NCEA LEVEL 3 BIO SPECIATION
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Species
individuals that normally interbreed to produce fertile offspring's and belong to the same gene pool

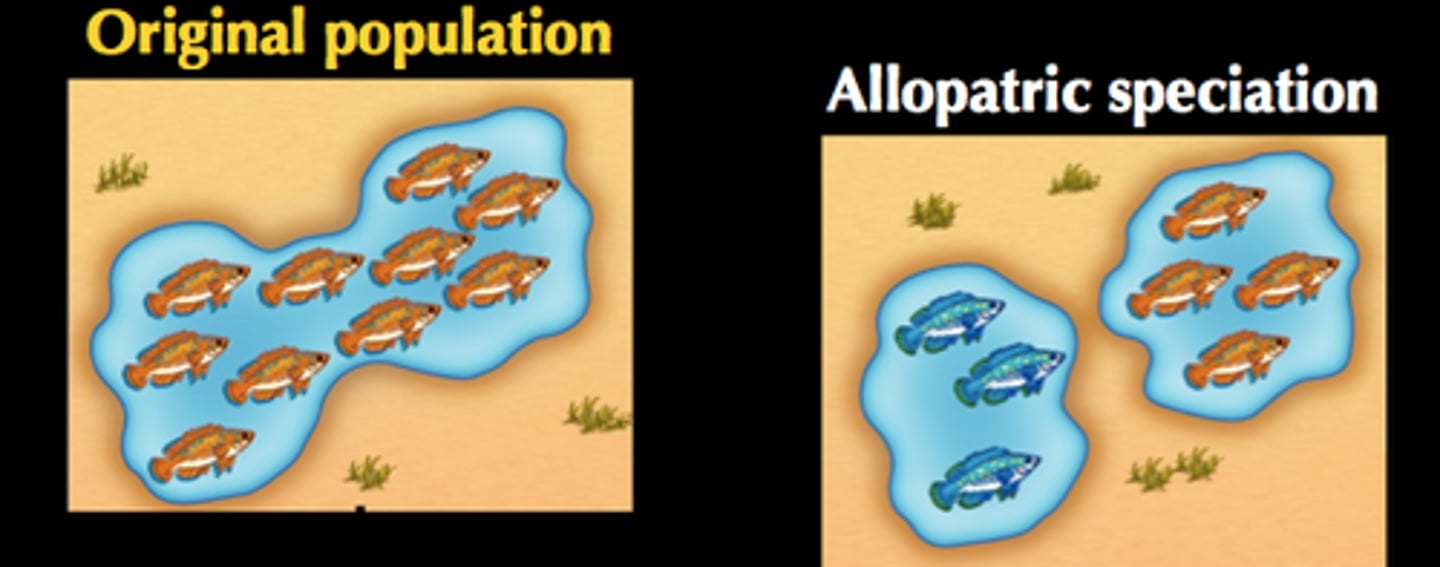
Allopatric Speciation
capable of interbreeding but cannot due to geographical isolation
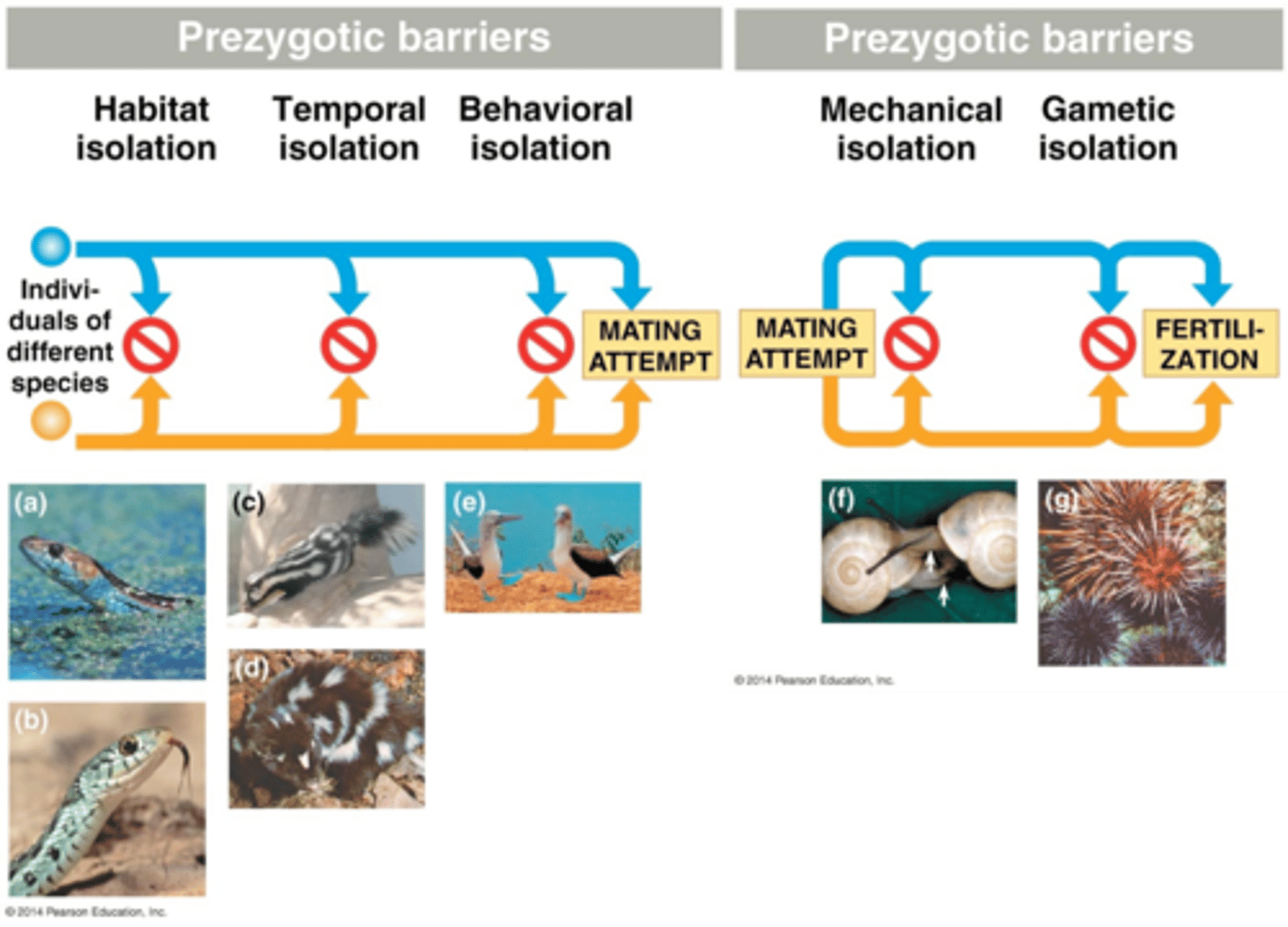
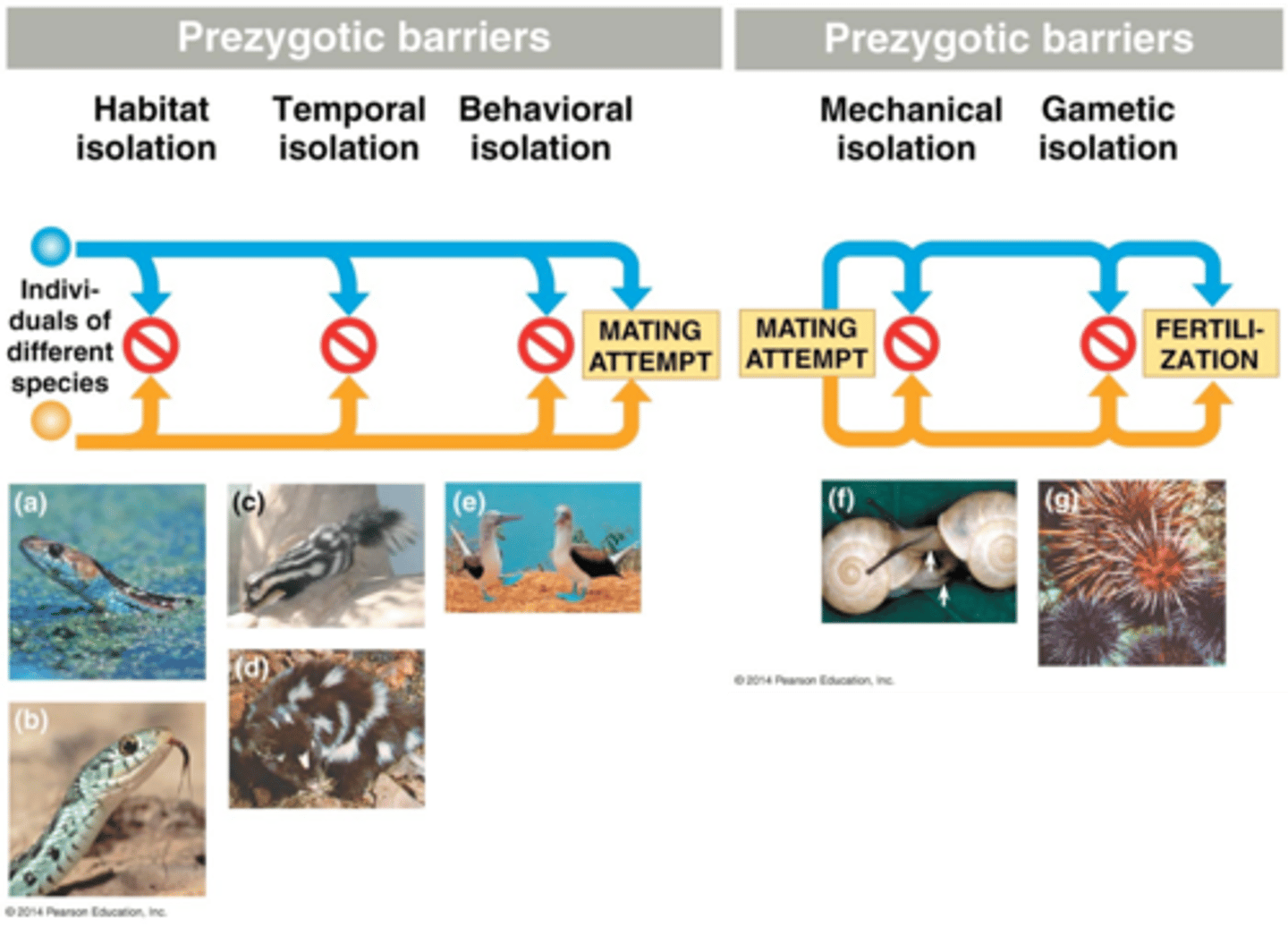
Prezygotic, Postzygotic
Two types of reproductive barriers
Hybrid inviability
A zygote is formed but does not develop properly
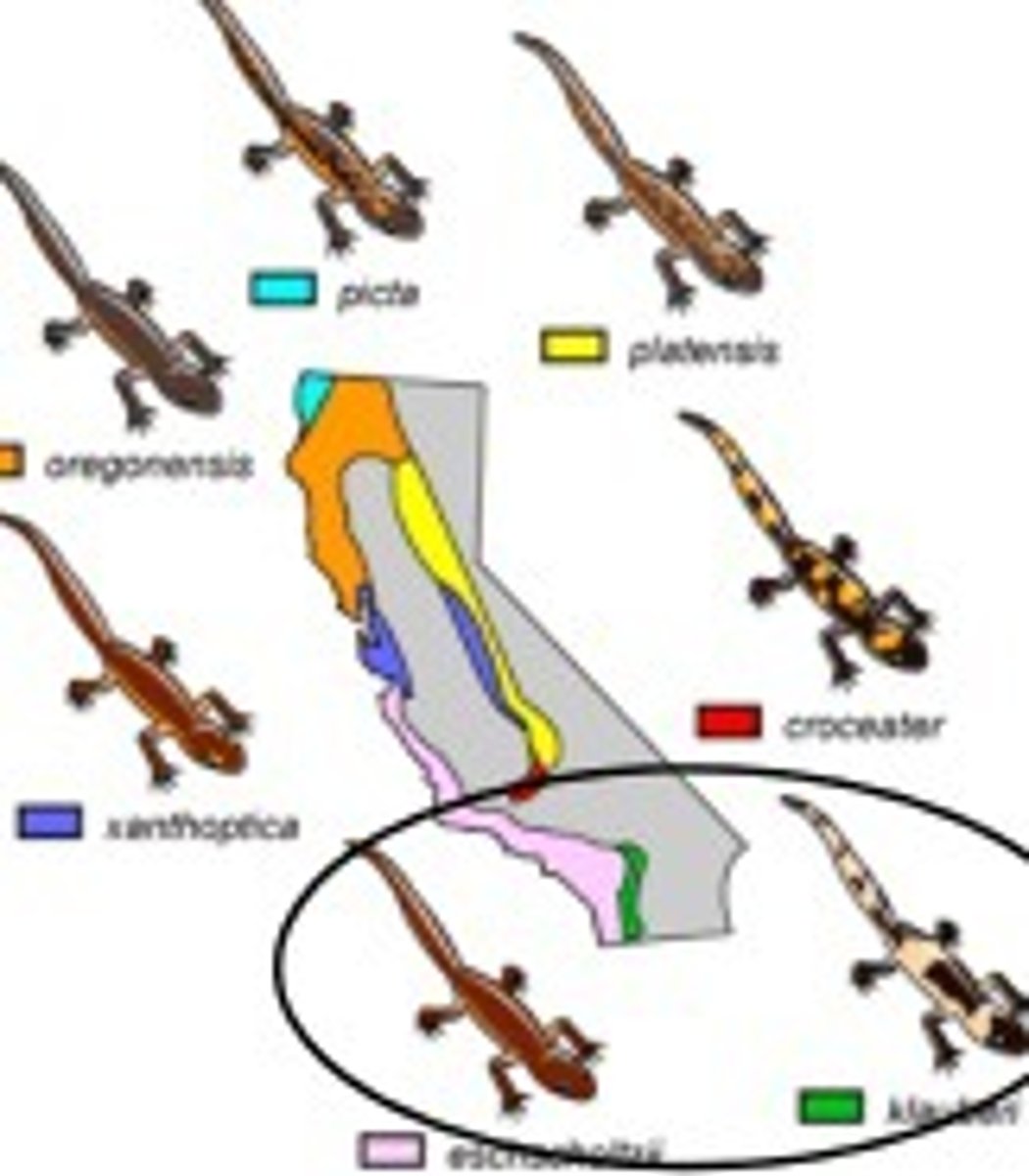
Ring Species
