EXAM 3 Sensory Systems: Pain and Sensory Processing
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Sensation
The process of detecting environmental stimuli.
Receptor Cells
Cells that convert stimuli into electrical signals.
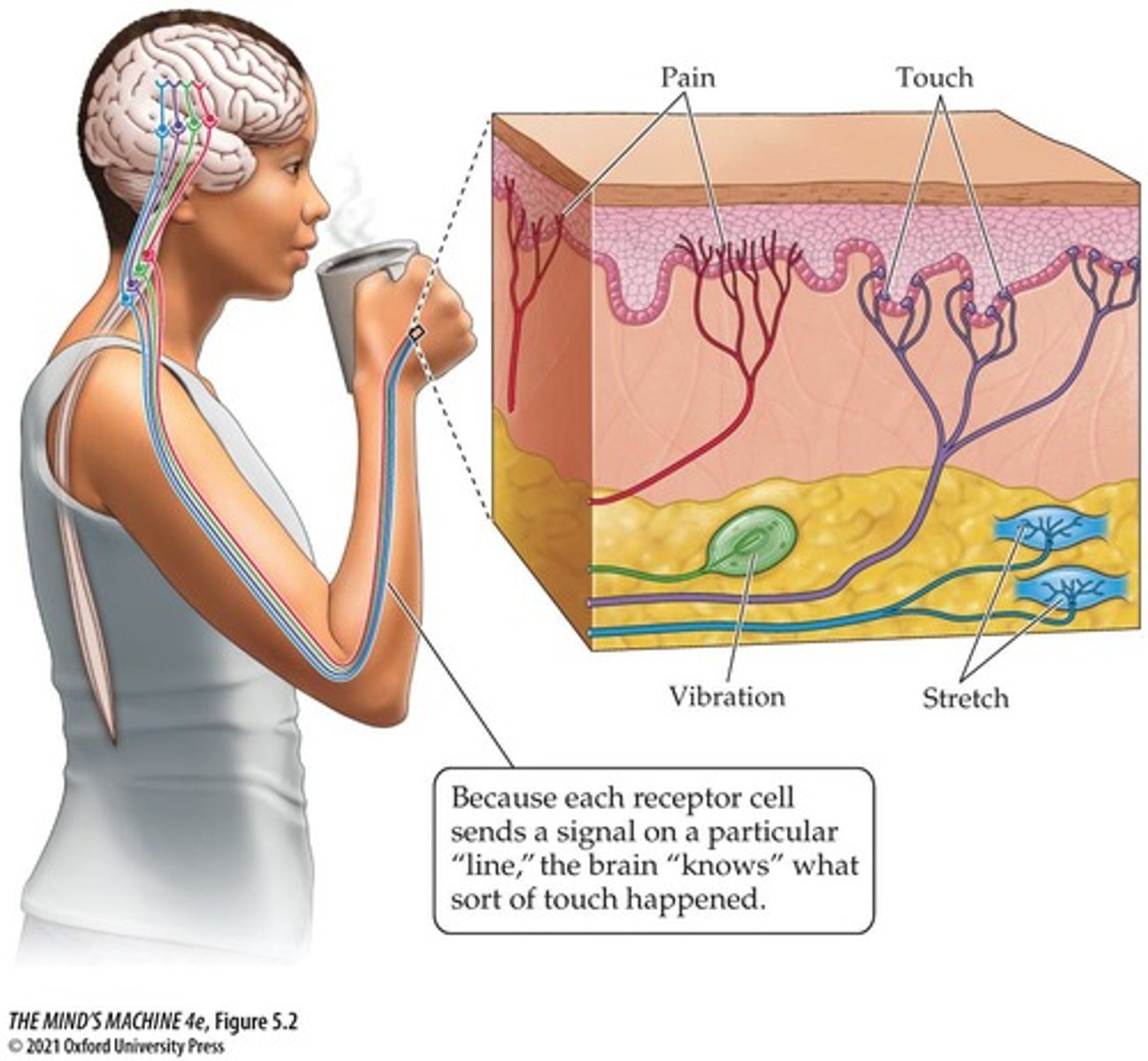
Labeled Lines
Distinct nerve tracts for different sensory experiences.
