INTERNAL MEDICINE EOR: PULMONOLOGY
1/437
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
438 Terms
Bronchiectasis
Permanent, abnormal dilation & destruction of bronchial walls → impaired mucus clearance → frequent infections
MCC of Bronchiectasis
cystic fibrosis
Bronchiectasis etiology other
recurrent lung infections
Bronchiectasis clinical presentation
chronic cough + copious mucopurulent foul smelling sputum
- Dyspnea
- Hemoptysis
- Recurrent pneumonia
Bronchiectasis physical exam findings
- crackles (MC)
- wheezing
- rhonchi
Bronchiectasis CXR
- "tram track" lung markings: dilated & thickened airways
- "Plate like" atelectasis
Bronchiectasis TOC
CT
Bronchiectasis CT
signet ring sign
Bronchiectasis PFTs
obstructive pattern
- ↓ FEV1, ↓ FEV1/FVC <70%
- hyperinflation: ↑ volumes (RV, TLC, RV/TLC, FRC)
Bronchiectasis acute management
- O2
- Antibiotics
Bronchiectasis chronic management
- Hydration
- Chest physiotherapy
- Inhaled bronchodilators
- Def → Lung Transplant
COPD
Progressive largely irreversible airflow obstruction due to loss of elastic recoil (emphysema) & ↑ airway resistance (bronchitis)
COPD types
Emphysema → gradual decline (pink puffer)
Chronic Bronchitis → episodic (blue bloater)
COPD risk factors
- MC = Smoking
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- Occupational/environmental exposures
- Recurrent airway infections
COPD clinical presentation
- DOE
- Cough
- Wheezing
COPD diagnostic studies
- oxygen saturation
- PFTs
- ABGs
- CXR
COPD gold standard diagnostic test
PFTs
COPD: CXR
- hyperinflation/flat diaphragm
- increased vascular markings
COPD: ABGs
- respiratory alkalosis (emphysema)
- respiratory acidosis (chronic bronchitis)
COPD: PFTs
obstructive
- FEV1 & FVC = low
- FEV1/FVC ratio = < 70%
- Lung Volumes = high
COPD screening
- low dose Chest CT
- 30+ pack year history
PaO2 and saturation to use oxygen in COPD
PaO2 ≤ 55mmHg or saturation ≤ 88%
COPD management
- STOP SMOKING
- O2
- lung reduction surgery
- Lung transplant
- replacement of ⍺1 antitrypsin in some patients
- SABA/LABA/ICS
COPD O2 home treatment indications
- paO2 < 55
- spO2 = < 88%
- Cor pulmonale
COPD management: lung reduction surgery
improves dyspnea by removing damaged lung which allows the remaining lung to expand & function more efficiently
COPD management: Mild s/s + low risk exacerbation
SABA or/+ SAMA PRN
COPD management: Moderate s/s + low risk exacerbation
- SABA/SAMA
- + LAMA (preferred) or LABA
COPD management: Mild s/s on day-to-day basis
- LAMA
- LAMA + LABA
- LABA + ICS
COPD management: Severe symptoms
- LAMA + LABA (preferred)
- LABA + ICS
COPD management: Hypercapnia
Acetazolamide
COPD exacerbation
An acute event characterized by a worsening of the pt's respiratory symptoms that is beyond normal day-to-day variations & leads to a change in medication
COPD exacerbation risk factors
• advanced age, productive cough
• longer duration of COPD, hx of abx therapy
• COPD-related hospitalization within the previous year
• chronic mucous hypersecretion
• peripheral eosinophil count >340cells/microL
• theophylline therapy
• presence of one or more comorbidities (IHD, HF, DM)
COPD exacerbation clinical presentation
Generally includes acute change in 1 or more of the cardinal symptoms:
• cough increases in frequency & severity
• sputum production changes in volume &/or changes character
• dyspnea increases
COPD exacerbation physical exam findings
- wheezing
- tachypnea
- difficulty speaking
- use of accessory muscles
- fever
- myalgias
- diaphoresis
COPD exacerbation management
- SABA + SAMA
- prednisone x 5-14 days
- antibiotics
COPD exacerbation management: antibiotics
- azithromycin 500mg x3d
- cefuroxime 500mg BID x10d
- doxycycline 100mg BID x10d
Chronic Bronchitis: criteria timeline
Productive cough - 3 months/year for 2 consecutive years
- Increases susceptibility to infections
Chronic Bronchitis etiology
- smoking MC
- air pollution
- hazardous dust
Chronic Bronchitis clinical presentation
- cough + sputum + dyspnea
- Cyanotic + obese (Blue Bloater)
Chronic Bronchitis physical exam findings
