Calc 3 Test 1 Things to Remember
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Circular Cylinder
x² + y² = c
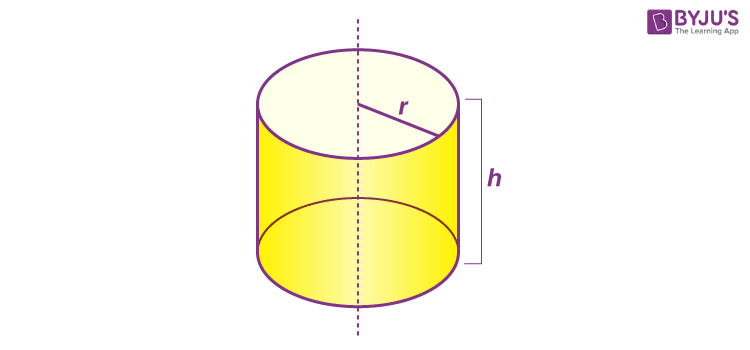
Parabola
z = c - y²
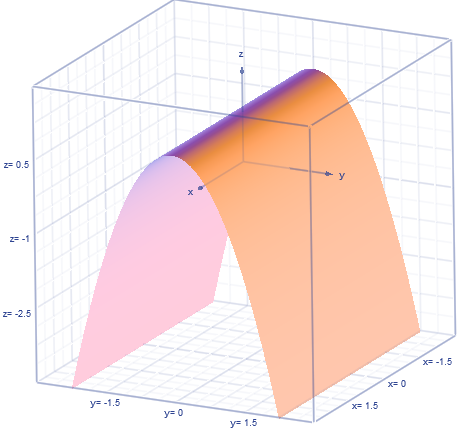
Ellipsoid
x²/a² + y²/b² + z²/c² = k