connected by a series of intermediate geographical and structural subspecies between which interbreeding can occur
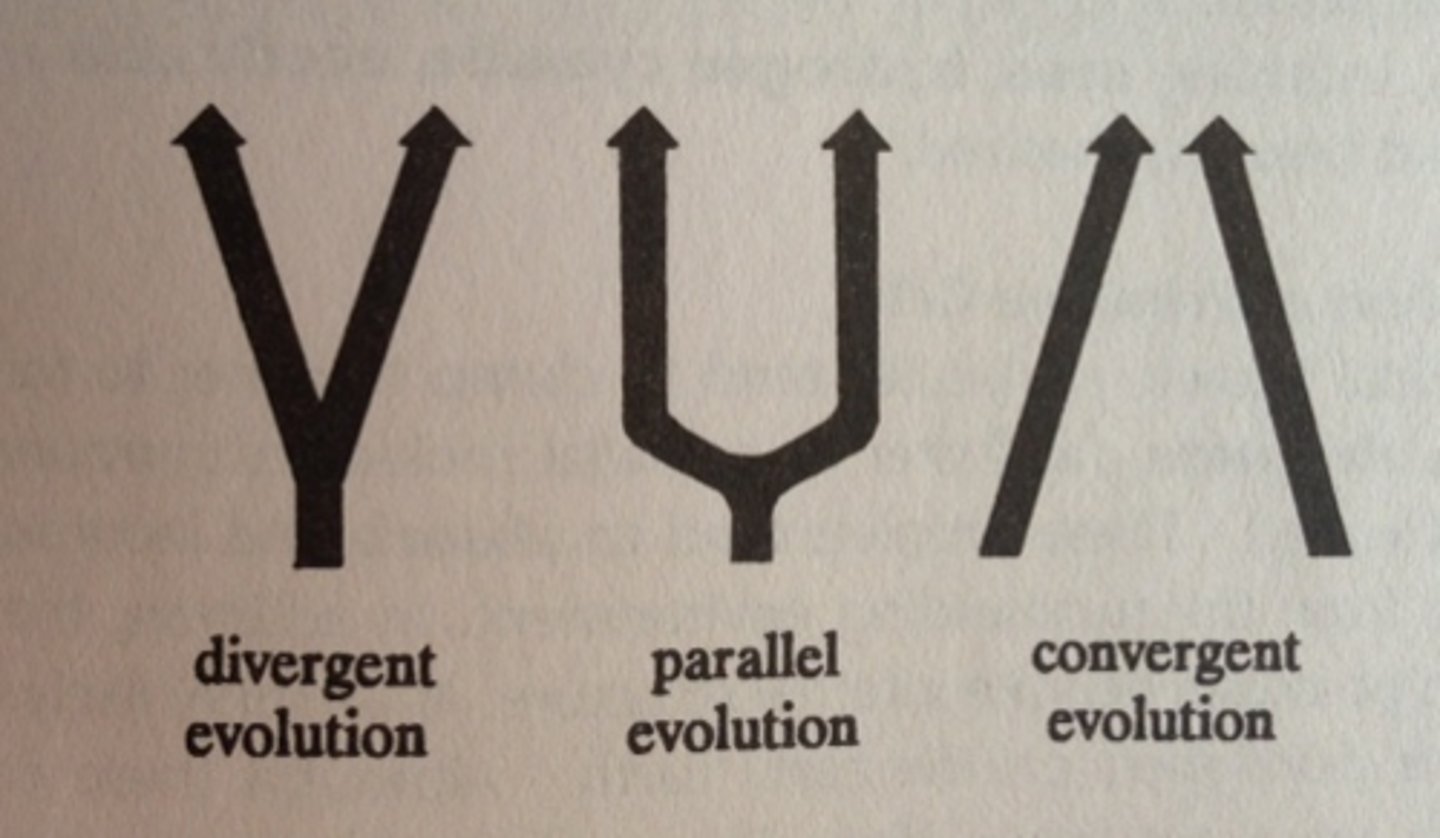
Covergent evolution
development of similar structures in UNRELATED ORGANISMS
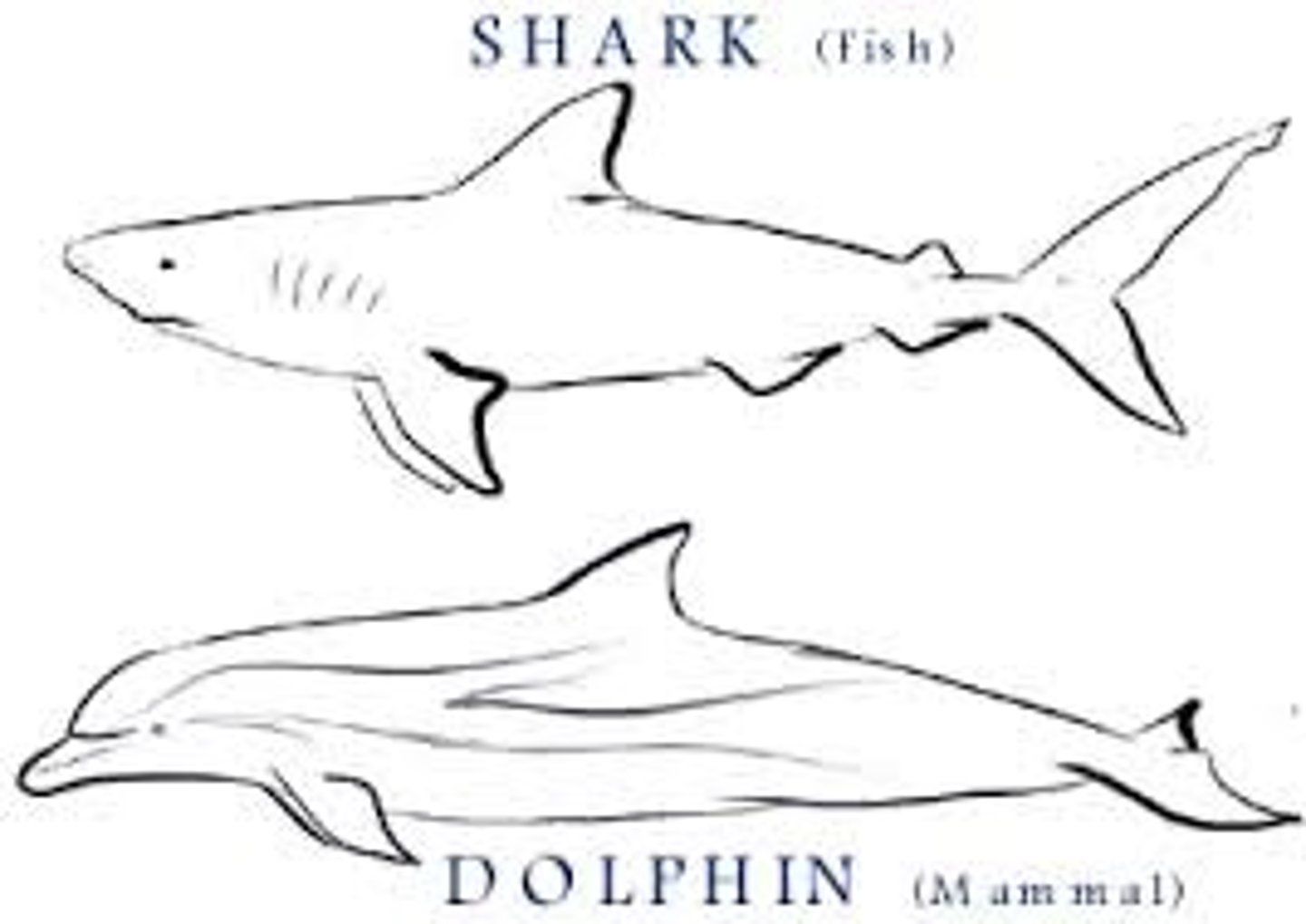
Analogous structures
Structures that are similar but have evolved in different ways
Divergent Evolution
common ancestors divide into two or more lines with dissimilar characteristics due to environment
Parallel Evolution
development of related species along similar evolutionary paths due to strong selective pressure acting on all them in the same way of
Hybrid Sterility