- crackles (rales)
- rhonchi
- wheezing
- cor pulmonale
signs of cor pulmonale
- hepatomegaly
- JVD
- peripheral edema
Chronic Bronchitis diagnostic studies
- CXR
- PFTs
- EKG
- V/Q
- CBC: increased Hgb & Hct
- hypoxia
Chronic Bronchitis CXR
pulmonary HTN
- enlarged right heart border
- ↑ AP diameter
- ↑ peribronchial/perivascular markings
Chronic Bronchitis PFTs
- gold standard: obstructive pattern that is not fully reversible
- ↓ FEV1 & FEV1/FVC <70% predicted, ↓ FVC
- ↑ volumes (RV, TLC, RV/TLC, FRC), normal DLCO
Chronic Bronchitis EKG
- multifocal atrial tachycardia
- cor pulmonale: RVH, RAE, RAD
Chronic Bronchitis V/Q
severe mismatch
Chronic Bronchitis ABG
respiratory acidosis
Chronic Bronchitis management
Antibiotics
- Macrolides
- Cefuroxime or Cefixime
- Amox/Clav
- FQs
Emphysema
Chronic inflammation (ex: cigs) → degrades elastin in alveoli → airway loses elasticity → alveoli collapse → decreased surface area for gas exchange + difficult exhale
Emphysema etiology
Centrilobular → smoking
Panlobular → A1AT Def
Distal acinar → young adults & spon. pntx
Paraseptal → both or pneumothorax
Emphysema clinical presentation
- DOE (Pink Puffer)
- Chronic cough +/- sputum
- Cachectic + Pursed lip breathing (Pink Puffer)
Emphysema clinical presentation: severe disease
- pursed lip expiration (increased airway & prevents airway collapse)
- semi-tripod positioning (sitting forward) to improve breathing
Emphysema physical exam findings
- Decreased breath sounds
- Decreased TF
- ↑ AP diameter: Barrel Chest
- Hyperresonance to percussion
Emphysema diagnostic studies
- CXR
- PFTs
- ABG
- V/Q scan
Emphysema CXR
- Decreased vas markings
- Enlarged lung fields
- Flattened diaphragms
- Hyperinflation: dark
- Bullae: airspace loss
Emphysema PFTs
OBSTRUCTIVE
- decreased DLCO
Emphysema ABG
respiratory acidosis - IF severe
Emphysema V/Q scan
matched defects
Emphysema management
acute bronchitis
Inflammation of the bronchi
acute bronchitis etiology
MC caused by viruses (adenovirus, parainfluenza, influenza, coronavirus, coxsackie, rhinovirus, respiratory syncytial virus)
acute bronchitis clinical presentation: timeline
Cough > 5 days ~ 2-3 weeks
- +/- sputum
- Constitutional sx
- +/- Fever
- Chest Discomfort
- SOB
- May have hemoptysis (MC cause along w/ bronchogenic carcinoma)
acute bronchitis physical exam findings
- less severe than pneumonia
- normal vital signs
- no rales
- no egophony
acute bronchitis diagnostic studies
clinical diagnosis
acute bronchitis CXR
usually normal or nonspecific
- only indicated if pneumonia is suspected (HR >100, RR >24, T >38C, rales, hypoxemia, mental confusion, systemic illness)
acute bronchitis admit Indications
O2 =/< 96%
acute bronchitis management
- Symptomatic management
- Antibiotics usually not indicated
acute bronchitis symptomatic management
- Suppressant → Dextromethorphan
- Expectorant, antihistamines, mucolytics
- Airflow obstruction → SABA
- Obstructive pulm disease → CS
- NSAIDs, ASA, APAP
acute bronchitis management: severe cardiopulm disease OR icomp
ribavirin
Influenza MCC
Orthomyxovirus
Influenza vaccination criteria
- > 6 months old x annually
- Avoid → egg allergy, rxn, GBS
- FluMist → avoid with asthma
Influenza diagnostic studies
- Rapid antigen
- Rapid serology: more accurate
- CXR
Influenza CXR
bilateral diffuse infiltrates
whooping cough etiology
- Bordetella pertussis
- gram neg
whooping cough vaccination doses
5 doses - Dtap
1 dose - Tdap
Pregnancy - 1 dose Tdap
whooping cough CC
- Severe paroxysmal hacking cough
- High pitched inspiration = whoop
- > 2 weeks in adults → suspect WC
whooping cough stages
- Catarrhal
- Paroxysmal
- Convalescent
Catarrhal stage
- 1-3 wks
- Cold sx + poor eating/sleeping + conjunctival injection + lacrimation
Paroxysmal stage
- 2-6 wks
- Whoop + inspiratory stridor
Convalescent stage
- 1-2 months
- residual cough
WC diagnostic studies
nasopharyngeal swab + culture
WC management
- Supportive: Steroids, SABA
- Antibiotics
WC management: antibiotics
1st line → Clarithro or Azithro
2nd line → Bactrim
Highly contagious!
