CT MPJE
1/334
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
335 Terms
Who is the "commissioner"
Commissioner of Consumer Protection
How many members are on the Commission of Pharmacy, and who are they?
7 members:
5 full-time pharmacists and 2 members of the public
At least 2 pharmacists from retail: 1 from independent and 1 from chain
At least 1 pharmacist from hospital
How often does the Commission of Pharmacy meet?
at least 6 times per calendar year on the 3rd Wednesday of each month at the office of commission, and at other times when a chairperson or a majority of the commission deems necessary
EXCEPT February, July, and December
the commission should keep a record of its proceedings
How often should the commissioner inspect each retail pharmacy?
not less than once every 4 years
What is the penalty for violating the Pharmacy Practice Act
If no other penalty provided in statute then violation is a Class D felony which can result in:
fines up to $5,000 per violation
imprisonment up to 5 years
or BOTH
Each instance of patient contact is considered a separate offense and penalties are cumulative
What does “Direct Supervision” of pharmacy personnel mean?
Means that the supervising pharmacist:
is PHYSICALLY PRESENT on the premises when routine dispensing activities are occurring; and
supervised personnel are also physically present on the premises; and
the pharmacist conducts IN-PROCESS and FINAL checks on the supervised personnel’s dispensing activities
What are the 6 requirements for a pharmacist LICENSE?
1) submitted a written application on a form approved by the department
2) graduated from a school of pharmacy approved by the commission
3) Hold entry-level professional degree at time of graduation
4) has professional experience as a pharmacy intern (≥ 1500 hours)
5) successfully passed any examinations required by the commissioner
6) eighteen years of age or older at the time of application
The Department of Consumer Protection shall issue a temporary permit to practice pharmacy to an individual who:
-practices under the direct supervision of a licensed pharmacist
-has an application for reciprocity on file with the commission
-is a licensed pharmacist in good standing in a state from which the state's board of pharmacy grants similar reciprocal privileges to pharmacists
-has no actions pending against their license
When will a TEMPORARY permit to practice pharmacy expire?
Upon licensure by CT or 3-months from the date of issuance, whichever occurs first
(the commission may authorize one three-month extension of the temporary permit)
What are the licensure requirements for a graduate from a foreign pharmacy school?
Comply with requirements for temporary permit other than pharmacy intern experience
But must provide proof of at least 1500 hours of equivalent practical experience
Provide documentation of date and place of birth
Pass proficiency tests for written and spoken English
Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE)
Provide proof of US citizenship or employment visa
Pass Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency Examination (FPGEE)
Appear for personal interview with Commission of Pharmacy
What are the requirements for a licensed pharmacist in another state/U.S. jurisdiction to be licensed in CT?
Met equivalent state licensing qualifications at time of licensure
Graduate of accredited/approved school (or meets requirements for graduate of foreign pharmacy school)
CT resident or intends to practice in CT
Practicing for at least 1 year in last 5 years at time of application (or equivalent experience), or licensed by examination within prior 12 months
Licensing jurisdiction grants similar reciprocating privileges to CT licensed pharmacists
Passes CT pharmacy law exam (i.e., CT-MPJE)
Appears for personal interview with Pharmacy Commission
What is the fee for issuance of a pharmacist license?
When does a license to practice pharmacy expire?
How do you renew your pharmacist license?
$200
annually
completion of an application
payment of $105
completion of CE credits
Pharmacy (Location) License Application Requirements
Application must disclose:
Name & address of applicant
Name & address of owner(s)
Name & address of the pharmacy
Name, address & license number of pharmacist manager
When does a pharmacy (location) application need to be submitted?
Application (and fee) must be submitted 15 days prior to next scheduled meeting of the Commission of Pharmacy for review of:
New pharmacy license
Relocation of pharmacy (includes relocating any area of premises licensed as a pharmacy)
A corporation holding a pharmacy license is undergoing changes in directors. Who, if anyone, must be notified and within what time frame?
A corporation (license is location specific) must notify Commission of any change in officers or directors within 10 days
A pharmacy undergoing administrative or legal action has how long to report to whom?
