Protein Synthesis and Protein Structures
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the 2 main steps in protein synthesis?
transcription and translation
Where does protein synthesis occur?
In the nucleus and the cytoplasm
What are the three types of RNA for protein synthesis?
mRNA (messenger), tRNA(transfer), rRNA(ribosomal)
What is the purpose of mRNA
To provide a DNA copy that can move from the nucleus into the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. mRNA uses complementary codes from the DNA to send messages to create proteins.
Where is mRNA found?
mRNA is originally found in the nucleus but can travel to ribosomes inside the cytoplasm.
What are codons?
They are mRNA triplets that code for an amino acid. They are read in threes and are codes for specific amino acids.
Codons are always read in...
Threes
How many types of amino acids are there?
20
What happens in Transcription?
mRNA is created by transcribing (writes/prints out) the DNA's code. This happens when DNA Polymerase (not helicase) temporarily unzips DNA and adds complementary RNA nucleotides to the growing mRNA strand. Once the mRNA strand is completed, it leaves the nucleus (exits via nuclear pores).
What types of RNA does translation use?
mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
What happens in translation?
Translation is a process in which the mRNA
that was manufactured during transcription is
translated into an amino acid sequence
(proteins)
What are anticodons?
A set of three nucleotide bases found on the tRNA. It is complementary/opposite to the codons on the mRNA and helps identify/create their corresponding amino acids.
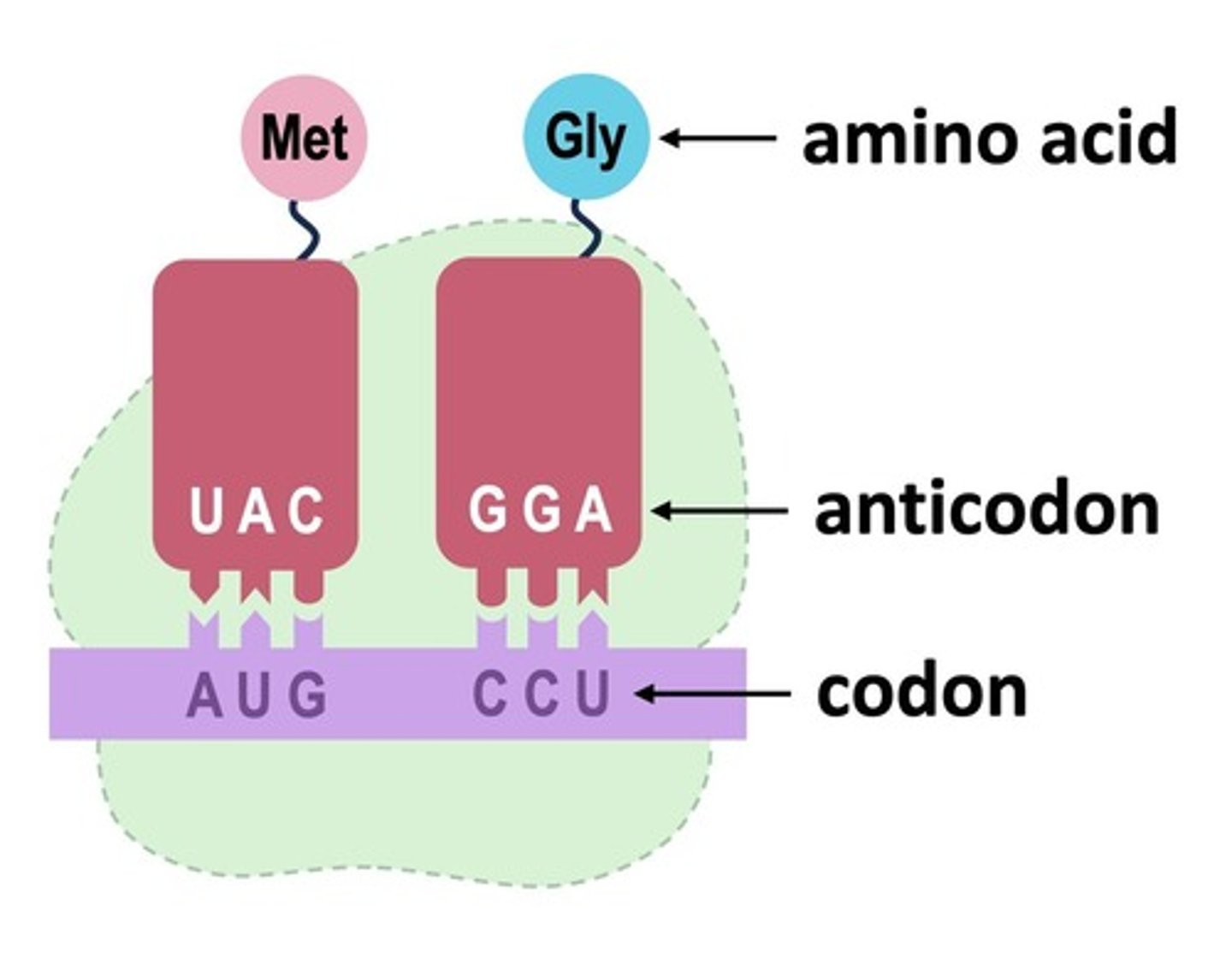
Where do tRNA send their amino acids?