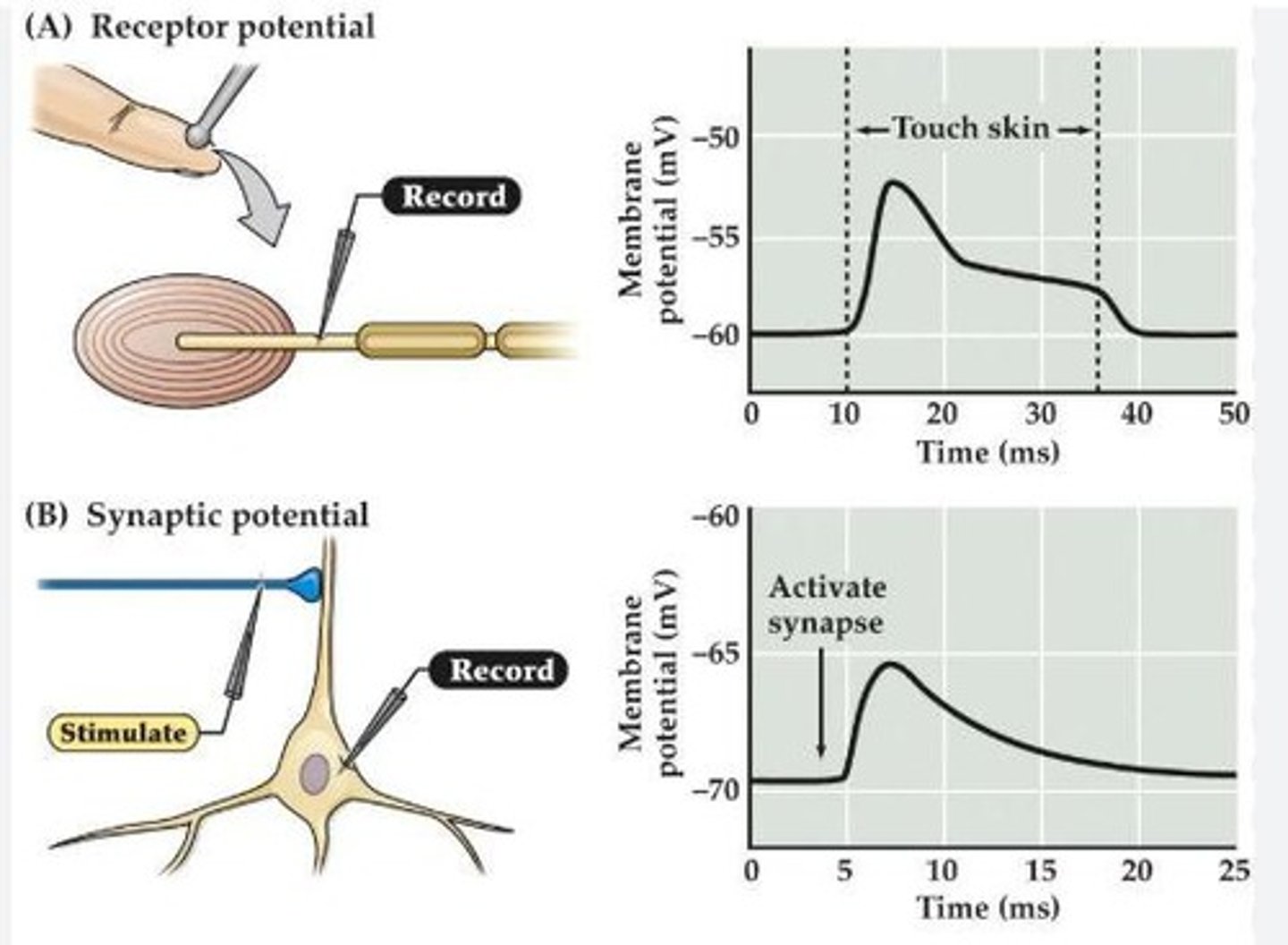
Receptor Potential
Local membrane potential change due to stimuli.
Sensory Transduction
Conversion of stimulus into membrane potential change.
Phasic Receptors
Receptors that adapt quickly to stimuli.
Tonic Receptors
Receptors that show little adaptation to stimuli.
