Medsurg: Pituitary Gland
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is something to consider with MRI or CT when imaging for the pituitary?
You might have to order special testing, to get thin enough slices to catch smaller tumors
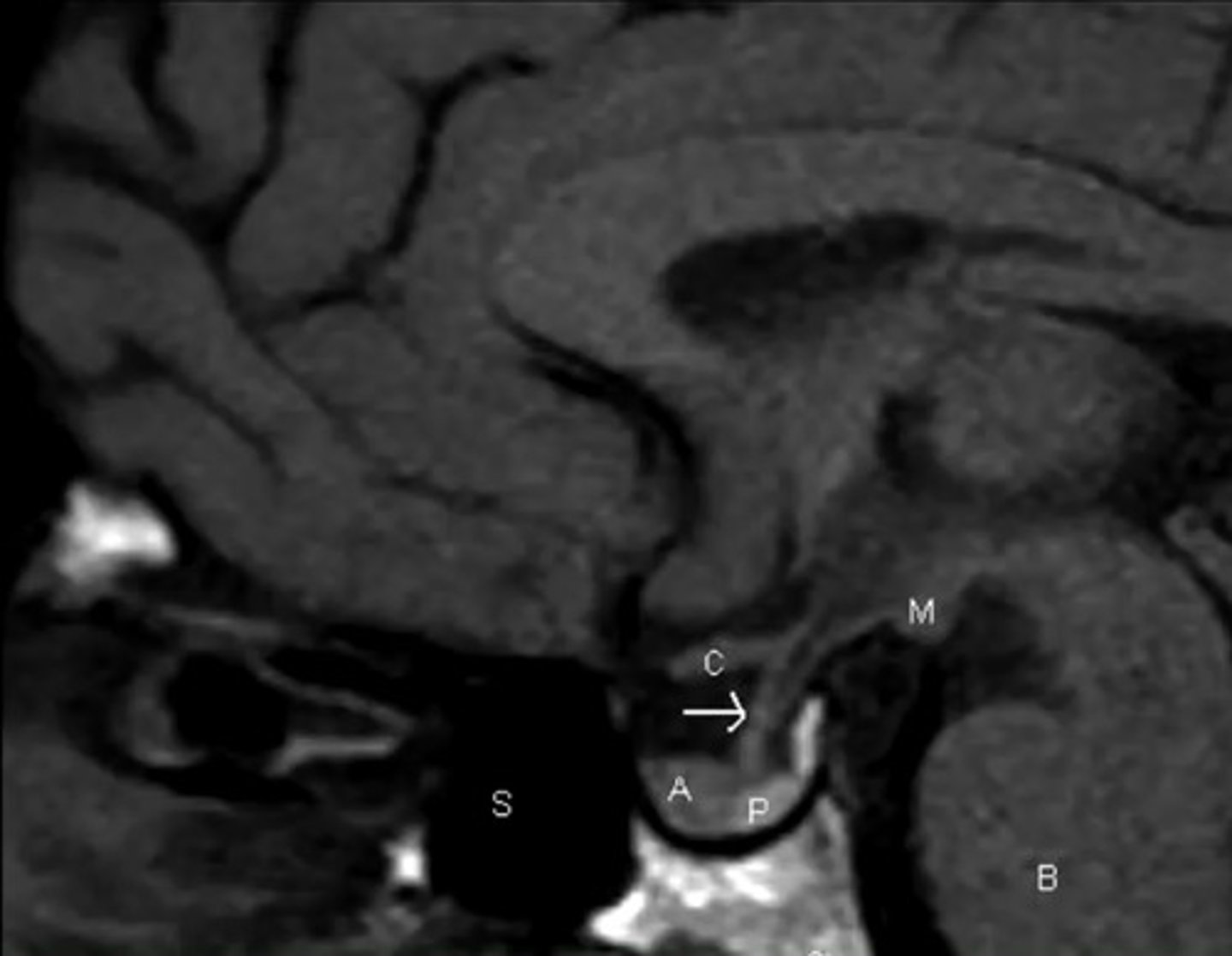
What is the most common pituitary tumor?