A hybrid forms but is sterile e.g a sterile mule
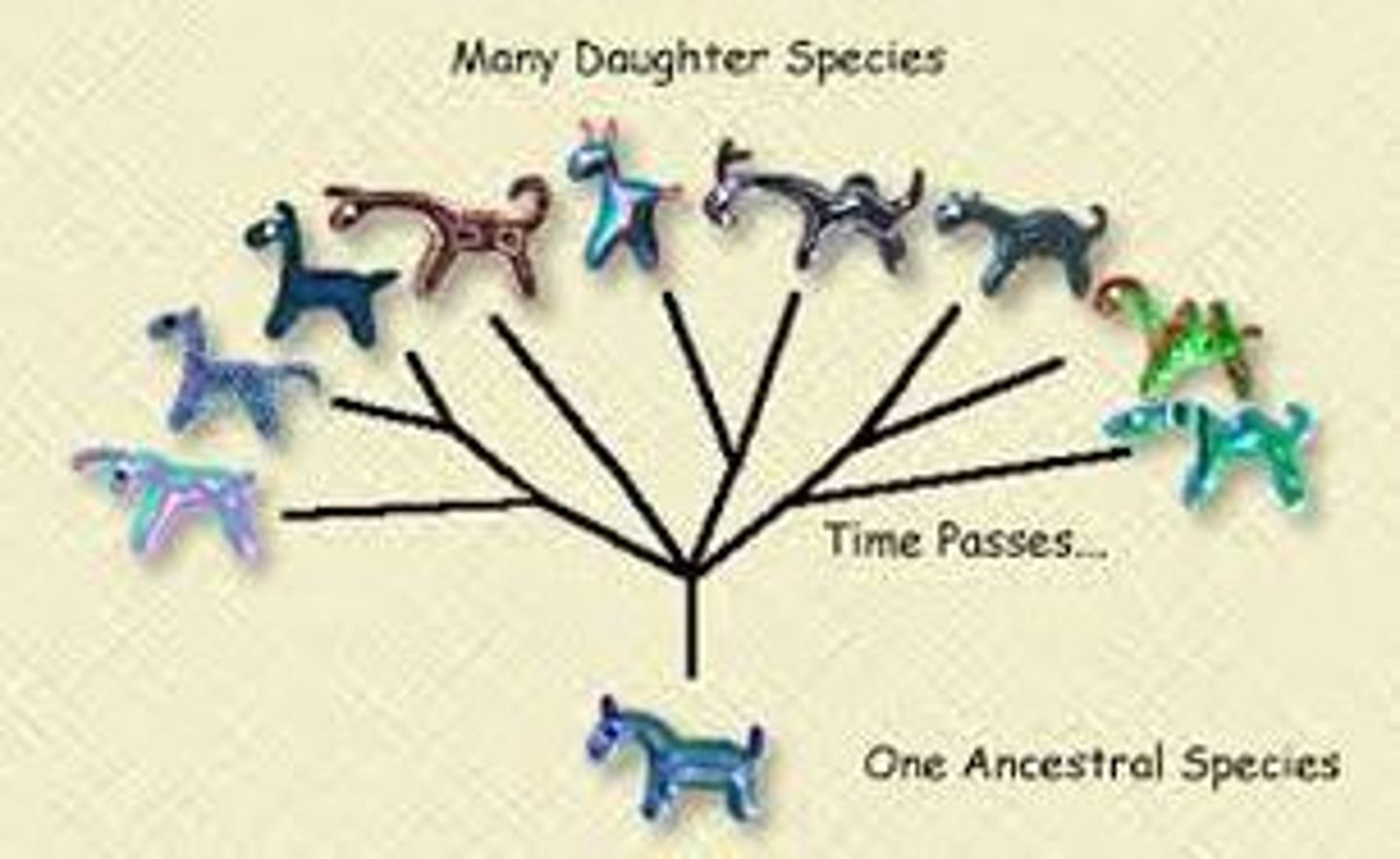
Evolution
gradual process by which the present diversity of plants and animals arose form the earliest and most primitive organisms
Cline
increase in numbers of forms ofvariation in the characteristics of a species or population over its geographical range
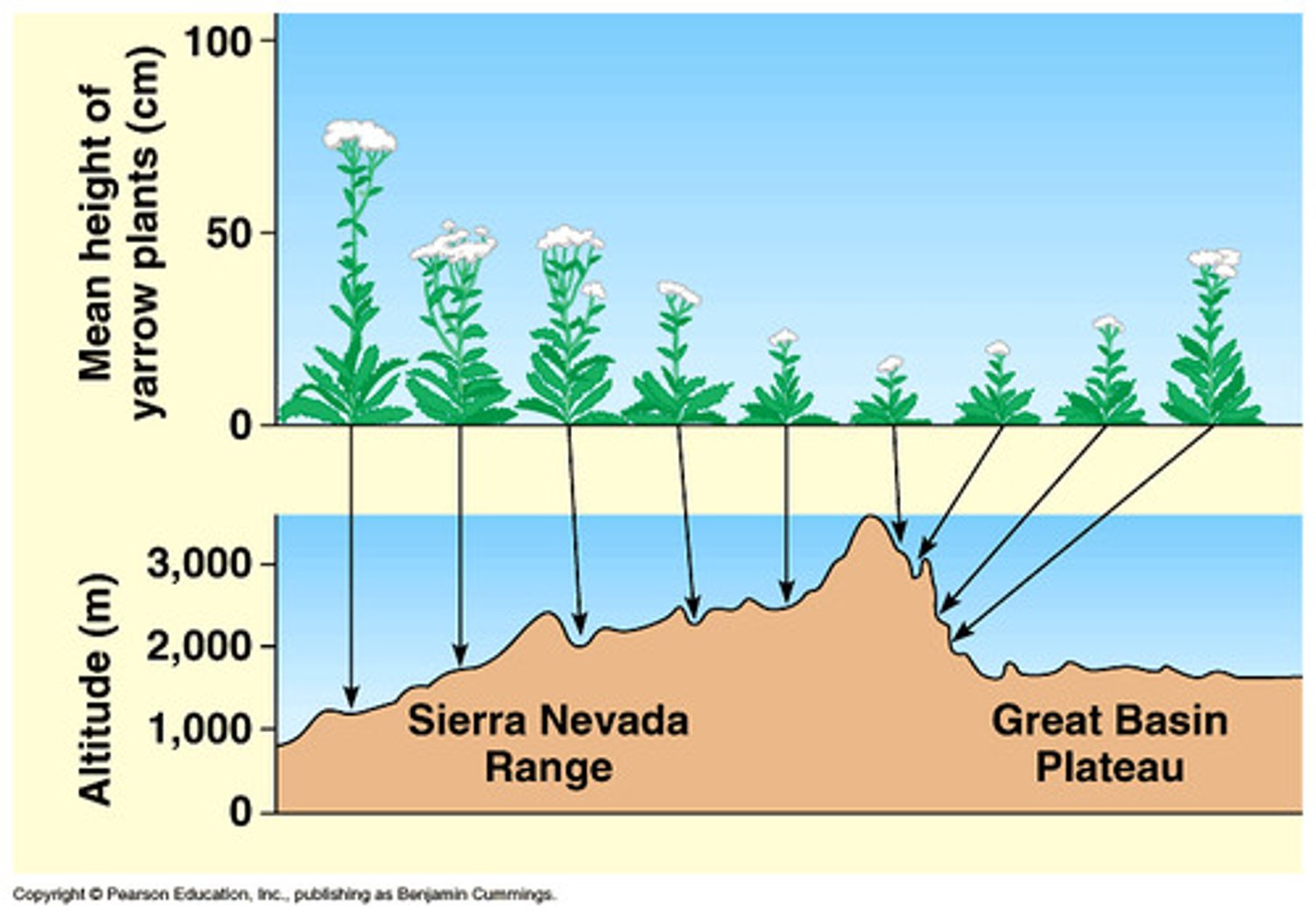
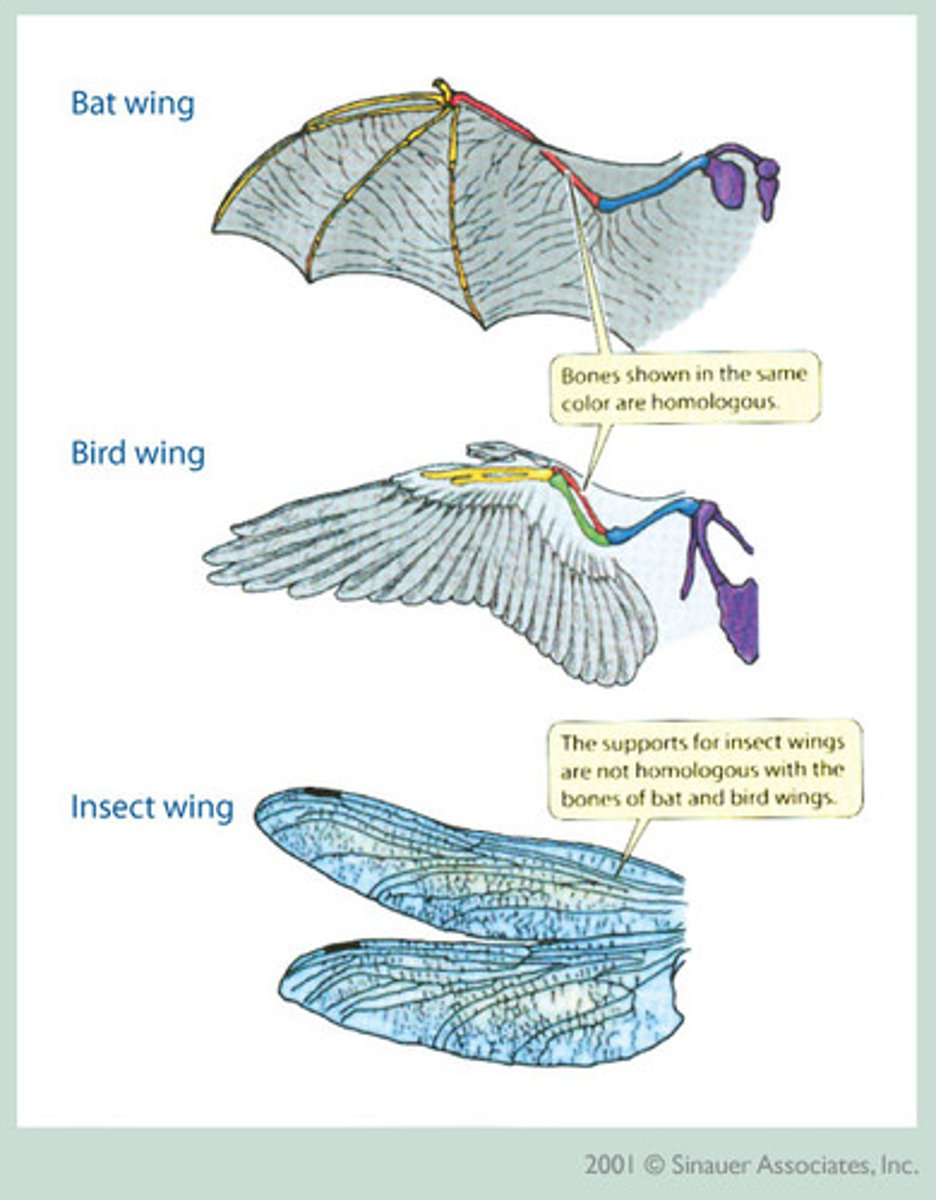
Homologous structures
similar evolutionary history but have developed to suit different functions e.g wing of bat, flippers of dolphin
Postzygotic
RIMS acts as fertilization to prevent exchange of genes between populations, by repairing development or fertility of offspring
