Marine Inverts Exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
1
New cards
What are invertebrates?
Animals that lack a backbone
2
New cards
Why are Inverts Important?
* Ecologically important for nutrient cycling, filtration, or habitat.
* Economically important for food, ecotourism (shelling), and pharmaceuticals.
* Economically important for food, ecotourism (shelling), and pharmaceuticals.
3
New cards
What is taxonomy?
a branch of science concerned with classification, especially of organisms, systematics.
4
New cards
why is taxonomy important?
classify new spieces with other like species, conservation
5
New cards
What is phylogeny?
The study of evolutionary reationships
6
New cards
Phylogenetic systematics
field within biology that reconstructs evolutionary history and studies the patterns of relationships among organisms.
7
New cards
homologous traits
Traits or structures that are similar in two or more species, showing that organisms have descended from a common ancestor
8
New cards
Binary characters
useful for classification because it allows for easy separation of groups by designating presence v. absence or selecting from one of two states, such as long v. short, one antenna v. two antenna, and so on.
9
New cards
Multistate Characters
a character that can occur in several character states
10
New cards
Character state
particular version of a character
11
New cards
Principle of Parsimony
The principle that the most acceptable explanation of an occurrence, phenomenon, or event is the simplest, involving the fewest entities, assumptions, or changes. In phylogenetics, for example, the preferred tree showing evolutionary relationships between species, molecules, or other entities is the one that requires the least amount of evolutionary change, that is, maximum parsimony.
12
New cards
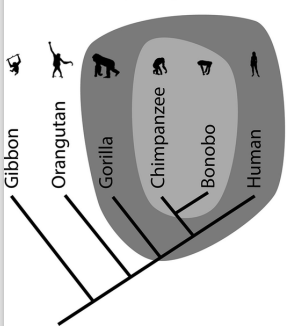
monophyletic
Describes a group of organisms that are classified in the same taxon and share a most recent common ancestor, traits are shared and derived (synapomorphy).
13
New cards
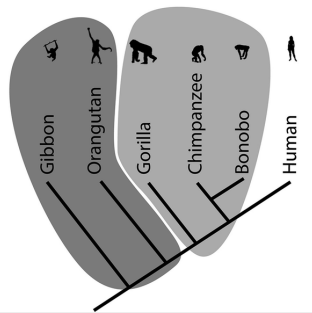
Paraphyletic
A group that contains a common ancestor and some, but not all, of the decendants. Implying that some members of the natural group have been places into another group.
14
New cards
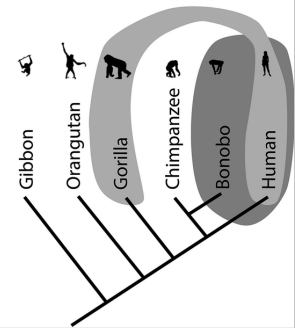
Polyphyletic
A group of that is of mixed evolutionary origin, but share similiar features (homoplasies)
15
New cards
Bilateral symmetry
Left and right vertical → helps with a head (humans)
16
New cards
Radial symmetry
Cut any direction, symmetrical(cnidarians, ecginoderms (pentaradial))
17
New cards
Asymmetrical
no symmetry (sponges)
18
New cards
Diploblastic
2 tissue layers (endoderm & ectoderm)
19
New cards
Triploblastic
3 tissue layers (endoderm, ectoderm, & mesoderm)
20
New cards
Coelom
body cavity found in metazoans that surrounds and contains th digestive trat and other organs
21
New cards
significance of a coelom
relates to potential for increased body size
22
New cards
Protostome
Mouth developes from blastopore
23
New cards
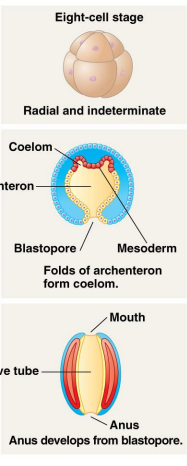
Deuterostome
Anus developes from blastopore
24
New cards
metazoan
animals that are multicellular, and have cells differentited into tissue and organs, using sspecialized cells.