Must report to DCP any administrative or legal action begun by government regulatory agency (federal or state) or accreditation entity within 10 days of receiving notice that action has begun
Define “long term care pharmacy”
Licensed by DCP
Stores/dispenses Rx only drugs and devices to patients/residents of “nursing homes, rest homes, residential care homes or other supervised residential facilities”(i.e., skilled nursing facilities or SNFs)
Includes pharmacies located inside and outside of SNF (but not hospital pharmacies)
Under a protocol may operate APDMs
Nuclear pharmacies must:
Have one nuclear pharmacist supervisor
Who may supervise only one nuclear pharmacy at a time
Must be present at all times pharmacy is open/providing services
Have applicable federal/state licenses & permits to possess/distribute radioactive material
Maintain records of radioactive material acquisition, inventory, and disposition
Comply with NRC and other applicable standards for radiopharmaceuticals
Dispense radiopharmaceuticals only upon order from either licensed prescriber or person authorized by NRC to possess radiopharmaceuticals
What must nuclear pharmacy record orders contain?
Prescribing practitioner/agent and name of institution
Dispensing date and calibration time
Name of procedure
Dose/quantity
Prescription number
Specific instructions
Identity of person dispensing
Patient’s name if Rx is for therapeutic or blood-product radiopharmaceutical
What should the outer container of a radiopharmaceutical have?
Pharmacy name & address
Prescriber’s name
Dispensing date
Prescription number
If radioactive, radiation symbol AND “Caution: Radioactive Material”
Name of procedure
Radionuclide and chemical form
Amount of radioactivity and calibration date
Expiration time
Dosage units
Number of items/weight (if solid) or ampules/vials (if gas)
Patient name OR “For Physician Use”
What should the inner container of a radiopharmaceutical have?
Radiopharmaceutical name
Serial number assigned to order
Standard radiation symbol
“Caution: Radioactive Material”
What is the required (minimum) equipment & supplies a nuclear pharmacy must have?
Radiation detection and measuring instruments
Radiation shielding
Quality assurance testing equipment and supplies
Refrigerator
Equipment and supplies necessary for compounding and dispensing sterile parenteral radiopharmaceuticals
What are the restrictions for having ownership and investment in a pharmacy? What are the exceptions?
Prescribing practitioner and their non-pharmacist spouse and dependent children, may NOT have an ownership or investment interest in a pharmacy.
Exceptions:
Had interest prior to July 1, 1993
Inherited interest
Prescriber is not required to maintain malpractice insurance (i.e., physician who only provides professional services without charge in a licensed tax exempt primary care clinic)
If prescriber re-activates license, must notify DPH and divest any interest in pharmacy within 30 days (or have prescriber’s license suspended until divested)
Interest is in investment securities held in publicly traded corporation if <0.5% of corporation's total issued shares
Pharmacies are to be supervised and managed by a pharmacist. What are the requirements of the pharmacy manager?
must be licensed in CT full-time
must be full-time at the store where acting as pharmacist manager
may not manage more than 1 pharmacy at a time
may be, but does not have to be the supervising pharmacist
name should be displayed for public viewing
if there is a change in position, the DCP must be notified of the change and immediately enroll a new manager
Pharmacy must report the absence of a pharmacist manager if:
>16 days (must be reported to the commission within 5 days)
>42 days (immediate notice to DCP & they are no longer enrolled as pharmacy manager; immediately enroll new pharmacy manager)
new first-time manager must conduct an interview with commission first
($90 fee for change in pharmacy management; $50 late fee added if late)
How long must a pharmacy be open a week? How may a pharmacy change those hours?
35 hours/week
If the pharmacy wishes to reduce their hours, they must apply to DCP.
Inspection will take place
If approved, cannot implement until 30 days after
Notice to public is posted
Pharmacist-Manager filed notice of hours with DCP
If they want to increase the hours, they may do so whenever as long as they give notice to DCP not more than 5 days after the change.
How is pharmacy security enforced in the event of a momentary absence of a pharmacist
Presence of intern or technician is considered “adequate security” for momentary absence
If intern or tech not available, and prescription department is not within pharmacist’s view must use method to physically or electronically secure the prescription department (e.g., locked barrier, alarm system)
What should be done when the prescription department is closed?