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
MC type of ILD
type = Miscellaneous
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patho
Progressive lung scarring → fibrosis
- cause unknown
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patient population
Men 40+ & Smokers
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis clinical presentation
Progressive SOB + dry cough
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis physical exam findings
- Fine, dry inspiratory crackles
- Clubbing
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis CXR or CT
- Diffuse patchy fibrosis: bases
- Reticular honeycombing
- Focal ground glass opacification
- Traction bronchiectasis
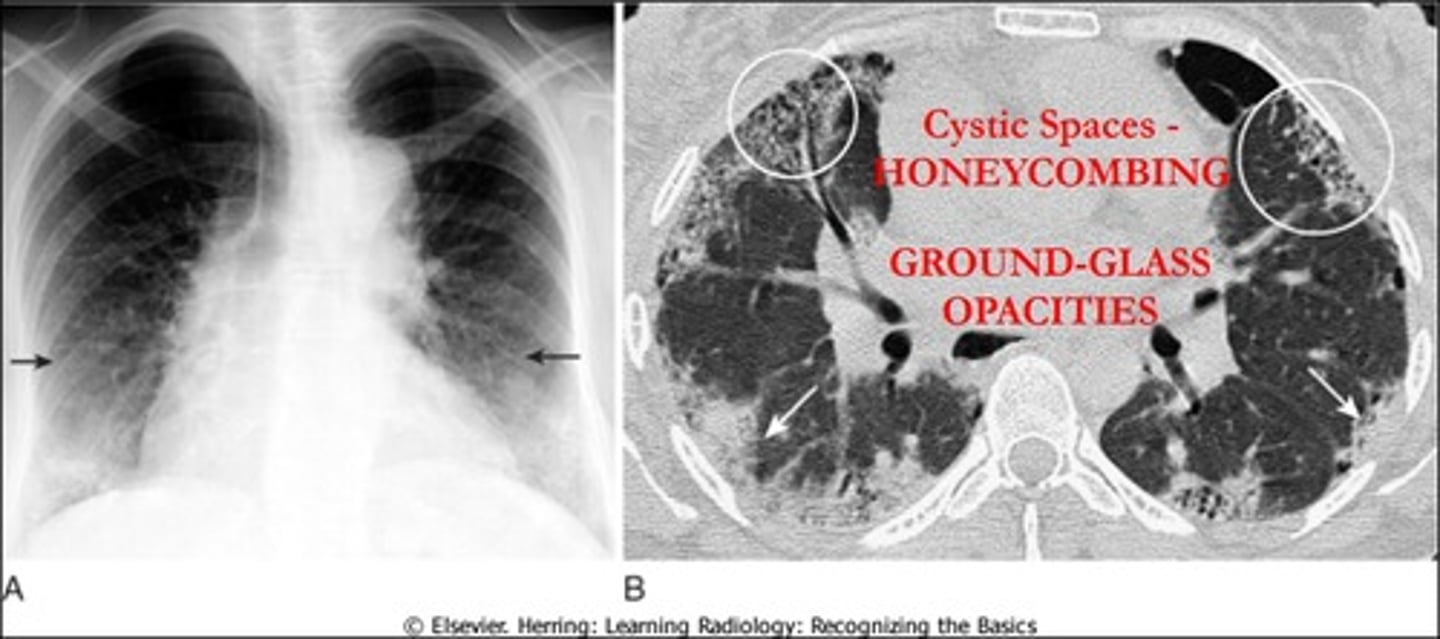
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis definitive diagnosis
Lung Biopsy → Honeycombing
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis management
- no effective medical treatment
- Symptomatic: O2, Corticosteroids
- Only cure → Lung Transplant
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis management: slow progression
- Pirfenidone
- Nintedanib
Pulmonary HTN
Elevated mean pulmonary arterial pressure ≥ 20mmHg
Pulmonary HTN patho
increased pulmonary vascular resistance leads to RVH, increased RV pressure, & eventually R-sided HF
Pulmonary HTN etiology
- Primary: idiopathic (MC in middle-aged or young women)
- Secondary: pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, PE
Pulmonary HTN Types
- Class I → idiopathic pulmonary arterial HTN (primary)
- Class II → due to left heart disease
- Class III → due to hypoxemic or chronic lung disease (COPD)
- Class IV → due to chronic thromboembolic disease
Pulmonary HTN clinical presentation
- dyspnea
- fatigue
- chest pain
- weakness
- cyanosis
- edema
Pulmonary HTN physical exam findings
- accentuated S2
- signs of R-sided HF
- pulmonary regurgitation
- right ventricular heave
- systolic ejection click
signs of R-sided HF
- ↑ JVP
- peripheral edema
- ascites