25
New cards
Choanocytes
fagellated cells that drive water through canals and chambers constituting the aquiferous system
26
New cards
pluripotency
function as stem cells
27
New cards
epithellial cells
surface cells that act as a “skin”, in sponges cells are connected but dont share materials through adheran junctions, but lack gap junctions
28
New cards
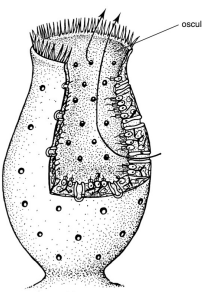
asconoid
* simpliest sponge body form
* ostia
* choanocyte in spongocoel
* osculum
* ostia
* choanocyte in spongocoel
* osculum
29
New cards
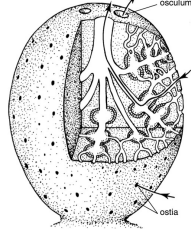
syconoid
* ostia
* choanocyte in radial canal
* apopyle
* spongocoel
* osculum a
* choanocyte in radial canal
* apopyle
* spongocoel
* osculum a
30
New cards
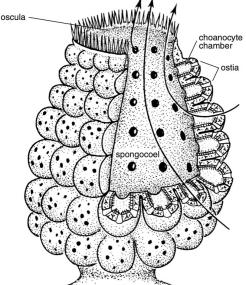
leuconoid
* complex ostia
* incurrent canal
* choanocyte in radial canal
* excurrent canal oscula
* incurrent canal
* choanocyte in radial canal
* excurrent canal oscula
31
New cards
spicules
skeletal elements that are composed of calcium carbonate, or silicon oxide
32
New cards
megascleres
large spicules
33
New cards
microscleres
small spicules
34
New cards
Spongin
a fiborous materal that forms part of the sponges skeletal system
35
New cards
Importance of sponges
* primary producers
* filtration
* habit
* filtration
* habit
36
New cards
Parasitic behavior of Cliona
common bioeroder
37
New cards
Osculum
large aperture in a sponge through which water is expelled
38
New cards
spongocoel
the large open cavity of sponges
39
New cards
mesohyl (mesoglea)
the gelatinous matrix within a sponge, incuding motile cells and some skeletal material
40
New cards
porocyte
allows water into the sponge through its opening (ostium)
41
New cards
pinacocytes
thin layer that keeps water out of the sponge
42
New cards
cnidae
gereal term for specialized cells for example nematocysts
43
New cards
endoderm
inner tissue layer
44
New cards
ectoderm
outer tissue layer
45
New cards
myoepithelial cells
epitheliomuscular cells and nutitive cells derived from endoderm and ectoderm to form musculature
46
New cards
epidermis
outmost body layer
47
New cards
mesoglea
an extracellular matrix that lays between the epidermis and the gastrodermis in cnidarians that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. Acellular.
48
New cards
siphonoglyph
a ciliated groove at one or both ends of the mouth of sea anemones and some corals.The siphonoglyph extends into a pharynx and is used to create currents of water into the pharynx
49
New cards
gastrodermis
the inner layer that serves as a lining memberane of the gastrovascular cavity (coelenteron) in cnidarians
50
New cards
gastrovascular cavity (coelenteron)
sac-like , partioned or branched, but with a single opening serving as both mouth and anus (cnidarians)
51
New cards
colloblast
multicellular structures found in ctenophores, they consist of collocyte lining and can be dischaged from the animals tentacles and used to capture prey. Not stinging cells but sticky to catch prey.
52
New cards
mesochyme
similiar to mesogela but has cells
53
New cards
velum
a membrane part that resembles a veil or curtain
54
New cards
ctene
a locomotor organ consisting of a row of strong cilia whose bases are fused (Ctenophores)
55
New cards
gonochoristic
a sexual system in which there are only two sexes and each individual is either male or female
56
New cards
hermaphroditic
an individual that possesses both male and female reproductive organs, structures, or tissues
57
New cards
soft corals (octocorals)
tentacles (cnidae) in multiples of 8
58
New cards
hard corals (hexacorals)
tentacles (cnidae) in multiples of 6
59
New cards
Rhopalia
small sensory structures that generally occur in multiples of four in cnidarieans (scyphozoan, and Cubozoan)
60
New cards
reproduction in corals
1. Gamete bundles released
2. bundles disassociate
3. fertilization
4. clevage → 4-cell → 8-cell
5. monrula
6. different shape stages
7. elongated planulae
8. searching
9. settlement
10. budding
11. Adult
12. repeat
61
New cards
importance of cnidaria
* primary producers
* habitat
* source of food
* habitat
* source of food
62
New cards
Common features of all worms
* cephalization
* central nervous system (CNS)
* bilateral symmetry
* triploblastic
* central nervous system (CNS)
* bilateral symmetry
* triploblastic
63
New cards
Protonephridia
a type of nephridia that are network of dead-end tubules without internal openings
64
New cards
metanephidia
a type of nephridia that are a type of eccretory glands with a ciliated funnel opening into the body cavity
65
New cards
Surface area to volume ratio
higher SA:V ratio allows for a more efficient diffusive processes than a low SA:V ratio
66
New cards
Pharynx
“throat”: smooth part following the mouth
67
New cards
Proboscis
an extensible tubular sucking organ
68
New cards
Rhynchocoel
coelomic hydrostatic chamber (Nemertea)
69
New cards
Renette cells
Specialized excretory cell in nematode worms
70
New cards
Metamerism
the repetition of homologous body segments
71
New cards
Segmentation
the division of some animal body into a series of repetitive segments
72
New cards
teloblastic growth
a large cell in the embryos of clitellate annelids which asymmertrically divide to form many smaller cells known as blast cells which further proliferate and diffeentiate to form the segmental tissues of the annelid
73
New cards
Open circulatory system
blood suffuse the body and may be directly open to the environment at places such as the digestive tract. has a hemocoel that is a central body cavity that may have some arteries but are not closed
74
New cards
closed circulatory system
blood stays within blood vessels, this way blood is kept separate from body tissues, this system has a heart that pumps blood through a continuous circulation pattern
75
New cards
trocophore larvae
a type of free-swimming plantonic marine larva with several bands of cilia
76
New cards
blastocoelic
a fluid filled or yolk filled cavity that forms in the blastula during early embryonic developemt
77
New cards
ganglion (ganglia)
dense group of nerve- cell bodies present in most animals above the level of snidarians
78
New cards
diverticulae
\*if viewing a cross section
the lining of the whit spaces
the lining of the whit spaces