Locked
Equipped with an alarm
Must be separate from other alarm systems, and able to detect entry when prescription department is closed
Only pharmacist shall have authority to deactivate alarm
May have one-way drop box (but must be accessible to authorized personnel only, from inside pharmacy, and only when pharmacist is present)
NO SALE of prescriptions when department is closed
Deliveries made when pharmacy department is closed must be kept in secure, locked area until pharmacist is available to supervise processing
What are the frequency restrictions for an unscheduled pharmacy closing? Who must be informed?
Unscheduled closing may not occur more than:
18 times in 365 days; or
two times in a 30-day period (no consecutive days of closing)
Pharmacist manager must report closing to DCP no later than 72 hours after unscheduled closing occured
What are the requirements to register as a pharmacy intern?
Must satisfy one of the following sets of conditions to register as pharmacy intern:
Enrolled at ACPE-accredited pharmacy program and school approved by Connecticut Pharmacy Commission and completed least 2 years of college
Completed graduation requirements of ACPE-accredited program and school approved by Connecticut Pharmacy Commission
Graduate of foreign pharmacy school who has passed the tests for
written English (TOEFL = Test of English as a Foreign Language)
spoken English (TSE = Test of Spoken English)
Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency Examination (FPGEE)
Register with Pharmacy Commission
Pay applicable fee of $65
What is the fee for registration as a pharmacy intern?
$65
A pharmacy preceptor for a pharmacy intern has the responsibility to do what?
Pharmacy preceptor may supervise only one pharmacy intern at a time
Sign, alongside the pharmacy intern, a statement validating hours & content of professional experience
A pharmacy intern must inform the Commission what within what time frame?
Intern must inform the Commission WITHIN 5 DAYS of any of the following:
Commencement of internship training
Change in place of supervision
Change in hours of supervision
Cessation of supervision
What is the fee for application for registration as a pharmacy technician?
When does registration expire?
What is the fee for renewal of registration as a pharmacy technician?
$100
Registration must be renewed annually (expires on March 31st)
$50
Three requirements/descriptions of pharmacy technicians
1) must be registered or certified with DCP to work as a pharmacy technician
2) does not include persons not engaged in dispensing/compounding of medications (i.e. store clerks)
3) must wear name tag that clearly identifies their roles
Tech DON'Ts in CT (7):
1) perform activities that encompass professional cognitive and judgmental decision-making that are the responsibility of the pharmacist
2) accept oral order for NEW prescriptions
3) consult with patient/practitioner about prescription or medical record
4) identify, evaluate, interpret, or clarify a prescription
5) interpret clinical data in a patient’s medical record
6) perform professional consultation
7) verify a prescription order
8) determine generically or therapeutically equivalent drugs
Tech DO's in CT (10):
1) type Rx label
2) enter Rx into computer
3) enter information into patient file
4) retrieve medications from stock
5) place medications in container
6) place label on container
7) prepare nursing home medication cards
8) reconstitute oral liquids
9) obtain REFILL authorization for non-controlled drug if:
supervising pharmacist is aware an authorization is being requested
the refill is IDENTICAL to OG prescription (drug, strength, form, quantity, route of administration)
supervising pharmacist reviews refill authorization to confirm there is no change
10) compound medications for dispensing
Tech ratio in community retail pharmacy
2:1
3:1 (if one tech is certified)
(pharmacist can refuse to supervise 3 techs, but refusal must be in writing given to the manager)
Tech ratio in COMMUNITY IV, unit dose, or bulk compounding/dispensing pharmacy
3:1
(pharmacists can't refuse to supervise 3 techs in this setting)
Tech ratio in institutional outpatient pharmacy
2:1
(can be up to 3:1 with demonstrated need + petition)
Tech ratio in institutional inpatient or satellite pharmacy
3:1
(can be up to 5:1 with demonstrated need + petition)
Documentation of pharmacy tech training must include:
-NAME of the person receiving training
-DATES of training
-general description of TOPICS
-SIGNATURES of both technician and pharmacy manager
(change in pharmacy manager? new manager must review and sign documentation of tech training)
When commencing work, or changing place of employment what must a pharmacist report to DCP within what time frame?
Pharmacists must report the following information to DCP (within 5 days) if commencing work, or changing place of employment, as a pharmacist:
Date of commencement/change
Name of employer
Address of practice location
Type of practice
What changes must both pharmacists and techs report to DCP within what time frame?
Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians must also report to DCP (within 5 days) any change of:
Name
Home address
What is the ratio of Advanced Pharmacy Technician to Pharmacist?
Supervision must be 1:1 ratio of APhT-to-pharmacist
APhT does not count toward other tech-to-pharmacist ratios
What activities may an advanced pharmacy technician perform?
Dispensing or redispensing drugs in compliance packaging
When delegated by pharmacist, final verifications of drug dispensed; administration of vaccines, and COVID-19, influenza, and HIV-related tests
What is a "continuing education unit" (CEU)?
ten contact hours of participation in accredited CE
What is a "contact hour" (CE)?
50-60 minutes of participation in accredited continuing professional education
What are the pharmacist continuing education requirements?
At least 15 contact hours per calendar year
at least 5 hours have to be live
at least 1 hours has to be on drug law
What is the fee for filing notice of a chance in name, ownership, or management of a pharmacy?
What is the late fee for failing to give such notice?
$90
$50 plus the fee for notice
What is the fee for issuance of a pharmacy license?
When do pharmacy licenses expire?
What is the fee for renewal?
$750
annually
$190
What is a clerk?
anyone who physically works in an area of a pharmacy where controlled substances or other prescription drugs are dispensed by pharmacists (or dispensed under a pharmacist’s supervision)
Does not include any person:
Already licensed or registered with DCP (e.g., pharmacist, temporary pharmacist, intern, or technician)
Employed or contracted to by pharmacy to deliver drugs to patients off the pharmacy premise
DONTS for a pharmacy clerk
review any drug to determine if appropriate
verify accuracy of the prescription, the prescription label or container contents, or the prescription data entered into computer
perform any task that requires professional pharmaceutical judgment
participate in order entry (i.e., generally, entering prescription data into the pharmacy’s electronic data processing system)
be involved in dispensing process or preparing a prescription for final verification
What are the stipulations for a hospital using telepharmacy?
Tech ratios apply
If technology malfunctions products, no distribution of CSP prepared by technician unless pharmacist either:
Personally reviews and verifies that CSP process was accurate; OR
when technology is restored, pharmacist uses it to confirm that tech took all proper steps
Orders must be verified by pharmacist before tech begins dispensing process
Hospital’s director of pharmacy is responsible
If using the technology, hospital must do periodic quality assurance evaluations (at least once per calendar quarter) and make evaluations available for inspection to DPH and/or DCP
What drugs have restriction sale in CT? What places may sale them at retail?
DRUGS WITH RESTRICTED SALE:
Legend drug/device;
injectable/ingestible antibiotics;
injectable biologicals;
sulfonamides and their compounds designed to be taken into stomach for systemic action;
Injectable or ingestible corticosteroids;
camphorated tincture of opium (a/k/a paregoric)
PLACES THAT MAY SELL THEM AT RETAIL
A licensed pharmacy
In limited circumstances, by a hospital if to the hospital’s:
Employee, or employee’s spouse/dependent children
Retiree or retiree’s spouse on hospital’s retirement/pension plan
What is the attitude toward price requests regarding a legend drug?
Pharmacist must disclose price of legend drug upon request of prospective purchaser
Pharmacist may ask prospective purchaser for the medication’s:
name
dose/strength
quantity
If a prospective purchaser does not know this info, and it is necessary to give price -- pharmacist may call prescriber to obtain the info prior to disclosing price
Types of fraudulent prescriptions
Altered prescriptions
Different color inks used
Different handwriting on same prescription
Printed prescription pads with false call back number
Stolen prescription pads
False caller transmitting oral prescription
Prescription looks photocopied
What makes a prescription “out of scope”?
Excessive volume of prescriptions
Excessive quantities prescribed
Patient gets prescriptions too frequently for legitimate use
Simultaneous prescribing of antagonistic drugs
Multiple patients (unknown/new) arrive together with similar prescriptions from same prescriber
Out-of-area (unknown/new) patients present with prescriptions from same physician
T/F A prescriber can DISPENSE drugs to his/her own patients
True (if within scope of practice)
In an institution, under what circumstances can a non-pharmacist dispense?
An emergency but it must also be:
Reviewed by nursing supervisor or physician prior to administration
Recorded by pharmacist (when one becomes available)
Is an electronic questionnaire solely sufficient for making a controlled substance prescription valid?