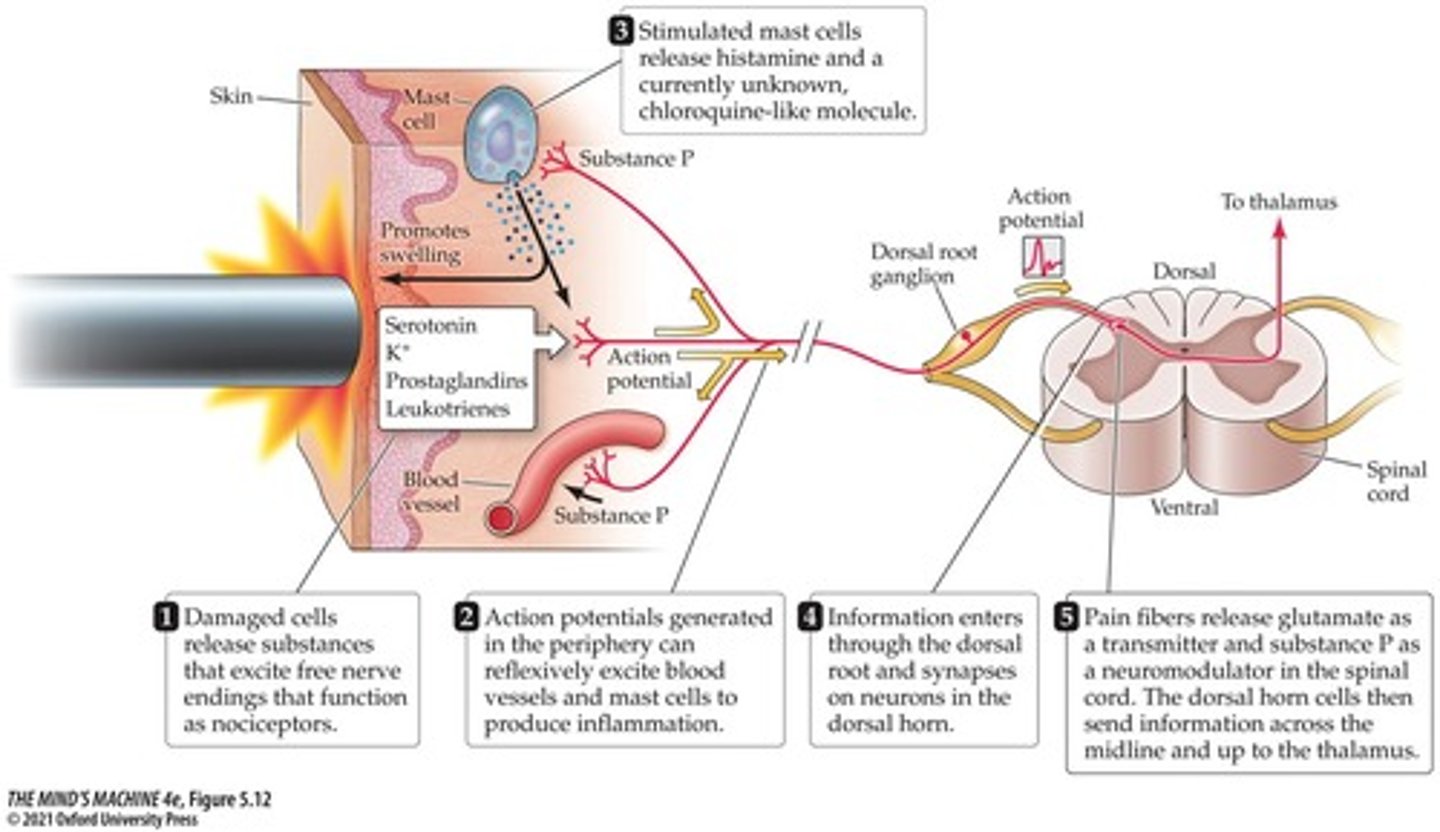
Nociceptors
Pain receptors responding to tissue damage.
Anterolateral System
Pathway for pain and temperature sensations.
