cc1 - chemical elements are joined to form biological compounds
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is an ion?
a charged particle
What is an element?
A substance containing a singular type of atom
What is a compound?
two or more elements chemically combined
What does an organic compound contain?
contains both carbon and hydrogen (can contain others too) e.g. C6H12O6
What does inorganic compounds contain?
does not contain BOTH carbon and hydrogen e.g. H2O
saturated
compounds in which there is a single bond present between two carbon atoms
unsaturated
compound that contains at least one double carbon to carbon bond
What is the role of calcium?
strengthen bones and teeth in animals
strengthens cell walls in plants
role of magnesium ion
a part of chlorophyll
role of iron ion
component of haemoglobin
role of phosphate ion
energy storage, structural integrity, and metabolic processes, key component of ATP
dipolar
an uneven distribution of charge over the molecule
hydrogen bonds
weak forces of attraction between and reliably positive and negative molecule
metabolism
all the reactions occurring in a cell/organism
Why is water is a good solvent and what’s the significance?
because its a dipolar molecule so it can attract charged particles and seperate them
significance: allows transportation in blood and xylem, allows reactions to occur in solution of cells
Why is water being a metabolite significant?
takes part in chemical reactions in organisms
significance: photosynthesis and respiration require water
How are water molecules are cohesive and what’s the significance?
there are hydrogen bonds between water molecules
significance: surface tension creates habitat for pond skaters, in xylem water is pulled up as an unbroken column
How is H2O solid is less dense than H2O liquid and what’s the significance?
because the particles are further apart
significance: ice floats in a pond insulating the water below, provides buoyancy
Why does water has a high specific heat capacity and what’s the significance?
hydrogen bonds makes it hard to increase kinetic energy
significance: aquatic habitats experience a less extreme range of temps than terrestrial, animals and birds are 2/3 water meaning maintaining a regular body temp is easier
Why is waters specific latent heat of vaporisation being high significant?
means lots of energy required to overcome hydrogen bonds between molecules
significance: sweating has a cooling effect on skin by evaporation, transpiration has a cooling effect in plants