No. Additionally there needs to be a documented patient evaluation that includes a physical examination
At least how far back must pharmacy computer systems be able to provide online retrieval of any patient's refill history (via visual display device or hard copy printout)?
How long should this information be retained for?
-at least 6 months from last dispensing
-must retain for 3 years
What are 2 ways to document non-control refill data?
1) daily printout, made within 72 hours of dispensing, which is verified and signed by dispensing pharmacist ASAP after receipt; OR
2) electronic record, but pharmacist's name/initials is presumed to be dispensing pharmacist
Pharmacies must be able to make 3 years of printed information available to Drug Control within what time frame of request?
within 48 hours of request
How long in advance do pharmacies need to give written notice to DCP if they are:
1) starting use of a computer system, OR
2) changing computer system, OR
3) discontinuing computer system
30 days
What are 2 ways to document CONTROL refill data?
1) daily printout, made within 72 hours of dispensing, which is verified and signed by dispensing pharmacist ASAP after receipt OR
2) bound log book or separate file signed by dispensing RPh on the date of dispensing (but no later than the RPh's first work date after the dispensing)
By signing, RPh is verifying that the refill information entered into computer is correct
If discontinuing use of system (closing, selling to another pharmacy, changing systems), what are 2 requirements for pharmacies?
In addition to a 30 day advance written notice to DCP, must:
Provide an up-to-date hard-copy printout of last 3 years of prescriptions (these will be "final records")
Make hard-copy records available to any nearby pharmacy if pharmacy is closing
Hospitals must establish a POLICY on electronic drug records that addresses:
- description of system used, with types of drug records maintained, and patient populations/physical locations where used
- how access is controlled
- types of electronic identifiers used, and how issued/maintained/terminated
- online retrieval of no less than 3 years of records
- recovery procedure for unscheduled down time
- backup procedure and prevention of loss or destruction
- method used to prevent/detect unauthorized alteration or erasure
- safeguards for confidentiality
(these are different requirements than for "licensed pharmacies")