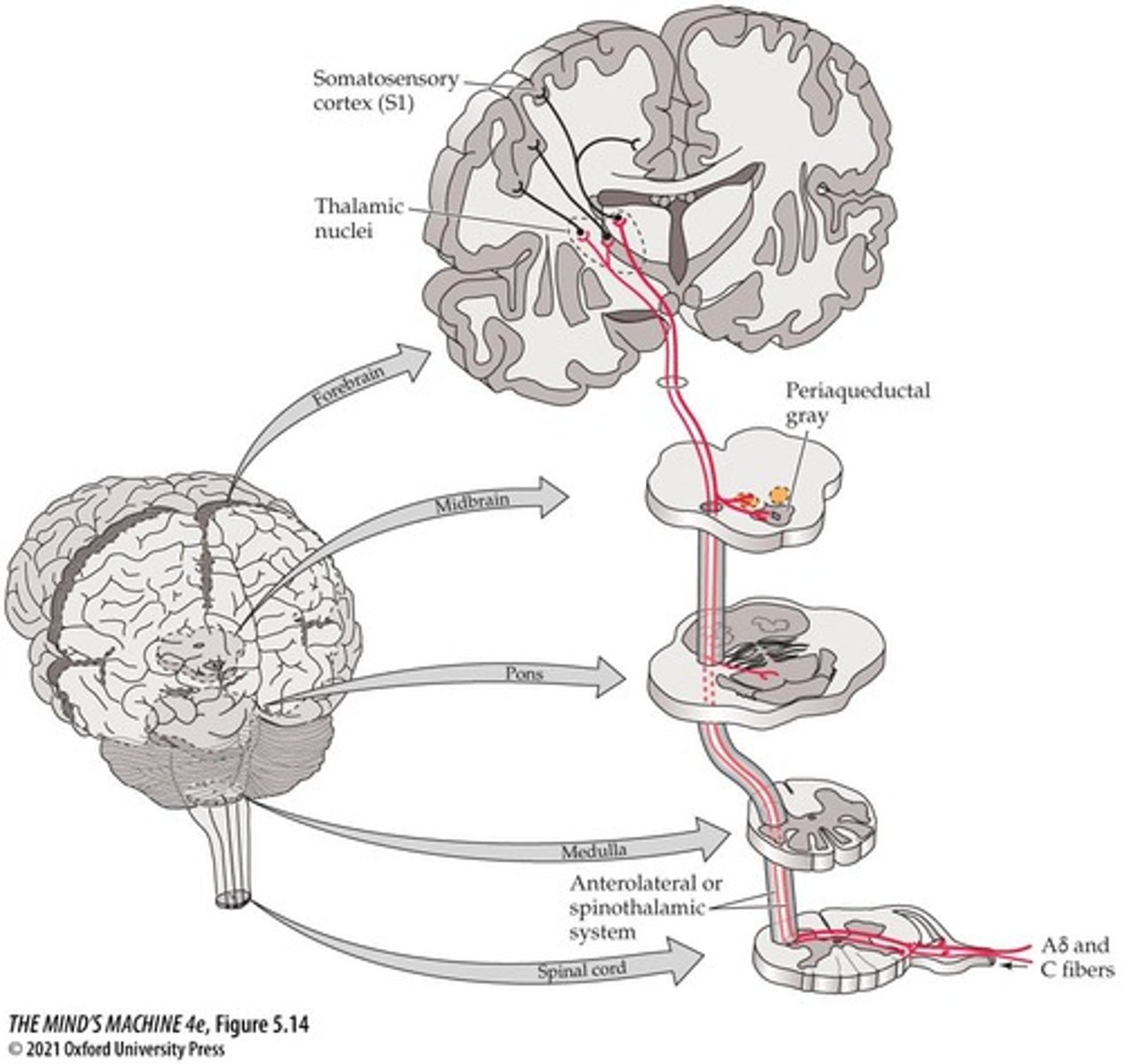
Cingulate Cortex
Integrates pain information in the brain.
Substance P
Peptide that enhances pain signal transmission.
Gate Control Theory
Theory explaining modulation of pain signals.
Analgesia
Absence or reduction of pain sensation.
Placebo Effect
Symptom relief from an inert treatment.