to the ribosomes
How many possible bases are there for amino acids?
64
What is the Start codon?
AUG (like the gun)

What are the stop codons?
UAA, UAG, UGA (sounds like cavemen)

What are the four main protein structures?
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
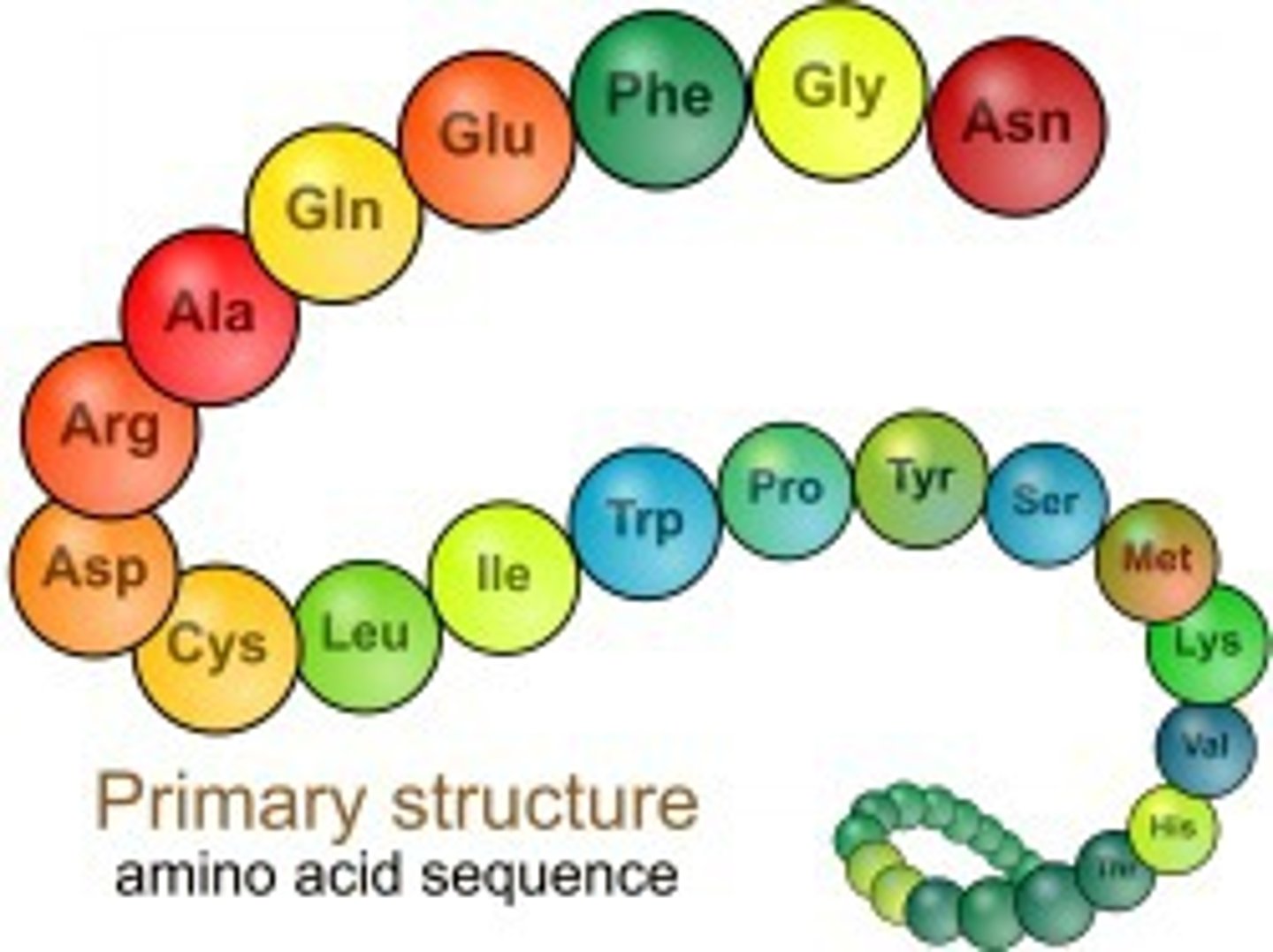
What is a primary structure?