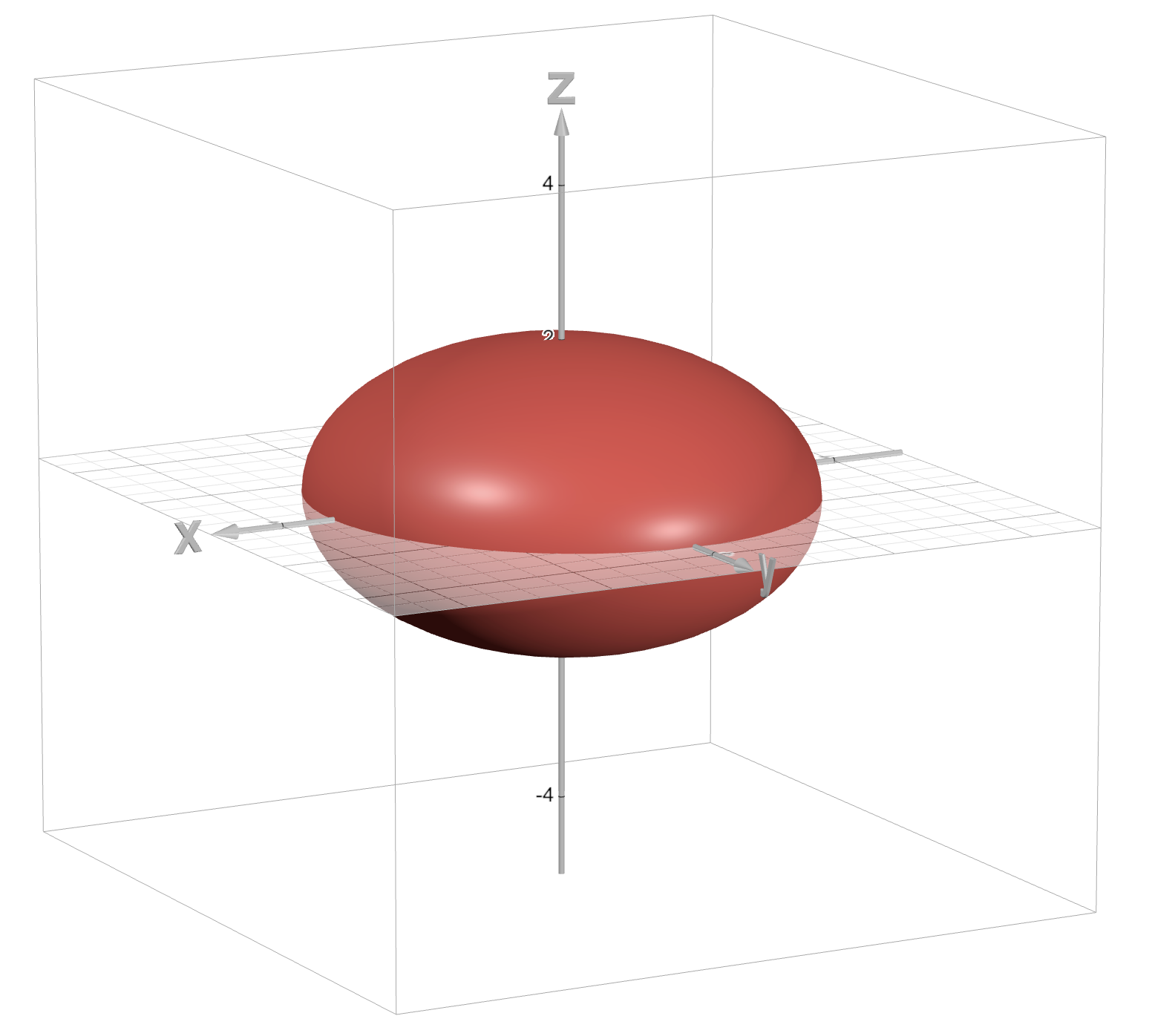
Hyperbolic Cylinder
x²/a² + y²/b² = -1
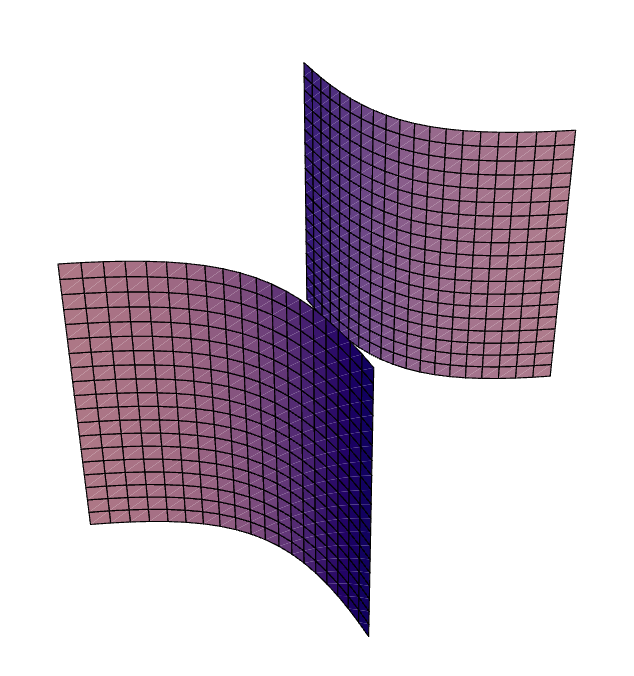
One Sheeted Hyperboloid
x² + y² - z² = 1
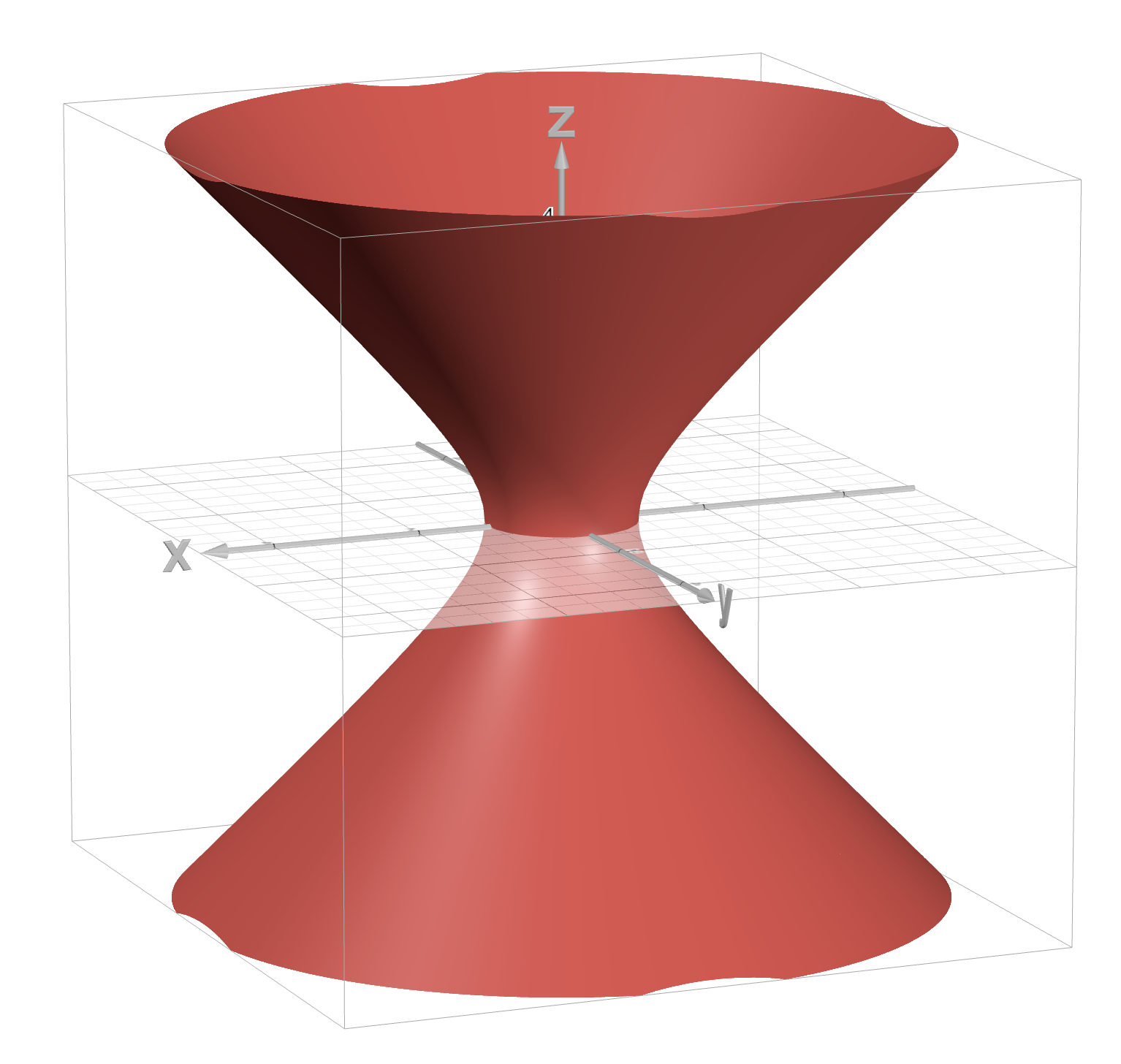
Two Sheeted Hyperboloid
z² - x² - y² = 1
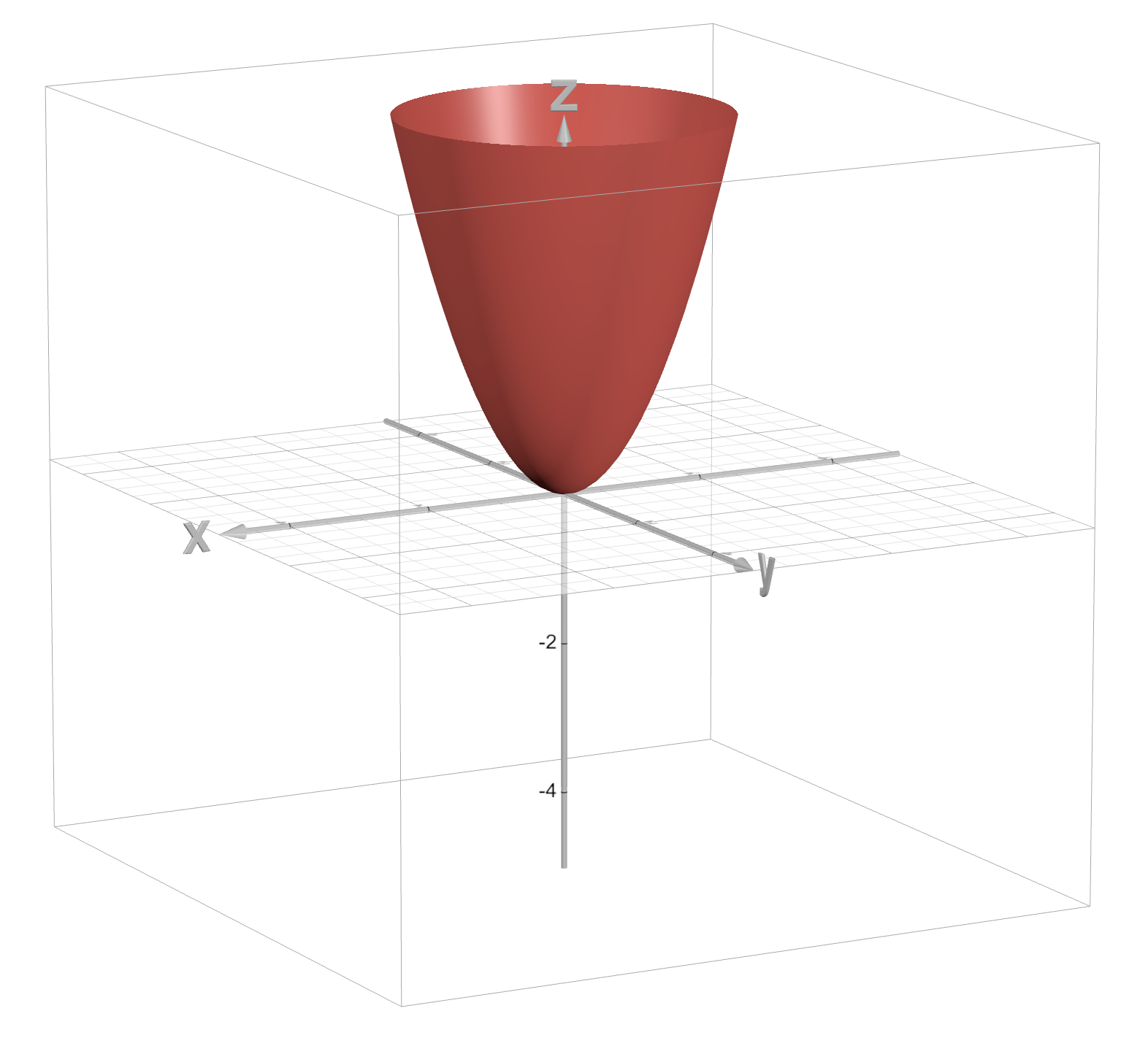
