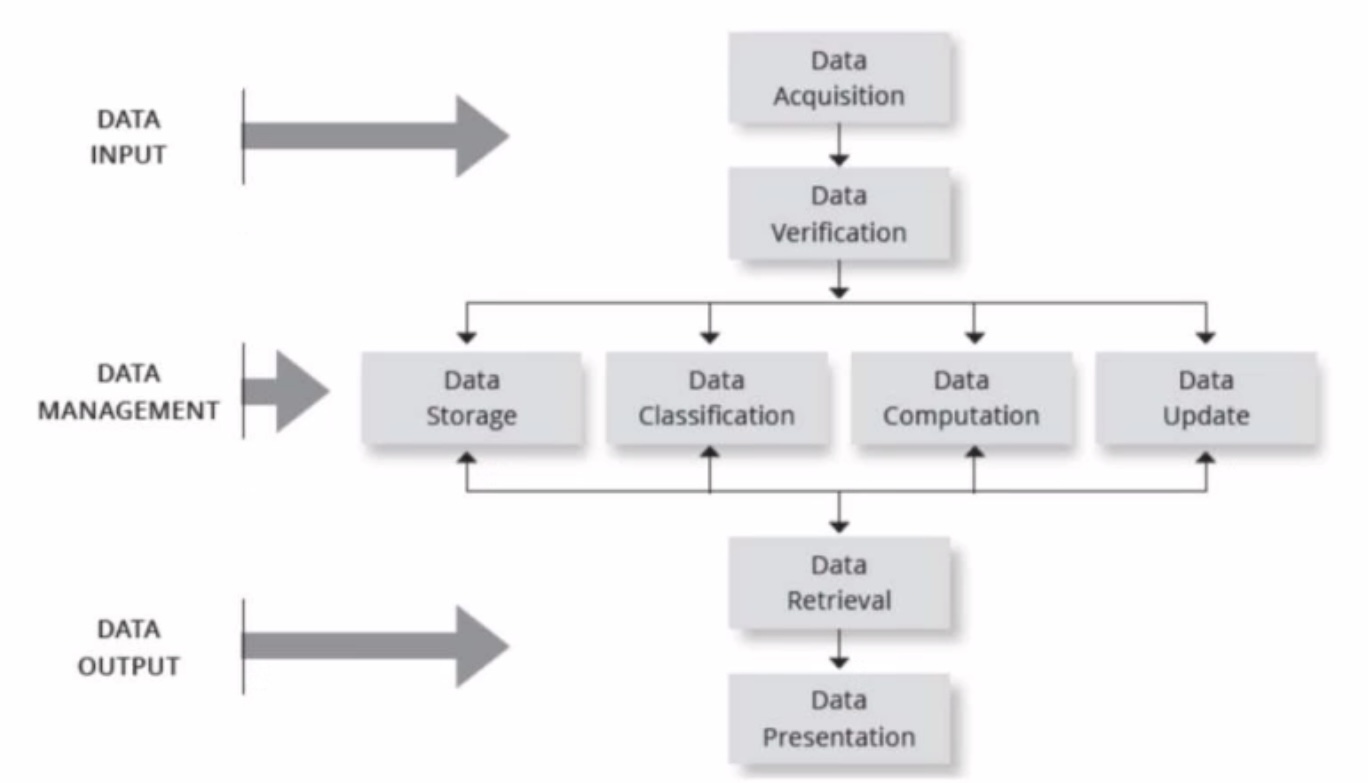
Classification
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data Acquisition, Data Verification
Data Management —> Data Storage, Data ______, Data Computation (computations of tests or fees), Data update
Data Output —> Data Retrieval, Data Presentation (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
Computation
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data Acquisition, Data Verification
Data Management —> Data Storage, Data Classification, Data ______ (computations of tests or fees), Data update
Data Output —> Data Retrieval, Data Presentation (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
Update
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data Acquisition, Data Verification
Data Management —> Data Storage, Data Classification, Data Computation (computations of tests or fees), Data ______
Data Output —> Data Retrieval, Data Presentation (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
Retrieval, presentation
Basic Functions of the HMIS