What’s the significance of water being transparent
significance: aquatic plants can photosynthesise in water because light passes through cells to reach chloroplasts
What are structural isomers
molecules with the same molecular formula but with different arrangements of their atoms
What are monosaccharides
single sugars, named according to the number of carbon atoms in the molecule
3 types of monosaccharides
trioses, pentoses and hexoses
What are disaccharides
sugars made from 2 monosaccharite units
what type of reaction forms disaccharites
condesation reaction (reverse is hydrolysis)
forms a glycoside bond between OH groups
maltose components and role
alpha glucose + alpha glucose
importance: intermediate in starch digestion
sucrose components and role
alpha glucose + fructose
significance: transported in phloem of plants
lactose components and role
beta glucose + galactose
energy source in milk for young mammals
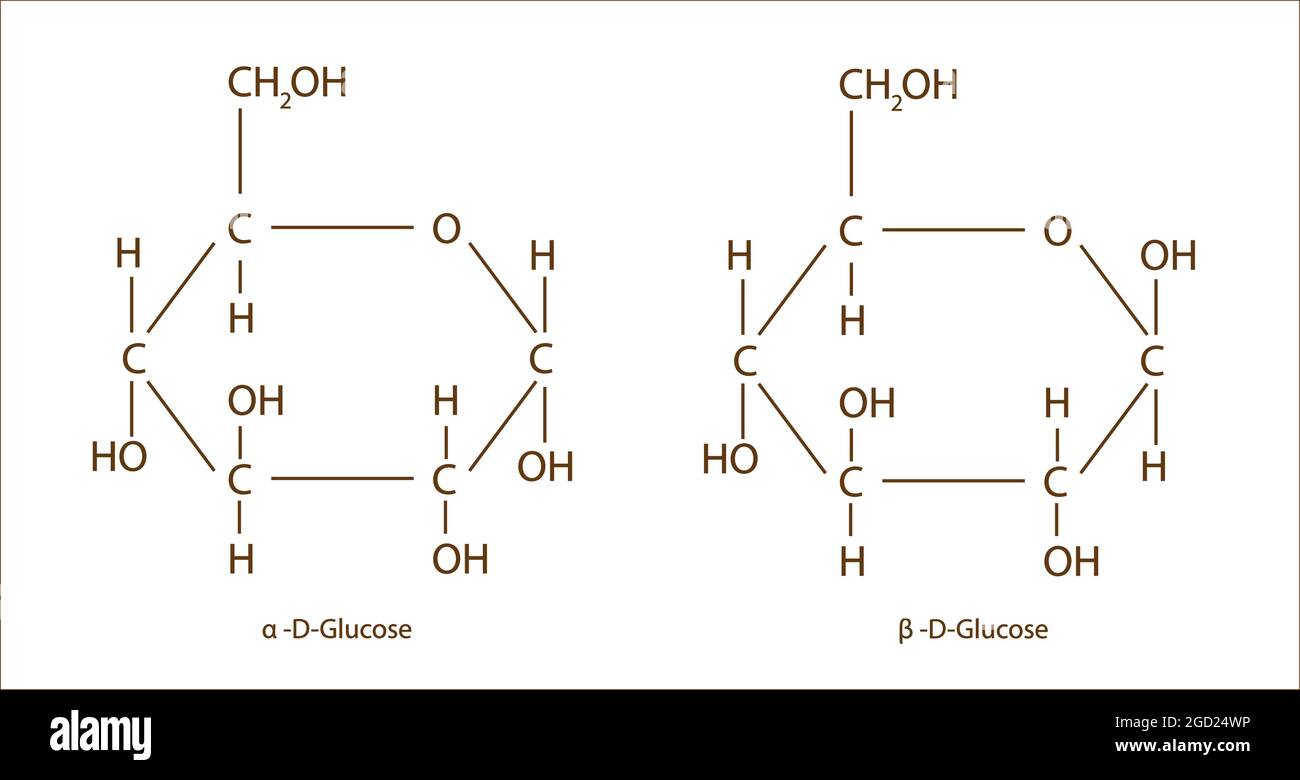
alpha and beta glucose structure
storage polysaccharides structure
folded shape to give a compact molecule
structural polysaccharides
coiled shape or straight chained
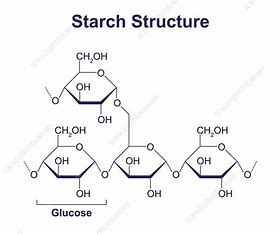
starch
storage polysaccharide, main carb source in plants, mixture of amylose and amylopectin compounds, compact - lots of energy stored and can easily be converted to glucose for energy
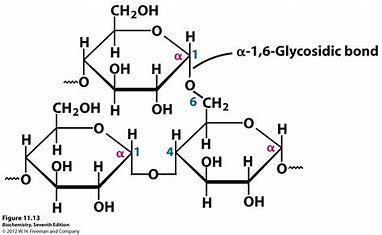
glycogen
storage polysaccharide, only carb store in animals, similar structure to amylopectin, provides rapid energy when needed and regulates blood sugar levels
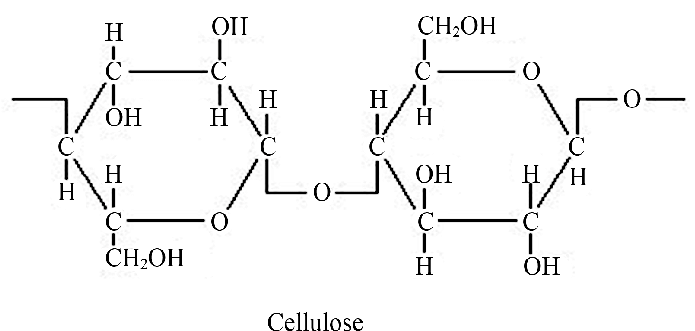
what is cellulose?
A structural polysaccharide, most abundant organic molecule in plant cell walls. It forms a strong, layered structure that allows water and solutes to enter.
chitin
structural polysaccharide, found in exoskeleton of insects and fungal cell walls, structure resembles cellulose with long chains of linked monomers - cross linked with hydrogen bonds, strong, waterproof and lightweight
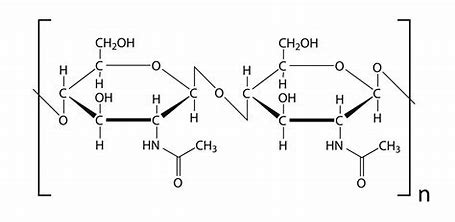
reducing sugars
act as a reducing agent in chemical reactions
all monosaccharides and some disaccharides
galactose, glucose, fructose, maltose, lactose
non-reducing sugars
do not act as a reducing agent in chemical reactions
includes most disaccharides and simple polysaccharides
sucrose
difference in polysaccharide to monosaccharide
polysaccharides are insoluble and not sweet to taste, monosaccharides are soluble and sweet
structural isomers of glucose
alpha glucose, beta glucose, fructose and galactose
What are amino acids?
