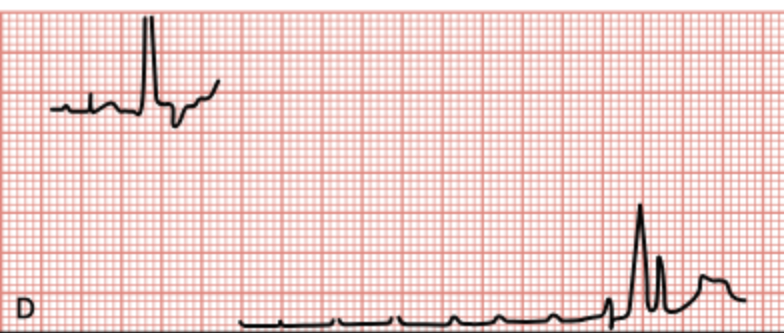
EKG Rhythms and Artifacts Vocabulary
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for EKG interpretation and arrhythmia recognition.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Segment (in ECG)
The region between two waves on an ECG.
Interval (in ECG)
Duration of time on ECG including one segment and one or more waves.
P wave
Represents atrial depolarization (contraction of the atria).
QRS wave
Represents ventricular depolarization (contraction of the ventricles).
T wave
Represents ventricular repolarization (relaxation of the ventricles).
U wave
Represents repolarization of the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers.
PR interval
Time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization.
QT interval
Time from the beginning of ventricular depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarization.
ST segment
Time from the end of ventricular depolarization to the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
Sinus rhythms
Normal rhythms originating from the SA node, with one P wave per QRS interval.
Sinus bradycardia
Heart rate less than 60/min.
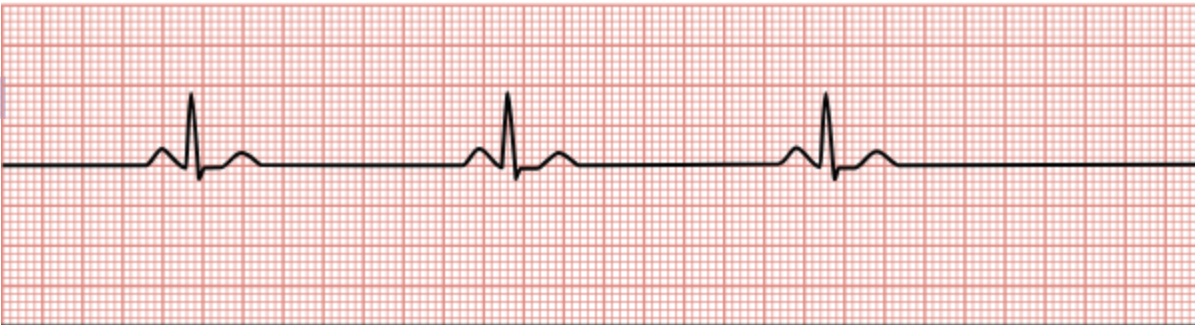
Sinus tachycardia
Heart rate greater than 100/min.
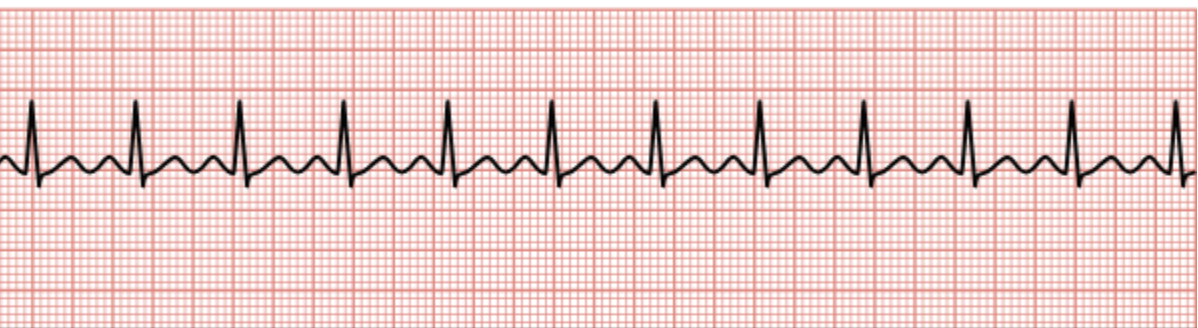
Sinus arrest
SA node fails to fire, causing a break in the normal EKG.