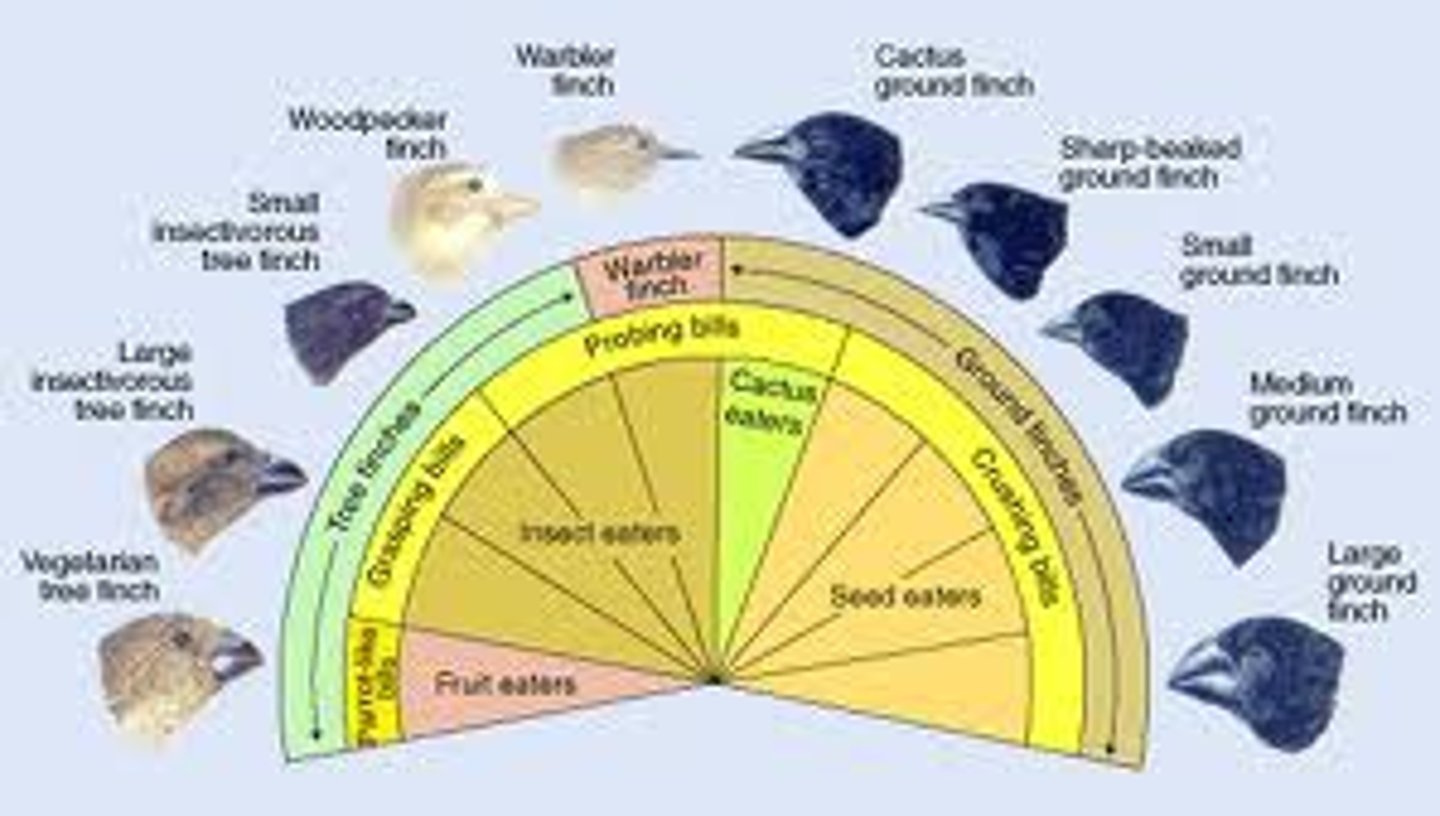
Adaptive Radiation
form of divergent evolution in which there is a rapid increase in numbers of forms from an ancestral type because of the sudden availability of niches.
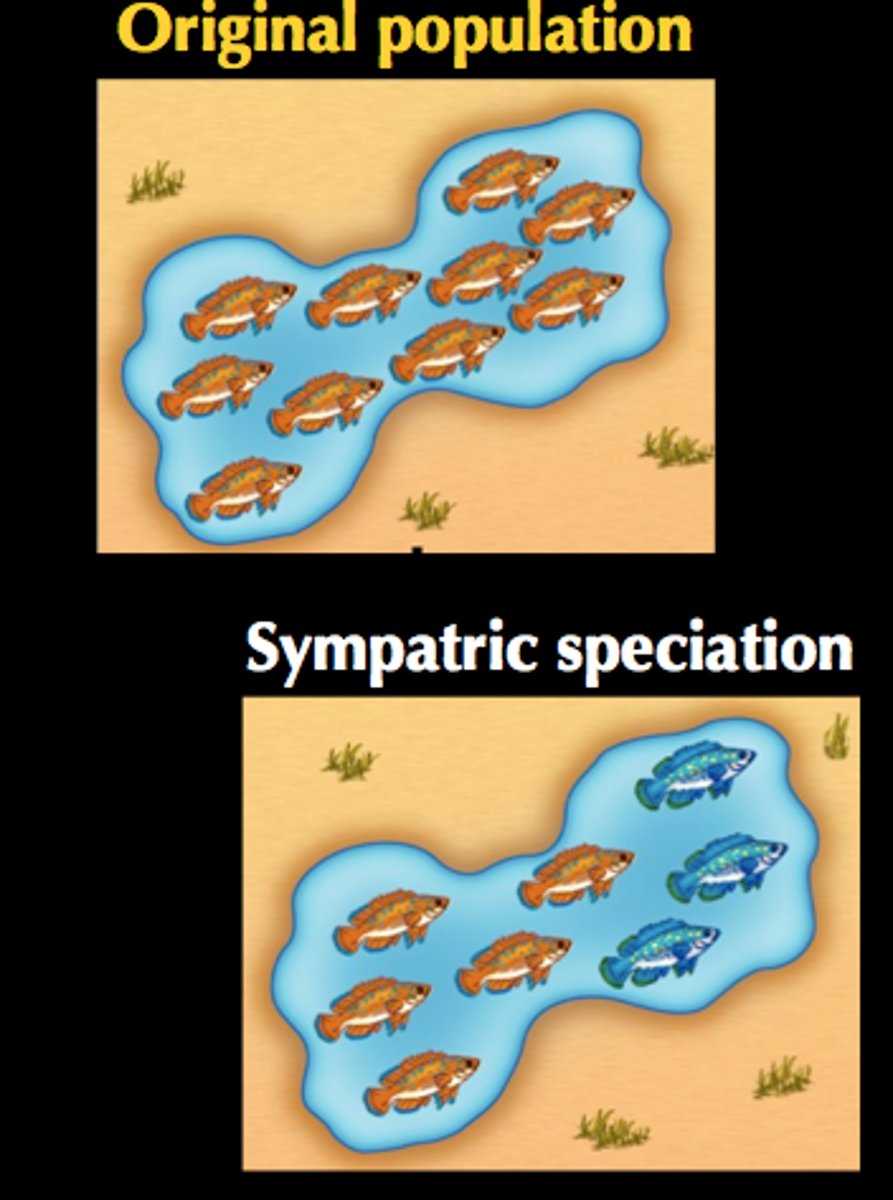
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation occurring where organisms living in the same area are theoretically capable of interbreeding, but cannot because of difference in behavior, flowering times
Instant Speciation