Data Input —> Data Acquisition, Data Verification
Data Management —> Data Storage, Data Classification, Data Computation (computations of tests or fees), Data update
Data Output —> Data ______, Data _______ (or printed copy of data or presented to dr.)
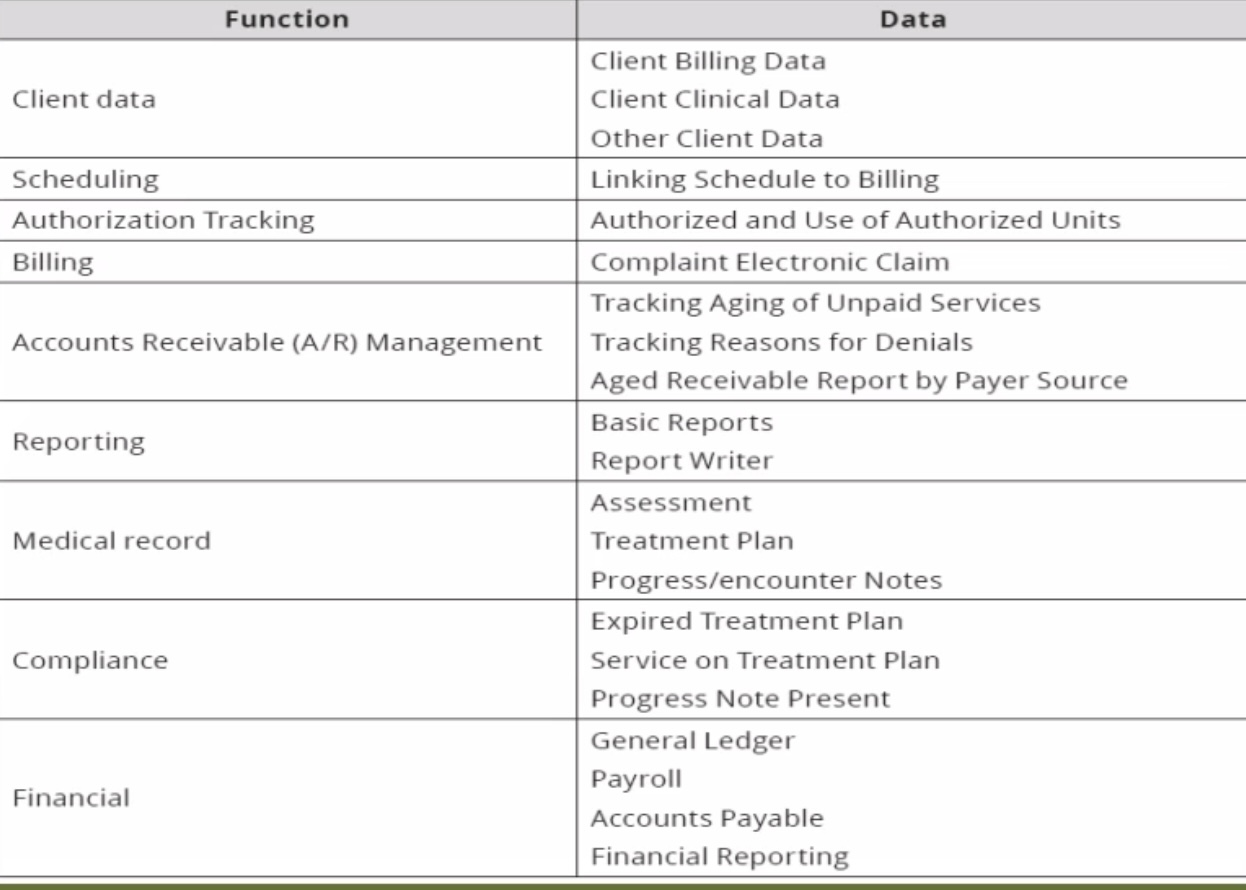
Client Data
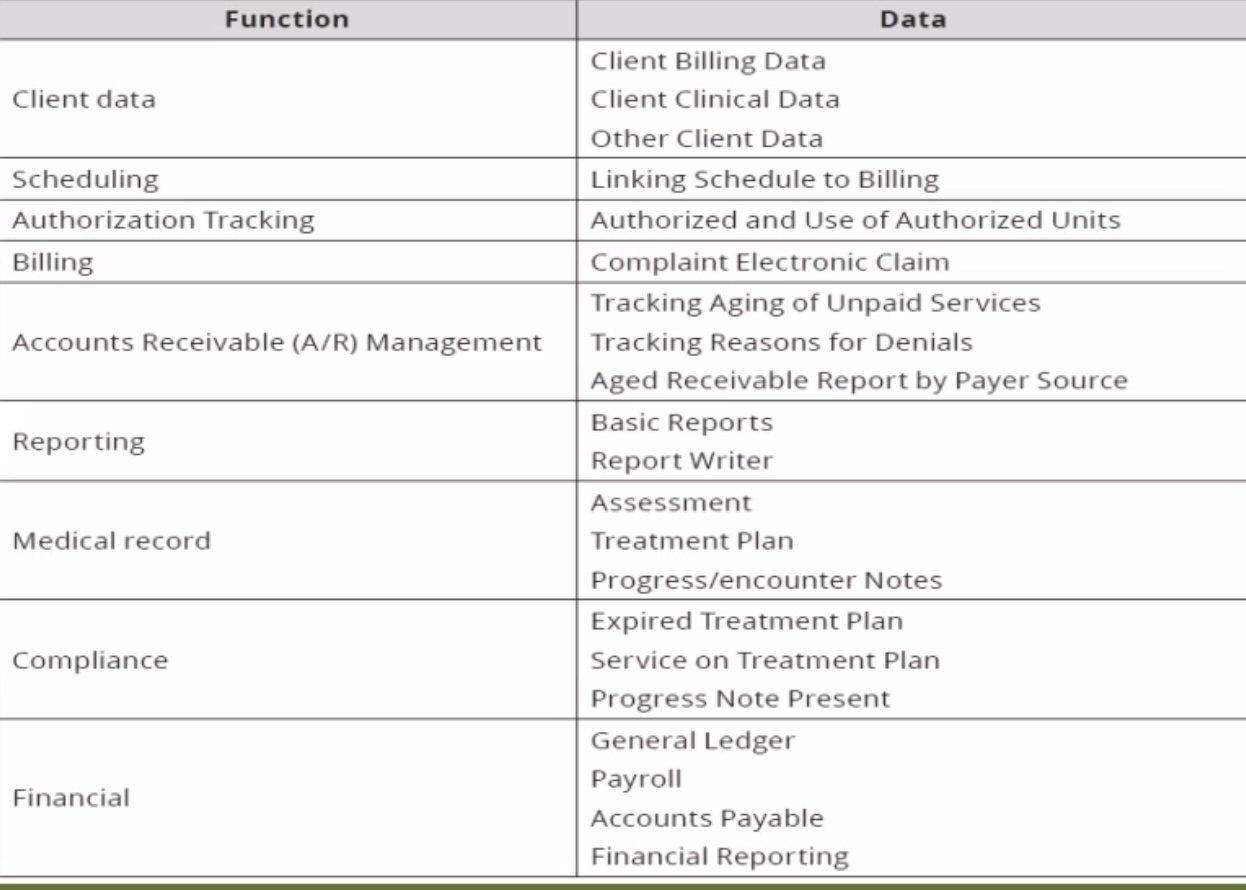
Functions in the HMIS
______ _____
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
Financial
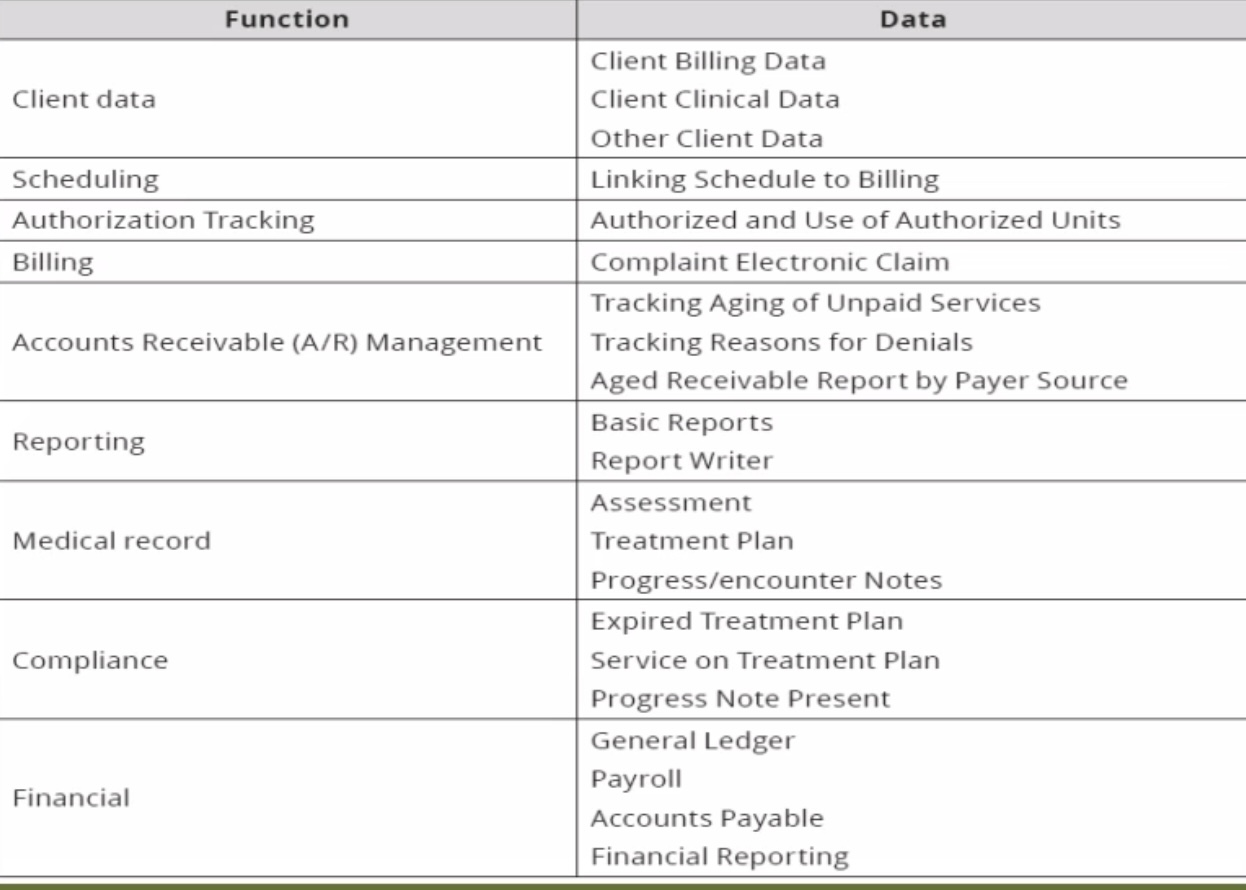
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
________:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
Compliance
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
_________:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
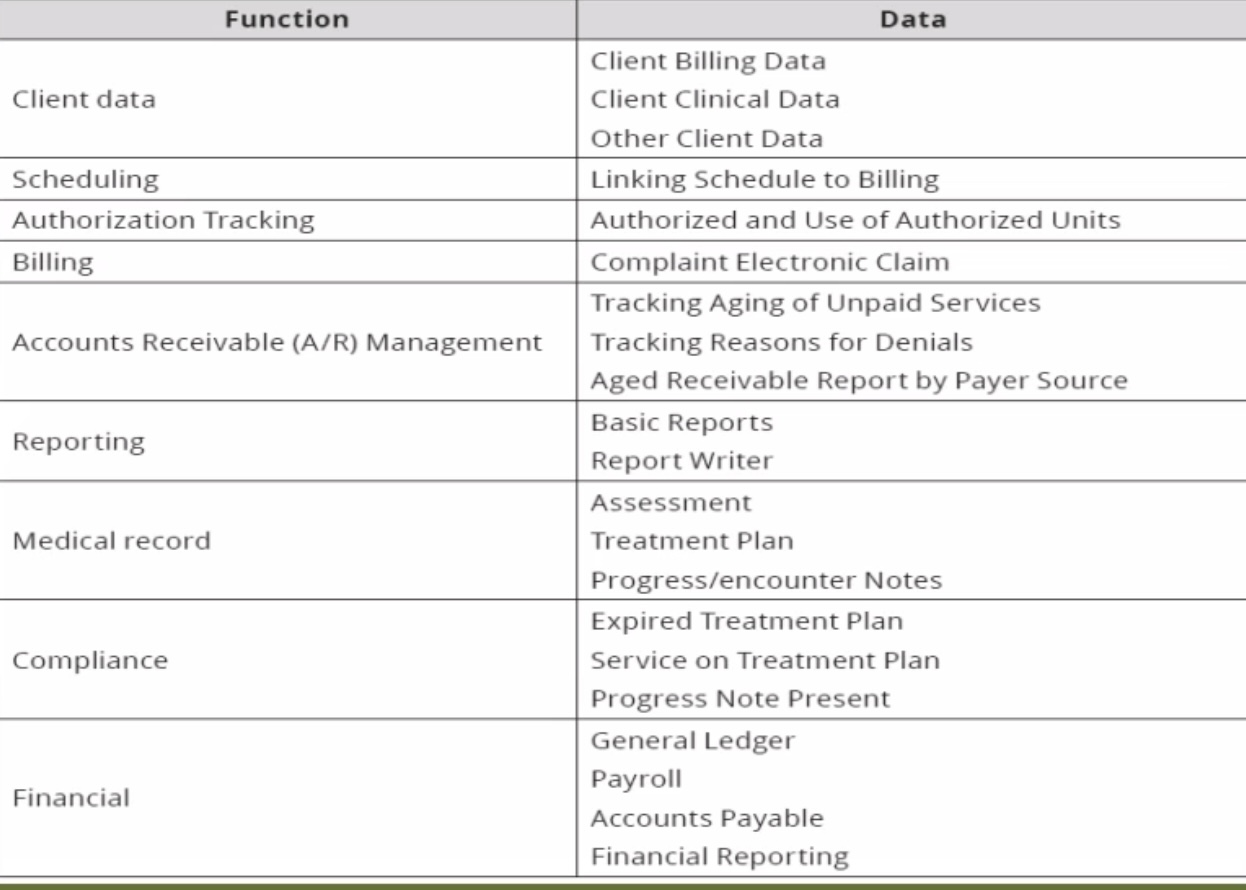
Medical Record
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
______ _______
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
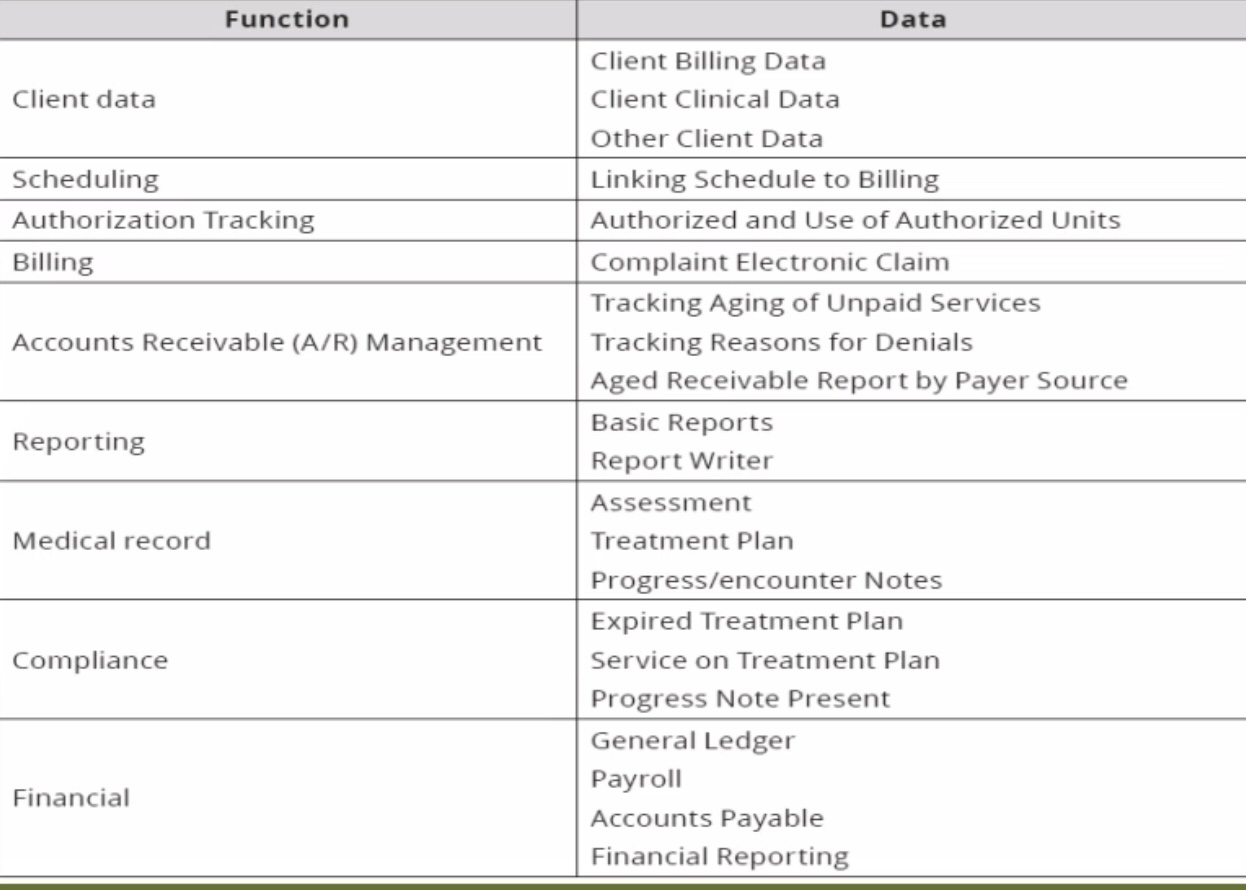
Account receivable (A/R) management
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