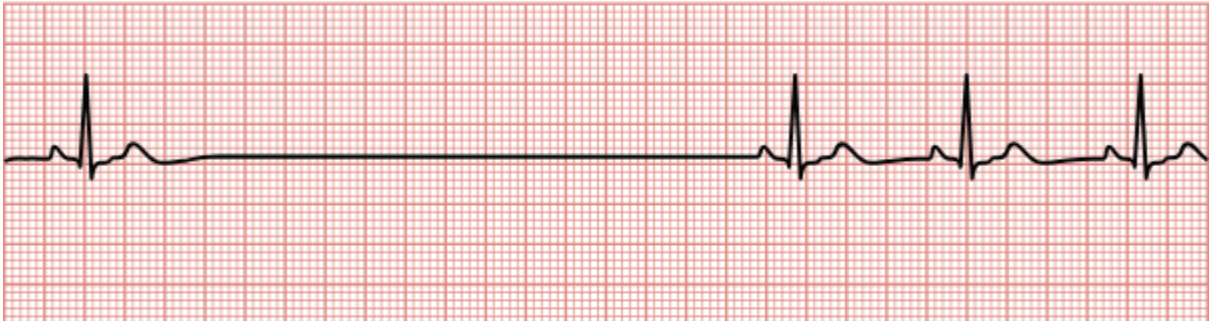
Abnormal Atrial Rhythms
Rhythms originating from atrial tissue characterized by the absence of P waves.
Atrial Flutter
Single area within the atrial tissue firing faster than the ventricles are responding, resulting in multiple flutter waves for each QRS complex.
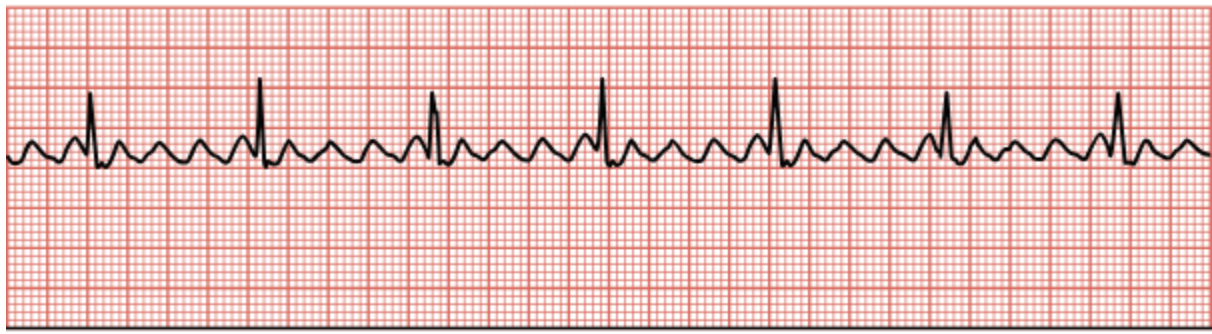
Atrial Fibrillation (A-fib)
Rapid, disorganized firing of multiple sites within the atrial tissue, resulting in irregular fibrillatory waves between QRS complexes and an irregular QRS rhythm.