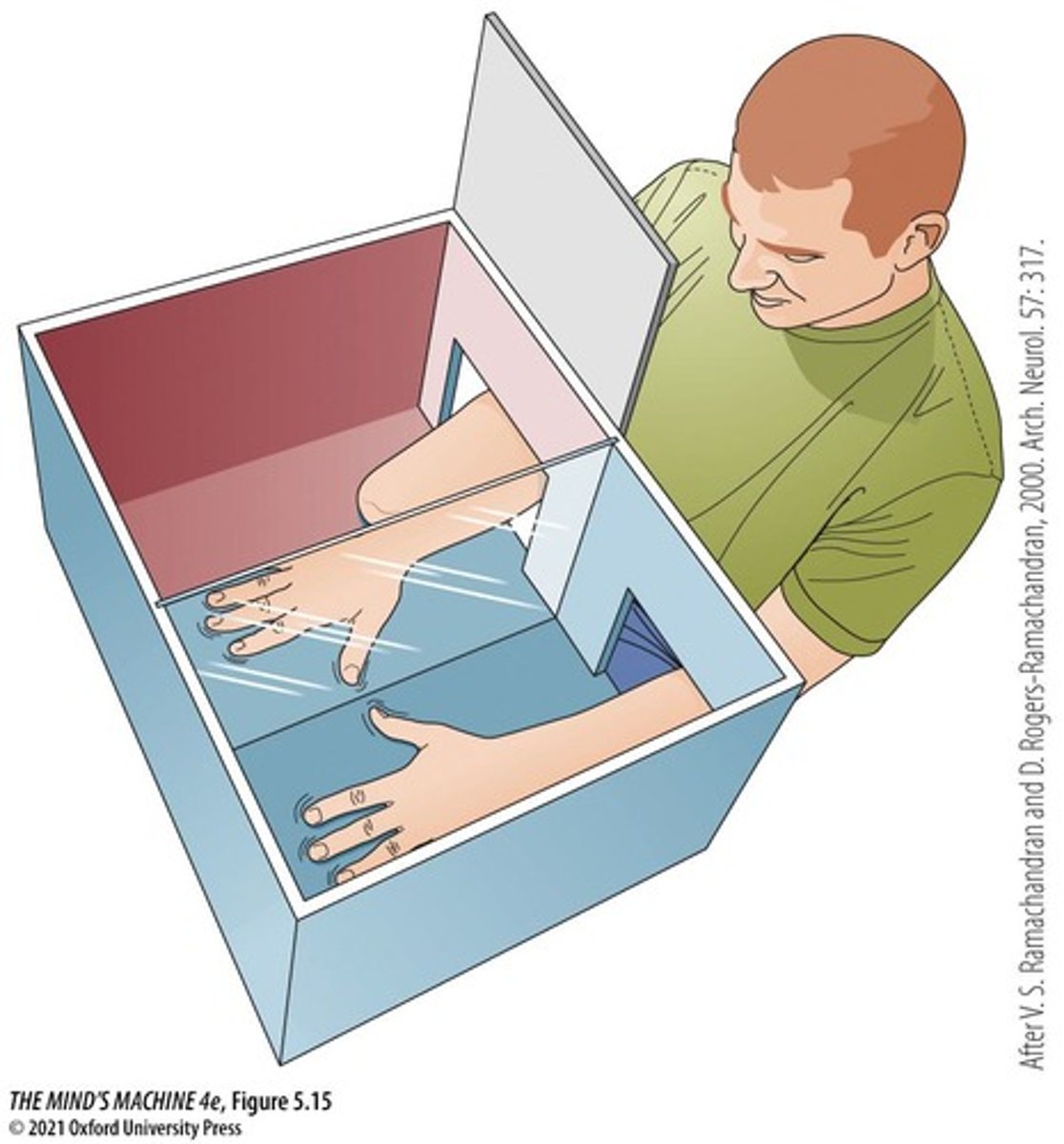
Phantom Limb Pain
Pain perceived in amputated limbs.