Formation of new species thru autopolyploidy or allopolyploidy, because the chromosome numbers of new "instant" species DO NOT match that of the original species, they cannot interbreed
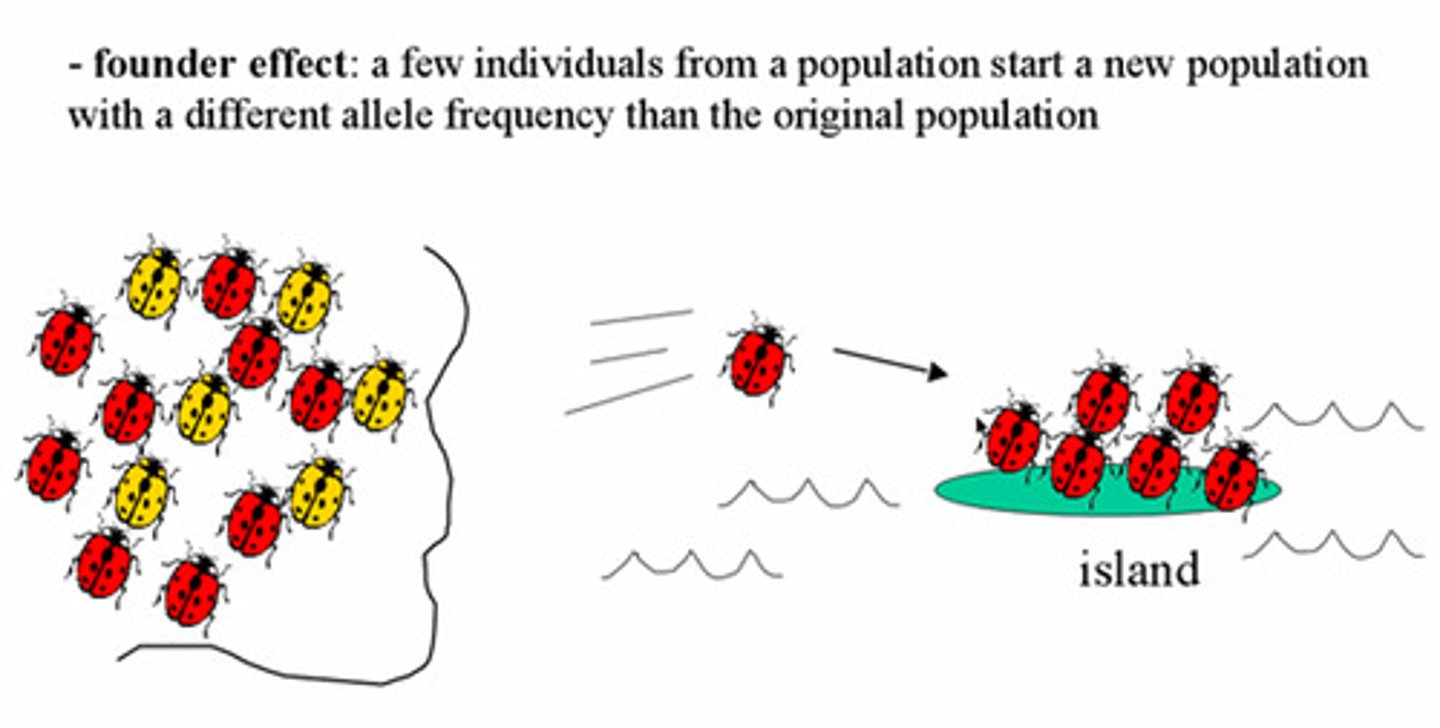
Founder effect
A chance change in allele frequency which occurs when a small group of individuals become detached from the main population
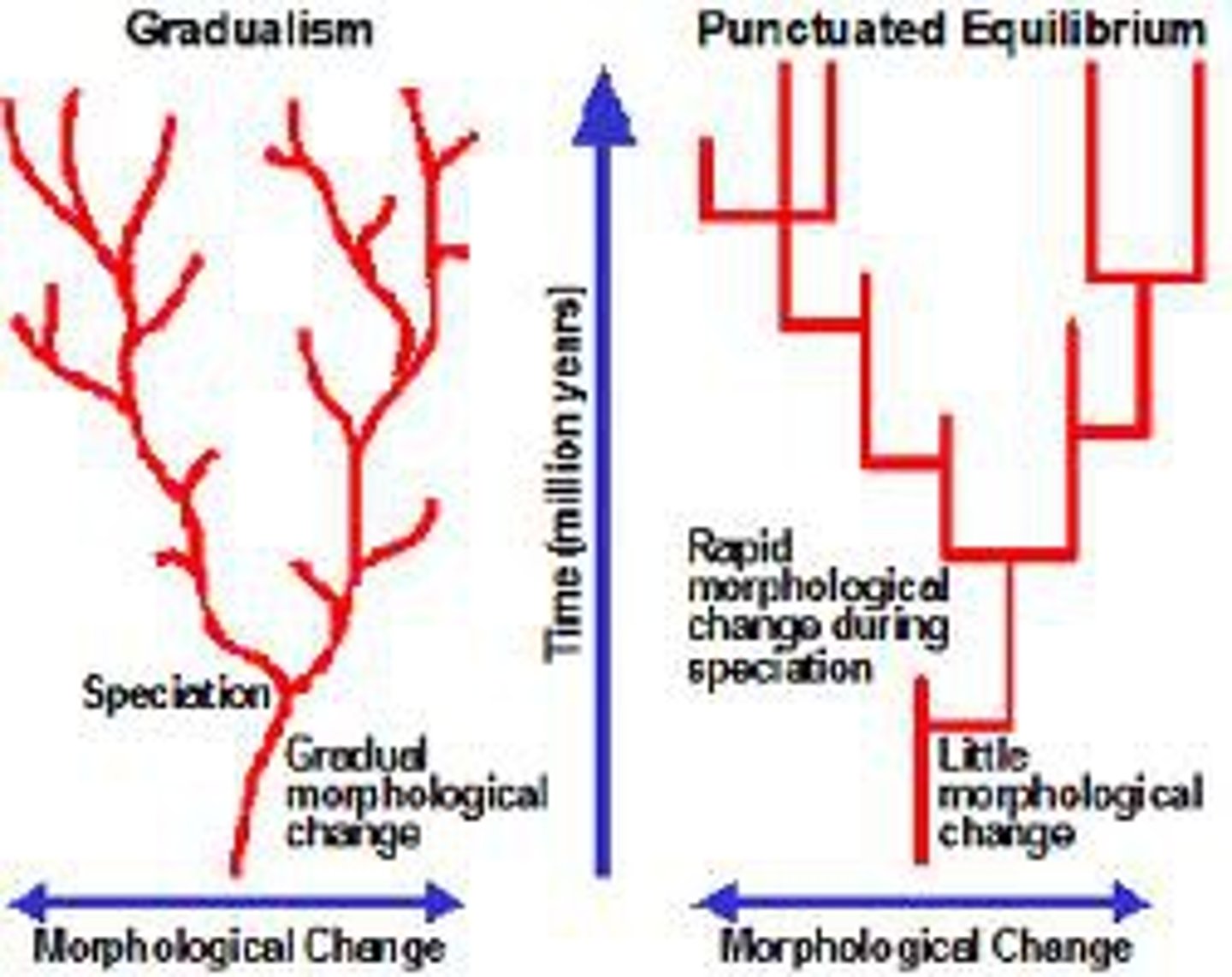
Punctuated equilibrium
long periods of little evolutionary change (stasis) interrupted by short bursts of rapid speciation
Hybrid breakdown
The hybrid offspring are fertile but produce infertile or non viable offspring
Geological record
Fossils persevered in sedimentary rock layers that ca be used to trace evolutionary history of a species