______ _______ ______
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
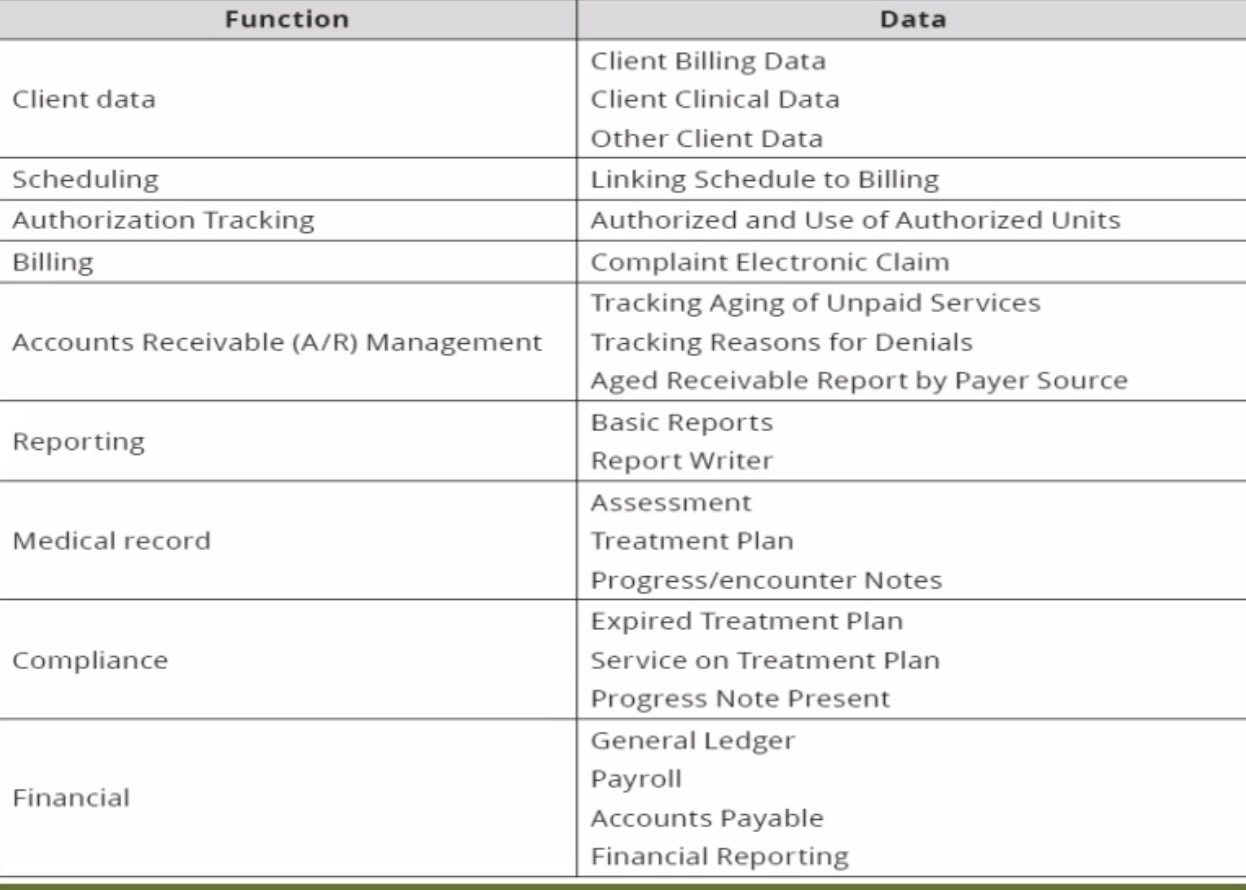
Authorization tracking
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
________ ______:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
Billing
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
_____:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
Reporting:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
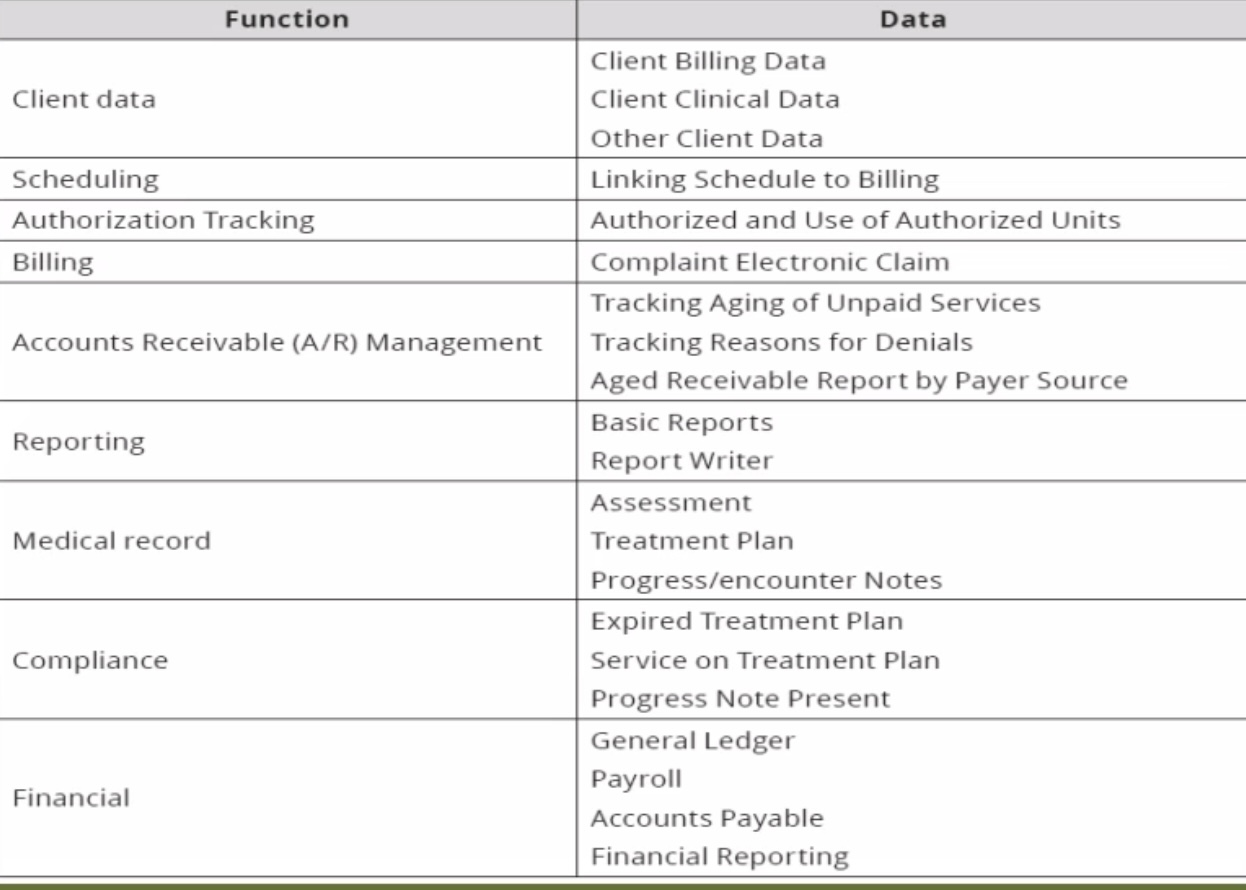
Reporting
Functions in the HMIS
Client Data:
Client Billing Data
Client Clinical Data
Other Client Data
Scheduling:
Linking schedule to billing
Authorization Tracking:
Authorized and use of authorized units
Billing:
Complaint electronic claim
Account Receivable (A/R) Management:
Tracking aging of unpaid services
Tracking reasons for denials
Aged receivable report by payer source (if a patient has been in the hospital for a long time)
_______:
Basic reports
Report writer
Medical Record:
Assessment
Treatment plan
