the animal kingdom - vertebrates (#15)
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Cambrian period
during this period, Earth’s ocean was teemed with various invertebrate life forms including early vertebrate ancestor Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa
Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa
early vertrebrate ancestor during the Cambrian period;
no protective spikes/appendages & glides through water
phylum Chordata
phylum vertebrates belong to which includes bilaterally symmetrical animals;
under clade deuterostome;
cephalocordata & urochordata
deuterostome
bilaterian animals which form their anus before mouth
notochord,
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
pharyngeal slits/clefts
muscular, post-anal tail
4 key characs. of phylum Chordata
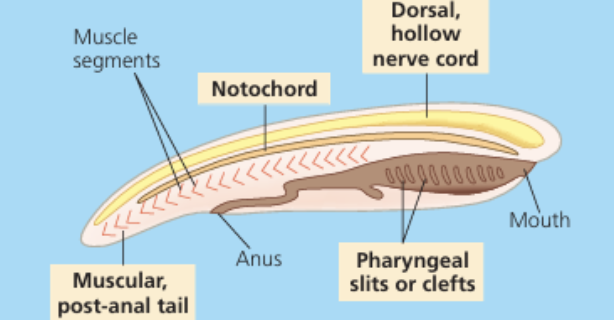
notochord
4 KEY CHARACS. OF PHYLUM CHORDATA:
flexible rod for structural support;
between digestive tube & nerve chord;
provides skeletal support throughout most of the chordate’s length;
becomes spinal cord
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
4 KEY CHARACS. OF PHYLUM CHORDATA:
nerve cord of the embryo develops to the CNS (brain & spinal cord);
developed from a plate of ectoderm that rolls into a tube
pharyngeal slits or clefts
4 KEY CHARACS. OF PHYLUM CHORDATA:
openings used for filter-feeding or gas exchange;
allow water to exit body w/o passing through digestive tract;
extends from mouth to anus
muscular, post-anal tail
4 KEY CHARACS. OF PHYLUM CHORDATA:
tail extending beyond the digestive tract, aiding in movement;
contains skeletal elements & muscles;
helps propel aquatic species
cephalocordata (lancelets) & urochordata (tunicates)
2 groups of invertebrates
cephalocordata, lancelets
2 GROUPS OF INVERTEBRATES:
basal chordates that retain chordate characteristics (notochord) throughout life;
show segmentation & a swimming motion similar to fish;
start of chordates
(format: answer, common name)
urochordata, tunicates
2 GROUPS OF INVERTEBRATES:
exhibit chordate characteristics mainly in the larval stage;
undergo radical changes upon maturing
larva settles in a substrate & undergo radical metamorphosis
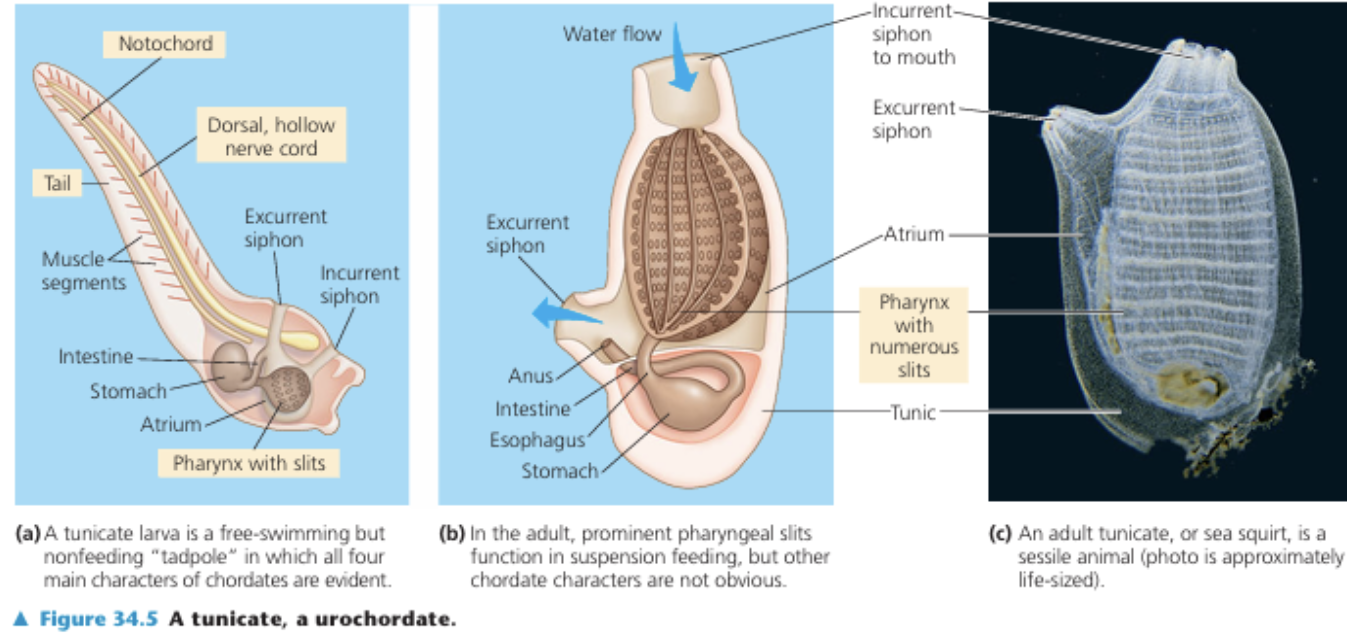
False; should be lancelets
TRUE OR FALSE:
Lancelets and tunicates are key to understanding vertebrate origins, with
tunicates closely resembling ancestral chordates.
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Genetic studies in tunicates reveal genes shared with vertebrates, suggesting early chordates had complex organ-related genes.
craniates
chordates that developed heads with brains, sensory organs, & skulls;