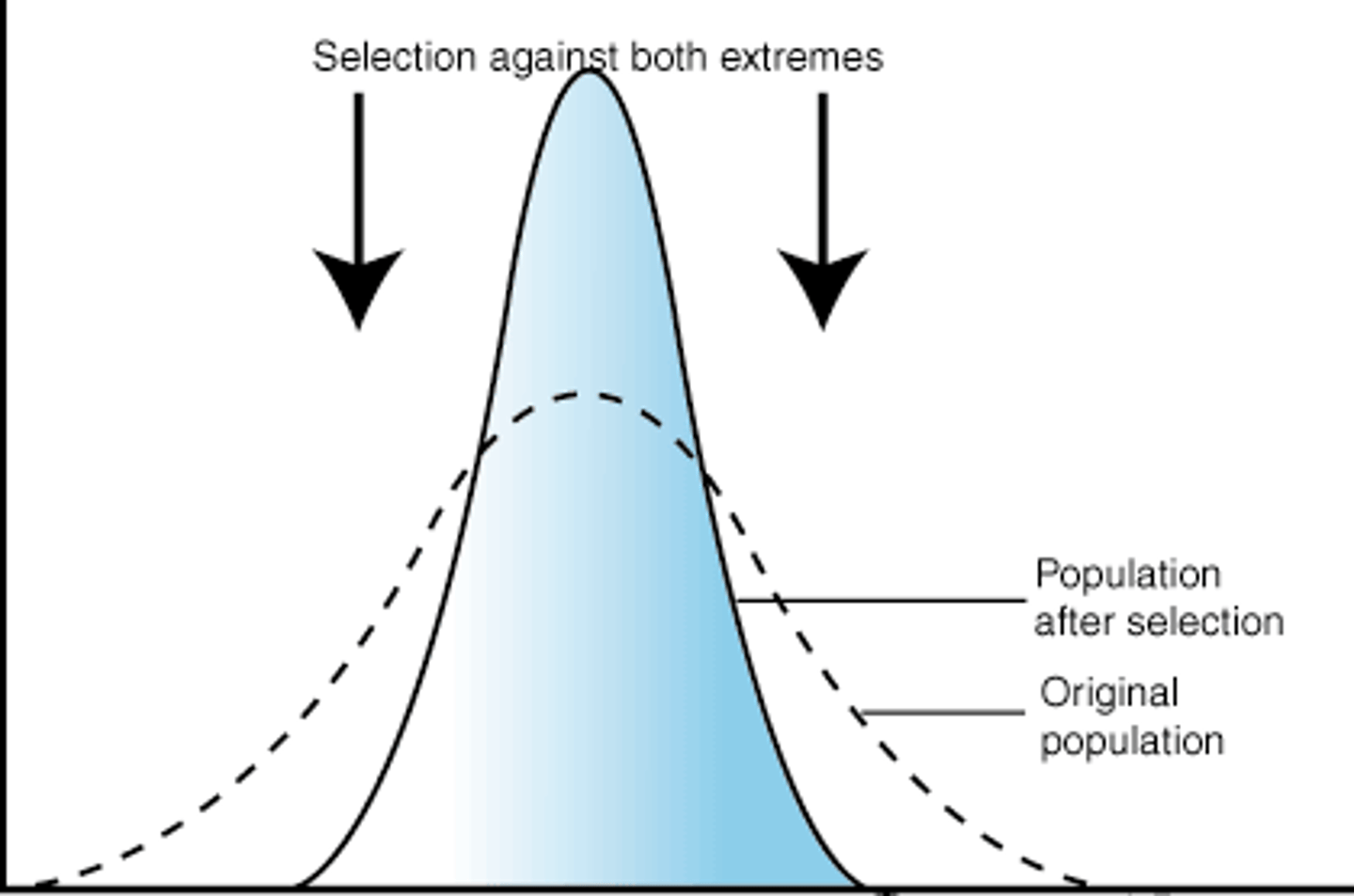
Stabilizing selection
Natural selection acting against the extremes of a range of variation, resulting in resistance to change in allele frequencies
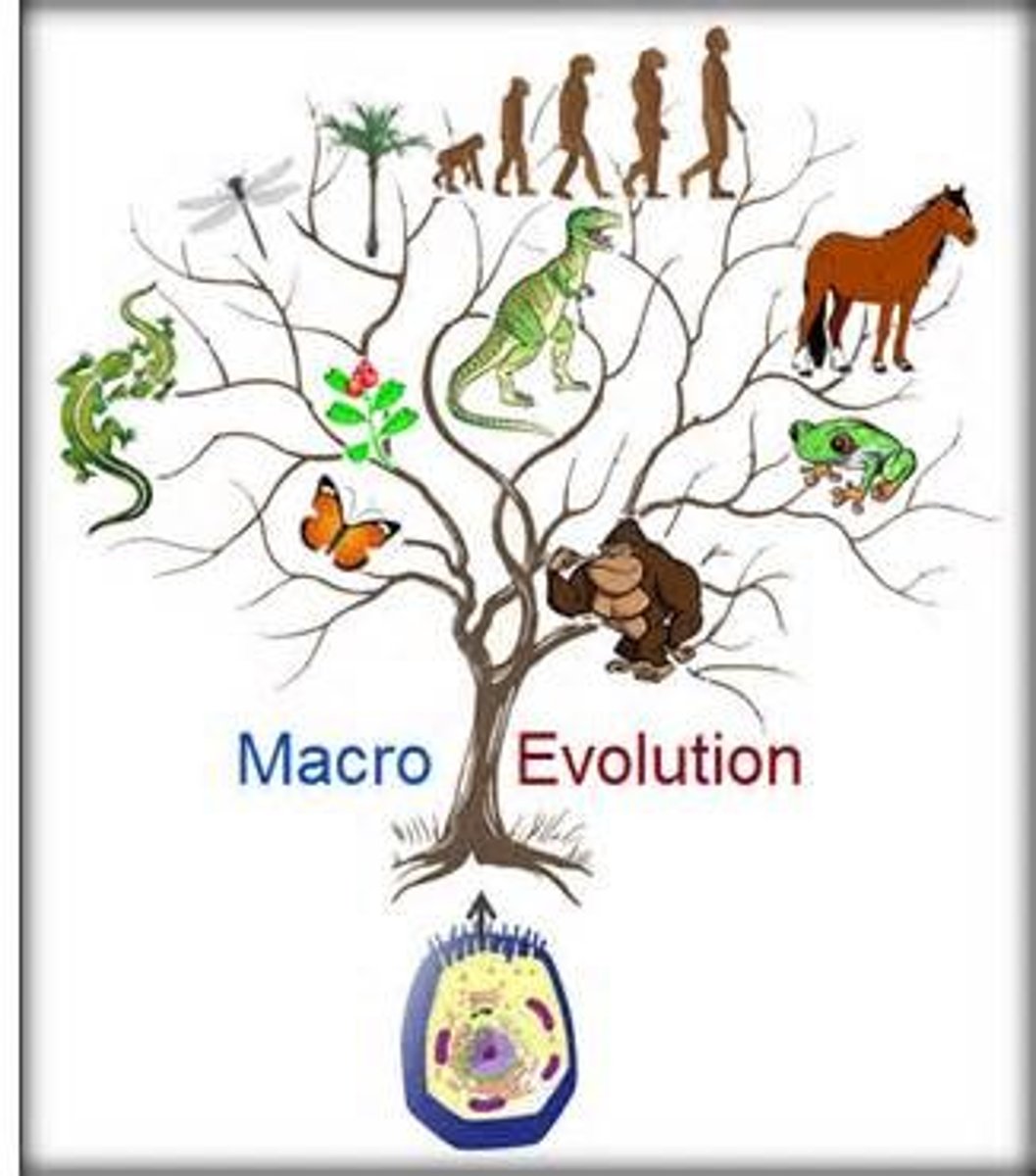
Macro-evolution
The formation of a completely new species, genera etc
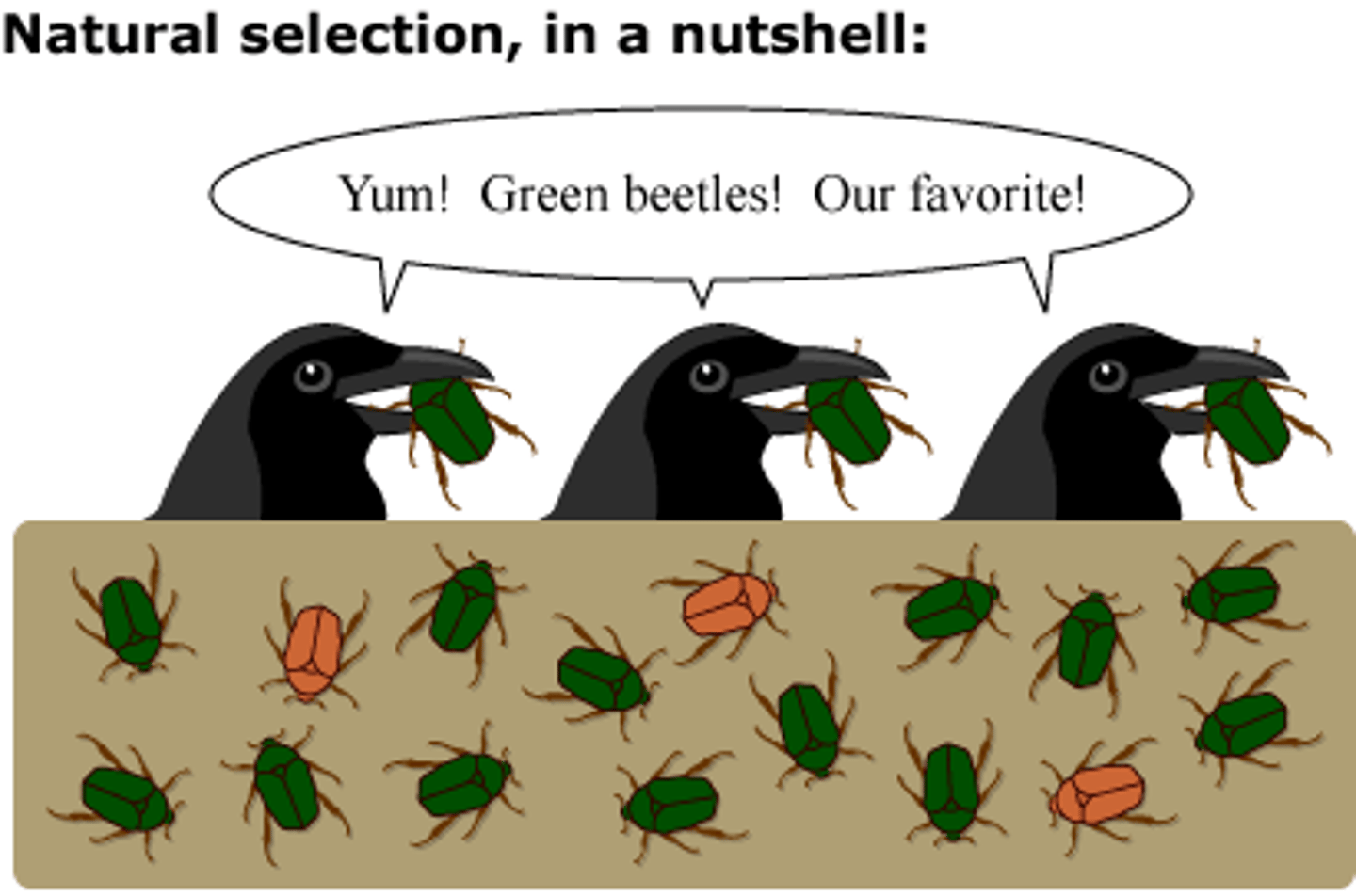
Natural selection
process that brings about new species by the elimination of the less adapted individuals and the survival of the organisms which are better adapted
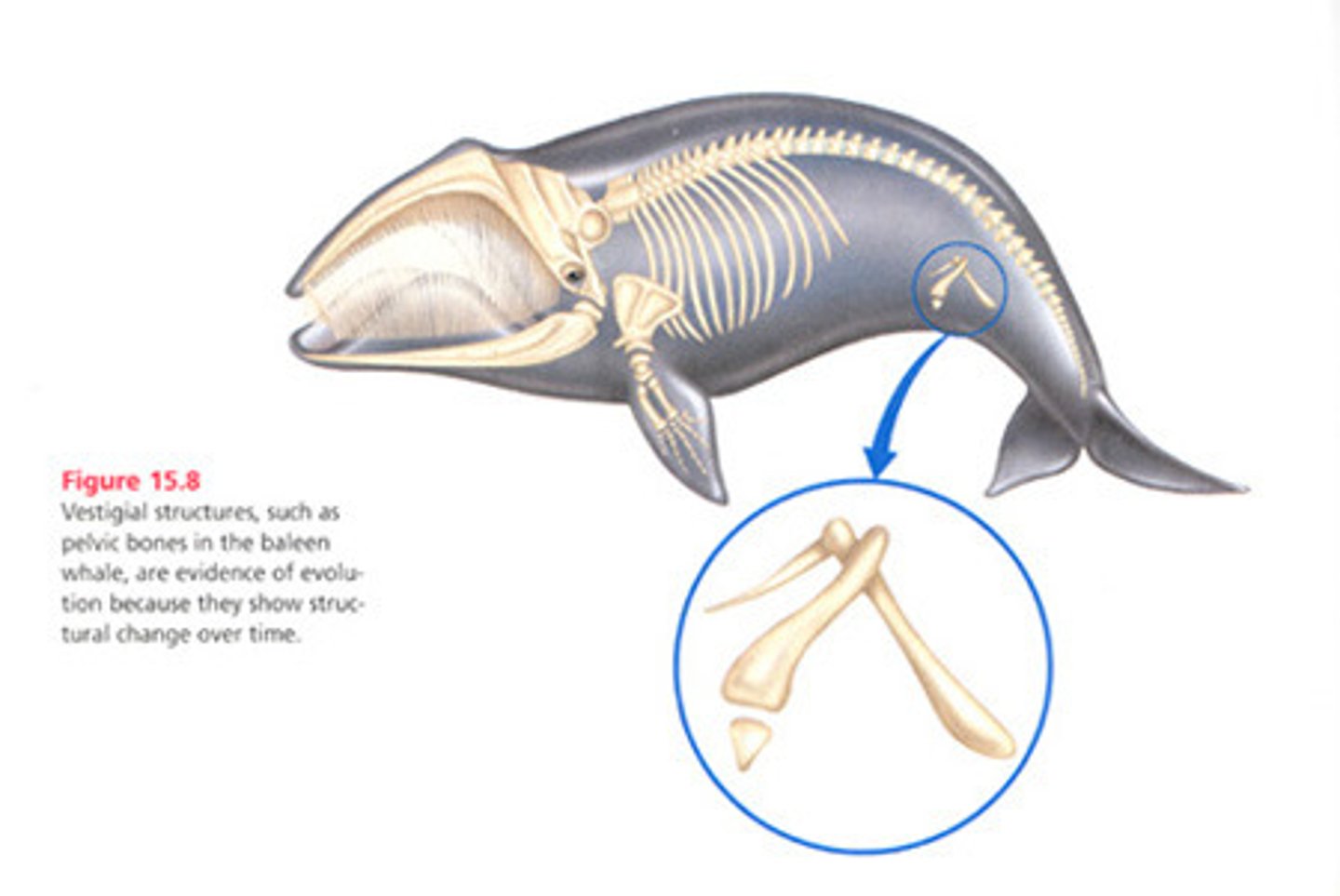
Vestigial organ
