Geography_ Term 3 & 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Last updated 7:41 AM on 11/24/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
Characteristics of the developed world
- industrialized and wealthy
- democratically elected governments
- capitalist economy
- democratically elected governments
- capitalist economy
2
New cards
Characteristics of the developing world
- poorer and still undergoing industrialization
- often unstable governments
- often economically dependent on other countries
- often unstable governments
- often economically dependent on other countries
3
New cards
Brandt line
- proposed by W.Brandt
- divided the world into the rich north and poor south
- divided the world into the rich north and poor south
4
New cards
Industrialized nations
Have many manufacturing industries
5
New cards
Gross National Income (GNI)
Value of all goods and services produced by a country in one year
6
New cards
GNI per capita
GNI divided by the number of people in the country
- gives an indication of the amount of money available to each person in the country if its income is evenly shared
- gives an indication of the amount of money available to each person in the country if its income is evenly shared
7
New cards
Millenium summit (2000)
Meeting held by the 189 member states of the United Nations, where 147 signed the Millennium Declaration in which they committed themselves towards a world of peace and security
8
New cards
Goals of the Millennium Declaration
- eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
- achieve universal primary education
- reduce child mortality
- improve maternal health
- achieve universal primary education
- reduce child mortality
- improve maternal health
9
New cards
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Measures the value of economic activity within a country
- sum of the market values/prices of all final goods and services produced in an economy during a period of time