distinct traits include multiple sets of Hox genes & the neural crest, which forms various body structures;
hagfishes (class Myxini) & lampreys (Petromyzontida)
ex. Haikouella
Hox genes, neural crest
UNDER CRANIATES:
set of genes in craniates (helps in segmentation)
forms various body structures
(separate answers using comma)
hagfishes, Myxini
2 GROUPS OF CRANIATES:
basal invertebrates with cartilage-based skulls, no jaws, & slime glands for defense;
retain notochord in adulthood as a strong, flexible rod of cartilage;
small brain, eyes, ears, nasal opening;

True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Hagfishes have a nasal opening that connects with the pharynx.
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Vertebrate evolution included additional Hox gene duplications and the formation of a vertebral column.
lampreys, order Petromyzontida
2 GROUPS OF CRANIATES:
basal invertebrates with cartilage skeletons;
notochord persists as main axial skeleton in adult (same in hagfishes)
gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates)
means “jaw mouth”;
superclass which includes groups like sharks, fishes, amphibians, & mammals;
jaws likely evolved from skeletal supports of gill slits
(include more common name in answer)
lateral line system
aquatic gnathostomes possess _____ _____ _____ which is sensitive to water vibrations
chondrichthyes
3 GROUPS/SUPERCLASSES OF GNATHOSTOMES:
cartilage-based skeletons, streamlined for swimming;
repro. strategies: oviparous, ovoviviparous, viviparous
ex. sharks, rays, & relatives
oviparous
DIFFERENT REPRODUCTIVE STRATEGIES:
development of embryo within an egg outside the mother’s body
ovoviviparous
DIFFERENT REPRODUCTIVE STRATEGIES:
development of embryo inside an egg within the mother’s body until it hatches
DIFFERENT REPRODUCTIVE STRATEGIES:
development and nourishment of embryo is within the mother’s body; birth may be followed by a period of parental care
chondrichthyes, osteichthyes, tetrapods
3 groups of gnathostomes
class osteichthyes
3 GROUPS/SUPERCLASSES OF GNATHOSTOMES:
have ossified (bony) endoskeletons with a hard matrix of calcium phosphate;
most breathe through gills covered by an operculum, a protective bony flap;
us a swim bladder for buoyancy
class Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes)
calcium phosphate
UNDER OSTEICHTHYES:
they have an ossified (bony) endoskeletons with a hard matrix of this
operculum
UNDER OSTEICHTHYES:
protective bony flap that covers gills which most bony fishes breath through
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Almost all fishes have bony scales and are oviparous.
