AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 4
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
State
a politically defined territory with established borders, a permanent population, and a sovereign government
sovereignty
the political authority of a state to govern itself within its own territory, meaning it has the ultimate power to make decisions without external interference from other countries or entities; essentially, the right to control what happens within its borders
nation
a group of people who share a common culture, language, history, and sense of identity, often identifying with a particular territory as their homeland, essentially forming a cohesive group distinct from other populations
Nation-state
a political entity where the boundaries of a state (a defined territory with a government) closely align with the cultural boundaries of a single nation (a group of people sharing a common identity)
Multi-nation state
a sovereign state where more than one distinct nation or ethnic group resides within its borders
Multi-state nation
a group of people sharing a common culture and identity, that extends across the borders of multiple states, essentially inhabiting more than one country
Stateless nation
a group of people with a shared culture and identity who do not have their own sovereign state
Semi-autonomous regions
a geographical area within a larger state that has a moderate (some) degree of self-governance
ex: teenagers
Autonomous region
a geographically defined area within a larger state that has a degree of self-governance
ex: adults
Self-determination
the principle that a group of people, usually sharing a distinct cultural identity, have the right to decide their own political status and form their own government
Political power
the ability of a state or government to influence or control the behavior of people and institutions within a defined territory
Territoriality
the act of a group or individual claiming, defining, and defending a specific geographic space as their own
Neo-colonialism
the continued economic dependence of former colonies on their previous colonial powers, even after gaining political independence
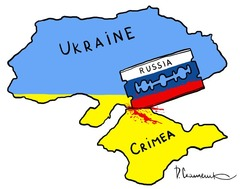
shatterbelts
an area of instability located between regions with opposing political and cultural values
ex: Ukraine— the Eastern and Western areas have different views and linguistic divides throughout the country between speaking Russian and Ukrainian.
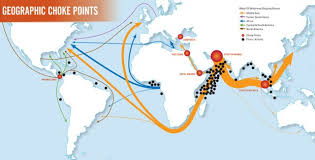
Chokepoints
a geographically narrow passageway, like a strait, mountain pass, or canal, where the movement of people and goods can be easily restricted or controlled, often holding significant strategic importance due to the potential to disrupt trade or military operations if blocked by a controlling power
ex: Strait of Malacca
Relic boundary
a former political boundary that no longer functions but still leaves a visible impact on the cultural landscape