- sum of the market values/prices of all final goods and services produced in an economy during a period of time
10
New cards
GDP per capita
GDP divided by the number of people in a country
- shows the average amount of money available to each person in a country
- shows the average amount of money available to each person in a country
11
New cards
Human Development Index (HDI)
Measure that looks at income, health and education to assess how well economies are doing
12
New cards
Gini Coefficient
Measure of the distribution of income across a population
- often used as a gauge of economic inequality
- often used as a gauge of economic inequality
13
New cards
Birth rate
Number of babies born per 1000 people in a population per year
14
New cards
Death rate
Number of deaths per 1000 people in a population per year
15
New cards
Infant mortality
Number of infant deaths per 1000 live births per year
- indicates the the medical systems in the country and how well the most vulnerable in society are looked after and protected in their early years
- indicates the the medical systems in the country and how well the most vulnerable in society are looked after and protected in their early years
16
New cards
People per doctor
The number of people there are for every doctor in a country or place
17
New cards
Literacy rate
Percentage of the country who are able to read and write as adults
- social measure, helps to indicate the standard of education
- social measure, helps to indicate the standard of education
18
New cards
Access to safe water
Percentage of people who have access to sanitary and safe water that is free from bacteria and parasites
19
New cards
Life expectancy
Average age a person can expect to live at birth
- reveals how good food security , water quality, shelter and medical care are
- reveals how good food security , water quality, shelter and medical care are
20
New cards
3 aspects looked at in HDI
Wealth: how much money citizens earn
Health: access to medical care and life expectancy