Actinopterygii
2 SUBCLASSES OF OSTEICHTHYES:
ray-finned fishes that have modifications in body form and fin structure which aid in maneuvering, defense, and other functions
ex. trout
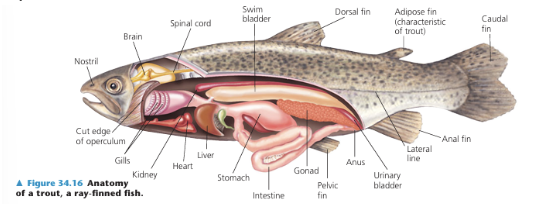
Sarcopterygii
2 SUBCLASSES OF OSTEICHTHYES:
lobe-finned fish that have rod-shaped bones surrounded by thick muscles in pectoral and pelvic fins;
many lived in brackish waters (ex. coastal wetlands) during the Devonian period;
some were gigantic predators with lobe-shaped teeth fossils the size of thumbs
Actinistia (Coelacanths) & Dipnoi (lungfishes)
class Actinistia, coelacanths
UNDER SARCOPTERYGII (LOBE-FINS):
once thought extinct, was rediscovered in 1938
class Dipnoi, lungfishes
UNDER SARCOPTERYGII (LOBE-FINS):
found in freshwater, evolved from ocean species;
breathe through both lungs & gills, surfacing to gulp air;
gills as main organs for gas exchange
False; lobed fins
TRUE OR FALSE:
Sarcopterygii likely used ray fins to swim and "walk" underwater across the substrate.
tetrapods
3 GROUPS/SUPERCLASSES OF GNATHOSTOMES:
evolved from lobe-fins around 365 million years ago;
have limbs with digits instead of fins, allowing movement on land;
early version of this group remain in water similar to amphibians;
has 4 appendages
feet with digits
UNDER SUPERCLASS OF TETRAPODS:
transmit muscle-generated forces to the ground
Tiktaalik
UNDER SUPERCLASS OF TETRAPODS:
fossil showing both fish and tetrapod traits
Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia
4 classes of tetrapods
Amphibia
4 CLASSES OF TETRAPODS:
many amphibians live both in water (early stages) and on land.
typically need water for breeding and have moist, permeable skin for gas exchange;
term derived from “both ways of life” (refers to frog life stages)
ex. salamanders, frogs, caecilians
Urodela/Caudata, Anura/Salientia, Apoda/Gymnophiona
3 ORDERS OF CLASS AMPHIBIA:
salamanders & newts
frogs & toads
caecilians that are legless and worm-like
(answer respectively)
reptiles, birds, mammals
3 classes that are part of the clade Amniotes
amniotes
adapted to land with the development of the amniotic egg (has specialized membranes);
shells protect eggs, unlike the shell-less eggs of amphibians;
use rib cage to ventilate lungs
warm, moist
Early amniotes were small predators living in _____, _____ environments.