Progress/encounter notes
Compliance:
Expired treatment plan
Service on treatment plan
Progress note present (progress from expired)
Financial:
General ledger
Payrol
Accounts payable
Financial reporting
Behavioral
Determinants of HMIS
______ - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
Organizational
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
_______ - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
Technical
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
_______ - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
scalability
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have _______
Leadership
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
______ and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
Financial resources
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
Patient/Admin engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
______ ______ - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
Patient/admin
Determinants of HMIS
Behavioral - People (Patients, Doctors, Nurses)
______/______ engagement (px portal)
Communication
Organizational - Internal factors related to the hospital structures
Structure/Culture of hospital
Leadership and management support (needs to have strong commitment)
Financial Resources - HIS/HMIS needs to be maintained
Technical - Internal factor of software
IT infrastructure - security measures should be robust (health insurance, portability, accountability)
Software
Hardware
System design and usability
HMIS should have the ability to integrate other systems and should have scalability
Performance of Routine Information System Management
PRISM Framework (tignan mo nalang yung pic)
Known as _____ ___ _____ ______ _____ (PRISM), this conceptual framework broadens the analysis of routine health information systems to include the three key factors which were discussed previously (puta same shit lang naman pala)
Behavioral determinants - Knowledge, skills, attitudes, values, and motivation of the people who collect and use data.
