ANFS345 Endocrine System
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
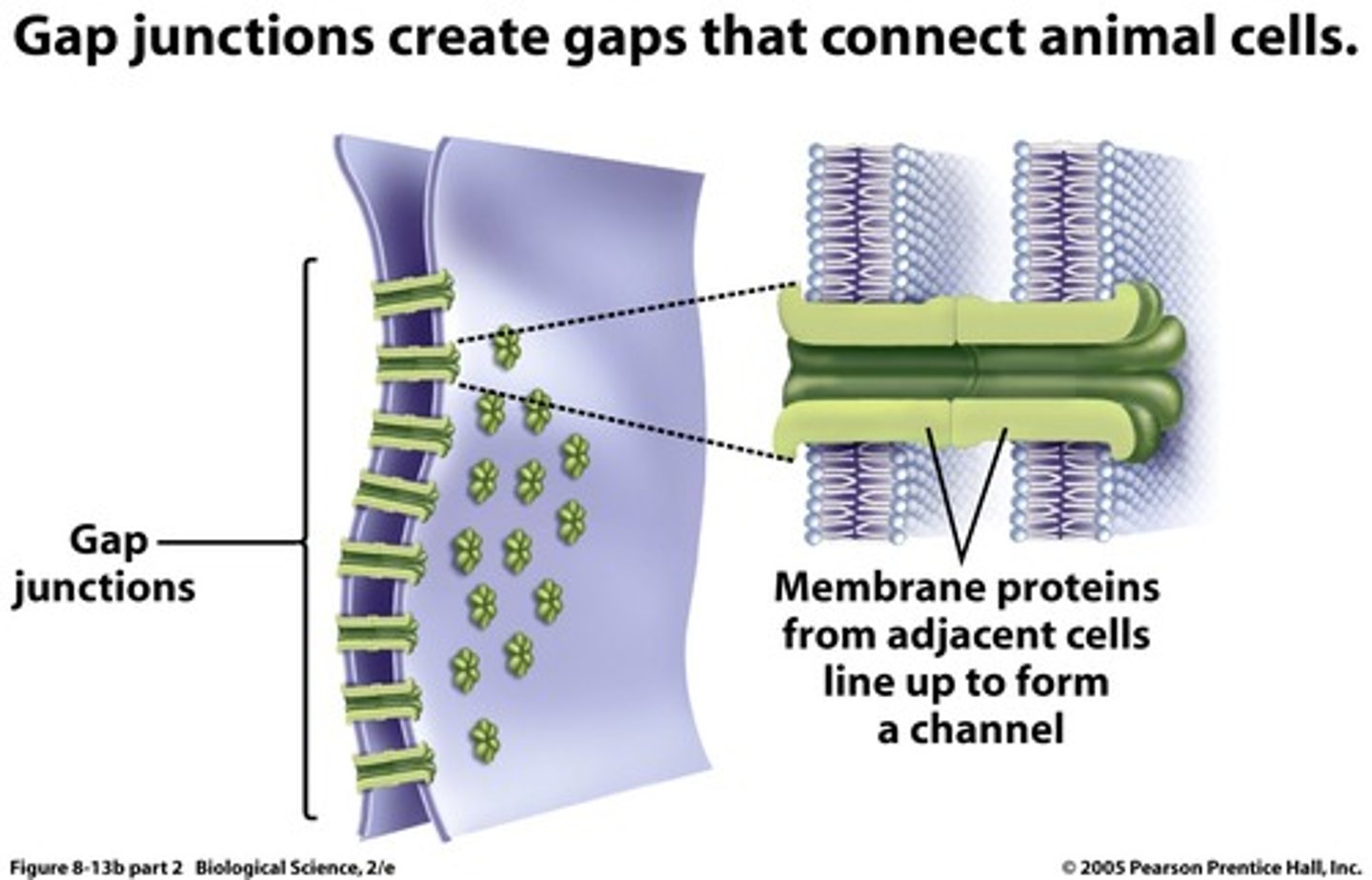
which type of cell contact is the least distance?