amnion, chorion, yolk sac, allantois
4 specialized membranes of the amniotic egg
Reptilia
4 CLASSES OF TETRAPODS:
have keratin scales for protection and lay shelled eggs on land;
has lungs with extensive folding;
are ectothermic
early kinds (parareptiles) were herbivores;
3-chambered heart (2 atria & 1 ventricle) except for crocodilia (4)
Reptilia
4 CLASSES OF TETRAPODS:
simple teeth with no living tissue, strong and bony skeletons;
has feet with claws
ectothermic/poikilothermic
animals that absorb external heat as their main source of body heat;
associated with being cold-blooded
ex. reptiles, fish, amphibians, arthropods
diapsids
UNDER CLASS REPTILIA:
included lineages leading to lizards, snakes, & dinosaurs
lepidosaurs
UNDER CLASS REPTILIA:
one lineage includes lizards, snakes, and the ancient tuataras
Rynchocephalia, Squamata, Chelonia, Crocodilia
4 ORDERS OF CLASS REPTILIA:
tuatara
snakes & lizards
turtles & tortoises
alligators & crocodiles
UNDER ORDER SQUAMATA (REPTILIA):
evolved from legged lizards and retain vestigial pelvic bones
turtles
UNDER ORDER CHELONIA (REPTILIA):
boxlike shell fused to skeleton; may have evolved in stages;
fossil evidence suggests possible aquatic origins
crocodilians
UNDER ORDER CROCODILIA (REPTILIA):
evolved from small terrestrial quadrupeds to larger, aquatic animals;
use upturned nostrils to breathe while submerged
Aves (birds)
4 CLASSES OF TETRAPODS:
body covering: feathers
reproduction: internal through hard eggs with shell
breathing: lungs with bronchial tubes
temp.: endothermic;
has hollow bones, toothless beaks, & feathers
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Birds have extraembryonic membrane consisting of chorion, amnion, yolk sac, & allantois.
Mammalia
4 CLASSES OF TETRAPODS:
amniotes that have hair & mammary glands which produce milk;
endothermic/homeothermic & warm-blooded;
larger brains & diverse range of teeth
hair & fat layer under the skin
UNDER CLASS MAMMALIA:
these help mammals’ bodies to retain heat
monotremes
SUBPHYLUMS OF CLASS MAMMALIA:
lay eggs, have hair, & produce milk but lack nipples;
ancestral for amniotes & retain in most reptiles
ex. platypus & 4 species of echidnas (spiny anteaters)
marsupials
SUBPHYLUMS OF CLASS MAMMALIA:
possess a placenta, though less complex than eutherians;
live young complete development in a pouch
ex. kangaroos, koalas
eutherians (placental mammals)
SUBPHYLUMS OF CLASS MAMMALIA:
longer pregnancies, with young developing in the uterus attached to a complex placenta
primates
ORDER IN CLASS MAMMALIA:
earliest known kind were tree-dwellers who had adapted grasping hands/feet & forward-facing eyes;
digits have flat nails instead of narrow claws;
developed social behaviors and parental care
ex. lemurs, monkeys, apes, humans
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
The head of craniates consist of the brain at anterior end of the dorsal nerve cord, eyes, other sensory organs, & a skull.
jawless fish
earliest vertebrates that had a cranium but no vertebral column;
lived between 500-600 MYA
450-400 MYA
about ____ - ____ MYA the first bony fish with a complete vertebral column evolved;
False; amphibians were the first
TRUE OR FALSE:
First land vertebrates were reptiles.
Gnathostome jaws evolved by modification of the skeletal rods that had previously supported the anterior phrayngeal (gill) slits.
one hypothesis about gnathostomes
benthos
organisms on the seabed
ex. starfish, corals, crab
nekton
organisms that swim
ex. fish, squid, shrimp
plankton
organisms that float or drift on water surface
ex. algae, bacteria, & sea urchin, fish, crustacean larvae (like starfish larvae)
Class Insecta
SUBPHYLUMS OF ARTHROPODA:
6 legs
Class Arachnida
SUBPHYLUMS OF ARTHROPODA:
8 legs
Class Crustacea
SUBPHYLUMS OF ARTHROPODA:
10 or more legs
ex. crab, lobster, shrimp
Class Diplopoda
SUBPHYLUMS OF ARTHROPODA:
a.k.a. millipedes;
2 pairs of legs per segment
Class Chilopoda
SUBPHYLUMS OF ARTHROPODA:
a.k.a. centipedes;
1 pair of legs per segment