Technical determinants - data collection processes, systems, forms, and methods
Organizational/Environmental determinants - information culture, structure, resources, roles, and responsibilities of the health system and key contributors at each level
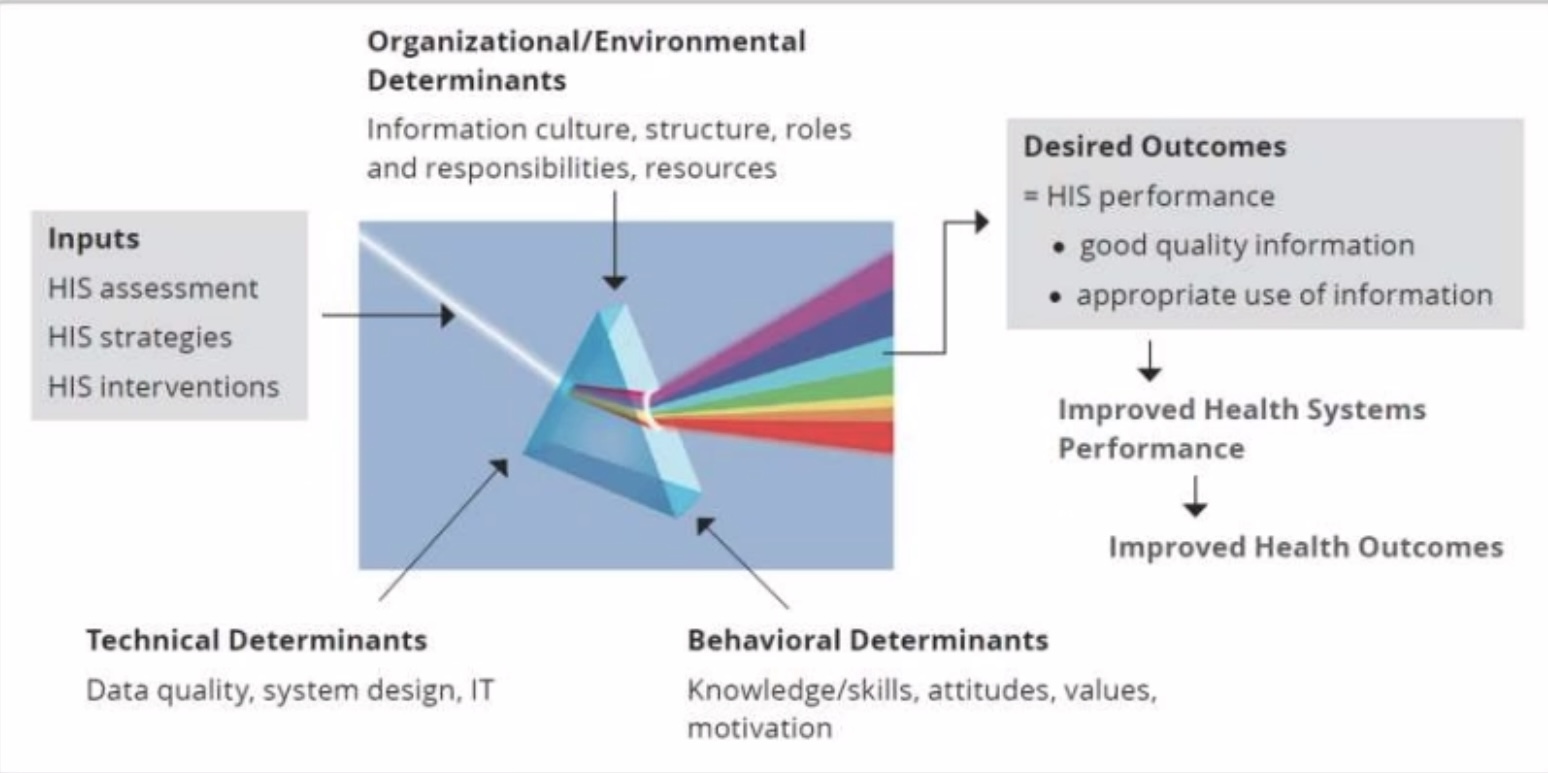
Behavioral determinants
PRISM Framework (tignan mo nalang yung pic)
Known as Performance of Routine Information System Management (PRISM), this conceptual framework broadens the analysis of routine health information systems to include the three key factors which were discussed previously (puta same shit lang naman pala)