Education: how good is the system and who has access to it
Health: access to medical care and life expectancy
Education: how good is the system and who has access to it
21
New cards
Development
Sustained combined effort of policy makers and the community to promote a good standard of living while protecting the environment
22
New cards
EPI
Environmental Performance Index
23
New cards
Historical factors affecting development and why
Colonialism - Colonial powers stole raw materials from colonies at a low cost and sole them at an expensive cost
The slave trade - Physically and mentally strong humans were taken from colonies and sold into slavery
The slave trade - Physically and mentally strong humans were taken from colonies and sold into slavery
24
New cards
Geographical factors affecting development and why
Climate - The poorest countries are in the tropics (infertile land, scarce water, disease)
Location - Landlocked countries have no direct access to the sea/overseas markets
Resources - Quantity and availability of natural resources + the skills needed to process them affect the rate of economic growth
Location - Landlocked countries have no direct access to the sea/overseas markets
Resources - Quantity and availability of natural resources + the skills needed to process them affect the rate of economic growth
25
New cards
Political factors affecting development and why
Conflicts & Corruption - Unstable political environment may reduce investment and economic development
26
New cards
Social factors affecting development and why
Health - Healthy populations live longer, are more productive and save more
Education - Raises people's productivity and promotes entrepreneurship and technological advances
Education - Raises people's productivity and promotes entrepreneurship and technological advances
27
New cards
Economic factors affecting development and why
Technology - Applications of better technology means the same amount of labour will be more productive and economic growth will advance at a lower cost