Superimposed boundary
a political border drawn by an outside power that completely ignores the existing cultural, ethnic, or linguistic divisions of the people living in that area, often leading to conflict as it disregards pre-existing social patterns
Antecedent boundary
a political border established before a region is significantly populated or developed
Subsequent boundary
a political border that is established after a region is already settled and developed
Geometric boundary
a political border drawn as a straight line on a map, usually following lines of latitude and longitude, without regard to physical or cultural features on the ground, essentially creating an artificial boundary that may not align with existing populations or landscapes
Consequent boundary
a political boundary that is drawn to align with existing cultural, ethnic, or linguistic differences within a region
median line principle
the principle that a nation's maritime boundaries should conform to a median-line equidistant from the shores of neighboring nation-states
prorupted state
a state that has a primary body of territory that comprises most of the state, but that also has a long extension that can dramatically increase the territorial power and significance of the country
ex: Thailand
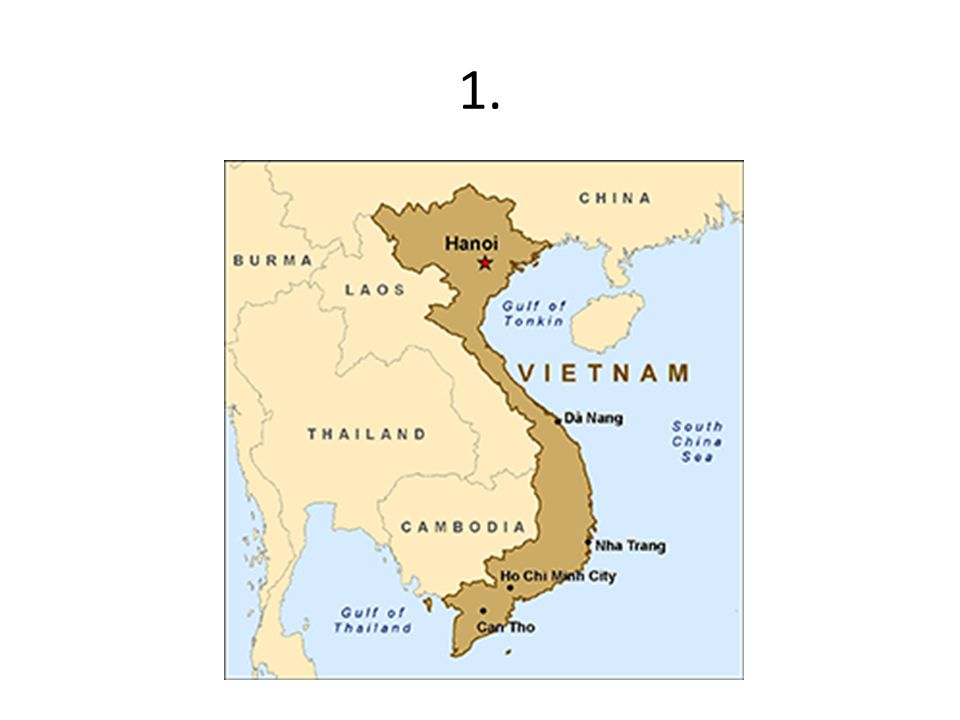
elongated state
countries that are significantly longer in one dimension than they are wide
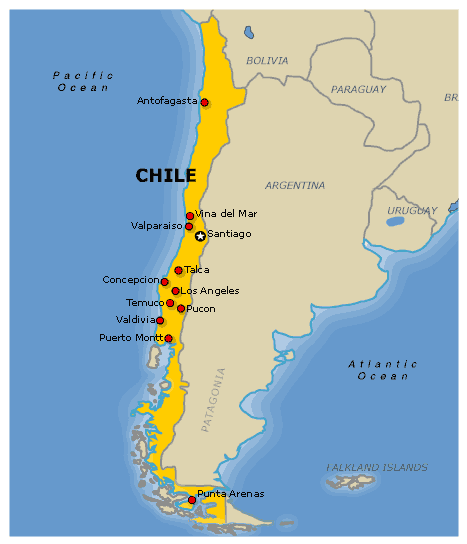
compact state
countries where the distance from the center to any boundary does not vary significantly, creating a roughly circular shape.
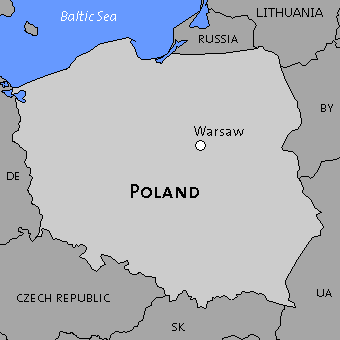
fragmented state
a state whose territory is physically divided into several distinct segments.
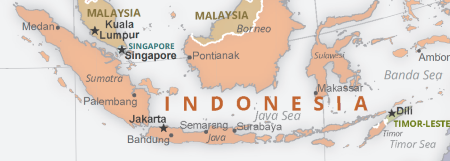
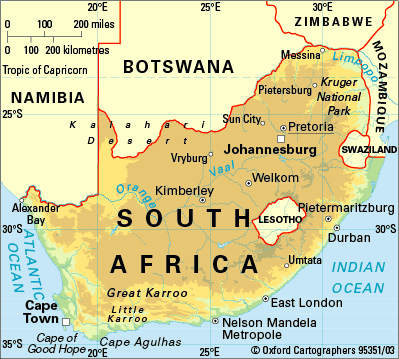
perforated state
a state that completely surrounds another state.
ex: Italy, South Africa
gerymandering
the practice of manipulating electoral district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group.
can carve up entire states
Basically a political land grab
Unitary states
a state where laws are administered uniformly by one central government.
ex: France, Japan, the UK
federal states
a system of government where power is shared (in various arrangements) between a centralized government and various regional authorities.
ex: the United States (national govt. and state govts.)
devolution
The movement of power from the central government to regional governments within the state or breakup of a large state (balkanization) into several independent ones
balkanization
The fragmentation of a region into smaller, often hostile, political units.
The term comes from the Balkan Peninsula of Europe
supranationalism
the process of nation states organizing politically and economically into one organization or alliance.
irredentism
a political movement that is strongly tied to nationalism. Intends to reunite a nation or reclaim a lost territory