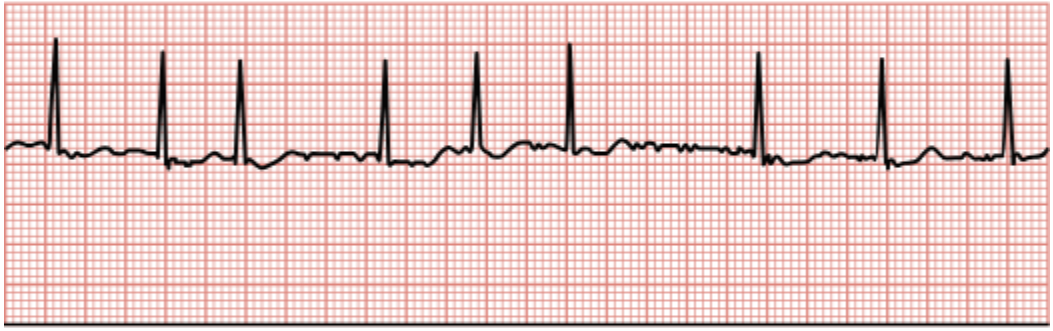
Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
Atria are triggered to contract earlier than they should, resulting in a premature contraction affecting the P wave.

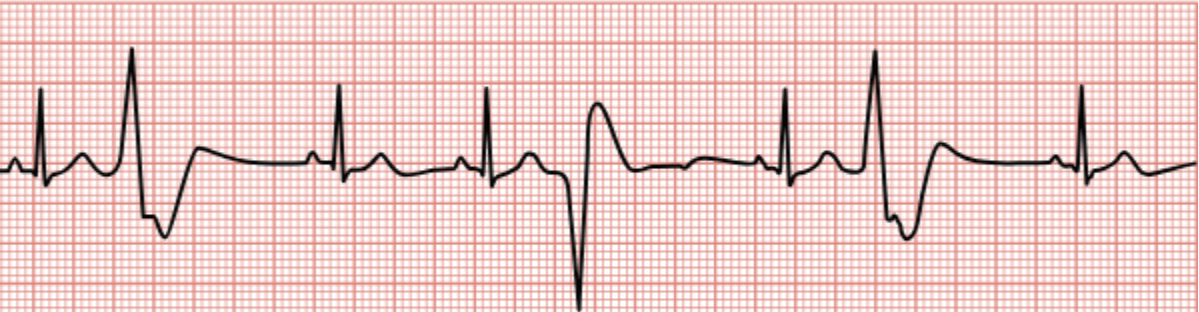
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
Premature contractions in the ventricles that affect the QRS wave.
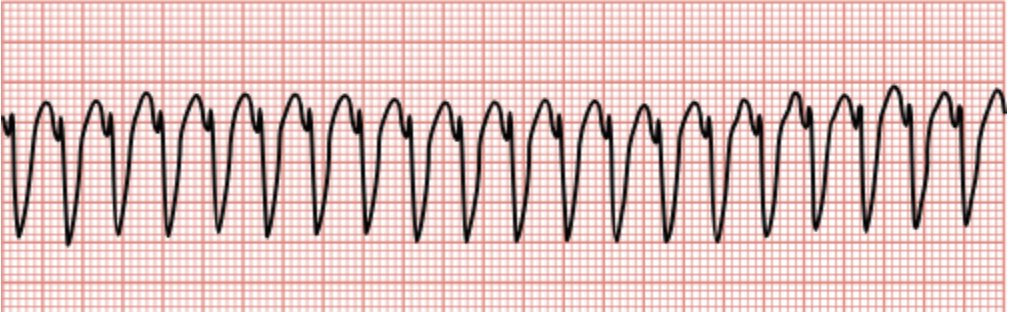
Ventricular Tachycardia (V-tach)
Regular, fast rhythm characterized by large, irregular, wide QRS complexes, often without visible P waves.
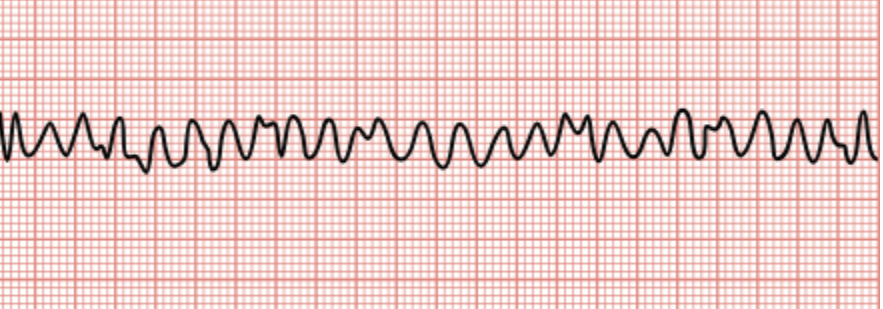
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricles twitch or quiver, not pumping blood. No pulse is produced, and patients become unconscious.