Building blocks of proteins, contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a distinctive side chain. They bond through condensation reactions, forming peptide bonds.
peptide bond
bond formed between the carbon and nitrogen when amino acids join
primary protein structure
straight chain of amino acids, only peptide bonds present, depends on type, number and sequence of amino acids
secondary protein structure
folding of the polypeptide chain, hydrogen bonds present formed between the N-H of one peptide bond and the C=0 of another, two types: alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
alpha helix - secondary protein structure
coiled structure held in place by hydrogen bonds, many weak bonds make the helix stable
beta pleated sheet - secondary protein structure
occur in polypeptide chains where sections run in parallel, many weak bonds make molecule strong
tertiary protein structure
further 3D folding of the secondary structure, forms a spherical and compact shape, gives a protein its complex and unique shape, other bonds present: disulphide bridge, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions
quaternary protein structure
large proteins that contain 2 or more polypeptide chains, e.g. haemoglobin has 4, same bonds as tertiary, tertiary structures interact to form quaternary
globular proteins
have a metabolic role, are compact and spherical, tertiary/quaternary structure, soluble, stability depends on temperature and pH level, very repetitive amino acid sequence, e.g. haemoglobin, antibodies, lysozomes and enzymes
fibrous proteins
have a structural role, has a rope-like structure with long fibres, secondary or occasionally quaternary, insoluble, very stable, repetitive sequences, e.g. keratin, collagen and elastin
hemoglobin
in red blood cells, respiratory pigment that binds to oxygen, primary structure pf 4 polypeptide chains (2 alpha and 2 beta), shape maintained by hydrophobic interactions, contains an iron ion (fe2+) in the haem group of each polypeptide chain
collagen
thousands of collagen molecules cross-link to form fibres , repetitive sequences of glycine, proline and hydroxyproline, hydrogen bonds form between chains giving great tensile strength and resistance to stretching
what are lipids made up of and how are they made
made up of fatty acids (contains carboxyl group COOH) and an alcohol that join via a condensation reaction, they are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
the roles of lipids
can release and store twice as much energy - useful in plants and animals (especially desert), useful insulator of heat and electricity, steroids (a complex lipid) form oestrogen, testosterone and cholesterol, they can protect animals and plants with their water repellence and shock absorbing layers, create membranes in cells
what does the hydrogen tail of lipids do?
determines properties such as insolubility in water, can vary in length
unsaturated fatty acid
contains one or more double carbon bonds C=C
saturated fatty acid
contains NO double carbon bonds
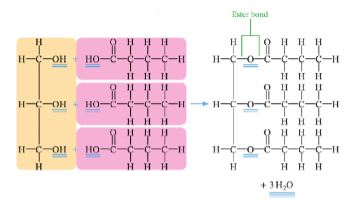
what is glycerol
an alcohol with 3 hydroxyl (OH) groups
how is triglyceride formed
the three OH groups in a glycerol molecule joins with three HO groups in three fatty acids through a condensation reaction
what are phospholipids and how are they formed?
they are lipids containing a phosphate group and they are joined by a condensation reaction between a glycerol with fatty acids and phosphoric acid
structure of phospholipids
a strongly polarised, hydrophilic head with two fatty acid, non-polar hydrophobic tails. they form a double or bilayer
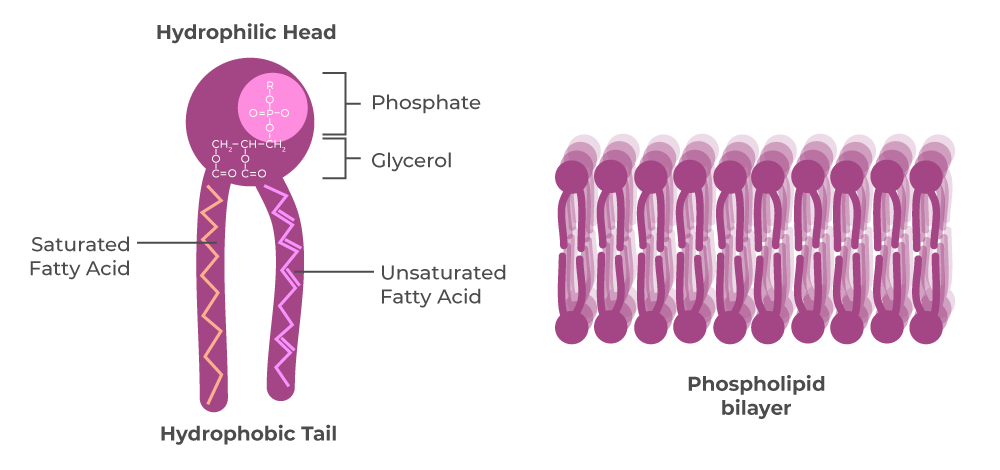
hydrophillic
attracted to water
hydrophobic
repels water
reducing sugars food test
benedict reagent, heat, colour change from green to orange to brick red if positive
non-reducing sugars food test
hydrochloric acid, heat, dilute sodium hydroxide, re-test with benedict reagent, colour change from green to orange to brick red if positive
protein food test
biuret solution, mix, purple if positive
lipid food test
ethanol, mix, add to water, cloudy white emulsion if positive
starch food test
iodine solution, add to sample, blue-black or red/purple colour if positive
Condensation reaction
Forms bonds, producing water
Hydrolysis reaction
Additional of water to break bonds
Where do glycosidic bonds form
Between hexoses in the production of disaccharides and monosaccharides
Where do ester bonds form?
Between glycerol and fatty acids in the production of triglycerides and phospholipids