Almost always benign adenoma—micro in size and non-functional
Many are incidentally found after death, up to 25%
What is the recommended treatment with vision changes related to pituitary tumors?
Surgery
Where are most pituitary surgical interventions performed?
Through the sphenoid bone (less invasive)
He said know this
Describe the symptoms of a prolactinoma, the most common functional tumor
Galactorrhea
Infertility
Amenorrhea
Decreased libido
*Prolactin elevation is proportional to the size of the tumor*
What is the treatment for prolactinoma?
1. DA agonist (Cabergoline, Bromocriptin)
2. Switch to second DA agonist
3. If DA agonists ineffective then transphenoidal resection
What medications should you look for with hyperprolactinemia, before doing invasive imaging, for sure?
Check meds for metoclopramide, haldol, risperidone
Also look for primary hypothyroidism (which cause secondary hyperprolactinemia) and pregnancy
What is the common presentation with acromegaly?
Change in face, hands and feet with smelly sweat
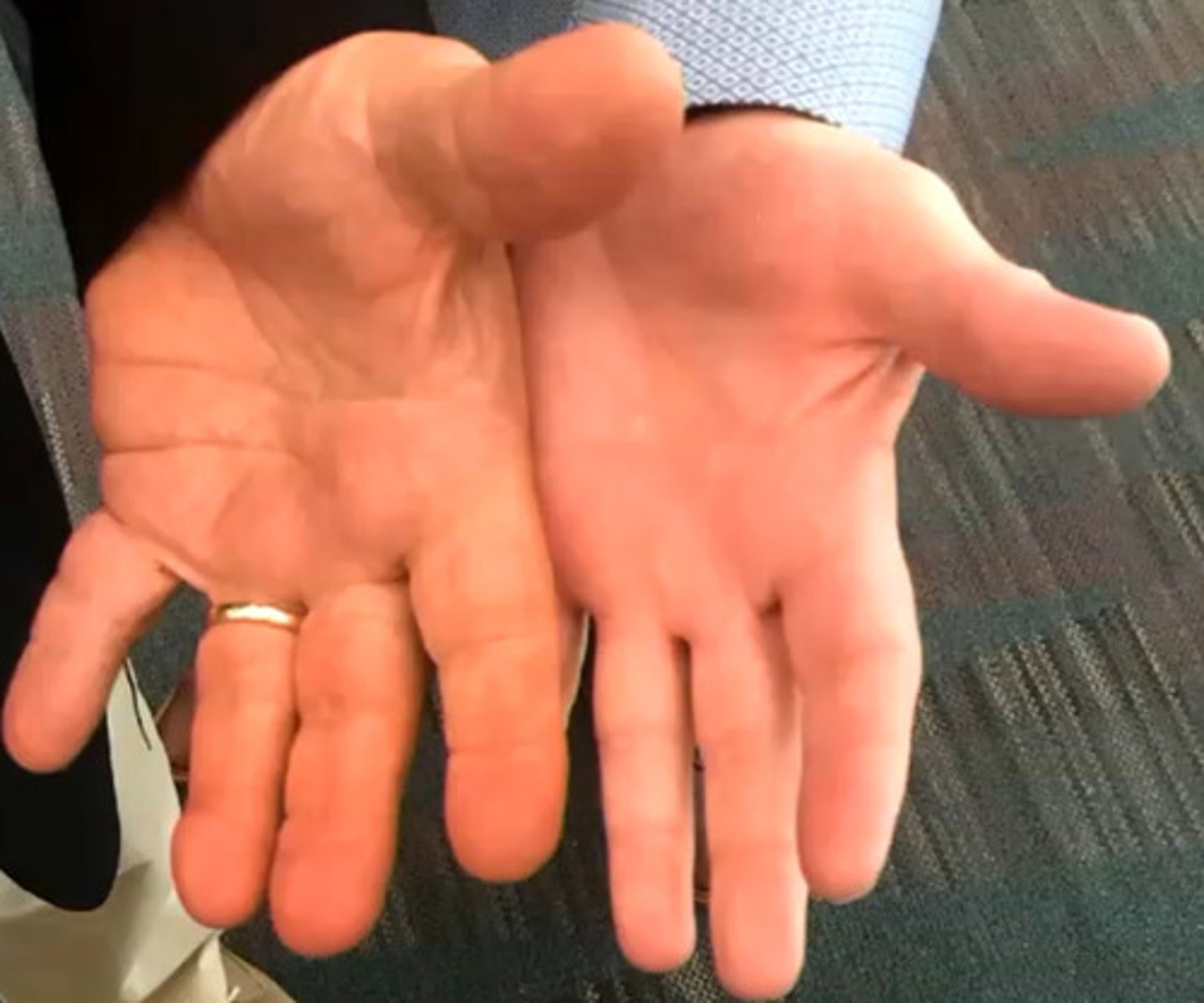
What testing should be done to rule out acromegaly?