Any part of an organism that has diminished in size during its evolution because the function it serves has decreased in importance, e.g appendix in humans
Reproductive Isolation Mechanisms
A barrier to breeding that exist due to differences in mating seasons or mating organisms
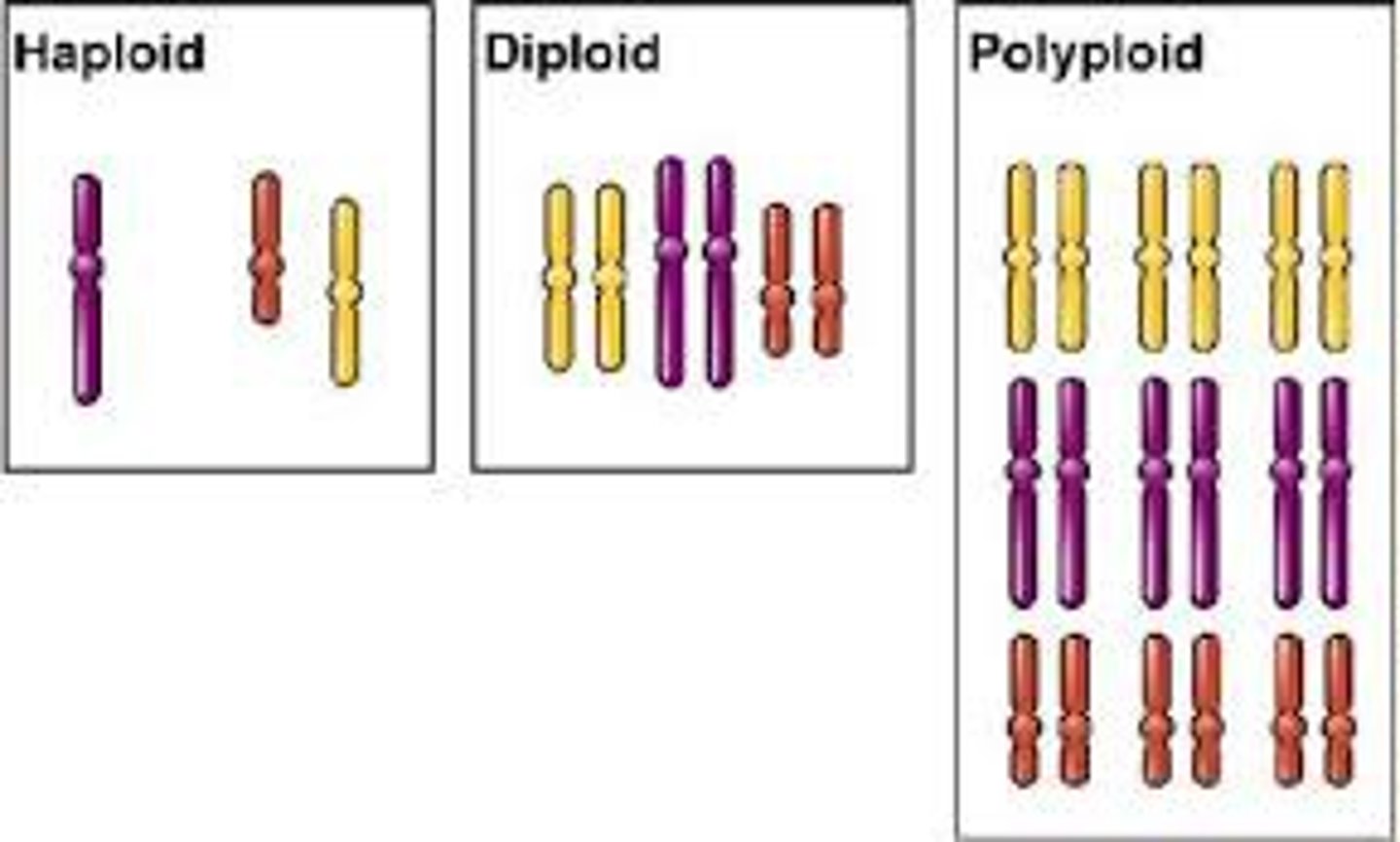
Polyploidy
Mutation producing more than twice the normal haploid number of chromosomes
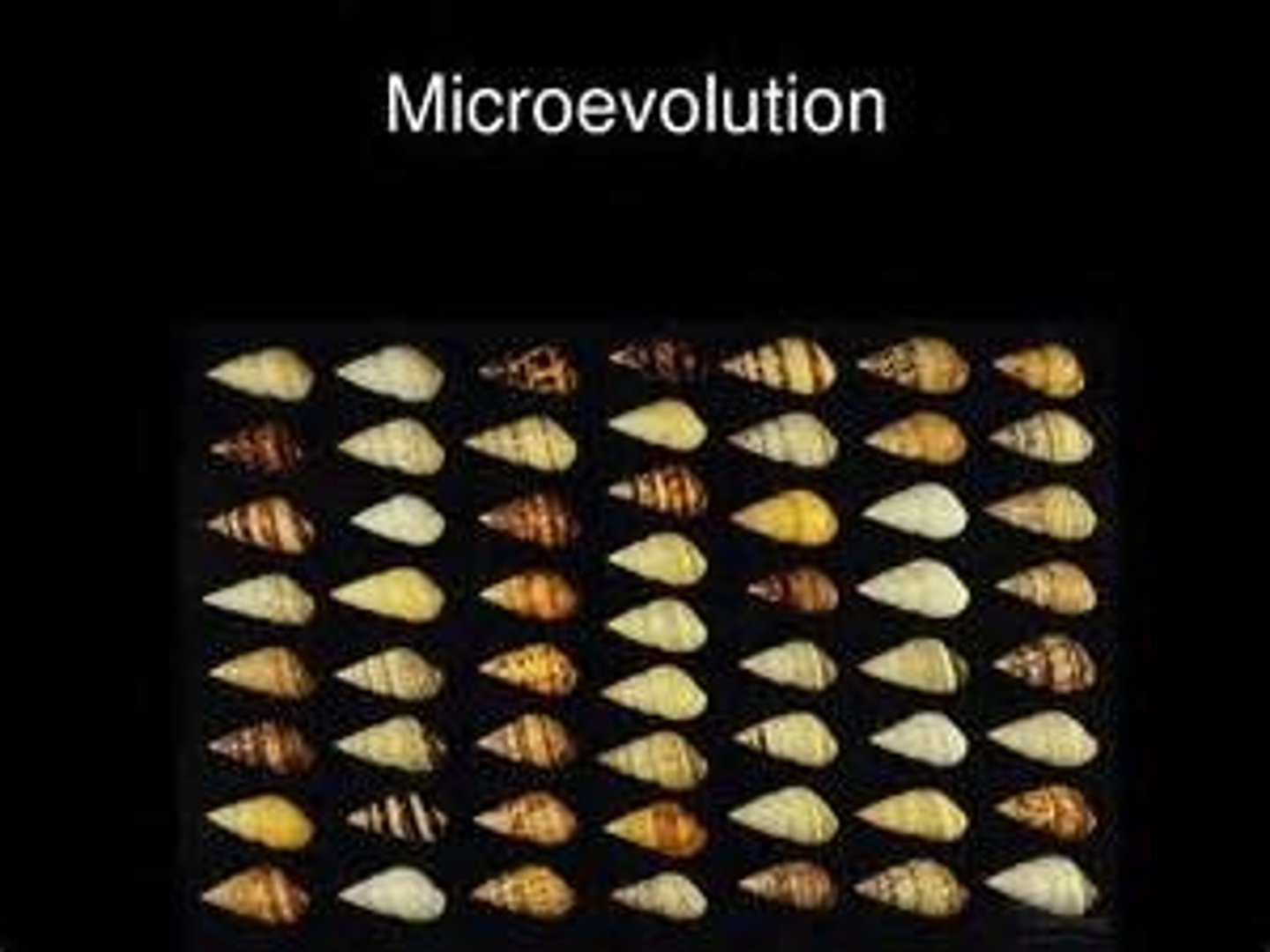
Micro-evolution
accumulation of (through mutation) new characteristics in a species

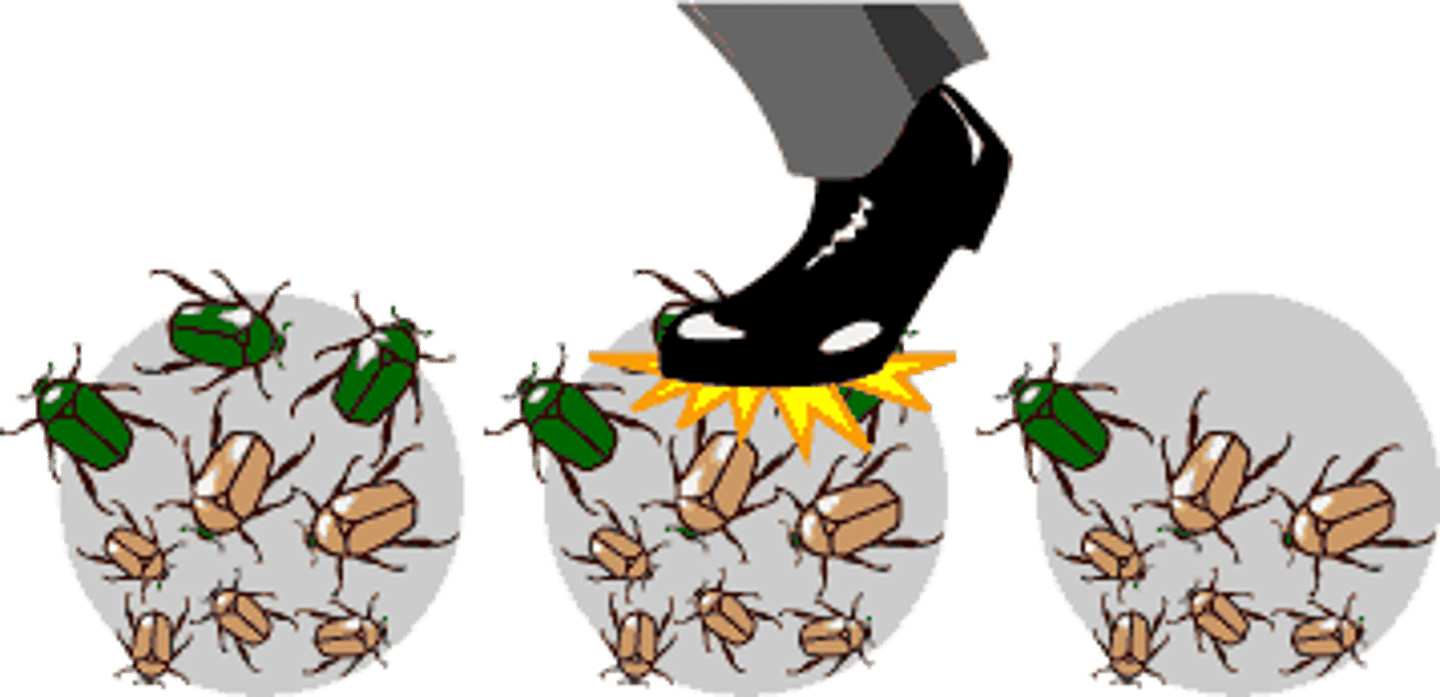
Disruptive selection
Natural selection acting against the middle of a range of variaton