_____ ______- Knowledge, skills, attitudes, values, and motivation of the people who collect and use data.
Technical determinants - data collection processes, systems, forms, and methods
Organizational/Environmental determinants - information culture, structure, resources, roles, and responsibilities of the health system and key contributors at each level
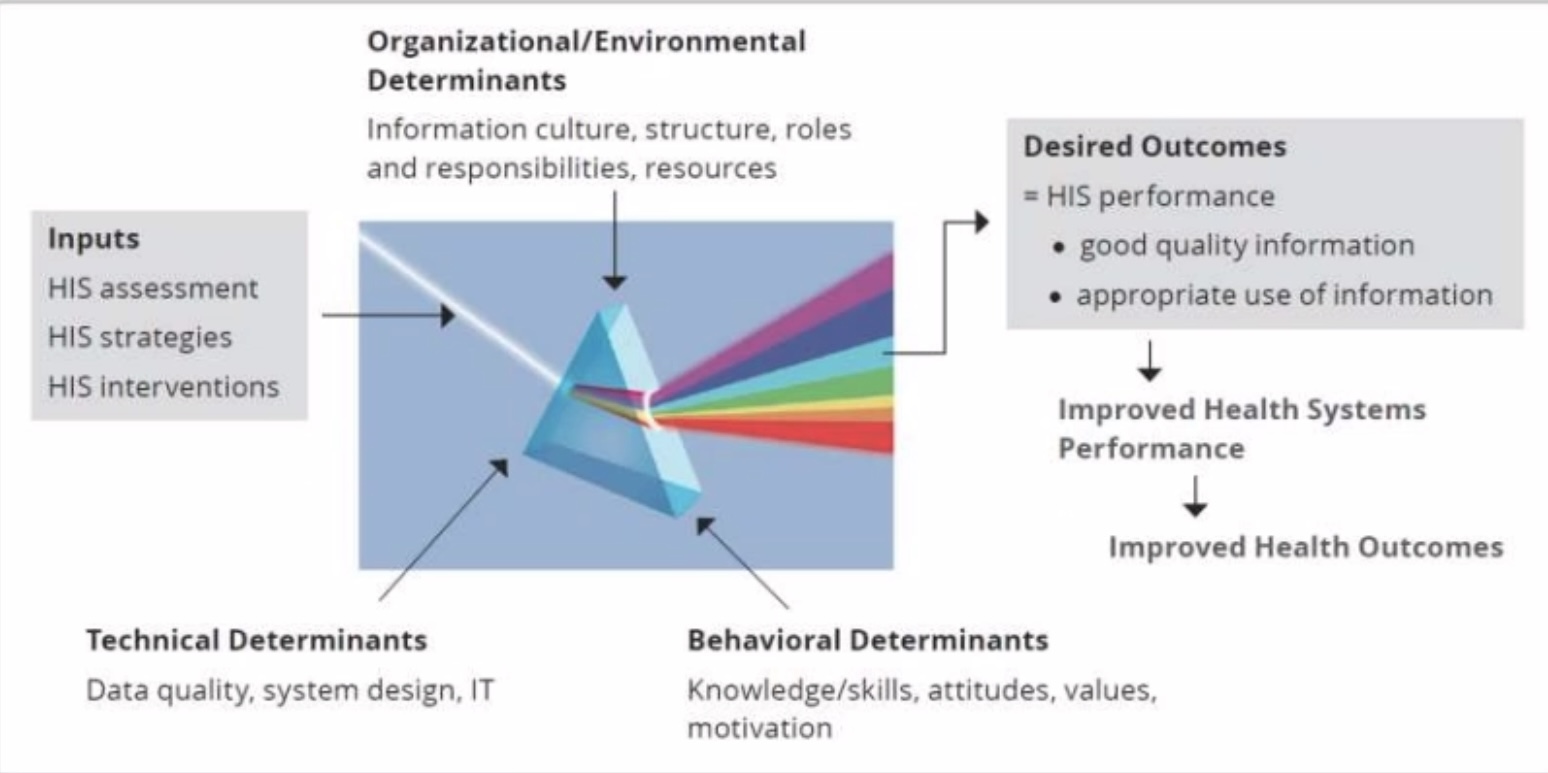
Technical Determinants
PRISM Framework (tignan mo nalang yung pic)
Known as Performance of Routine Information System Management (PRISM), this conceptual framework broadens the analysis of routine health information systems to include the three key factors which were discussed previously (puta same shit lang naman pala)
Behavioral determinants - Knowledge, skills, attitudes, values, and motivation of the people who collect and use data.
______ ______- data collection processes, systems, forms, and methods
Organizational/Environmental determinants - information culture, structure, resources, roles, and responsibilities of the health system and key contributors at each level
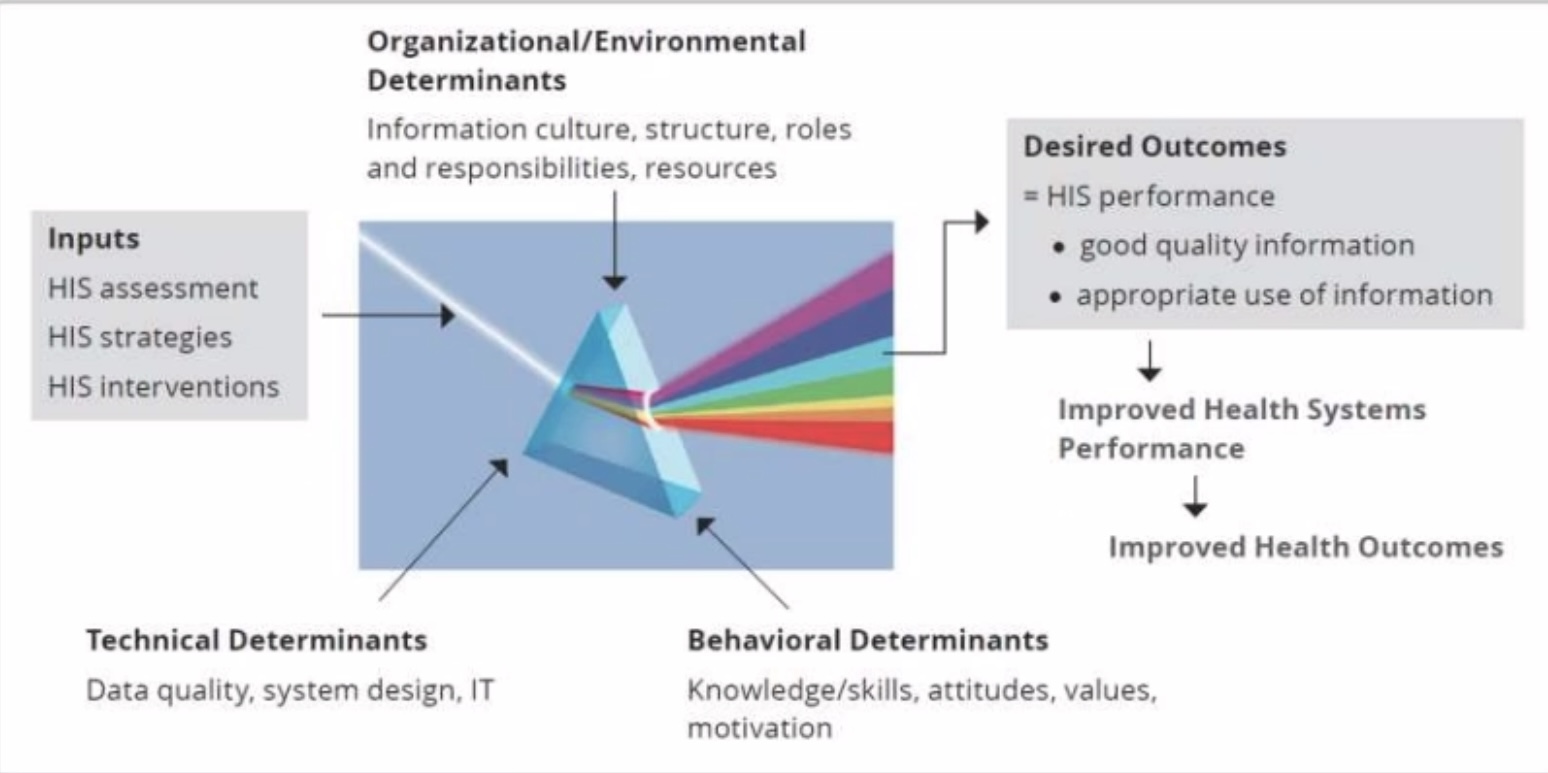
Organizational/Environmental determinants
PRISM Framework (tignan mo nalang yung pic)
Known as Performance of Routine Information System Management (PRISM), this conceptual framework broadens the analysis of routine health information systems to include the three key factors which were discussed previously (puta same shit lang naman pala)
Behavioral determinants - Knowledge, skills, attitudes, values, and motivation of the people who collect and use data.