IGF-1/GH leaves
Oral Glucose test—excess glucose should suppress GH. If they don't change—acromegaly
How does TSH secreting tumor present differently than other thyroid disorders?
All of them may have a goiter and all could show pituitary hypertrophy
However, TSH tumors result in high TSH, T3 and T4
Keep in mind, this is rare—check for other reasons first (like metabolism of levothyroxine)
When should a T3/T4 be drawn?
At least 8 hours after dosing—otherwise falsely high
How is cushing disease diagnosed?
24 hour urine: need to account for pulsatile release of cortisol
Dexamethasone suppression test
Same as other testing: Labs always first, confirm with imaging
What is the actual issue with Cushing Disease?
Pituitary source of excess cortisol; ACTH dependent. This will show high ACTH and high cortisol
ACTH independent high cortisol is an issue with the adrenal gland (probably a tumor—this is Cushing SYNDROME). Labs will show low ACTH and high cortisol
How does the dexamethasone suppression test work?
Dexamethasone should normally suppress morning cortisol, but does not suppress cortisol in someone with cushing syndrome
What is the presentation of empty sella disease?
Sometimes—nothing
The herniation may or may not affect labs
What are the two symptoms associated with compression of the pituitary stalk?
Typically elevated prolactin or diabetes insipidus
This would also cause changes in the visual feilds
What is the primary cause of pituitary hyperplasia?
Pregnancy—don't treat this :)
Primary Gland failure of the thyroid (Hashimoto) or gonads (ovarian/testes)
Pituitary specific: Somatotroph/Corticotroph secreting tumors
How does apoplexy vary from other tumors?
It is a surgical emergency
Sudden bleeding causes acute hemorrhage
They will have symptoms of mass effects (HA, cranial nerve impact, vision changes)
What is the pathological changes associated with diabetes insipidus?
Inability to concentrate urine due to a loss of vasopressin
So:
Hypernatremia
Dehydration
High Serum osmolarity and dilute urine
These patients can become dehydrated very quickly if they cannot maintain fluids in for fluids out (common in NH)
Compare osmolality versus osmolarity:
Osmolality: particles per kg
Osmolarity: particles per liter solution
Higher values mean higher concentration for both
How does a water deprivation test determine DI?
Both can show dehydration—keep them from a water source
A normal patient will show concentration of urine
DI patient's urine will retain the same osmolality no matter what
What does administering desmopressin in a water deprivation test do to a DI patient?
If there is a response and urine corrects, the problem is central (pituitary)
If there is no response, it is the kidney (nephrogenic DI)
What are some of the causes of nephrogenic DI?
Lithium
Hypercalcemia
Hyperparathyroidism
ADH is always elevated and ineffective because the kidney can't respond
What are the symptoms of hypopituitarism, which can occur after hemorrhagic pregnancy?
Flu like symptoms
Lack of: gonad hormones, growth hormones, urine volume changes
Prolactin levels can be low—but not critical
LH and FSH should be high in older men and postmenopausal women
GH and IGF-1 should be normal
How should TSH be evaluated?
In conjunction with T4
What would hyperkalemia tell you about pituitary function?
It is likely primary hypopituitarism, not secondary
What patient should receive GH replacement?
ONLY with deficiency
Never for general wellness
What do you give to treat SIADH?
NOT diuretics
Treat the cause, if possible
Serum sodium is low
Urine sodium is normal
Urine osmolality is elevated
Replace sodium, but fluid restriction is primary