AICE Marine A Level Chapters 1-3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
1
New cards
Solid
least kinetic energy; more rigid, vibrate in place; strong intermolecular forces
2
New cards
liquid
more than solid; can pour/flow easily
3
New cards
gas
most kinetic energy; fast moving; attractive forces between molecules are weak
4
New cards
temperature
measure of average kinetic energy of all of the molecules, phase change occurs when energy changes
5
New cards
Evaporation
occurs at surface of liquid
6
New cards
structure of atoms
nucleus(contains protons and neutrons); electrons in electron shell
7
New cards
valence electrons
in outermost electron shell
8
New cards
Salinity
Concentration of solids and gases/salts in dissolved seawater
9
New cards
covalent bond
sharing of electrons between atoms (co= together/valent=valence electrons
10
New cards
Know covalent molecules in water, co2, o2, sulfur dioxide and glucose
…
11
New cards
ion
charged atom or molecule
12
New cards
positive ion when…
losing an electron
13
New cards
negative ion when…
gaining an electron
14
New cards
identify ionic substances such as…
sodium chloride and calcium carbonate
15
New cards
chem formula for sodium chloride
NaCl
16
New cards
chem formula for Magnesium sulfate
MgSO4
17
New cards
Chem formula for Calcium carbonate
CaCO3
18
New cards
formation of hydrogen bonds
* Polar molecule
* Attraction between positive H and negative O of 2 different water molecules
* Attraction between positive H and negative O of 2 different water molecules
19
New cards
how does hydrogen bonding effect solvent action
* fats and oils won’t dissolve
* Solubility decreases as temp of water increases
* Solubility decreases as salinity increases
* Solubility decreases as temp of water increases
* Solubility decreases as salinity increases
20
New cards
how does hydrogen bonding effect density
* lower temps=increased density
* Solid water (ice) = less dense than liquid
* Increase salinity= increase density
* Solid water (ice) = less dense than liquid
* Increase salinity= increase density
21
New cards
how does hydrogen bonding affect heat capacity
* liquid water has higher heat capacity than air
* it takes more energy to change the temperature of water\`
* it takes more energy to change the temperature of water\`
22
New cards
solute
particles/substance that is dissolved
23
New cards
solvent
substance that dissolves other substances
24
New cards
solution
homogeneous mixture with dissolved particles/substances
25
New cards
solubility
ability of a substance to dissolve
26
New cards
effect of water temperature on solubility of salts
* as temp increases, solubility of salts increases
* higher temp = water molecules moving faster; more collisions with salt
* higher temp = water molecules moving faster; more collisions with salt
27
New cards
salinity
concentration of dissolved salts in seawater
28
New cards
pH scale is..
a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in water
29
New cards
acidic
more hydrogen ions; 0-6
30
New cards
basic
more hydroxide ions; 8-14
31
New cards
solubility of oxygen in water
low
32
New cards
effect of water temp on solubility of GASES
colder/lower temp = greater solubility of gases
33
New cards
effect of pressure (depth) on solubility of gases
increased pressure = greater solubility
34
New cards
effect of atmospheric pressure on solubility of gases
increased pressure = greater solubility of gases
35
New cards
effect of salinity on solubility of gases
increased salinity = decrease solubility of gases
36
New cards
why is there more O2 near the surface
* turbulence/waves and wind increases atmospheric dissolution (more in atmosphere than in water)
* photosynthetic organisms live near surface due to sunlight intensity
* photosynthetic organisms live near surface due to sunlight intensity
37
New cards
why does O2 decrease beyond 200m
* no photosynthetic organisms, only respiring organisms
* decay (dead organisms sink)
* decay (dead organisms sink)
38
New cards
why is there a slight increase in O2 in deeper waters
* lower temperature= higher solubility
* higher pressure = higher solubility
* higher pressure = higher solubility
39
New cards
effect of temperature on density
lower temp = denser water bc water molecules are closer together, thus increasing the density
40
New cards
effect of pressure on density
increased pressure = denser water
41
New cards
effect of salinity on density
increased salinity = denser water bc it increases the mass
42
New cards
density formula
mass/volume = density (kgm^-3)
43
New cards
density of ice is lower than sea water causing it to…
float
44
New cards
why does density lower when water freezes
* hydrogen bonds expand which decreases the mass/volume
* Less dense floats on denser molecules
* Less dense floats on denser molecules
45
New cards
importance of ice floating
