pKa, oxidation and reduction
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what does pKa show
the pH at which the acid is half-dissociated
equilibrium in terms of pKa for two molecules together in solution
equilibrium shifts towards the most stable conjugate base (lowest pKa)
how to deprotonate a molecule
use a base with a higher pKa value
how to protonate a molecule
use an acid with a lower pKa value
what is oxidation level
number of bonds to heteroatoms from the carbon atoms that are part of or attached to the functional group
oxidation in terms of oxidation level
lower to higher level
reduction in terms of oxidation level
higher to lower level
effect of unsaturation on oxidation level
greater degree of unsaturation = higher oxidation level
eg alkenes 1, alkynes 2
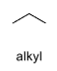
oxidation level
0
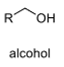
oxidation level
1
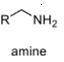
oxidation level
1
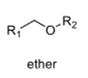
oxidation level
1
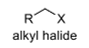
oxidation level
1
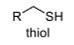
oxidation level
1
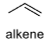
oxidation level
1
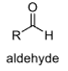
oxidation level
2
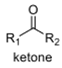
oxidation level
2
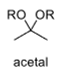
oxidation level
2
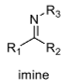
oxidation level
2

oxidation level
2
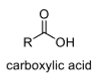
oxidation level
3
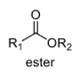
oxidation level
3
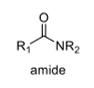
oxidation level
3
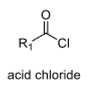
oxidation level
3

oxidation level
3
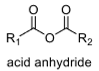
oxidation level
4
to get from alkane → acid anhydride there are 4 oxidation steps
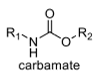
oxidation level
4
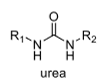
oxidation level
4
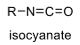
oxidation level
4
oxidation definition
gain of oxygen/loss of hydrogen/loss of electrons
reduction definition
gain of hydrogen/loss of oxygen/gain of electrons
how are oxidation levels used in terms of changing functional groups
if oxidation levels don’t change then we don’t need to use an oxidation or reduction reaction so no oxidising or reducing agents needed