Infrastructure - Improvements and investments in roadways/machinery/factories will reduce cost and increase efficiency
Infrastructure - Improvements and investments in roadways/machinery/factories will reduce cost and increase efficiency
28
New cards
Trade factors affecting development and why
Balance of Trade - Poorer countries export lower-value raw materials, richer countries export higher-value manufactured goods
Unfair Trade - Developed countries make business laws that put themselves at an advantage over trading partners
Unfair Trade - Developed countries make business laws that put themselves at an advantage over trading partners
29
New cards
Balance of Trade
Value of exports minus the value of imports
30
New cards
Economic indicators
Provide information about health and income
- GDP
- GDP per capita
- GDP
- GDP per capita
31
New cards
Social indicators
Measures things that are about quality of life
- Gini-coefficient
- Infant mortality
- Life expectancy
- Literacy levels
- Gini-coefficient
- Infant mortality
- Life expectancy
- Literacy levels
32
New cards
Environmental indicators
Show the impact of human activity on the environment
- water quality in rivers and lakes
- rate of deforestation
- carbon dioxide emissions
- water quality in rivers and lakes
- rate of deforestation
- carbon dioxide emissions
33
New cards
Indicators of the economic aspects of development
Per capita income
How a country earns it income (economic sectors)
How a country earns it income (economic sectors)
34
New cards
Indicators of the social aspects of development
Quality of life
Access to social services
Infrastructure
Access to basic needs
Access to social services
Infrastructure
Access to basic needs
35
New cards
Indicators of the environmental aspects of development
Sustainability
36
New cards
Environmentally sustainable development
Causes as little long-term damage to the environment as possible, leaving enough resources for future generations