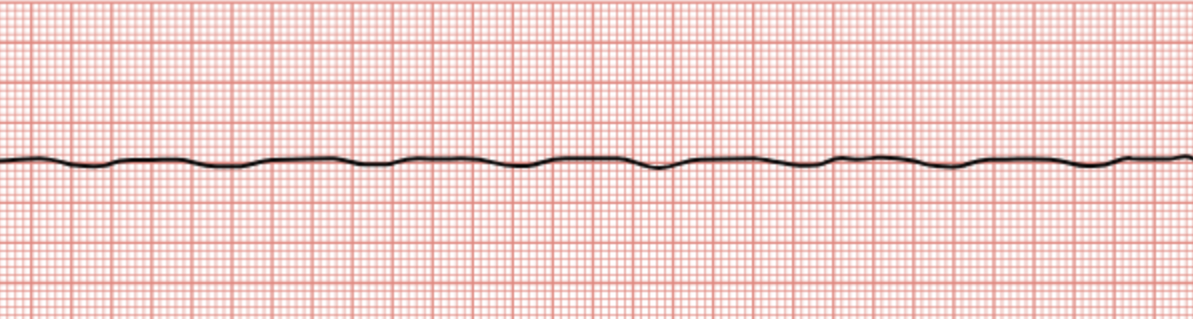
Asystole
Complete absence of any waves on the EKG tracing.
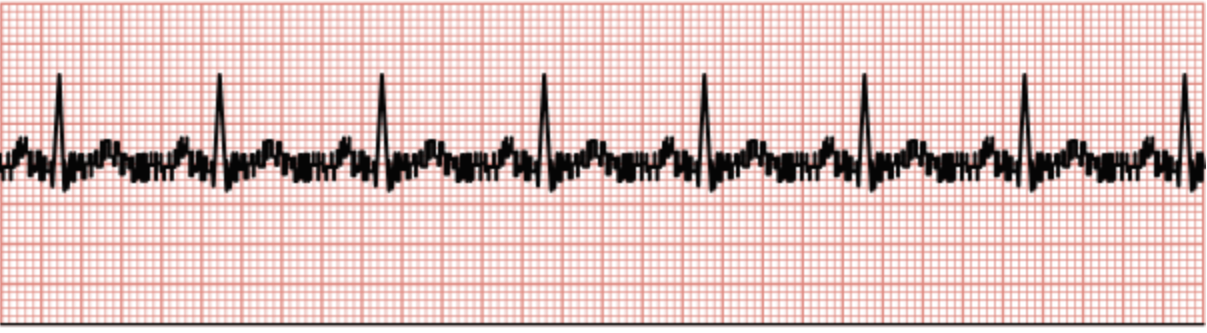
Somatic Tremor
Irregular spikes throughout the tracing related to muscle movement.
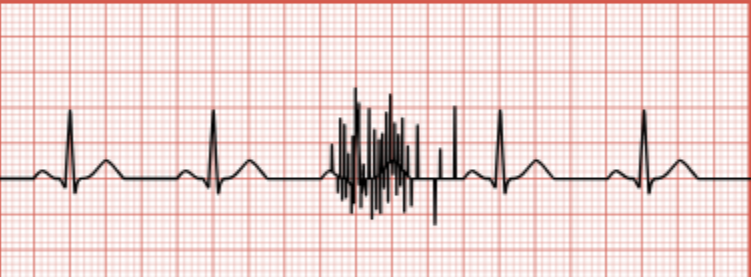
Electrical Interference
Regular spikes in the EKG tracing related to poor grounding or external electricity.
Wandering Baseline
Baseline wanders away from the center of the paper due to movement or poor electrode connection.
Interrupted Baseline
Break in the tracing, usually related to a disconnected or broken lead wire.