Elliptic Parabaloid
z = x² + y²
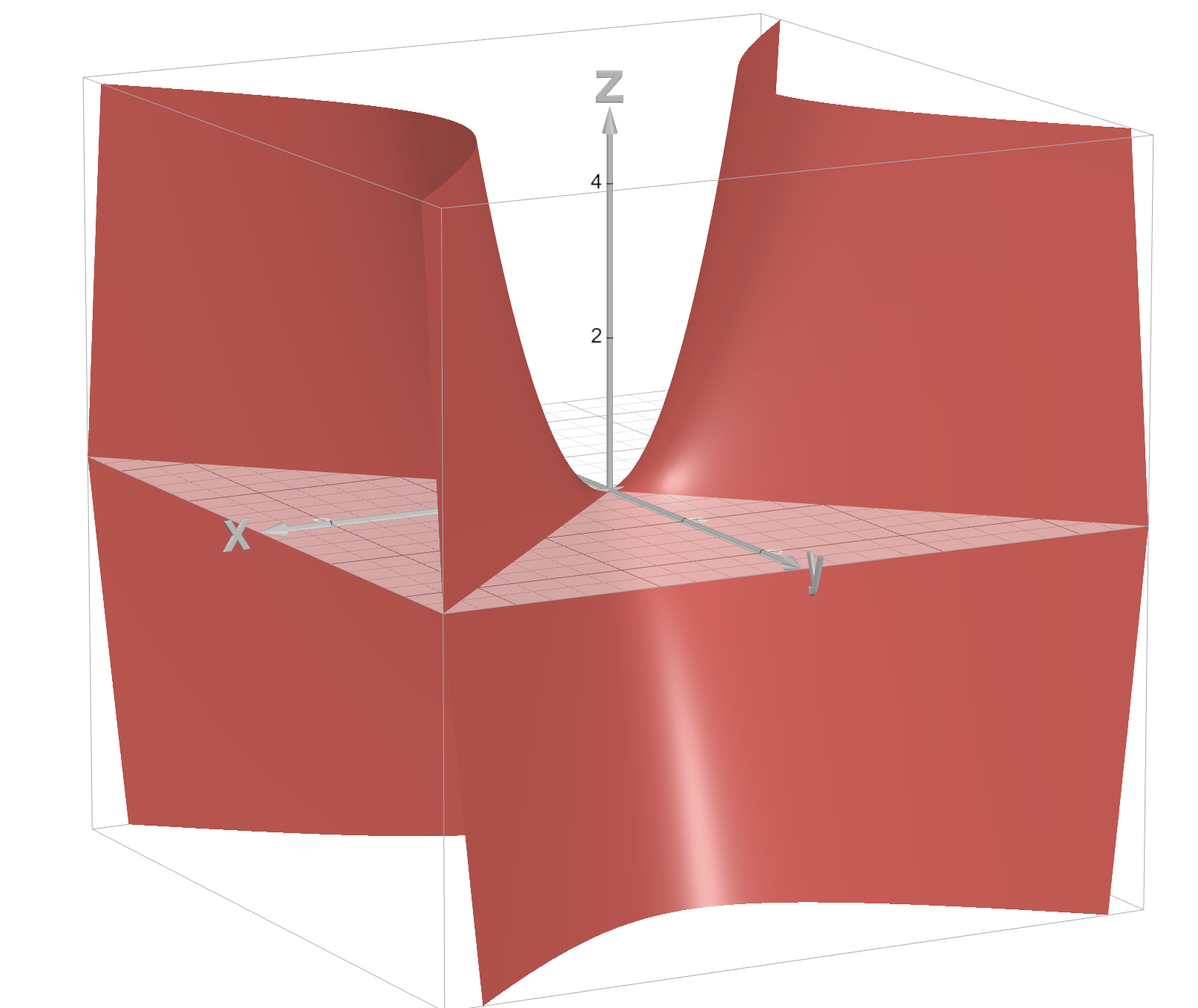
Hyperbolic Parabaloid
z = x² - y² (“saddle”)
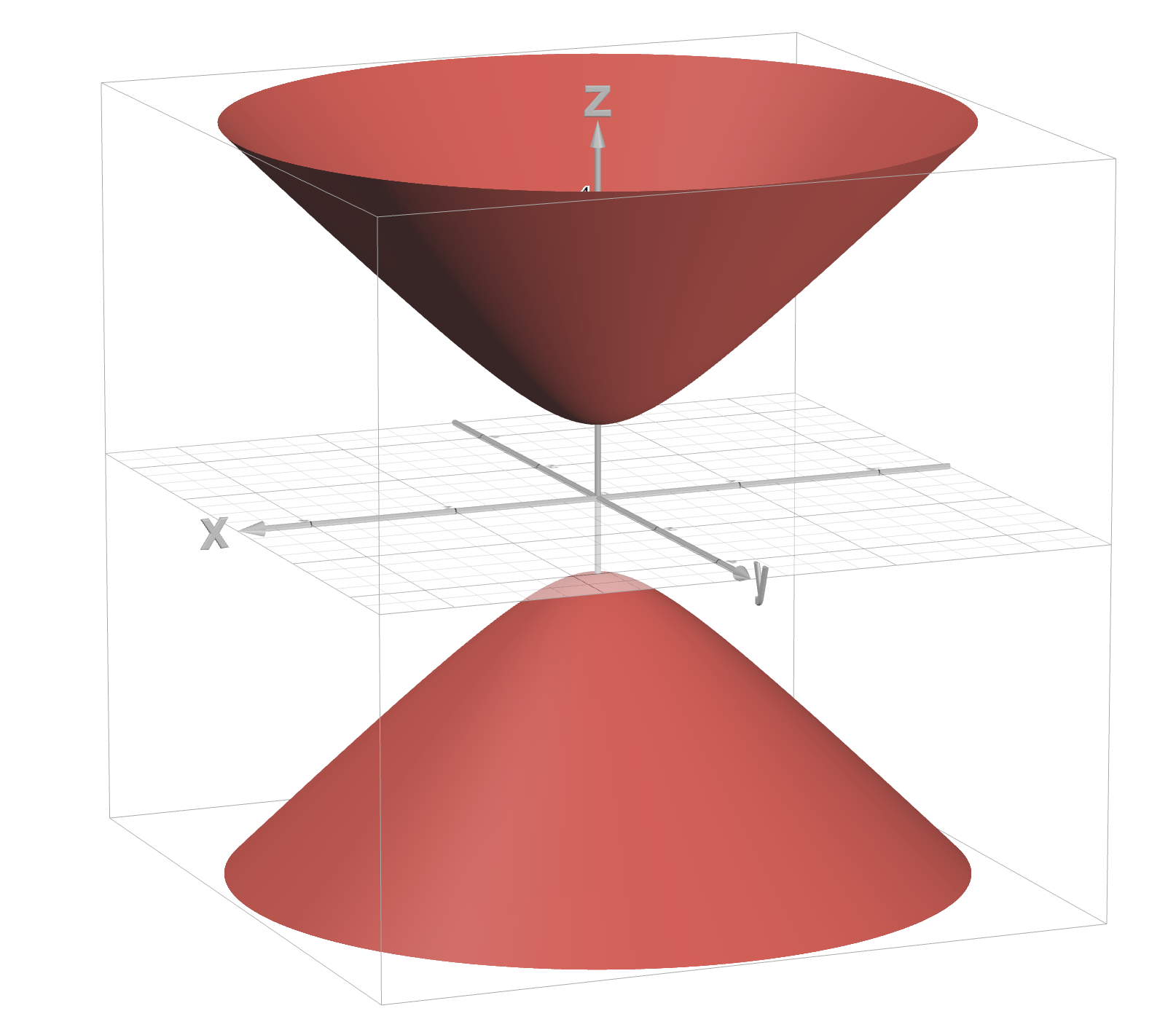
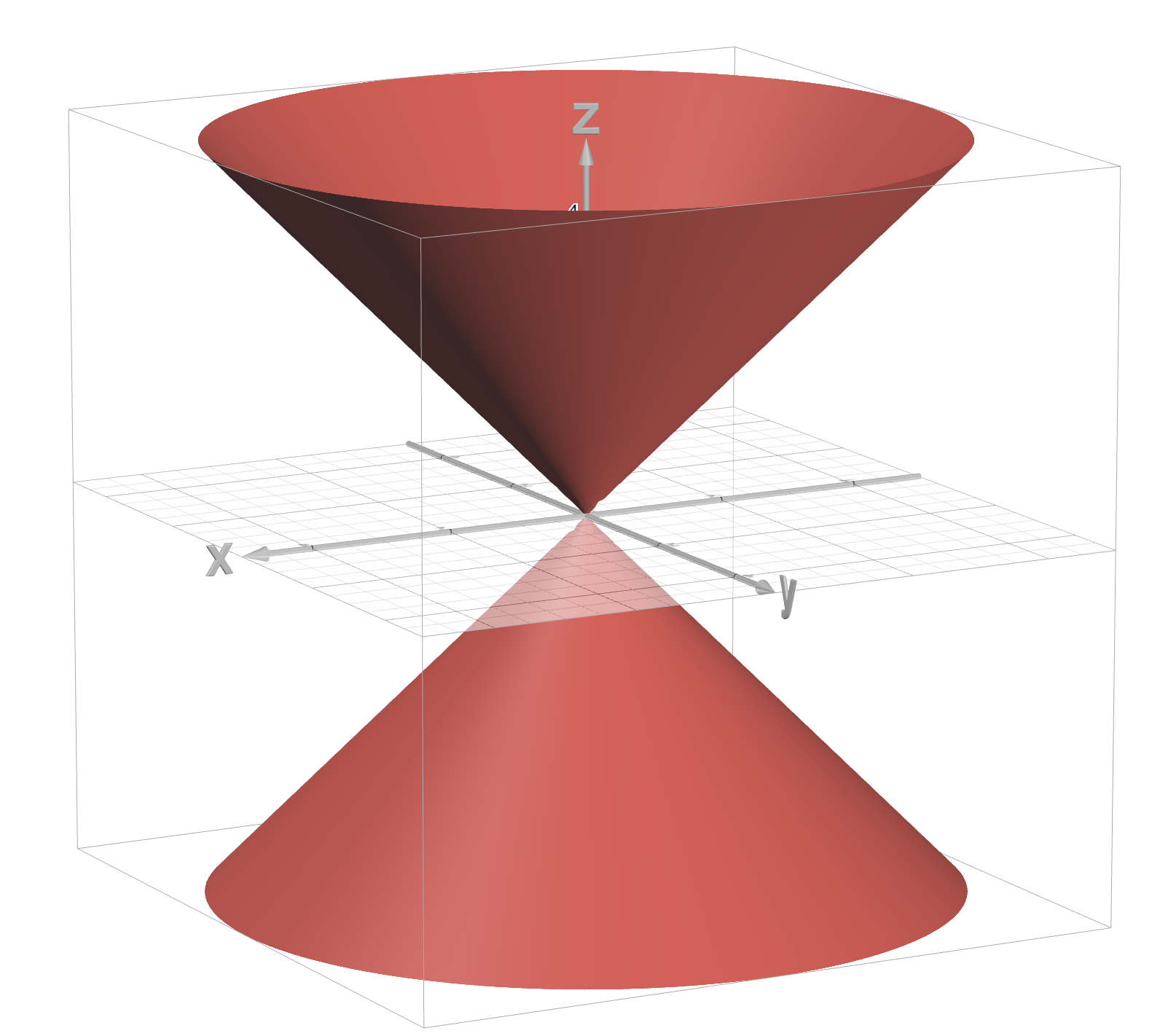
Cone
z² = x² + y²
dy/dx for a parametric curve <x(t),y(t)>