37
New cards
LEDCs
Less Economically Developed Countries
- export mainly raw materials with less value and therefore earn less
- export mainly raw materials with less value and therefore earn less
38
New cards
MEDCs
More Economically Developed Countries
- export manufactured and specialized equipment
- export manufactured and specialized equipment
39
New cards
Trade
The exchange of goods and services from producers to consumers
40
New cards
Sustainable resource use
The use of natural resources in a way and at the rate that does not lead to the long-term decline of biological diversity, thereby maintaining potential to meet the needs and aspirations of present and future generations
41
New cards
Resource
Any physical material constituting part of earth that people need and value
42
New cards
Renewable resource
A natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted
43
New cards
Non-renewable resource
Resources that are not easily replenished by the environment
44
New cards
Overgrazing
When plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods
45
New cards
Overfishing
The removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate that the species cannot replenish in time, resulting in those species either becoming depleted or very underpopulated in that given area
46
New cards
Food security
When all people at all times, have physical social and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food which meets their dietary needs and food preferences for a healthy and active life
47
New cards
Genetically modified crops
Foods derived form organisms whose genetic material have been modified in a way that does not occur naturally
48
New cards
Sustainable farming
Farming in ways which meet society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
49
New cards
Sustainable fishing
Leaving enough fish in the ocean, respecting habitats and ensuring people who depend on fishing can maintain their livelihoods