What must be included on the prescription record for a prescription?
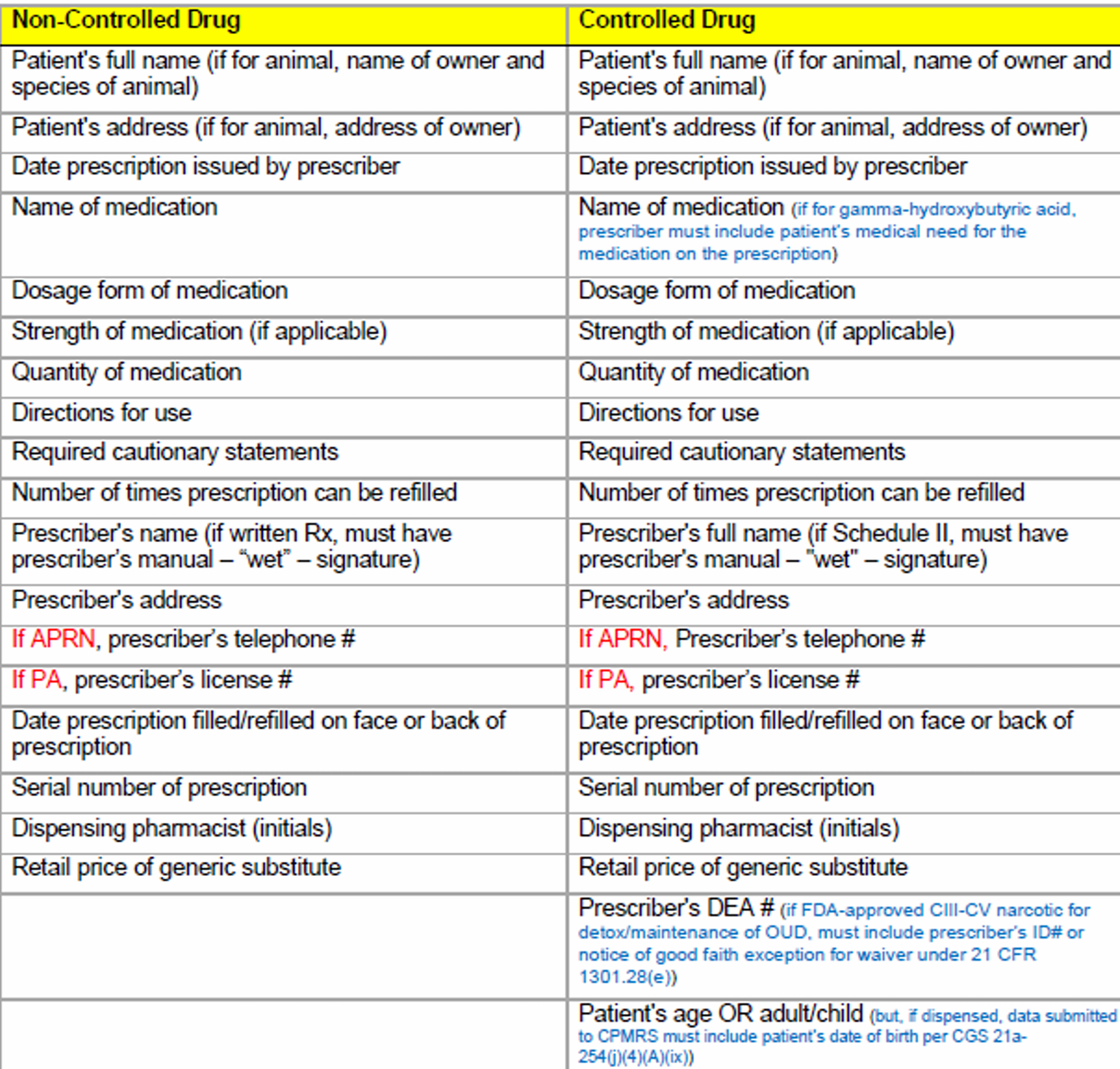
10 requirements on a prescription label in CT
1) drug name (generic + brand)
(if no brand name, generic name + name of manufacturer/distributor + Medwatch toll-free number and internet address)
2) drug strength
3) name & address of pharmacy
4) serial # of Rx
5) date of filling/refilling (everything except CII)
6) prescriber's name (can be last name only)
7) patient's FULL name (or animal owner's name & animal species)
8) directions for use
9) quantity & expiration date
10) any required cautionary statements (ex. controlled Rx "CAUTION: Federal law prohibits transfer of this drug to any person other than the patient for whom it is prescribed")
What are the additional labeling requirements for a prescription?
CT requirement of printed statement on receipt, in bag or similar packaging:
"If you have a concern that an error may have occurred in the dispensing of your prescription you may contact the Department of Consumer Protection, Drug Control Division, by calling (Department of Consumer Protection telephone number authorized pursuant to section 21a 2 of the general statutes)"
Federal Requirements:
Patient Package Insert (e.g., oral contraceptives, estrogen)
REMS Medication Guide (e.g., testosterone gel)
Side Effects Statement
Controlled Substance Warning Statement
What statement on side effects is required on prescription label?
"Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088"
this statement must be included on either the label, vial cap, med guide, medication info, or a separate sheet of paper
does NOT have to be included on the meds for inpatients or supervised home health care
What is a Medication Guide prescribed for? Is this required? Who writes it?
Issuance of a medication guide written by the drug company is FDA required if:
certain information is necessary to prevent serious ADEs
patient decision-making should be informed by info about a known serious ADE with a product, or
patient adherence to directions are essential for effectiveness
What is the exception to required provision of Medication Guides? (Federal)
prescriber may (using clinical judgment) instruct dispenser not to provide medication guide
BUT if patient asks for information, dispenser must provide medication guide despite prescriber instruction
Which ACT requires dispensing is child-resistant packaging?
Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970
What are the requirements under the Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970
Requires child-resistant packaging (CRP) for most oral OTC drugs and almost all prescription drugs unless:
If Rx only, either physician prescribing or patient can request non-CRP (can be prescription specific or blank waiver) (document it, doesn’t need to be written order)
Drugs exempt or in special/exempt packaging
SL NTG
UD K+ Supplements
Oral contraceptives
Medrol dosepak
If OTC in multiple package sizes, mfr can market one size of an OTC that is non-CRP but must contain statement "This Package for Households Without Young Children" or "Package Not Child-Resistant"
Doesn’t apply to inpatient
Name 6 types of prescribing practitioners and 3 types of midlevel prescribing practitioners:
Practitioners: physician, dentist, podiatrist, veterinarian, osteopath, optometrist
Midlevel practitioners: nurse-midwife, physician assistant, APRN
Do prescriptions from APRNs need a co-signature from collaborating MD?
name of collaborating MD allowed by not required
but APRN's prescription form must contain name, address, signature, and phone # of APRN
May cause the same to be administered by an RN or LPN under APRN's direction and supervision
Can APRNs prescribe controlled substances?
yes if APRN has:
current certification from American Association of Nurse Anesthetists (i.e., a certified nurse anesthetist or CRNA)
written collaborative agreement with CT licensed physician, collaborative agreement must specify level of CII & CIII that can be prescribed
3 years and 2,000 hours of practice under a collaborative agreement, APRN may practice independently (i.e. without written colaborative agreement)
Which mid-level practitioners can request, sign for, receive & dispense professional samples
APRNs and PAs
In what setting can a nurse-midwife (LNM, CNM) prescribe
In CT must first be an APRN, then must:
practice within a health care system
have a clinical practice relationship with an OB/GYN that provides for consultation, collaborative management, or referral
Do prescriptions from nurse-midwives need a co-signature from collaborating MD?
no co-signature necessary
but nurse-midwife's prescription form must contain name, address, signature, and phone # of APRN
RN and LPN can administer under the direction and supervision of nurse-midwife
Do prescriptions from PAs need a co-signature from collaborating MD?
co-signature no longer necessary
but PA's prescription form must contain name, address, signature, and license number of PA then sign and print name of all orders
APRN, RN, and LPN may administer ordered med under physician’s direction
Can PAs prescribe controlled substances
yes
pursuant to written "delegation agreement" between PA and supervising physician licensed to practice in CT
supervising MD must document approval of CII/CIII in medical record in accordance with delegation agreement
What can optometrists prescribe?
For diagnosis or treatment of eye and eyelid conditions or diseases:
Topically administered agents
Orally administered agents,
But OUTSIDE of an optometrist’s scope to prescribe “nonemergency glaucoma oral agents”
Controlled drugs (CII-CV)
may prescribe oral analgesics used for alleviating pain caused by diseases or abnormal conditions of the human eye or eyelid
Which groups of people are practitioners prohibited from prescribing CII-CIV substances to? What are the exceptions?
“immediate family member” or self EXCEPT:
For animal in the residence (only veterinarians)
In an emergency where no other qualified prescribing practitioner is available, then can prescribe, dispense, or administer up to 72-hour supply
Emergency must be documented
Who are considered “immediate family members”?
Spouse
Child
Sibling
Parent-in-law
Son- or daughter-in-law
Brother- or sister-in-law
Step-parent
Step-child
Step-sibling
Or other relative residing in the same residence and the prescribing practitioner
BUT NOT A PET
Can a prescriber use a stamp to sign a written prescription?
No, the prescriber must use their actual signature.
How may oral prescriptions be taken in the community setting?
new prescriptions must be communicated directly to a pharmacist or pharmacy intern
renewals/refills (no changes) of non-controlled drugs may be communicated to a pharmacy tech; but technician may not accept oral orders to renew (i.e., authorizations to refill) controls
Supervising pharmacist must review all “refill authorizations” (renewals) obtained by pharmacy tech
May be communicated by the prescriber’s employee or “agent”
Are there any requirements to be an authorized agent of a prescriber? Is any documentation required?
agent does not have to be a healthcare professional
Agent does not have to be registered, licensed, or certified by any entity
The agency relationship does not have to be in writing (although it is highly recommended)
What are the authorities of an authorized agent?
may prepare the prescription for signing or authentication
But ONLY the prescribing practitioner is authorized to issue the prescription
The agent may convey an oral prescription to the pharmacy
The agent may fax a written prescription to the pharmacy
What is required on an oral or electronic non-controlled prescription? + electronic record?
What is required on a written non-controlled prescription?
Oral or Electronic:
patient's name and address (owner name and address of pet, animal species)
prescriber's name and address
date of issuance
drug name, dosage form, strength, quantity
directions
cautionary statements
refills (if any) — may use “ad lib” or “prn”
serial number of prescription
dispensing pharmacist (initials)
retail price of generic substitute
date filled/refilled
Written:
all of the above and wet signature of prescriber
What is required on a controlled prescription? + electronic record?
