The Atomic Model
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Who gave the name to the smallest particle of matter (atom)?
Demotricus
Who revived Demotricus’ atomic theory?
John Dalton
Who invented the Plum Pudding model in 1904?
J.J. Thomson
What did the Plum Pudding model suggest?
An atom is a sphere of positive charge, with negatively charged electrons embedded in it
Who conducted the Gold Foil experiment or the alpha particle scattering experiment in 1909?
Ernest Rutherford
What did Ernest Rutherford discover?
nuclear model
What is the evidence behind Rutherford’s model of the atom?
particles passing through the foil so was mostly made of empty space
positive charge in atom since like charges repel
particles coming back meant had positive charge + mass are concentrated in nucleus
The way electrons are arranged can be changed if…
they are hit with light energy
If an electron is hit by a photon…
then it moves to a higher energy state - it is now in an excited state
When an electron moves to a lower energy state,…
it releases out the energy
What is radioactivity measured in?
Becquerels (Bq)
What does 1Bq equal to?
1 decay per second
What piece of equipment displays the amount of radioactivity in Bq?
Geiger-Müller tube
count rate
number of decays per second
How does a Geiger counter detect ionising radiation?
uses Geiger-Müller tube with low pressure gas
radiation enters tube, ionizes gas then creates charged particles
particles attracted to oppositely charged electrodes cause short electrical impulses - no. of pulses/ clicks indicates level of radiation
isotope
An element that has the same number of protons but different number of electrons
radioactive
when a substance has unstable nucleus that emits energy
Who discovered the concept of shells in 1913?
Niels Bohr
Who discovered neutrons in 1932?
James Chadwick
What are the types of radiation?
alpha (α), beta (β), gamma (γ)
What does alpha radiation consist of?
2 neutrons and protons (helium nuclei)
What is the charge and atomic mass of alpha radiation?
+2, 4
What is the ionizing and penetration power of alpha radiation?
strongly ionizing, stopped by paper or a few cm of air
What does beta radiation consist of?
a high energy electron
What is the charge and atomic mass of beta radiation?
-1, 1/1860th of proton
What is the ionizing and penetration power of beta radiation?
weakly ionising, stopped by few mm of aluminium
What does gamma radiation consist of?
high energy electromagnetic radiation
What is the charge and atomic mass of gamma radiation?
0, 0
What is the ionizing and penetration power of gamma radiation?
very weakly ionising, stopped by several cm of lead
Order the types of radiation by deflection, first one having strong deflection
beta, alpha, gamma
How can alpha radiation be represented?
as a helium atom
How can beta radiation be represented?
e or beta symbol with 0 at top and -1 at bottom
How can gamma radiation be represented?
γ
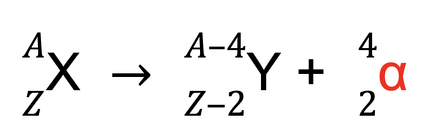
nuclear equation for alpha decay
memorised
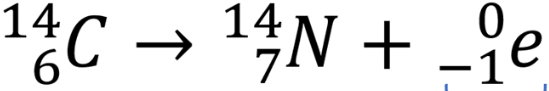
nuclear equation for beta decay
memorised
contamination
unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms and occurs if on and/or in the object
irradiation
when an object is exposed to nuclear radiation and does not cause object to become radioactive
characteristics of contamination
radiation can not be blocked
can be very difficult to remove
causes object to be radioactive for as long source is on or in it
occurs if radioactive source is on or in object
characteristics of irradiation
doesn’t cause object to become radioactive
occurs when object exposed to source of radiation outside
can be blocked from object
can stop when source is removed
Sievert (Sv)
unit of radiation dosage
uses of irradiation
sterilise medical equipment
destroy cancer cells using gamma rays
uses of contamination
tracers inside body
isotope emits gamma rays that easily pass through body to a detector outside body
find leaks in pipes
natural sources of background radiation
radon gas from rocks
living things and food
cosmic rays
human sources of background radiation
medical applications + waste
fallout from nuclear bomb testing
nuclear accident
How do you measure background radiation?
Remove any extra radioactive sources from the room.
Use a Geiger-Müller tube and count how many clicks there are in a minute.
Number of clicks / 60 seconds to get the count rate in Becquerels (Bq).
Repeat and find an average count rate.
half life
time it takes for half the number of radioactive particles in a sample to decay
background radiation
natural radiation that is always present in the environment