50
New cards
Unsustainable resource
There are finite amounts of these resources on Earth and once they are depleted they are gone forever
51
New cards
Causes of soil degradation
Overgrazing
Deforestation
Agricultural activities
Overexploitation
Industrialization
Deforestation
Agricultural activities
Overexploitation
Industrialization
52
New cards
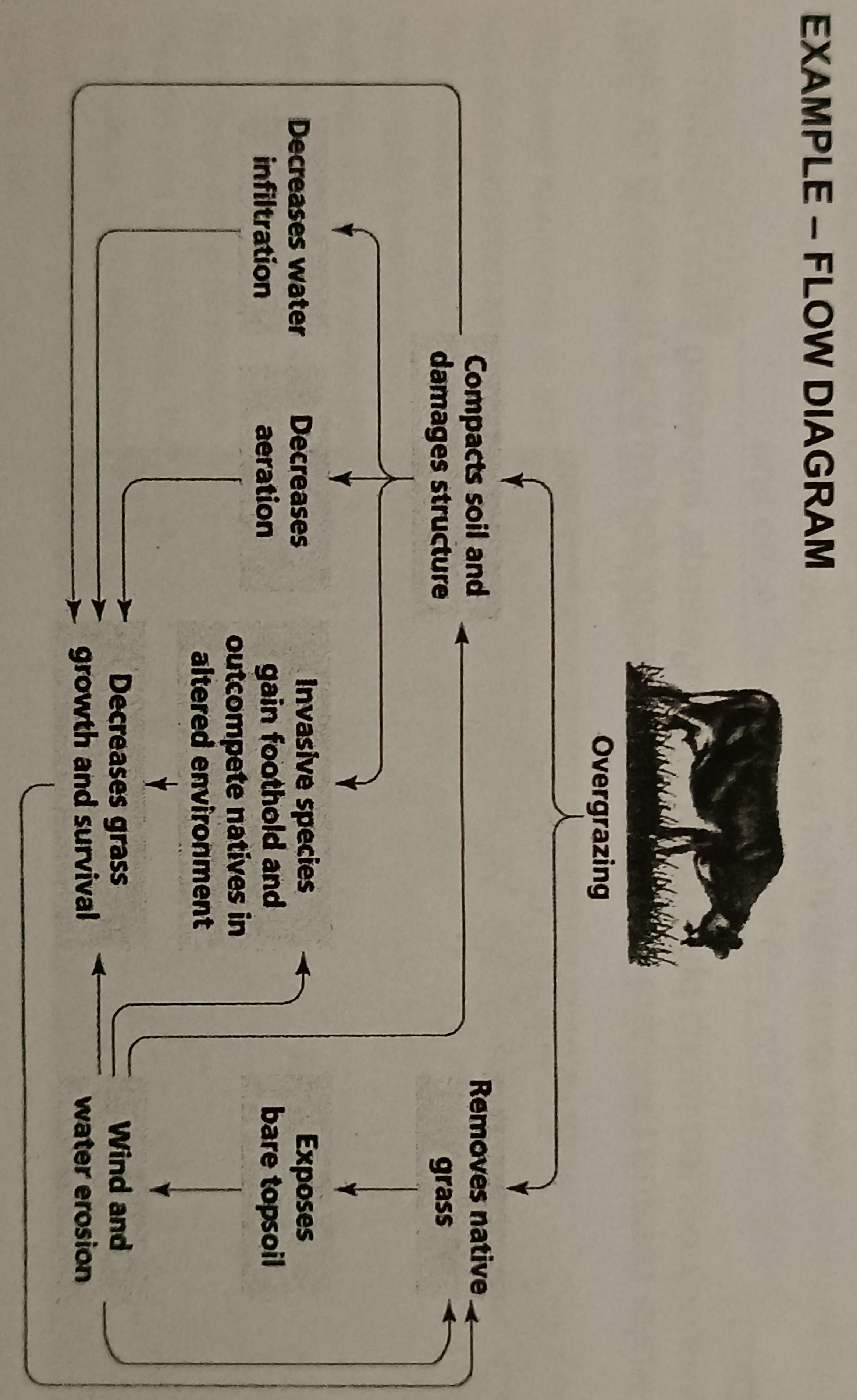
Consequences of overgrazing
- loss of species of herbs and grasses
- compacting soil, preventing seeds form germinating
- soil becomes loose and susceptible to wind and water action
- soil loses infiltration capacity
- compacting soil, preventing seeds form germinating
- soil becomes loose and susceptible to wind and water action
- soil loses infiltration capacity
53
New cards
Rotational grazing
Process of planned grazing that encourages pasture growth
54
New cards
Sustainable land use for farming
Shifting large herds of livestock form already overstocked communal land
Controlled breeding and early weaving
Feeding livestock on a crop residue
Reserving communal land for small-scale farmers
Quota system whereby a number of livestock is allowed to graze on a pasture land
Controlled breeding and early weaving
Feeding livestock on a crop residue
Reserving communal land for small-scale farmers
Quota system whereby a number of livestock is allowed to graze on a pasture land
55
New cards
Effects of overfishing
Loss of habitat
Loss of coral reefs
Loss of a a valuable food source many depend upon
Loss of coral reefs
Loss of a a valuable food source many depend upon
56
New cards
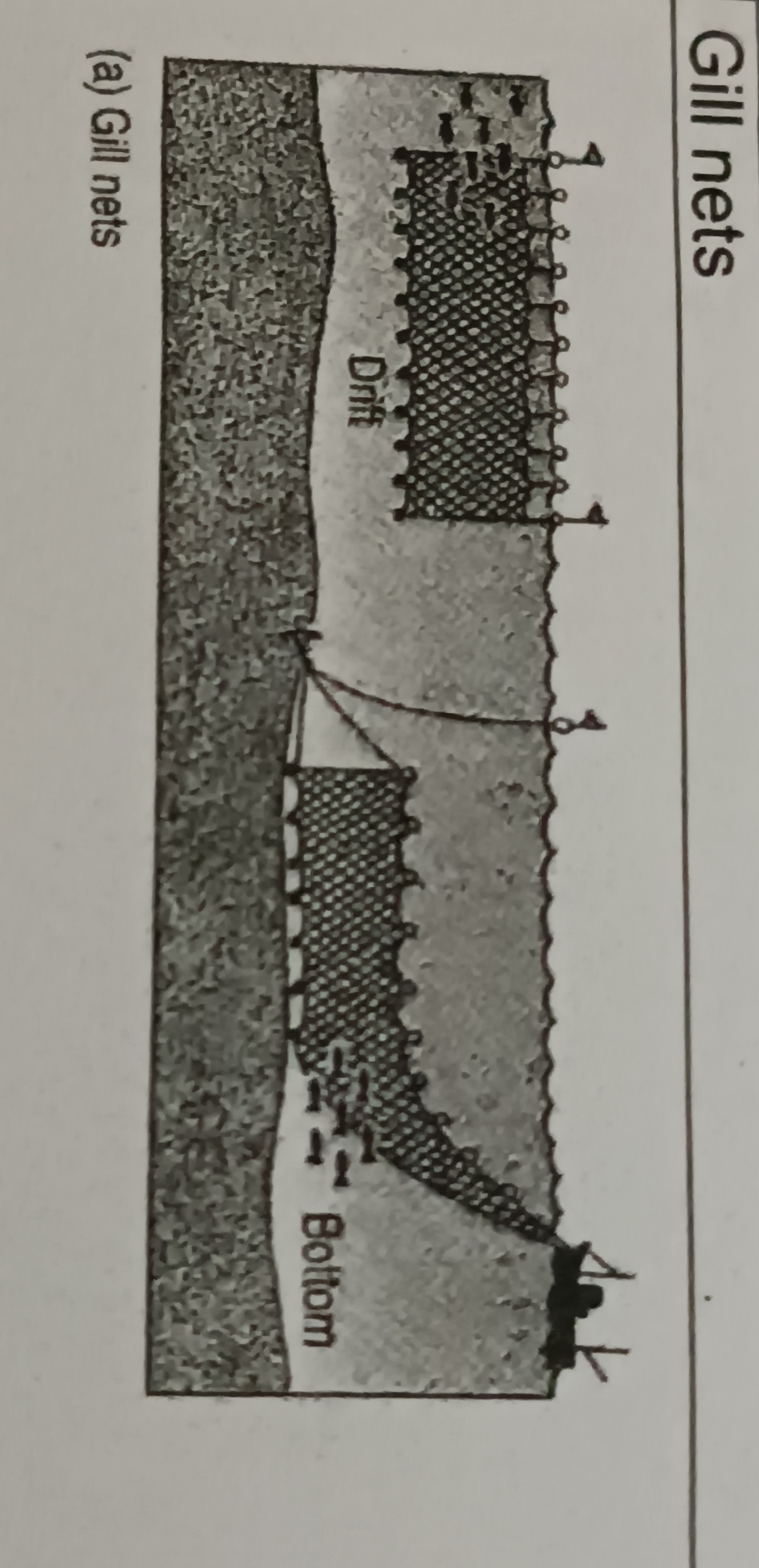
Gill nets
Involves the use of a net, up to 32km in extent, that is generally anchored to a boat and left to float with the tide
- can scoop up half a ton of fish
- results in an over harvesting of non-commercial marine species
- can scoop up half a ton of fish
- results in an over harvesting of non-commercial marine species
57
New cards
By-catch