Technical determinants - data collection processes, systems, forms, and methods
_______/______ ______- information culture, structure, resources, roles, and responsibilities of the health system and key contributors at each level
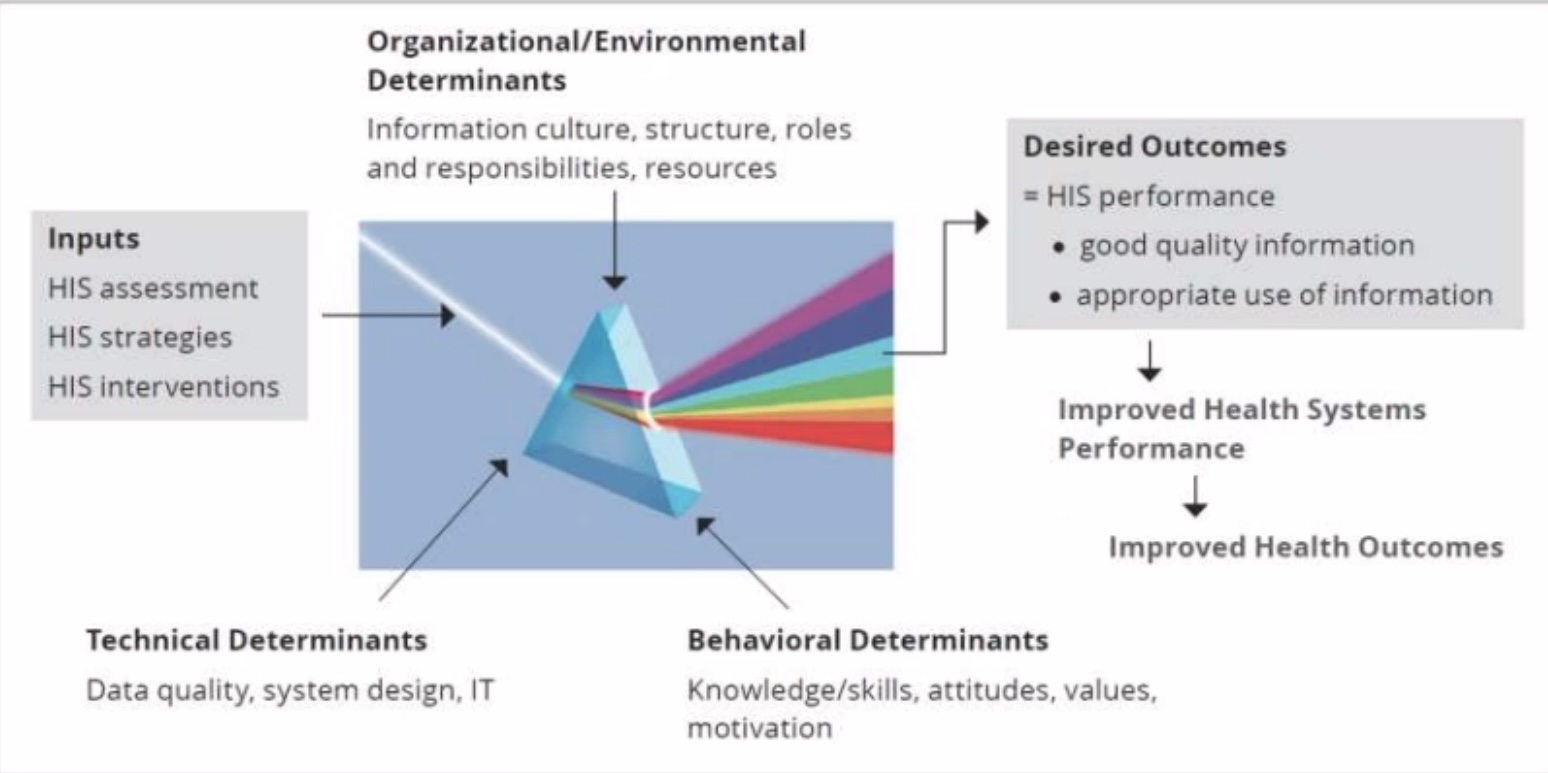
RHIS Determinants
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
____ ________ - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Technical factors
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
______ ______ (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Organizational factors
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
______ _____ -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Computer software
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
______ ______.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Planning
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
______.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Behavioral factors
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
_______ ________-
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
RHIS Processes
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
______ ______-
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Feedback
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
_______
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Improved RHIS performance
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
_______ _____ _______ -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Improved health systems performance
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
______ ______ ______ _____
Improved Health Status
Improved health status
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
______ ______ ______
Collection
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data ______.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Quality check
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data ______ _______.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Knowledge
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of _______ of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Problem solving
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
_____ _____ for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Competence
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
________ in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
Motivation
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
Finances.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
_______.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status
FInances
Technical and Organizational Factors of the PRISM
RHIS Determinants - Routine Hospital Information System - structured or continuous activity from the hospital
Technical Factors (Processes from earlier) -
Complexity of the reporting form
Procedures.
HIS design.
Computer software.
IT complexity
Organizational Factors -
Critical Management functions and information needs.
Governance.
Planning.
Availability of resources.
Training. Supervision.
________.
Information distribution.
Promotion of culture of information
Behavioral Factors -
Level of knowledge of content of HIS forms.
Data quality checking skills.
Problem solving for HIS tasks.
Competence in HIS tasks.
Confidence levels for HIS tasks.
Motivation.
RHIS Processes -
Data collection.
Data quality check.
Data transmission.
Data processing.
Data analysis.
Data displays.
Feedback
Improved RHIS Performances -
Data quality information use
Improved Health Systems Performance
Improved Health Status