ANSC 424- 4.1 Food Intake and Pancreas
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what were the different theories about the regulation of food intake?
Lipostatic hypothesis
Glucostatic hypothesis
what is the lipostatic hypothesis?
Kennedy 1953- adipose tissue produces specific lipostatic factor
what is the glucostatic hypothesis
Mayer and Thomase 1967- fluctuations of glucose/ glycemia lead to stimulation/inihibtion of food intake
what actually regulates food intake
complex homeostatic process regulated by many endocrine and metabolic factors
—> and other factors: visual, olfactory, taste sensation, emotions, memory and life conditions
what kind of hormones regulate food intake
gastrointestinal hormones
what hormones are produced by the stomach and their function?
ghrelin: hunger, growth hormone release
gastrin: acid secretion
what hormones are produced by the duodenum of SI and their function?
cholescustikinin ( CCK): gall bladder contraction, GI motility, pancreatic exocrine secretion
secretin: pancreatic exocrine secretion
GIP: incretin acvtivity
Motilin: GI motility
wha is incretin activity?
modulating glucose homeostatisis by regulating insulin and glucagon
what hormones are found in the pancreas and their function
insulin and glucagon
pancreatic polypeptide: gastric motility, satiation
amylin: glucose homeostatisis
what hormones are found in the colon and their function
GLP1: incretin activity, satiation
GLP2: GI motility and growth
oxyntomodulin: satiation , acid secretion
PYY: satiation
what nervous systems help control food intake?
hypothalamus: chronic and long term food intake
brain stem: food intake on acute regulation
what nuclei control food intake?
VMH: satiety center
lateral hypothalamus (LH) nucleus: hunger center ( lesions lead to anorexia)
SCN: regualtes TIMING of food intake
PVN and ARC: integration of signals from HPT and HPA axes
Vagus: satiety signals to the brain stem after ingestion of a meal ( neural regulation)
Nucleus tractus solitarius and PVN: connection of brainstem with hypothalamus (serotoninergic neurons)
what is the role of arcuate nucleus on food intake?
Arcuate nucleus is the center of energy homeostasis regulation - food intake, energy expenditure and nutrient partitioning
what two main types of neurons are found in ARC help control food intake
alpha- MSH
NPY neuron peptide Y
neurons receive hormonal input from peripheral organs
what is the function of alpha- MSH
⍺-MSH neurons regulate neurons that stimulate anorexia and catabolism (VMH)
—> STOP eating and energy metabolism
act upon the VMH
what is the function of NPY neurons
NPY neurons stimulate orexia and anabolism (LH)
food intake and store energy!
what is the only non anorexigenic hormone
ghrelin ( promotes eating orexia)
what is the endocannabinoids system?
Endocannabinoids: Anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
what are the receptors associated with endocannabinoids
Receptors: CB1 and CB2 – GPCRs with G⍺i ( inhibitory of cAMP)
produced from the body receptor:
explain how the endocannabinoids pathway
promote feeding
increased absorption
metabolism
storage
kind of works like grehlin
what are the effects of endocannabinoids on food intake metabolism
treatment: CB1 receptor antagonist
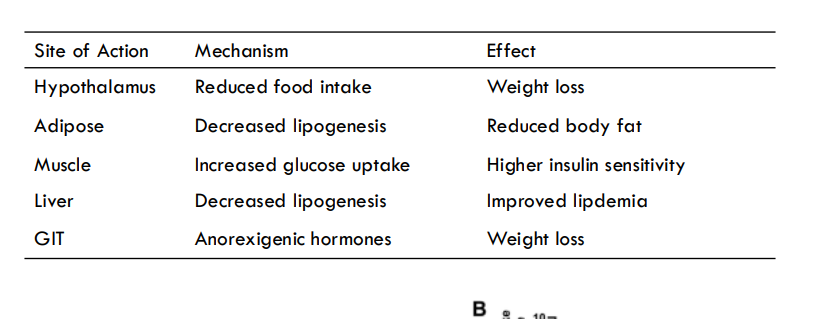
effects: reduced food intake, decreased lipogenesis, glucose uptake, lipogenesis, anorexigenic hormones
what are the two parts of the pancreas?
endocrine
exocrine
what are the cells found in exocrine pancreas
main function is just producing digestion enzymes
Acinar cells: Secretion of digestive enzymes (proteases, amylase, lipase)
Duct cells: Secretion of NaHCO3 ( sodium bicarbonate neutralize stomach acid)
—> Secreted into duodenum
what found in encodrine pancreas
Islets of langerhans
what are the different cell types in Islets of Langerhans?