All the animals caught in nets or on lines which are unintentional and are usually dead and thrown overboard
58
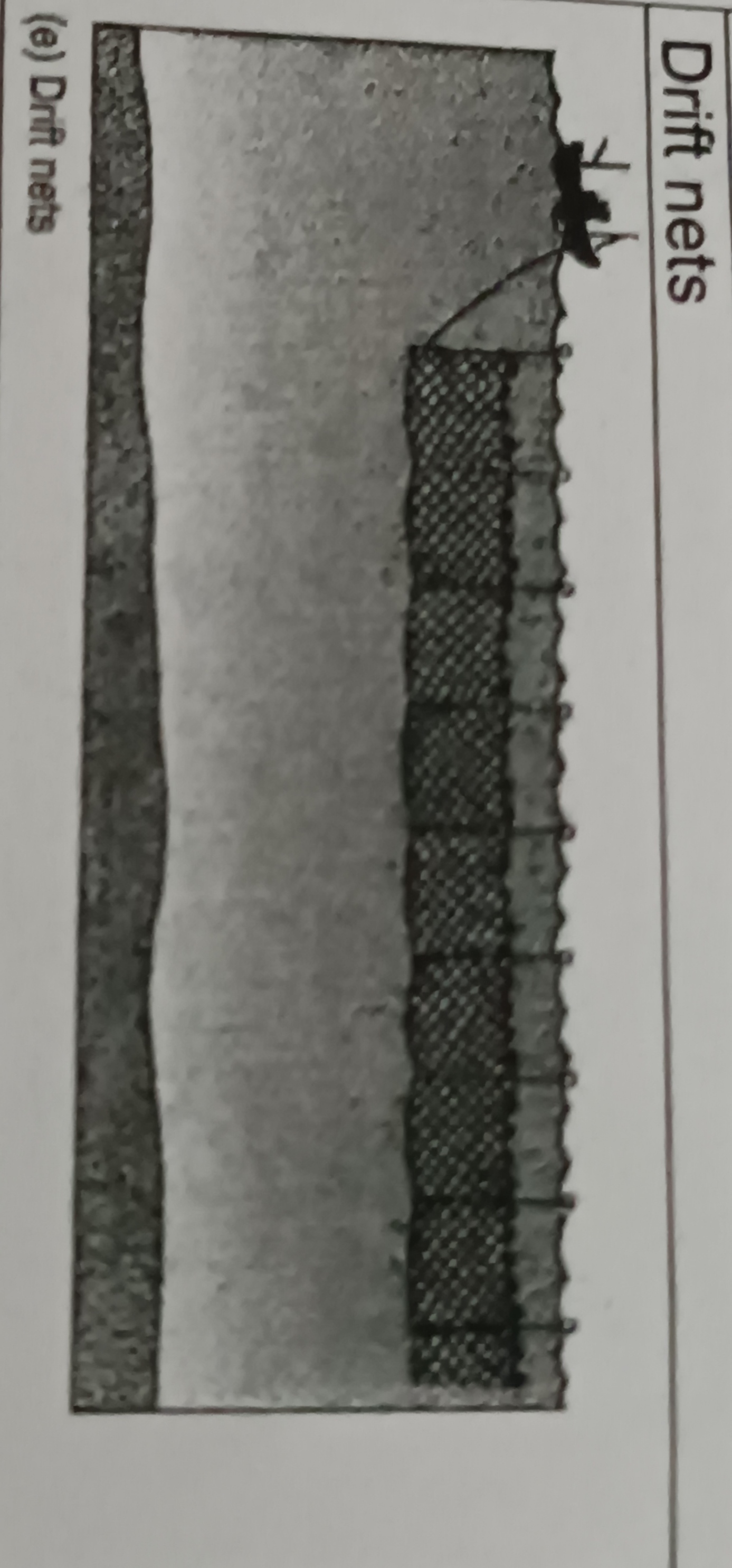
New cards
Drift nets
Nets hang vertical in the water column without being anchored at the bottom
- used to snare fish by their gills
- used to snare fish by their gills

59
New cards
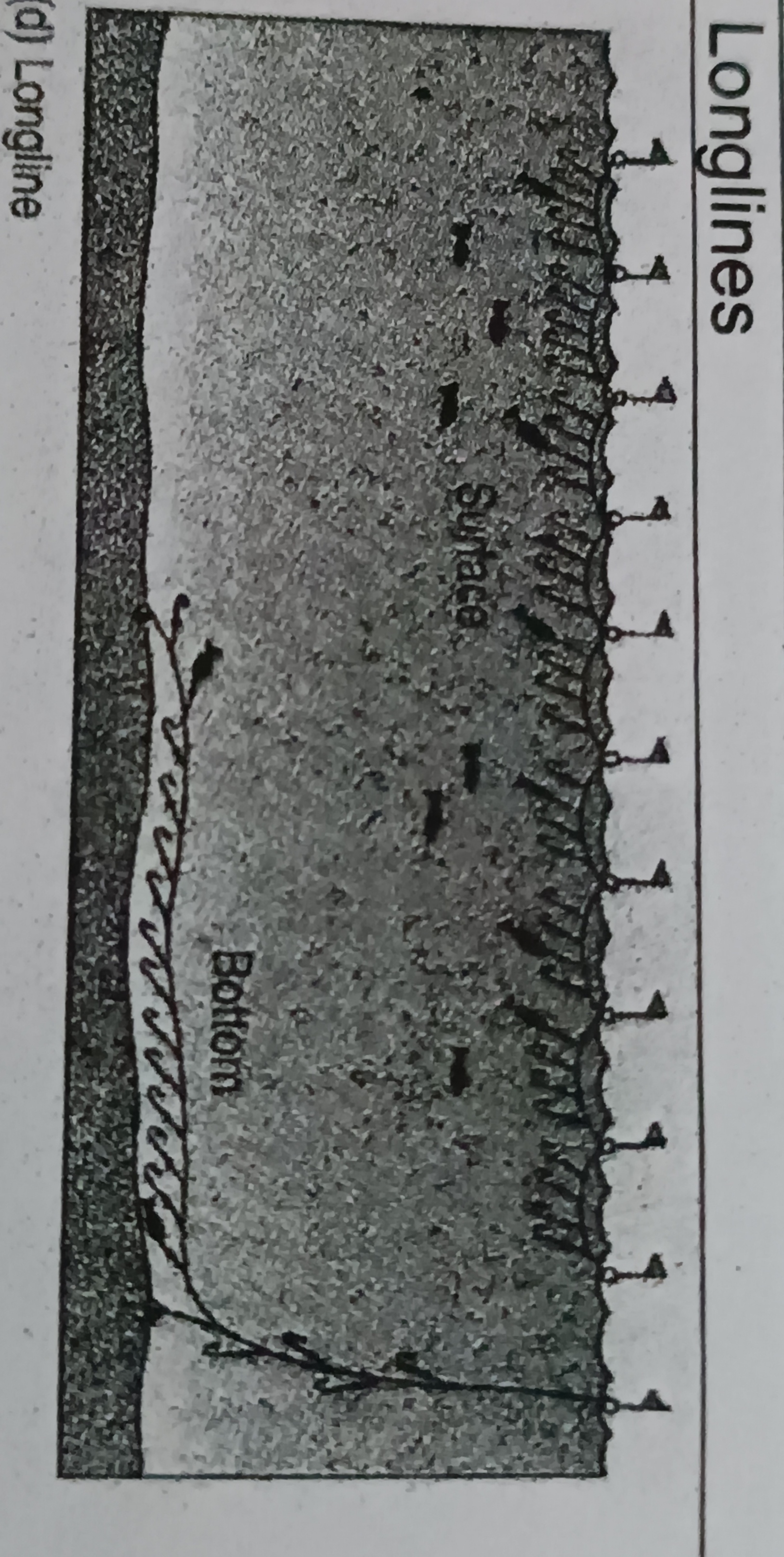
Longlines
Includes a main fishing line up to 100km in length, with secondary lines branching off it, each set with hundreds or thousands of barbed, baited hooks
- used to catch fish in open waters
- targets tuna, swordfish and Patagonian tooth fish
- used to catch fish in open waters
- targets tuna, swordfish and Patagonian tooth fish
60
New cards
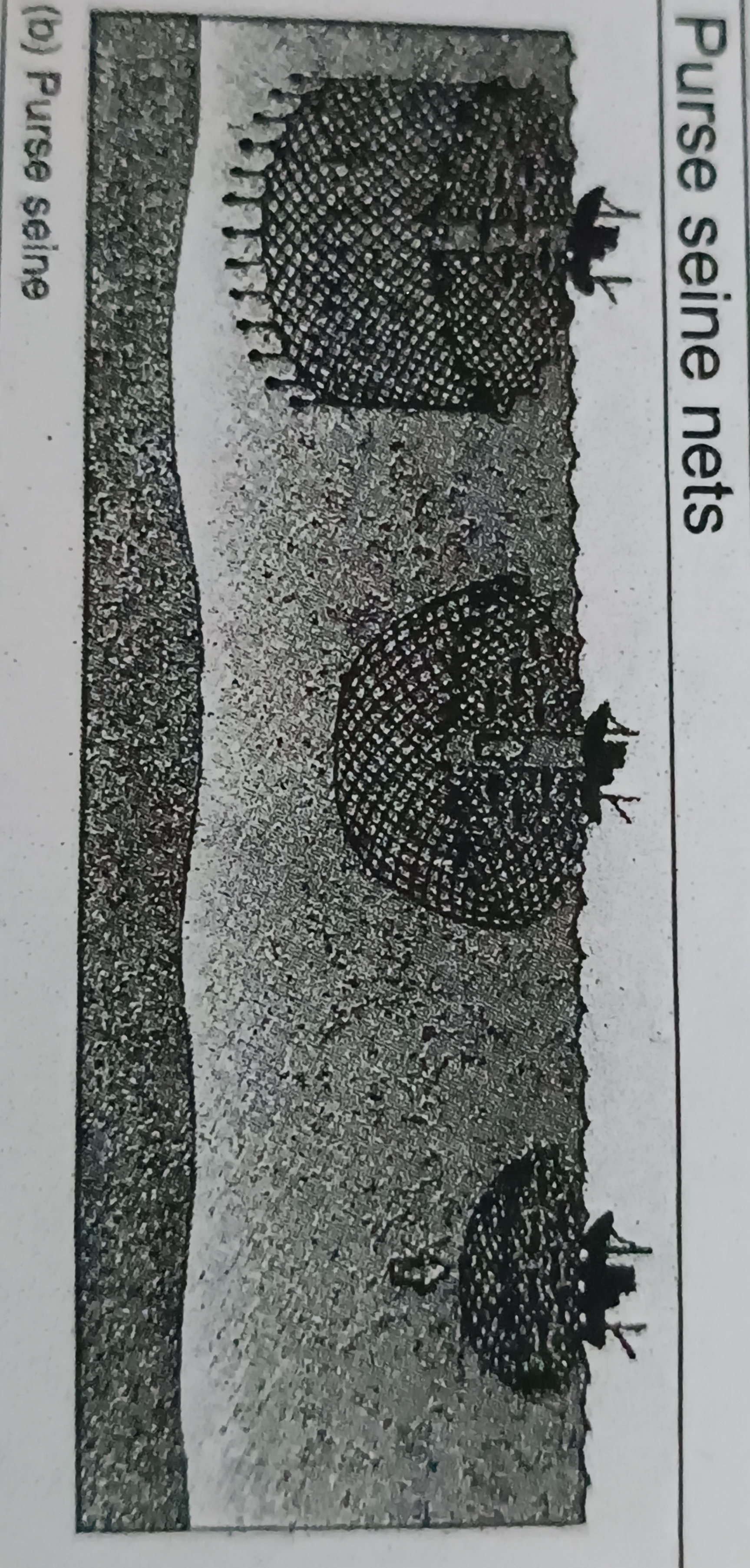
Purse seine nets
Large wall of netting deployed around an entire area or school of fish
- will close at the bottom by means of passing a line through rings attached along the lower edge of the net
- usually used to catch tuna
- will close at the bottom by means of passing a line through rings attached along the lower edge of the net
- usually used to catch tuna
61
New cards
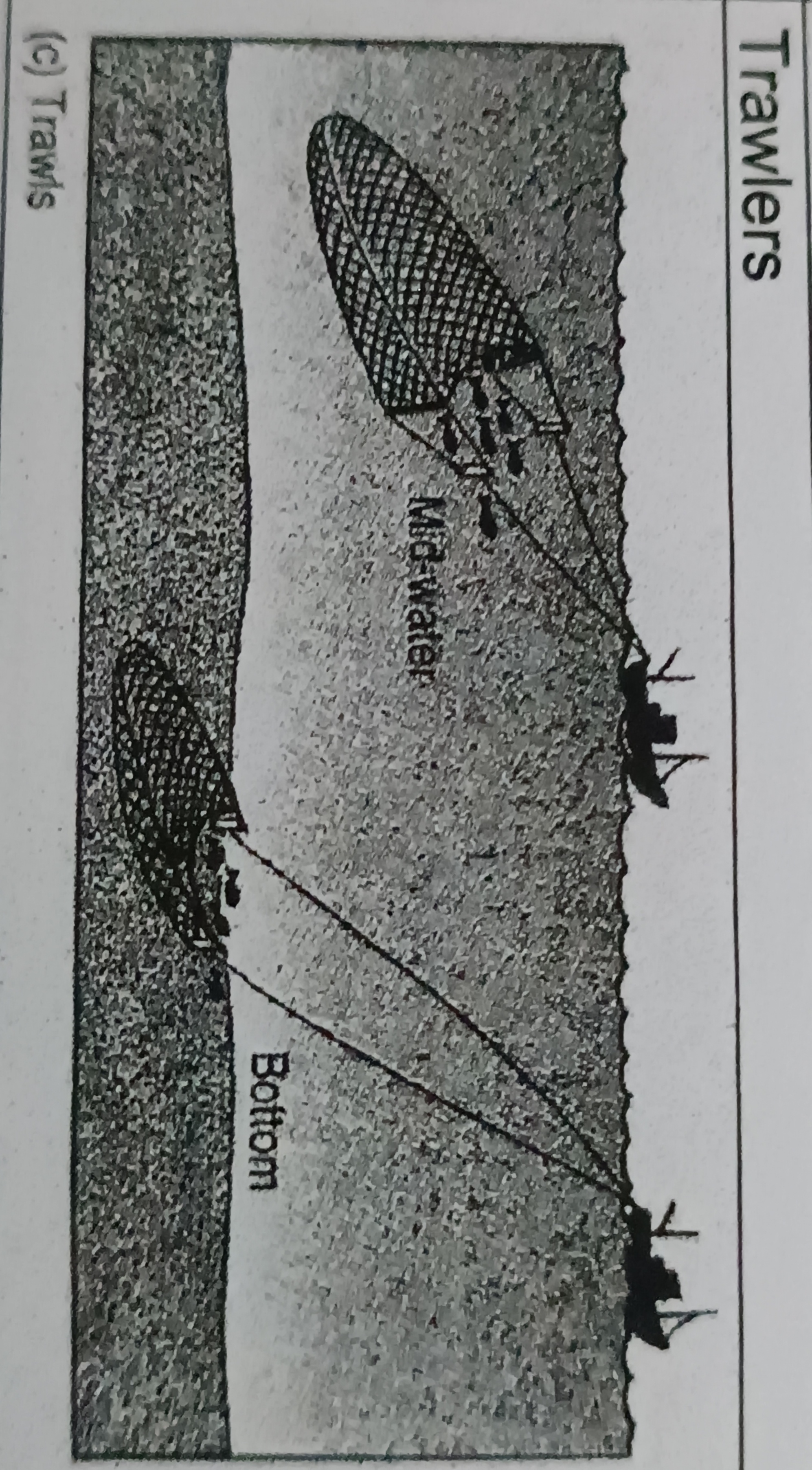
Trawlers
Grid of bars with and opening either at the top or bottom
- grid is fitted into the neck of a shrimp trawl, small animals like shrimp slip through the bars into the bad end of the trawl
- large animals, when caught at the mouth of the trawl, strike the grid bars and are ejected through the opening
- grid is fitted into the neck of a shrimp trawl, small animals like shrimp slip through the bars into the bad end of the trawl
- large animals, when caught at the mouth of the trawl, strike the grid bars and are ejected through the opening
62
New cards
Invasive species
Harm not only the environment but also have industrial, social, recreational and economic impacts
63
New cards
Overcapacity
Oversized fishing fleet takes more than our oceans can sustainably support
64
New cards
Unselective fishing practices and gear