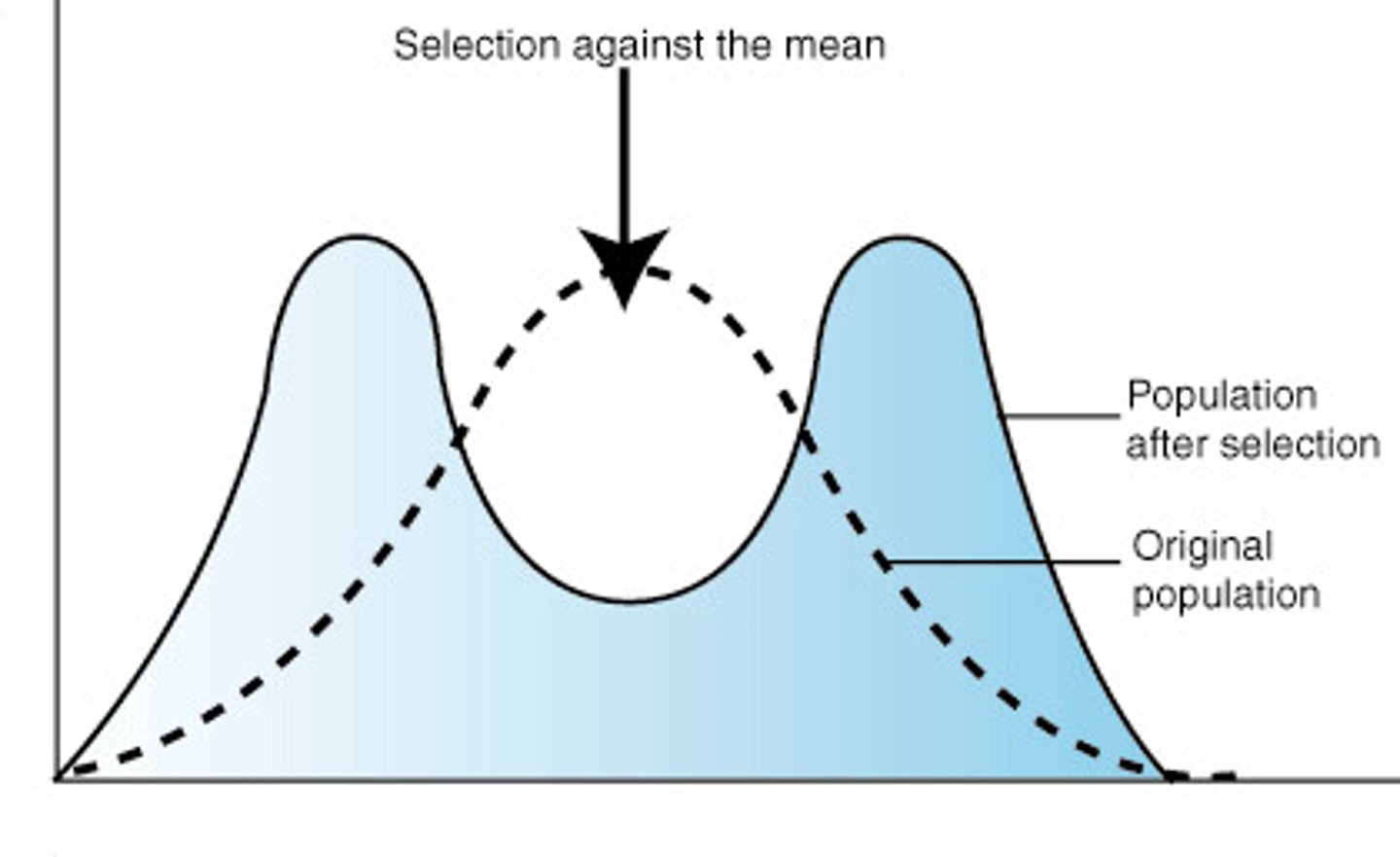
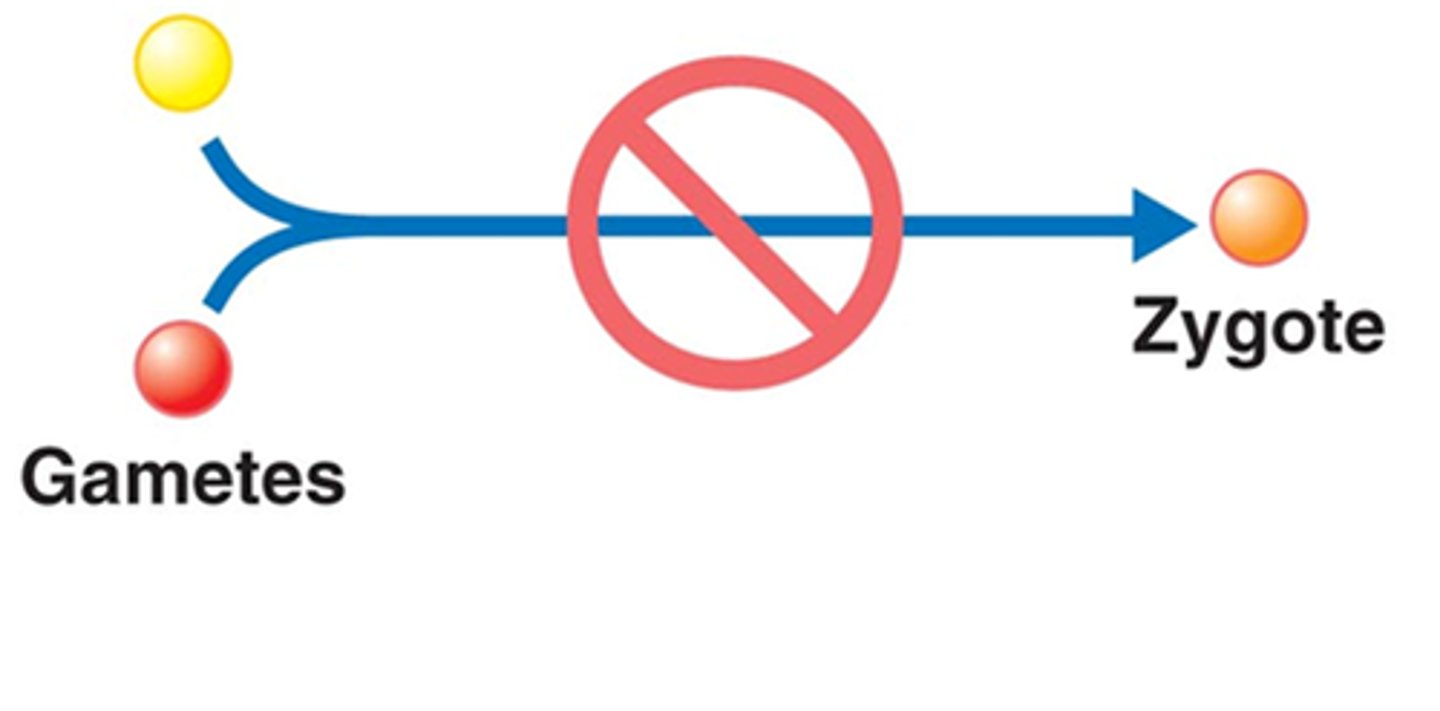
Prezygotic
RIMs that acts to prevent the fusion of gametes from different populations
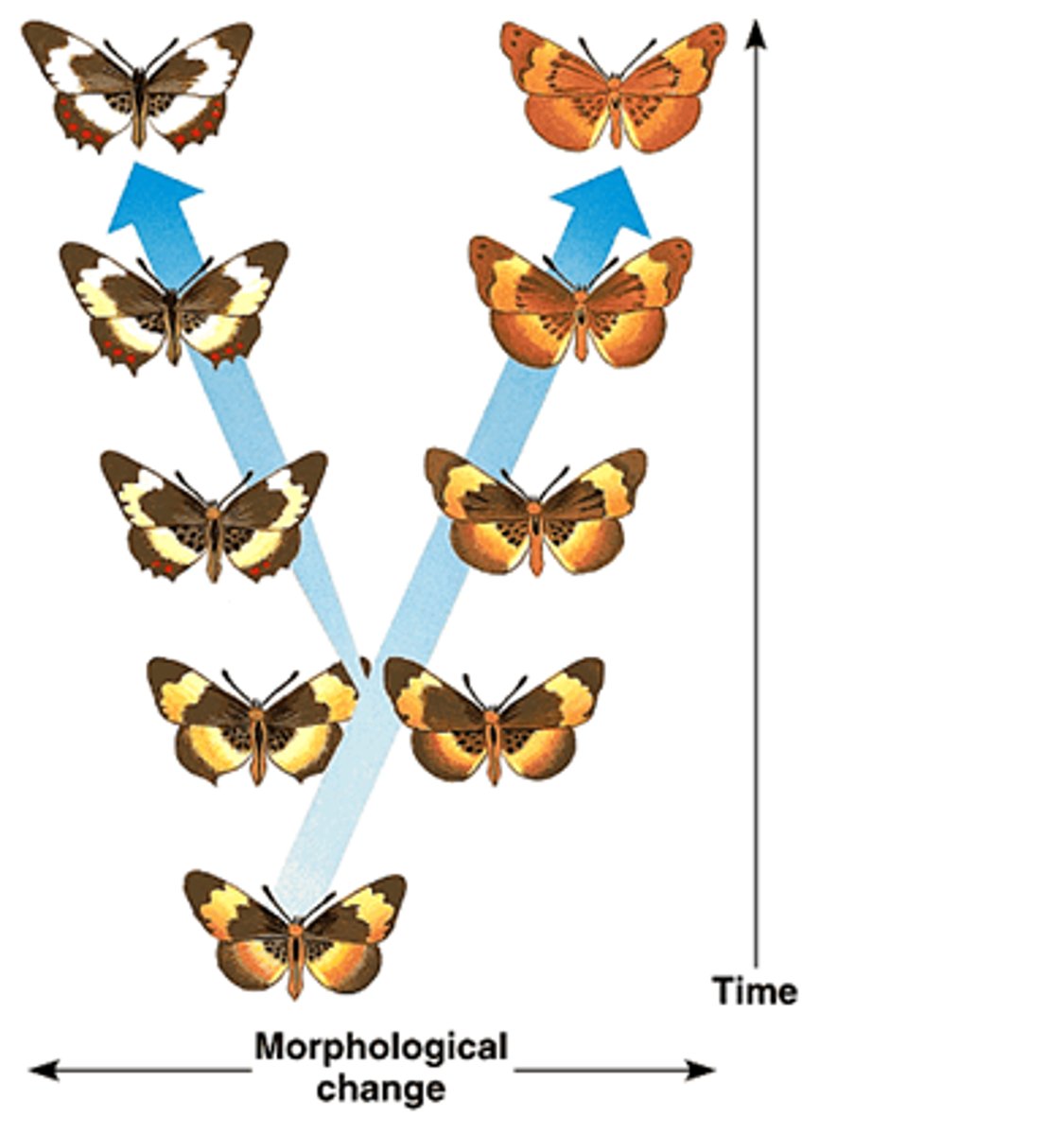
Gradualism
Evolution proceeds slowly but continuously. Eventually the accumulated changes result in speciation
Genetic Drift
The change in allele frequency due to the accumulated effects of chance

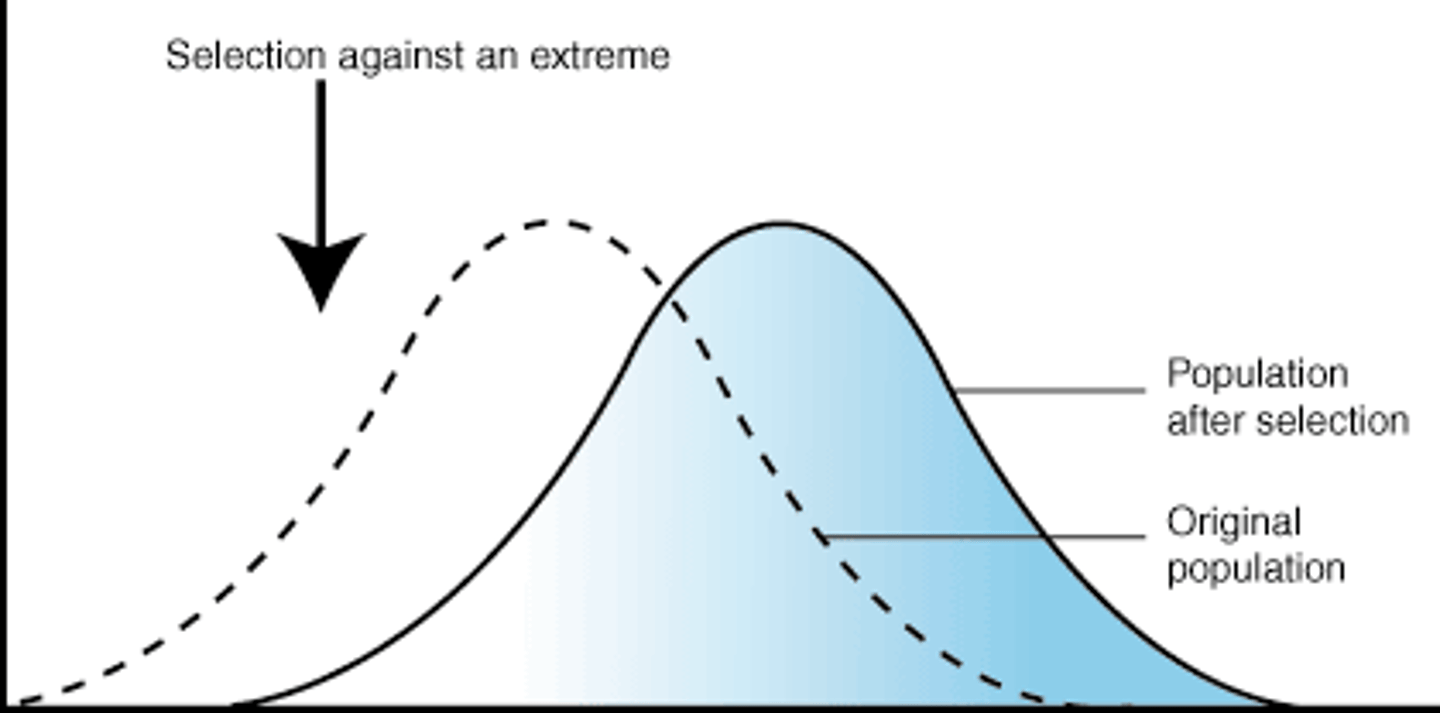
Directional selection
Natural selection against one end of a range of variation, resulting in a progressive change in allele frequency
Endemic
Found only in that country