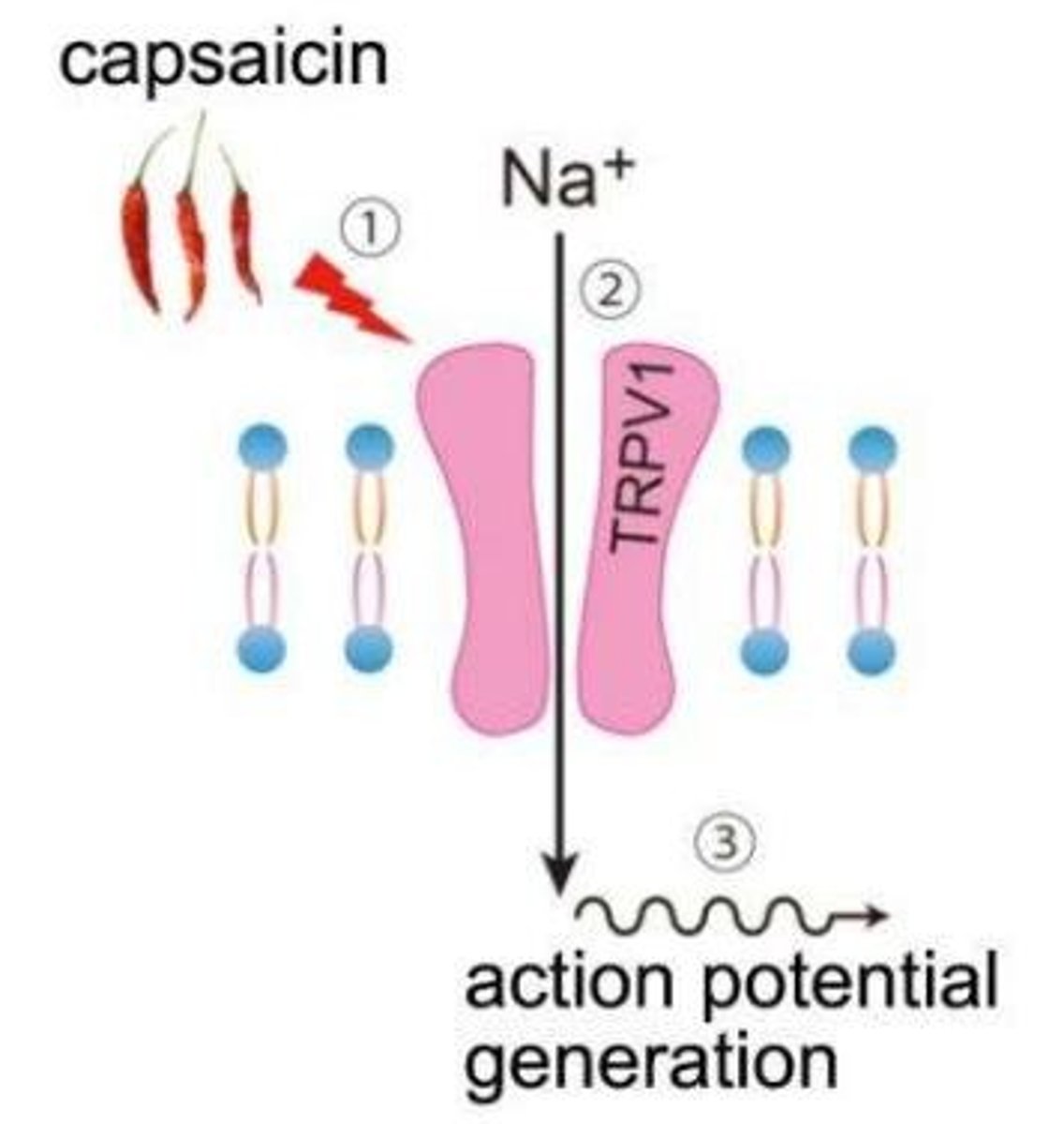
Capsaicin
Chemical in chili peppers causing burning sensation.
TRPV1
Ion channel activated by heat and capsaicin.
Receptive Field
Area affecting a sensory neuron's firing rate.
Sensory Cortex
Brain area processing sensory information.
Primary Sensory Cortex
Cortex dedicated to specific sensory modalities.