Dated and signed on day issued
full name and address of patient (owner name and address of pet, animal species)
If patient is an adult or child or patient’s specific age (need DOB for PDMP)
prescriber's name, address, and DEA #
drug name, form, strength, quantity
directions
wet signature (if CII written)
cautionary statements
refills (if any)
serial number of prescriptions
dispensing pharmacist initials
retail price of generic substitute
date prescription filled/refilled on face or back of Rx
Requirements of faxed prescriptions
Along with prescription order requirements, must contain
name receiving pharmacy
If for LTC inpatient, name of the facility from which it is being transmitted
If hospice, must note it is for hospice patient
should clearly display statement: "This prescription is valid only if transmitted by means of a facsimile machine"
should be maintained as prescription record (3 years in CT; 2 years federal)
General rule for faxed CII prescriptions and the 3 exceptions
General Rule: OG prescription must be received and reviewed by pharmacist before dispensing (i.e., fax is only a record of transmittal, it is not considered an original RX).
Exceptions:
Compounded narcotic for parenteral IV, IM, SC, or intraspinal infusion administration
LTC
Narcotic for hospice patient (practitioner must note that prescription is for a hospice patient)
What is Electronic Data Intermediary (EDI)? Who does it need to be approved by?
- an entity that provides the infrastructure for electronic transmission of prescription orders between prescribers and pharmacies in order to facilitate the secure transmission of electronic prescription orders, refill authorization requests, communications, and other patient care information between such entities
- EDI may not operate without approval of Pharmacy Commission
In what format and for how long must records for e-prescriptions for controlled substances must be kept?
If created, signed, transmitted, and received electronically, all related records must be retained electronically
DEA requires 2-year retention period for records (but CT requires 3 years)
Records regarding must be
Readily retrievable from all other records
Easily readable or easily rendered into readable formats
What are some additional requirements (record keeping and verification of Rx) pharmacists have with e-prescriptions for controlled substances
If a pharmacist would make a notation on the prescription if it was paper then must make same notation electronically and the prescription and all required annotations must be retained electronically.
When pharmacist gets a paper/oral prescription that indicates it was originally sent electronically, pharmacist must check its records to ensure that the electronic version was not received and dispensed.
If both prescriptions were received, must mark one as void.
When getting a paper or oral prescription that indicates that it was originally transmitted electronically to another pharmacy, must check with that pharmacy to determine whether the prescription was received and dispensed.
if it was then must mark one as void or d/c paper prescription if electronic one was filled
What is the general rule for a prescriber ordering a controlled substance? What are the exceptions (5)?
General Rule : CT prescriber ordering CS to be filled in a CT pharmacy, must transmit prescription electronically
Exceptions:
Temporary technological/electrical failure (e.g., power outage)
Impractical for patient to get e-prescription and delay would adversely impact them, BUT limited to 5-day supply (e.g., patient does not know where Rx will be filled after nighttime ED visit)
Prescription will be dispensed by out-of-state pharmacy
Use of electronic transmission would negatively impact patient care (e.g., compounded, complicated, direct administration to patient, DEA requires additional info, or LTC patient)
Prescriber does not have technological capacity to issue e-prescriptions (DCP Registration waiver requested by prescriber).
telehealth provider may not use this exception
CII PRESCRIPTION REQUIREMENTS
(day supply, expiration, partial, etc.)
ONLY written or e-prescribed (no oral)
1 drug per Rx
no refills (but multiple prescriptions up to 90-day supply allowed)
no limit on quantity (day supply) for SINGLE rx
NO EXPIRATION (but pharmacists must determine medical need)
partial dispensing allowed (when out of stock OR if requested by patient/prescriber)
emergency dispensing allowed (when oral/faxed in)
Under what circumstances can a patient get multiple CII prescriptions for the same drug?
CT state law permits multiple prescriptions provided the following:
up to a 90-day supply
Each separate Rx is for a legitimate medical purpose by a prescriber acting in usual course of practice.
prescriber provides earliest date each prescription can be filled (except on prescription to be filled first)
prescriber concludes there is no undue risk of diversion or abuse