gap junctions (cytoplasmic contact)
ex: between myocardial cells
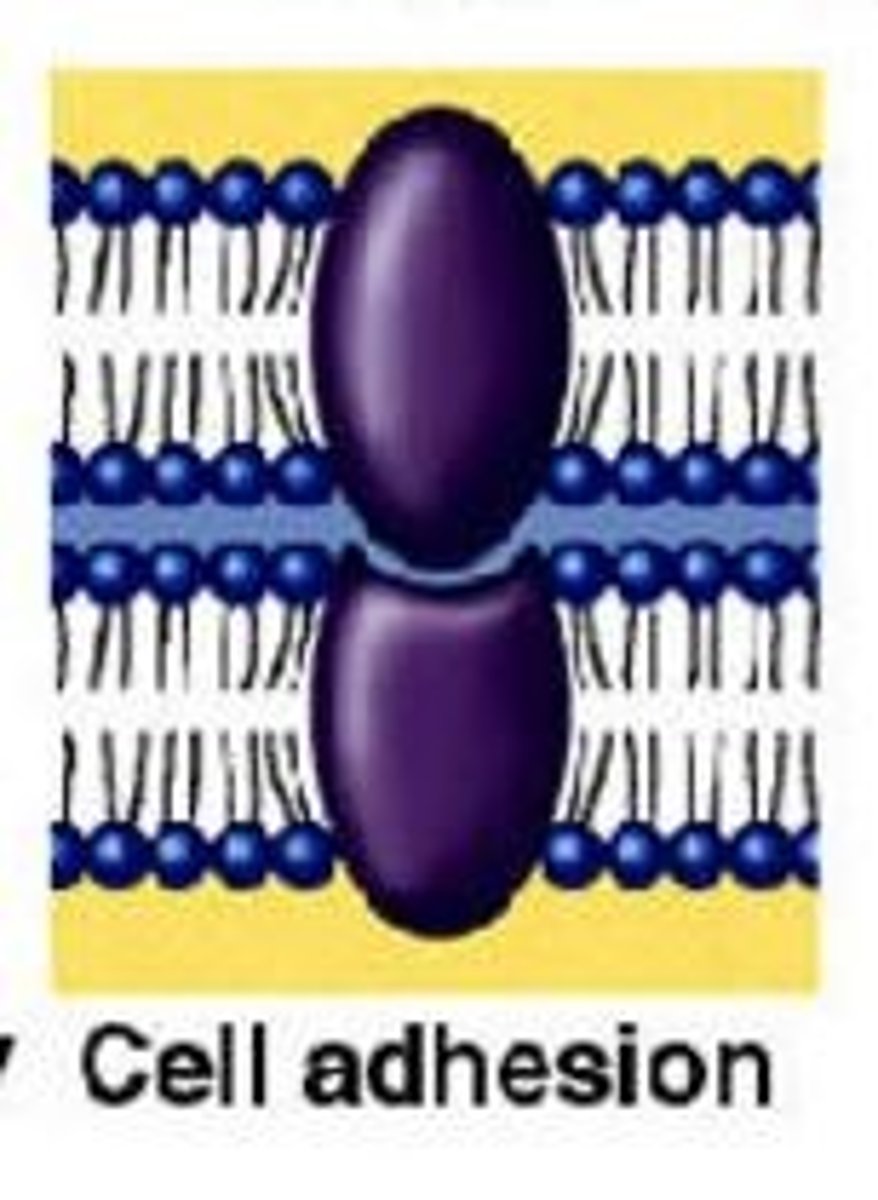
what is characteristic of cell adhesion molecules?
recognition of molecules on adjacent cells
ex: mammary glands during pregnancy
which type of diffusion is neurotransmitters?
local diffusion
what is characteristic of paracrines and autocrines?
