Carbonyls (Aldehydes/Ketones/Carboxylic acids / Esters)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are carbonyls
Consist of carbon-oxygen double bond
aldehydes and ketones
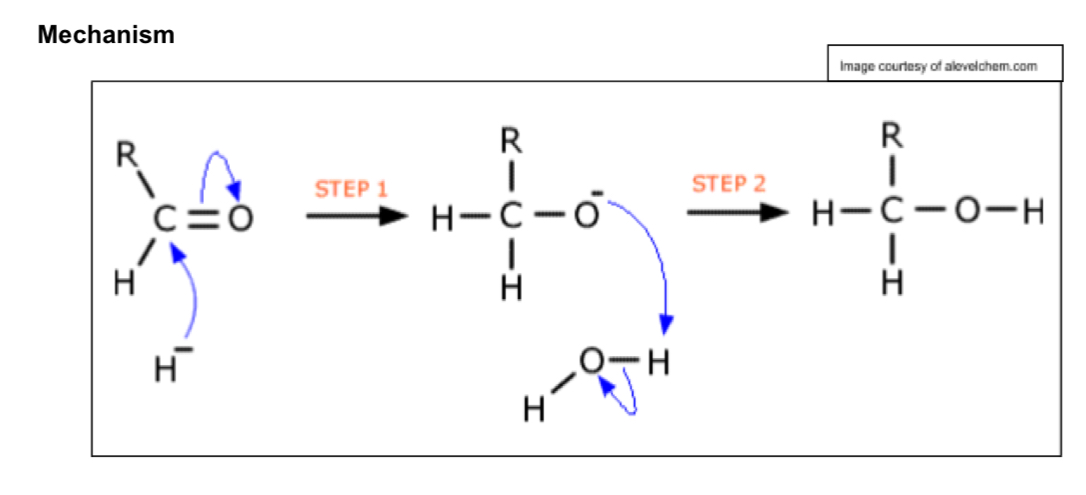
Describe nucleophillic addition reactions
Reduces carbonyls to alcohols
Reagent: NaBH4 or LiAlH4
→ BH4- ion a source of Hydride ion
Conditions: aqueous ethanol
→ produces primary alcohols + OH- ion
Why do we prefer NaBH4 to LiAlH4
NaBH4 is less reactive than LiAlH4
LiAlH4 reacts violently with water and alcohols
LiAlH4 must use ether as a solvent
How are hydroxynitriles formed
Nucleophillic addition
cyanide nucleophile
Why is potassium cyanide used instead of hydrogen cyanide
HCN is difficult to store as a gas
Produces dangerous byproducts
Why can nucleophillic addition reaction occur
C=O bond is polar so the carbon attracts negatively charged lone pair of electrons from hydride ions
Why can aldehydes and ketones be reduced but not alkene
Hydride ion is a nucleophile attacks positive c in c=o
hydride ion repelled by electron rich C=C
Why are enantiomers produced in carbonyl reduction
carbonyl groups are planar due to C=O bond
Can be attached from either side with equal probability of above or below attack
Equal amounts of enantiomers are formed - racemic mixture ( not optically active)
Test for carbonyls
Bradys reagent
Red or orange ppt with carbonyl vs clear/no ppt
What is esterification and what are some uses
Carboxylic acid heated under reflux + alcohol + acid (H2SO4) catalyst → ester
sweet smelling compounds for perfumes + flavourings
Plasticisers
Solvents for polar organic substances
Solvent in glue→Volatile, evaporates easily leaving sticky glue substance
Why can esters be used in perfumes
non-toxic
Soluble
Volatile
Does not react with water
What are some properties of Carboxylic acids
high boiling point → hydrogen bonding
Very soluble in water → polar, form H-bonds
Hydrocarbons chain size increases the solubility decreases as more of the molecule is non-polar
What are general reactions with Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid + metal → metal salt + hydrogen
Carboxylic acid + metal oxides → metal salt + water
Carboxylic acid + metal hydroxide→ metal salt + water
Carboxylic acid + metal carbonates → metal salt + water + CO2
Describe the formation of a triglyceride ester
Conditions: heat under reflux + acid catalyst (H2SO4)
Formed from propan-1,2,3-triol (glycerol)
Forms 3 water molecules
What’s biodiesel
Ester produced from vegetable oils + methanol in presence of strong acid catalyst
What is hydrolysis
Chemical reaction where water causes breaking of a chemical bond in a decomposition reaction
Hydrolysis of esters in acidic conditions
Esters are refluxed with catalyst of hot aqueous acids
Decompose → Carboxylic acid + alcohol
Water present in excess to favour products side of equilibrium
→ reversible reaction
Hydrolysis reaction of esters in alkaline conditions
esters refluxed with hot aqueous alkali e.g KOH
Decompose → alcohol + carboxylate salts
Non-reversible products are easier to separate
→ makes soaps/ saponification
What are the derivative molecules of carboxylic acids
acid anhydrides- formed when water is removed from two carboxylic acids
Acyl chlorides- react violently (COCL group very polar)
Amides
What is an Acyl chloride + how is it formed
Contain function group R-COCL ,R is alkyl group
Formed by reacting SOCl2 (thionyl chloride) + Carboxylic acid in dry conditions
Acyl chloride separated by distillation
Properties of Acyl Chlorides
polar + reactive
Colourless liquids fume in moist air HCl
Undergo nucleophillic addition-elimination reactions (aqueous conditions)
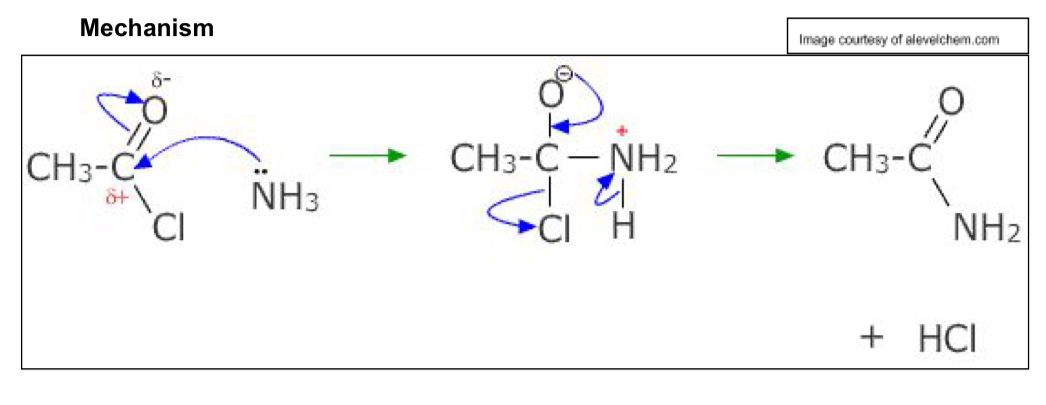
Describe Acyl Chloride nucleophilic addition-elimination
Addition: carbon of C=O attracts lone pair of e- from nucleophile
Pair of e- in C=O transferred to oxygen→ negatively charged
Elimination: double bond reformed
C-Cl bond breaks
Cl reacts with hydrogen atom → HCL
What reactions occur with acyl chlorides
Water → carboxylic acids
Alcohols → esters
Ammonia → amides
Amines → N-substituted Amides
How is aspirin produced
Salicylic acid + ethanoic anhydride
Why is ethanoyl chloride not used to make aspirin
Expensive
Produces harmful HCL fumes
Ethanoic anhydride much safer