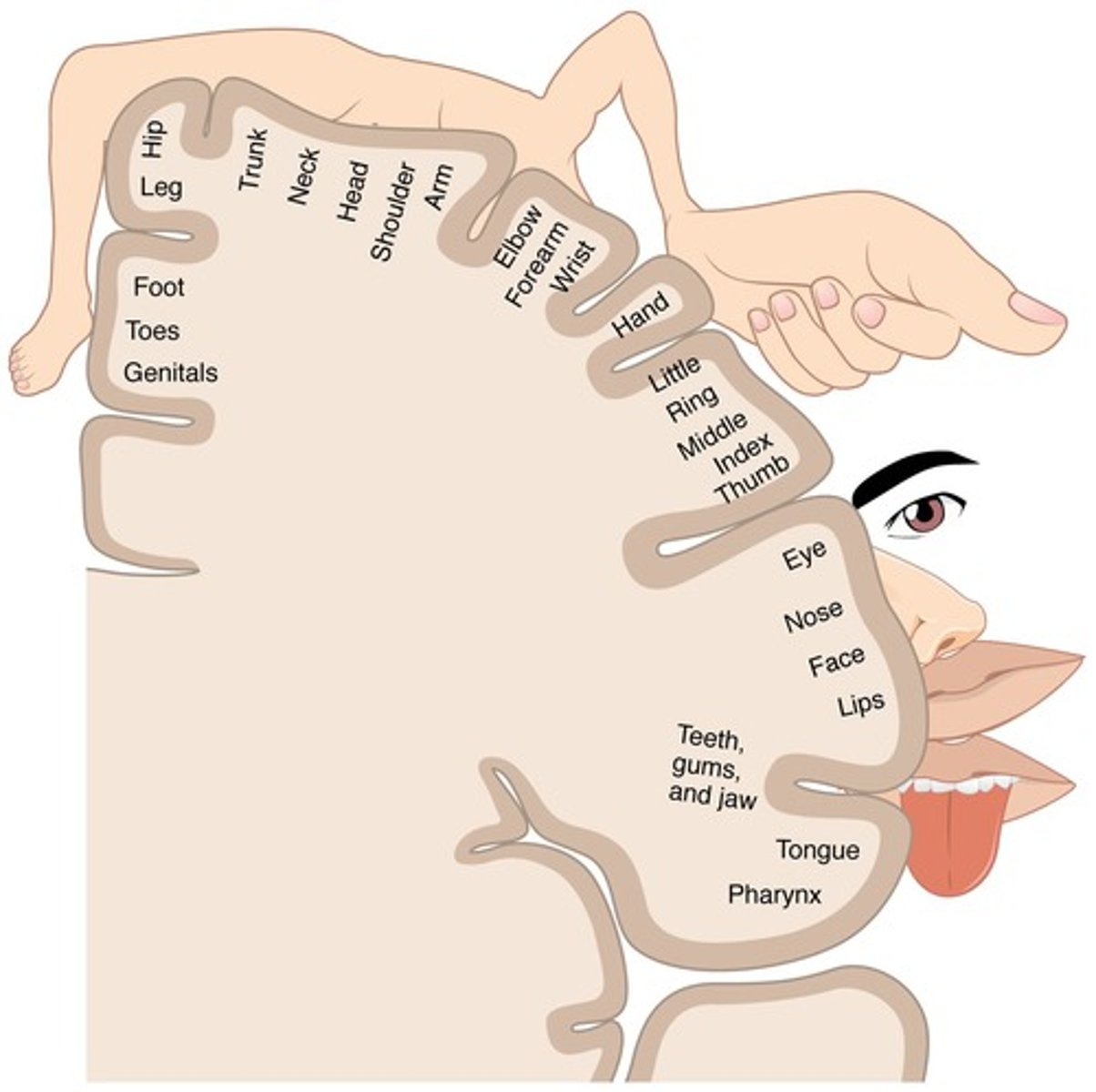
Sensory Homunculus
Map of body representation in sensory cortex.
Motor Pathway
Neural pathways controlling muscle movement.
Motor Plan
Set of commands for muscle actions.
Electromyography (EMG)
Records electrical activity of muscles.
Proprioception
Awareness of body position and movement.
Muscle Spindle
Receptor responding to muscle stretch.
Golgi Tendon Organs
Receptors sensitive to muscle tension.
Pyramidal System
Pathway controlling voluntary muscle movements.
Extrapyramidal System
Pathway controlling involuntary muscle movements.
EPSPs
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials in neurons.
Adaptation
Decrease in receptor response to constant stimuli.
