ALKENES
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What’re alkenes?
unsaturated hydrocarbons
general formula is CnH2n
arrangement of bonds around the C=C is planar and has a bond angle of 120
What type of bonds does the C=C double covalent bond contain?
one sigma bond
one pi bond
pi bonds are exposed and have high electron density
they’re vulnerable to attack by electrophiles
What is stereoisomerism?
have the same structural formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms
alkenes exhibit E-Z stereoisomerism due to restricted rotation about the C=C bond
When do stereoisomers arise?
when theres restricted rotation about the C=C double bond
when there are 2 different groups attached both ends of the double bonds
Why do alkenes attract electrophiles?
due to the double bond which has a high electron density
What occurs in the electrophilic addition reaction between bromine and ethene?
forms a dihalogenoalkane
reagent - bromine
conditions - room temperature
What is the mechanism in the electrophilic addition reaction between ethene and bromine?
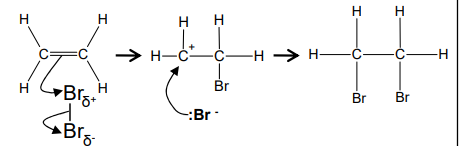
What is the electrophilic addition reaction between a hydrogen bromine and alkene?
forms a halogenoalkane
reagent - HCl or HBr
conditions - room temperature
What is the mechanism of the electrophilic addition reaction between but-2-ene and HBr?
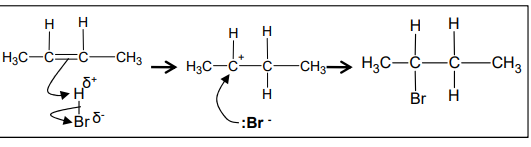
What is ‘Markownikoff’s rule’?
bromine will be added to the carbon with the fewest hydrogens attached to it
Why would one product be made more than another product in electrophilic addition reactions?
the carbocation intermediate is more stable because the methyl groups on either side of the positive carbon are electron releasing and reduce the charge on the ion which stabilises it
What is the order of stability for carbocations?
tertiary
secondary
primary
What is the major product in electrophilic addition of alkenes?
formed via the more stable carbocation intermediate
What’re the 2 steps in forming an acohol from an alkene?
electrophilic addition to form an alkyl hydrogensulfate
hydrolysis to form an alcohol
What occurs when forming an alkyl hydrogensulfate?
reagents - concentrated H2SO4
conditions - room temperature
CH2=CH2 + H2SO4 → CH3CH2COSO2OH
What is the mechanism for electrophilic addition between propene and sulfuric acid?
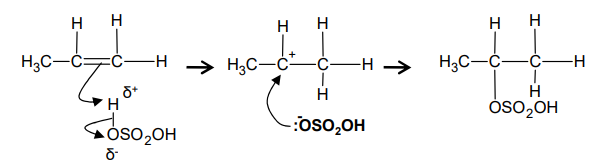
What occurs during the hydrolysis of the alkyl hydrogensulfate?
forms an alcohol
reagents - water
conditions - warm mixture
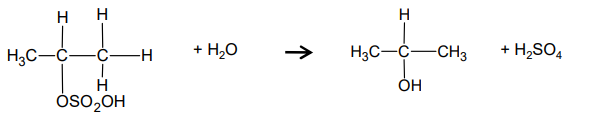
CH3CH2OSO2OH + H2O → CH3CH2OH + H2SO4
What is the mechanism for the hydrolysis of propyl hydrogensulfate and water?
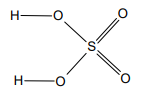
What is H2SO4 displayed formula?
What is hydrolysis?
a reaction where the molecule is split by the addition of water
How are alkenes converted into alcohols in the industry?
reacted with water in the presence of an acid catalyst
high temperature of 300 to 600
high pressure of 70 atm
catalyst of concentrated H3PO4
How can you test for alkenes with bromine water?
decolourises in the presence of a double bond
turns from orange to colourless
How are addition polymers formed?
from alkenes
What is one repeating unit?
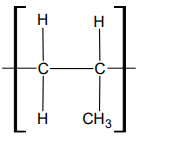
What is a repeating unit?
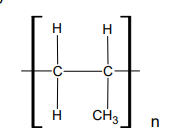
What is poly(chloroethene)?
polymer
waterproof, an electrical insulator, doesn’t react with acids
pure form is a rigid plastic due to strong intermolecular bonding
as a plasticiser its intermolecular forces are weakened, allowing the chains to move more easily