Light and Sound
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the thin lens formula?
“1/f = 1/di + 1/do”
f = focal length of the lens
do = object distance (from the lens)
di = image distance (from the lens)
How is fraction the same as a ratio?
Yes! A fraction represents a ratio — it compares two quantities:
a/b = a:b
What is the relationship between wave speed, wavelength, and period?
"Waves travel: Length over Time!"
(Think: wavelength ÷ period)
What is myopia, and where are light rays focused?
Myopia (nearsightedness) is a condition where distant objects appear blurry because light rays are focused in front of the retina.
✅ Near objects can still be seen clearly.
❌ Distant objects are blurry.
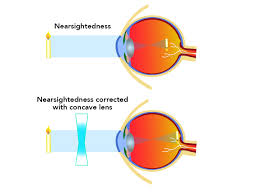
How is myopia (nearsightedness) corrected?
Myopia is corrected using a divergent lens (also called a concave lens).
This lens spreads out incoming light rays so they focus on the retina, rather than in front of it.
Allows distant objects to appear clear again.
What is a diverging lens and how does it affect light?
A diverging lens, or concave lens, is a lens that spreads out (diverges) incoming parallel light rays.
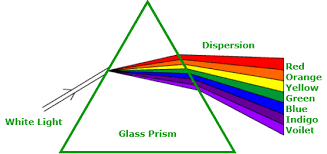
What is dispersion in the context of waves (especially light)?
"Different colors, different speeds—light splits like a deck of cards!"
How does the frequency of light relate to its index of refraction and refraction amount?
Light with a higher frequency (shorter wavelength, like violet or blue) has a higher index of refraction in a material and therefore bends (refracts) more than lower-frequency light (like red).
What is chromatic aberration and what causes it?
Chromatic aberration is a type of optical distortion in lenses where different colors of light do not focus at the same point, causing blurry or color-fringed edges in images.
What is the relationship between a lens's power and its focal length?
“Fewer meters, more power!”
(Shorter focal length = stronger lens)
The power (P) of a lens is the inverse of its focal length (f) in meters:
P = 1/f
What is a diopter, and how is it defined?
“Diopters are just meters flipped!”
A diopter (D) is the unit of lens power, defined as the inverse of the focal length in meters:
1 diopter = 1/meter
When is optical power positive or negative?
“Converging = Positive power, Diverging = Negative power”
How do you find the combined optical power of multiple lenses in a system?
In a multi-lens system (with lenses placed close together), the total power is the sum of the individual powers:
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3 +…
How does air temperature affect the speed of sound?
“Heat up the air, sound gets there!”
“Cool it down, waves slow down.”