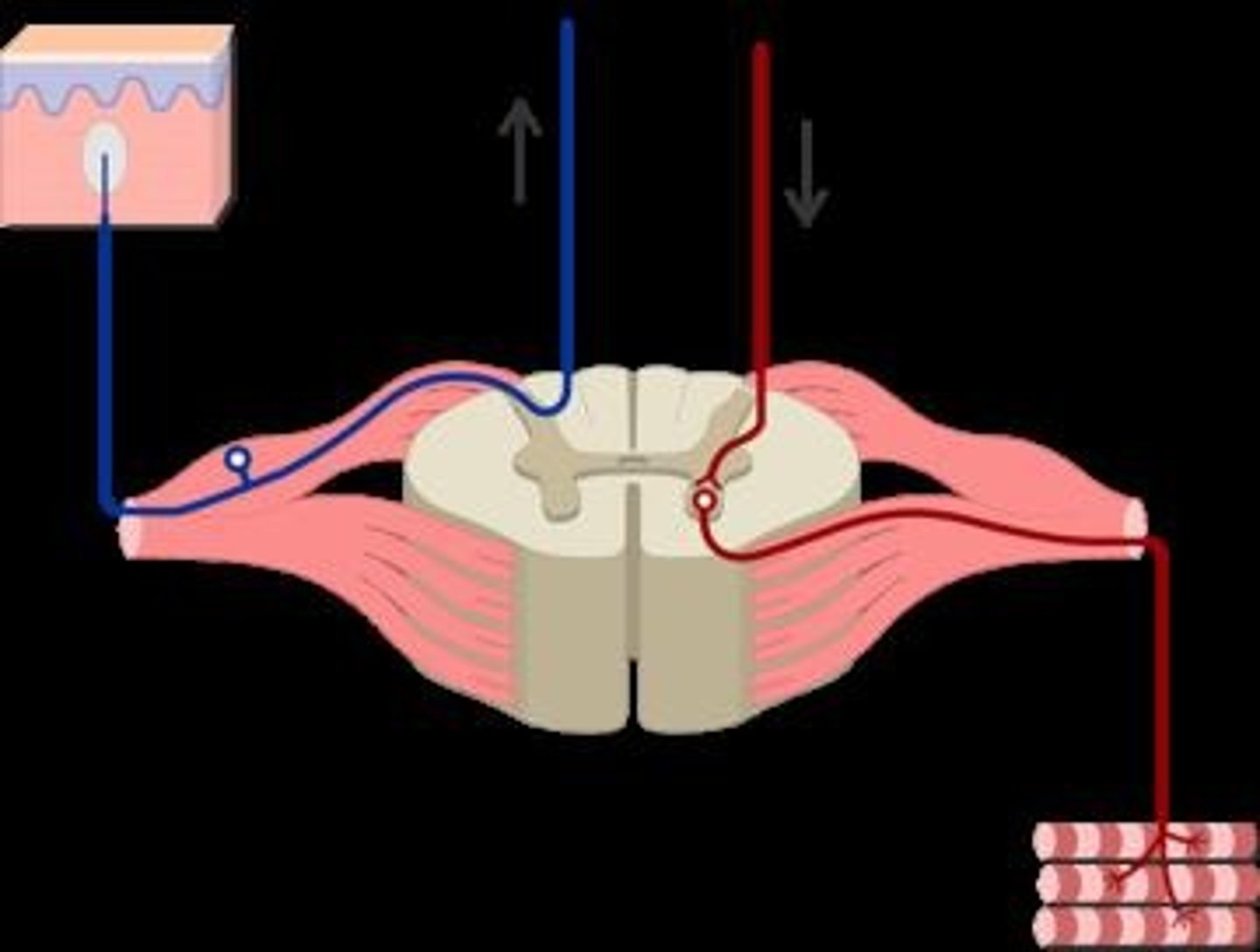
Pain Withdrawal Reflex
Immediate reaction to painful stimuli.
Neuropathic Pain
Chronic pain without tissue damage.
Opiate Drugs
Medications that reduce pain perception.
Epidural Injections
Direct delivery of pain relief into spinal cord.
Cognitive Strategies
Mental techniques to cope with pain.
Acupuncture
Pain relief technique using needles.
Endorphins
Natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body.
Inflammation
Body's response to injury causing pain.
Thermal Pain
Pain caused by extreme temperature changes.
Chronic Pain
Long-lasting pain affecting daily life.
Acute Pain
Short-term pain signaling immediate harm.
Social Communication of Pain
Nonverbal cues indicating pain to others.
Mirror Therapy
Visual feedback technique for phantom limb pain.
Burning Sensation
Sensation caused by capsaicin activation.
Endogenous Opioid System
Body's natural pain relief mechanism.
Action Potential (AP)
Electrical signal transmitting information in neurons.
Intensity Encoding
Representation of stimulus strength by AP frequency.
Sensory Adaptation
Decreased response to unchanging stimuli.
Nerve Fibers
Axons transmitting sensory information to the brain.
Dorsal Horns
Spinal cord area receiving sensory input.
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter enhancing pain signal transmission.
Cognitive Pain Relief
Using mental techniques to alleviate pain.
Pain Networks
Brain areas involved in processing pain.
Motor Feedback
Sensory information guiding muscle movements.