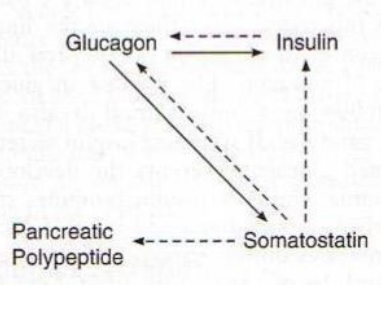
❖ α-cells: Glucagon
❖ β-cells: Insulin
❖ 𝝳-cells: Somatostatin
❖ ε-cell: Ghrelin
❖ F-cells (PP cells): Pancreatic Polypeptide
❖ Hormones secreted into blood
what are charactersitics of islets of langerhans
heterogeneous
highly vascularized
blood first supplies centrally located in beta cells
travels to peripheral alpha and beta cells
how do beta cells work
work together!
cell proliferation of b-cells?
Proliferation of β cells is minimal after 5 years of age
❖ Average lifespan of β cells – 25 years
❖ Neogenic niche at the periphery of islets – immature β cells and Transdifferentiation of ⍺ and 𝝳 cells under extreme beta-cell loss
explain relation of the different hormones in pancrease
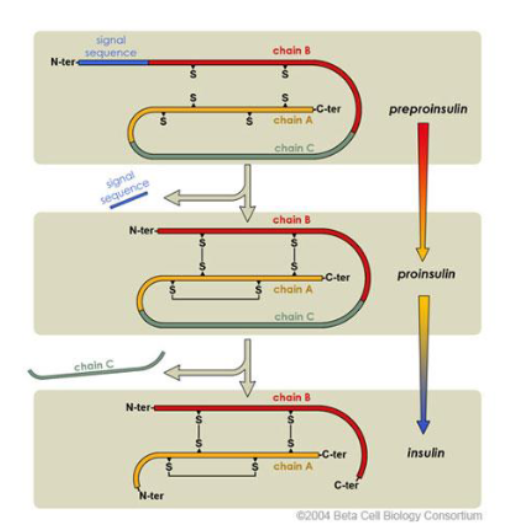
describe structure of insulin
51 a.a. - 2 peptide chains connected by 2 disulphide bridges
what metabolizes insulin
insulin metabolized—> liver
but c-peptide metabolized in kidney
what should be used to measure insulin secretion
C-peptide
how is glucagon produced
glucagon also produced as preproglucagon processed to proglucagon to glucagon
❖ single chain (29 a.a.)
what do beta cells contain
5000-800 granules
—> Half-life – about 5 days; younger granules are deeper in the cytoplasm, but more mobile than the older granules
what happens to older granules
Older granules are degraded intracellularly – intracellular degradation of insulin!
how are insulin stabilized in granules
organized as HEXAMERS stabilized by calcium and zinc
what is the main stimulator of insulin synthesis and release
GLUCOSE
how does glucose regulate insulin secretion in beta cells
glucose enters beta cells through GLUT2
metabolized through glycolysis
first enzyme glucokinase
end product of glycolysis—> ATP
when high ATP to ADP ratio, inhibits the ATP sensitive potassium channel
exotocysis of K+ions decreased, decrease negativity of cell
depolarize the cell
stimulate voltage Ca channel
increase Ca in cell
exocytosis of insulin granules
what is the main glucose sensor in beta cells
glucokinase
what transporters regulate glucose
GLUT2 and 4
explain steps of release of insulin from beta cells
Glucose enters the β-cell through a special transporter called GLUT2.
Glucose is broken down via aerobic glycolysis, increasing the ATP/ADP ratio in the cell.
The rise in ATP closes potassium (K⁺) channels, causing less K⁺ to leave the cell and depolarizing the membrane.
This depolarization opens calcium (Ca²⁺) channels, allowing Ca²⁺ to enter the cell.
The increased Ca²⁺ inside the cell triggers insulin release (exocytosis of insulin-containing granules).
Calcium-activated potassium channels open, helping the membrane repolarize (reset for the next signal).
Byproducts of glucose metabolism (like fatty acids and succinate) support insulin release and insulin production.
Hormones like GLP-1 (from the gut) bind to their receptors and boost insulin release by increasing cAMP, which helps enhance signaling and exocytosis.
what are the neural regulations of insulin secretion
Vagus nerve ( longest nerve in our body)
—> acts as a sensory neuron and motor neuron ( provide and receive signals from peripheral organs)
explain main function of vagus nerve
Main neuronal coordinator of appetite control, digestion and metabolism
Release of acetylcholine (cholinergic) in the pancreas stimulates insulin release
POSITIVE REGULATOR OF INSULIN SECRETION