Cause destruction on non-target species
65
New cards
Sustainable fishing practices
Reduce the use of fishmeal
Introduce quota policy
Effective regulation should be consistent with biology
Establish Marine Protected Areas and Marine reserves
Improve fisheries
Introduce quota policy
Effective regulation should be consistent with biology
Establish Marine Protected Areas and Marine reserves
Improve fisheries
66
New cards
Carbon footprint
Amount of carbon dioxide, or other carbon compounds emitted into the atmosphere by the activities of an individual, company, country
67
New cards
Tips on reducing pressure on resources as an individual
Take shorter showers
Do not let the tap run while brushing teeth
Install fluorescent bulbs in every room in the house
Unplug appliances not in use
Recycle
Do not let the tap run while brushing teeth
Install fluorescent bulbs in every room in the house
Unplug appliances not in use
Recycle
68
New cards
Tips on reducing pressure on resources as a business
Use electric vehicles, locomotives, and fuel efficient planes when delivering goods
Use energy efficient machinery
Try to make sure bus routes end up near the company
Try to recycle all your paper
Turn off computer and lights when leaving the building
Use energy efficient machinery
Try to make sure bus routes end up near the company
Try to recycle all your paper
Turn off computer and lights when leaving the building
69
New cards
Tips on reducing carbon emissions as the government
Set policies to curb the emission of greenhouse gases
Give incentives to companies that minimizes their emission of greenhouse gases
Impose fines to those who exceed the limit of emissions
Setting targets to reduce emissions
Advocacy campaign on lowering carbon footprint
Give incentives to companies that minimizes their emission of greenhouse gases
Impose fines to those who exceed the limit of emissions
Setting targets to reduce emissions
Advocacy campaign on lowering carbon footprint