* thermal insulator - prevents heat loss from water below; keeps water below warmer than air; barrier between water and air; prevents whole water column from freezing
* habitat- for penguins and seals (Antarctica)
* habitat- for polar bears, seals, and other terrestrial mammals (Arctic)
* habitat- algae and small organisms attach to the underside of ice
* habitat- for penguins and seals (Antarctica)
* habitat- for polar bears, seals, and other terrestrial mammals (Arctic)
* habitat- algae and small organisms attach to the underside of ice
46
New cards
density is dependent on…
temperature and salinity
47
New cards
does denser water sink or float
sink
48
New cards
thermocline
rapid decrease in temperature over depth
49
New cards
halocline
rapid increase in salinity over depth
50
New cards
pycnocline
increase in density over depth
51
New cards
how does mixing of these layers occur at the surfaces
wind, waves, currents, upwelling
52
New cards
how does mixing of these layers at deeper depths occur
dense water sinking, deep currents, and upwelling
53
New cards
structure of the earth
\
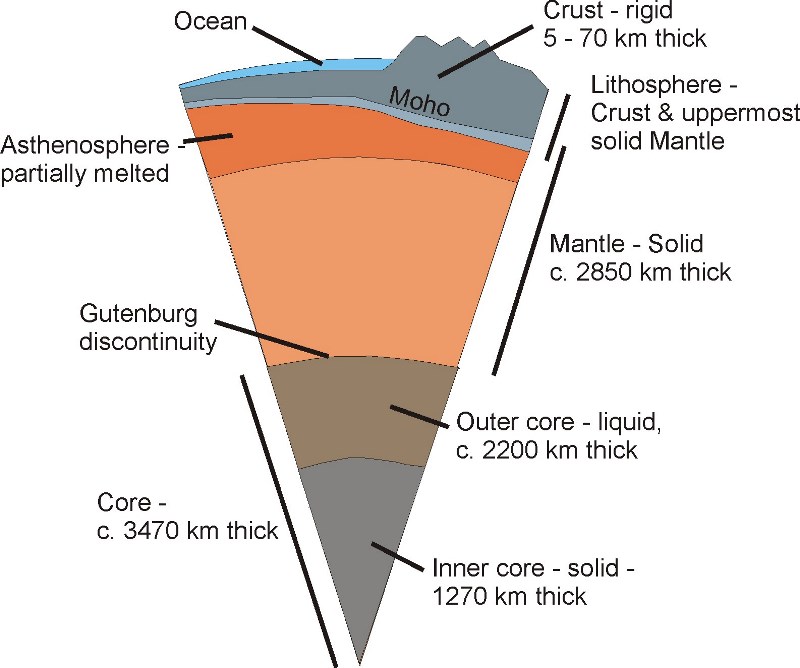
54
New cards
theory of plate tectonics
1. earth’s crust is broken into plates
2. that float on the (denser) asthenosphere/mantle
3. due to convection currents in the mantle
4. causing plates to diverge (any boundary is okay)
5. once 1 single supercontinent (Pangaea)
55
New cards
evidence that proves that there was once 1 single supercontinent
1. rock strata are the same on separate continents
2. same fossil species on separate continents
3. paleomagnetic stripes on seafloor
4. puzzle-like/jigsaw fit of the continents’ edges
56
New cards
divergent
plates separate due to convection currents in the mantle
57
New cards
what do divergent boundaries produce
* mid-ocean ridges
* hydrothermal vents
* abyssal plains
* volcanoes
* earthquakes
* new crust
* hydrothermal vents
* abyssal plains
* volcanoes
* earthquakes
* new crust
58
New cards
convergent
plates move towards each other
59
New cards
what do convergent boundaries produce
* trenches
* volcanoes
* earthquakes
* tsunamis (fast moving waves→ displacement of water) created by the built-up pressure
* loss of crust
* volcanoes
* earthquakes
* tsunamis (fast moving waves→ displacement of water) created by the built-up pressure
* loss of crust
60
New cards
transform
plates slide past each other
61
New cards
what do transform boundaries produce
* earthquakes
* fault lines
* fault lines
62
New cards
how do hydrothermal vents form
1. cold ocean water seeps through cracks in the crust
2. oxygen and potassium are removed from the seawarer
3. calcium, sulfate, and magnesium are removed from the fluid
4. Sodium, calcium, and potassium from the surrounding crust enter the fluid
5. when the fluids have reached their highest temp, Copper, zinc, iron, and sulfur from the crust dissolve in the fluids
6. hot fluids carrying dissolved metals rise up through the crust
63
New cards
when do hydrothermal vent plumes form
when water coming from hydrothermal vents which is hot and rich in dissolved nutrients is under pressure
64
New cards
weathering
break down of rocks/sediment produces small fragments
65
New cards
erosion
carried away/removal of sediment
66
New cards
chemical weathering
more acidic water will break down rocks, shells, and coral’s exoskeleton
67
New cards
physical weathering
the movement of water (waves and currents) and suspended sediment/sand will break down rocks and coral’s skeleton
68
New cards
organic weathering
AKA biological weathering; burrowing animals and coral’s predators
69
New cards
erosion by ice
glaciers move and weather/carve and create fjords; deposit sediment in new locations as the glacier moves
70
New cards
erosion by water
rivers, waves, currents, and tides will deposit sediment elsewhere
71
New cards
erosion by wind
wind can carry sediment great distances
72
New cards
erosion by gravity
particles will be dragged down through the depths due to gravity
73
New cards
four main types of erosion
ice
water
wind
gravity
water
wind
gravity
74
New cards
sedimentation
deposition/build-up/accumulation of sediment/suspended particles
75
New cards
littoral zone
the intertidal region on a shoreline, between the HIGHEST and LOWEST spring tide marks = between the highest high tide and the lowest low tide mark on the coast
76
New cards
examples of the littoral zone
rocky shores, sandy shores, muddy shores, estuaries and deltas
77
New cards
characteristics of ROCKY shores
* waves, currents, and tides weather the rocky shore/rocks
* little erosion (granite and igneous rocks are resistant to weathering)
* very little sedimentation
* can form rock/tide pools
* rocks provide and attachment site/hiding places/more habitats than sandy shores
* more producers = higher productivity = more food than sandy shores
* little erosion (granite and igneous rocks are resistant to weathering)
