Photosynthesis: light-dependent stage
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what two stages does photosynthesis take place?
The light-dependent reactions which rely on light directly
the light-independent reactions, which do not use light directly though do rely on the products of the light-dependent reactions
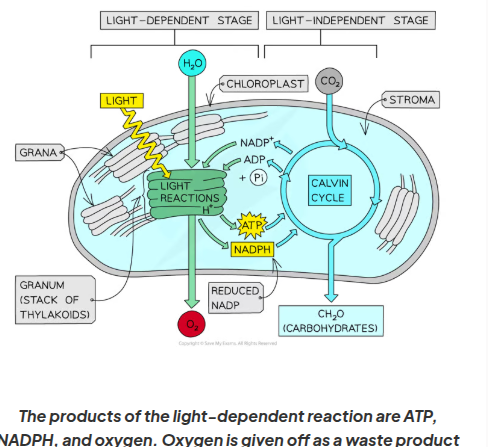
where do light dependent reactions take place
both light dependent an dlight independent reactions take place in the chloroplast
The light-dependent reactions take place across the thylakoid membrane
where do light-independent reactions take place
stroma
main function of light dependent stage of photosynthesis
During the light-dependent reactions light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and reduced NADP. ATP supplies energy to build carbohydrates. They provide the source of reducing power and energy respectively in the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis to make glucose
to break up water molecules in a photochemical reaction, providing hydrogen ions to reduce carbon dioxide and produce carbohydrates in the light-independent stage
why light energy needed in light dependent reactions
enables the splitting of water molecules in a reaction known as photolysis
what does photolysis of one molecule of water produce
2 hydrogen ions (protons)
2 electrons (2e-)
One atom of oxygen (O)
The hydrogen ions and electrons are used during the light-dependent reactions while the oxygen is given off as a waste product
how ATP and NADPH produced
ATP and NADPH are produced during the light-dependent reactions as a result of a series of events that occur on the thylakoid membrane known as photophosphorylation
Photo = light
Phosphorylation = the addition of phosphate; in this case to ADP to form ATP
when a photon of light hits a chlorophyll molecule, the energy is transferred to the electrons of the chlorophyll molecule
the electrons are excited and are raised to higher energy levels
if an electron is raised to a sufficiently high energy level it leaves the chlorophyll molecule compeltely
the excited electron is collected by a carrier molecule called an electron acceptor and this results in the synthesis of ATP by either cyclic photophosphorylation snd non-cyclic photophosphorylation
both these process occur at same time and in both cases ATP is formed as the excited electron is transferred along an electron transport chain
what are the 2 types of photophosphorylation that take place?
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
This produces both ATP and NADPH
Cyclic photophosphorylation
This produces ATP only
what do both cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation invo
what happens in non cyclic photosphorphorylation
light energy hits photo system 11 in thylakoid membrane (PS 1)
2 Electrons are excited to a higher energy level
The excited electrons from PS 11 is collected by am electron acceptor and pass along the electron transport chain, releasing energy as they do so. Now the chlorophyll molecule in PS2 os moissing 1 electron and so is unstable
At the same time photolysis occurs to trstore electron lost from chlorophyll molecule. Ions produced due to dissociation of water molecules given to chlorophyll molecule in PS2 so its restored to its original state and ready to be excited again when hit by another photon of light.
The energy released as the electrons pass down the electron transport chain through electron carriers provides energy to drive the process of chemiosmosis
H+ ions are pumped from a low concentration in the stroma to a high concentration in the thylakoid space, generating a concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane
H+ ions diffuse back across the thylakoid membrane into the stroma via ATP synthase enzymes embedded in the membrane
The movement of H+ ions cause the ATP synthase enzyme to catalyse the production of ATP
At the end of the electron transport chain the electrons from photosystem II are passed to photosystem I
Light energy also hits photosystem I, exciting another pair of electrons which leave the photosystem
The excited electrons from photosystem I also pass along an electron transport chain
These electrons combine with hydrogen ions from the photolysis of water and the coenzyme NADP to form reduced NADP
H+ + 2e- + NADP+ → NADPH
The reduced NADP and the ATP pass to the light-independent reactions
what is NADP converted to
NADP is a type of molecule called a coenzyme; its role is to transfer hydrogen from one molecule to another
during non cyclic photos phosphorylation water molecules are broken down porividng H+ to reduce NADP
When NADP gains hydrogen it is reduced, and can be known as either reduced NADP or NADPH
The useful products of the light-dependent reactions, ATP and NADPH, are transferred to the light-independent reactions within the chloroplast
how many electrons need to be gained for production of 1 molecule of oxygen
many hydrogen ions are removed by NADP and many hydroxide ions remain
the hydroxide ions react together to form oxygen and water
electrons are freed as a result of the reaction and are absorbed by chlorophyll 4 chlorophyll molecules regain electron in the production of one molecule of oxygen
4OH- -4e- (lost ot chlorophyll)—> O2 + 2H2O
what happens in cyclic photophosphorylation
Involves only photosystem 1 and drives production of ATP
when light hits a chlorophyll molecules in PS1 electros excited to a higher energy level and leave the photosystem
it is collected by an electron acceptor and transferred directly along an electron transport chain releasing energy as they do so
The energy released as the electrons pass down the electron transport chain provides energy to drive the process of chemiosmosis
H+ ions are pumped from a low concentration in the stroma to a high concentration in the thylakoid space, generating a concentration gradient across the thylakoid membrane
H+ ions diffuse back across the thylakoid membrane into the stroma via ATP synthase enzymes embedded in the membrane
The movement of H+ ions cause the ATP synthase enzyme to catalyse the production of ATP
At the end of the electron transport chain the electrons rejoin photosystem I in a complete cycle; hence the term cyclic photophosphorylation
The ATP produced enters the light-independent reaction
explain role of light in light dependent reactions in photosyntehsis
• because {it / light} is needed for photolysis (1)
• because {electrons released (from the water) are needed to replace those lost from the photosystems / hydrogen ions are used to reduce NADP} (1)
• because {it / light} is needed to {excite / release} the electrons of the {photosystems / chlorophyll / PS / photosynthetic pigments} (1) • electrons (from photosystems) used to produce ATP (and reduced NADP) (1)