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
What is a secondary structure?
-alpha helix or beta pleated sheet (in certain areas of the polypeptide chain, repeated coil or fold)
-Interactions between nonconsecutive amino acids
-are maintained by HYDROGEN BONDS

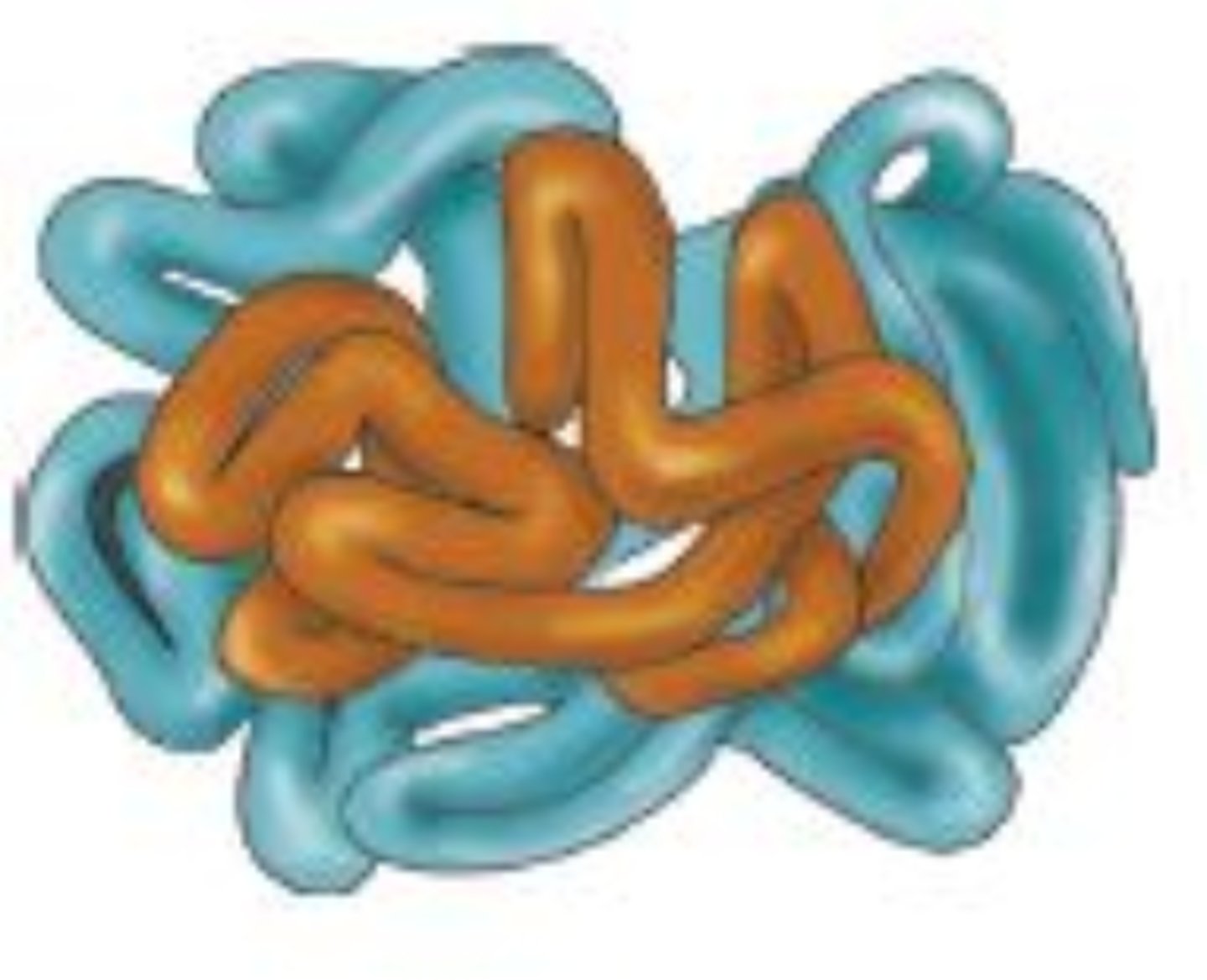
What is a tertiary structure?
The interaction between R groups. These are the hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions which cause the polypeptide chain to become closer or repel other amino acids, resulting in a complex, 3D shape.

What is quaternary structure?
multiple polypeptide chains