* very little sedimentation
* can form rock/tide pools
* rocks provide and attachment site/hiding places/more habitats than sandy shores
* more producers = higher productivity = more food than sandy shores
78
New cards
Marine terraces
wave-cut terraces
weathered and eroded when the sea level was higher
weathered and eroded when the sea level was higher
79
New cards
characteristics of SANDY shores
* typically smaller waves than on a rocky shore
* gradual slope
* sand/sediment constantly shifts (not much energy is needed to move the small particles)
* animals burrow/infauna
* waves, currents, tides, and wind weather and erode sediment (more in winter months)
* waves, currents, tides, and wind deposit sediment (more in summer months)
* gradual slope
* sand/sediment constantly shifts (not much energy is needed to move the small particles)
* animals burrow/infauna
* waves, currents, tides, and wind weather and erode sediment (more in winter months)
* waves, currents, tides, and wind deposit sediment (more in summer months)
80
New cards
characteristics of MUDDY shores
* somewhat protected from waves
* very little weathering/erosion
* formed by sedimentation
* smallest particle size (silt)
* low in oxygen
* animals burrow/infauna
* very gradual slope
* very little weathering/erosion
* formed by sedimentation
* smallest particle size (silt)
* low in oxygen
* animals burrow/infauna
* very gradual slope
81
New cards
characteristics of deltas
* where a river ends at the sea
* rivers’ moving water weather and erode; deposit sediment at the end, on the continental shelf
* shaped by sedimentation
* rivers’ moving water weather and erode; deposit sediment at the end, on the continental shelf
* shaped by sedimentation
82
New cards
characteristics of estuaries
* sheltered or semi-enclosed bodies of water where fresh and salt water mix → low salinity
* sheltered from weathering and erosion by waves, silt and fine sand is deposited here; can have high turbidity
* sheltered from weathering and erosion by waves, silt and fine sand is deposited here; can have high turbidity
83
New cards
4 types of estuaries
* drowned river valley(coastal plain)
* fjord
* bar-built
* tectonic
* fjord
* bar-built
* tectonic
84
New cards
drowned river valley (coastal plain)
formed at the end of the last ice age; increase in sea level flooded the river delta
85
New cards
fjord
formed as a result of weathering and erosion from moving glaciers
86
New cards
bar-built
formed by a sand bar or barrier island
87
New cards
tectonic
formed by tectonic activity; land subsided and sea water flooded in
88
New cards
tides
the vertical movement of water on the coast/ the change in water height on the coastline; due to the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun
89
New cards
tidal range
the distance on the coast between high and low tides (changes daily)
90
New cards
what is tidal range affect by
* alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun
* coastal geomorphology
* wind
* air pressure
* size of the body of water
* coastal geomorphology
* wind
* air pressure
* size of the body of water
91
New cards
how is tidal range affected by the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun
* in a straight line → greater gravitational pull → larger tidal range = spring tides
* at right angles → less gravitational pull → smaller tidal range = neap tides
* at right angles → less gravitational pull → smaller tidal range = neap tides
92
New cards
how is tidal range affected by coastal geomorphology
* as the coast narrows, water piles up on itself, increasing tidal range
93
New cards
how is tidal range affected by wind
* increased wind speed will push more water on and off of the coast, increasing the tidal range
94
New cards
how is tidal range affected by air pressure
* low air pressure = increased tidal range
95
New cards
how is tidal range affected by the size of the body of water
* larger bodies of water have greater tidal ranges
* small bodies of water have little/no tidal range
* small bodies of water have little/no tidal range
96
New cards
spring tide
* largest tidal range
* occurs twice a month
* greatest gravitational pull
* when Earth, Moon, and Sun are in a straight line
* New and Full moon
* occurs twice a month
* greatest gravitational pull
* when Earth, Moon, and Sun are in a straight line
* New and Full moon
97
New cards
Neap tide
* smallest tidal range
* occurs twice a month
* weakest gravitational pull
* when earth, moon, and sun are at right angles
* 1st and 3rd quarter moon
* occurs twice a month
* weakest gravitational pull
* when earth, moon, and sun are at right angles
* 1st and 3rd quarter moon
98
New cards
currents
continuous moving ocean water-- deep and surface currents
99
New cards
cold surface currents move from…
* high latitudes to low latitudes
100
New cards
warm surface currents move from…
low latitudes to high latitudes