dy/dt ÷ dx/dt
d²y/dx² for a parametric curve <x(t),y(t)>
d/dt(dy/dx) ÷ dx/dt
integral from a to b of a parametric curve <x(t),y(t)>
integral from ta to tb of [y(t)x’(t)dt]
arclength for a parametric curve <x(t),y(t)>
integral from ta to tb of sqrt(x’(t)²+y’(t)²)
(dot product) a•b = ….
|a||b|cosθ
Unit tangent vector T(t)
r’(t)/|r’(t)|
Unit normal vector N(t)
T’(t)/|T’(t)|
Unit binormal vector B(t)
T x N
scalar projection of b onto a
(a • b)/|a|
vector projection of b onto a
(a • b)/|a| * a/|a|
sin2t (double angle identity)
2sintcost
cos2t (double angle identites)
2cos²tsin²t, 1 - 2sin²t, 2cos²t - 1
sin(x ± y)
sin(x)cos(y) ± cos(x)sin(y)
cos(x ± y)
cos(x)cos(y) ± sin(x)sin(y)
equation for a plane (given normal vector <a,b,c> and point (x0,y0,z0))
a(x−x0)+b(y−y0)+c(z−z0)=0
area of parallelogram formed by two vectors (double area of the triangle)
|PQ x PR|
|AxB| =
|A||B|sinx
direction vector for line of intersection between two planes
a = n1 x n2
Formula for distance from a point to the plane
D = (ax1 + by1 + cz1)/sqrt(a²+b²+c²)