paracrine: the hormone acts locally by diffusing from its source to target cells in the neighborhood
autocrine: the hormone acts on the same cell that produced it
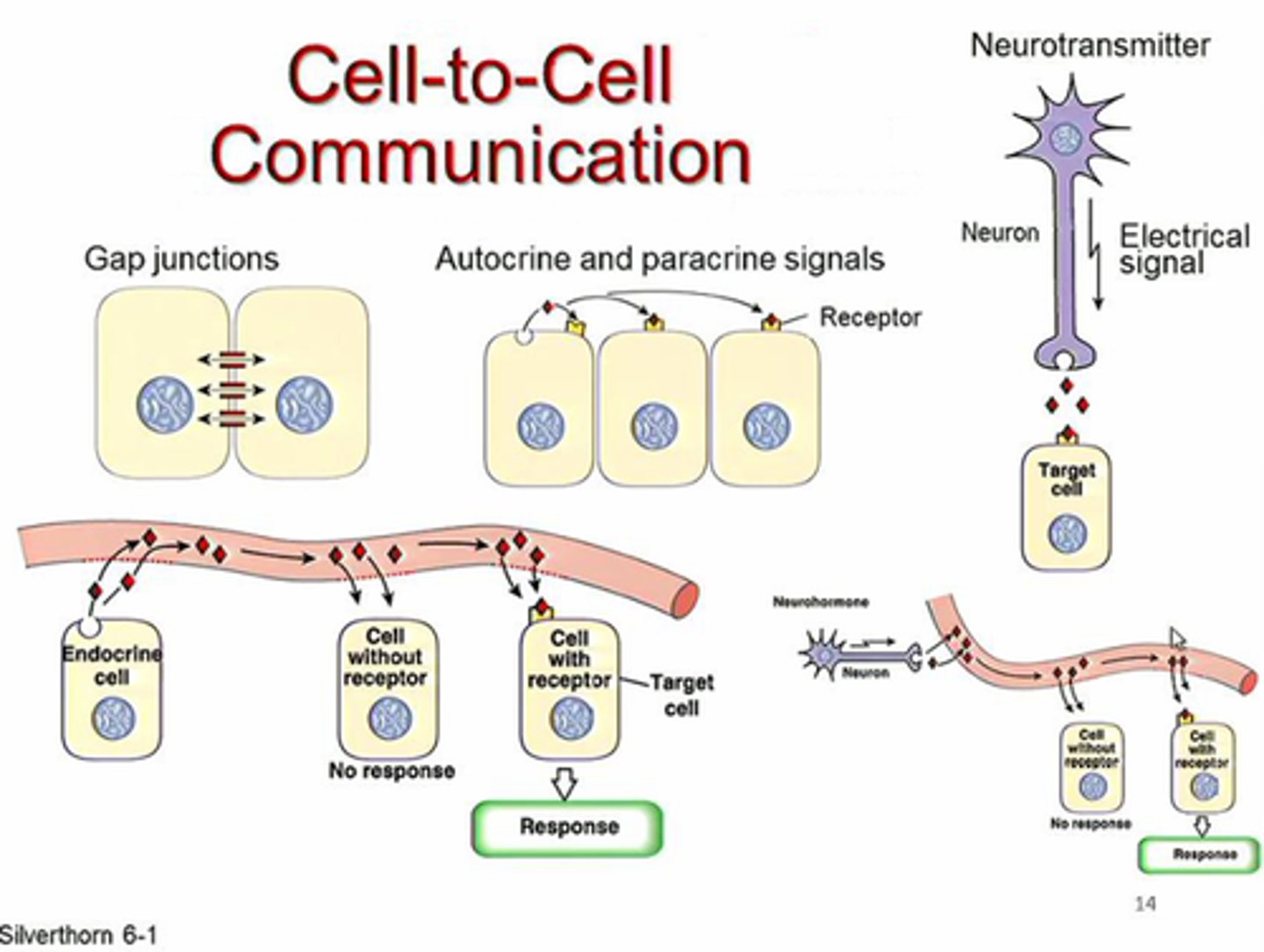
which two types of chemical signaling require the longest distance?
hormones transported in the blood and phermones transported in the outside environment
are steroid hormones fat-soluble or water-soluble?
fat-soluble
what are steroid hormones derived from?
cholesterol
how is pregnenolone formed?
cleaving of the six-carbon side chain on the cholesterol
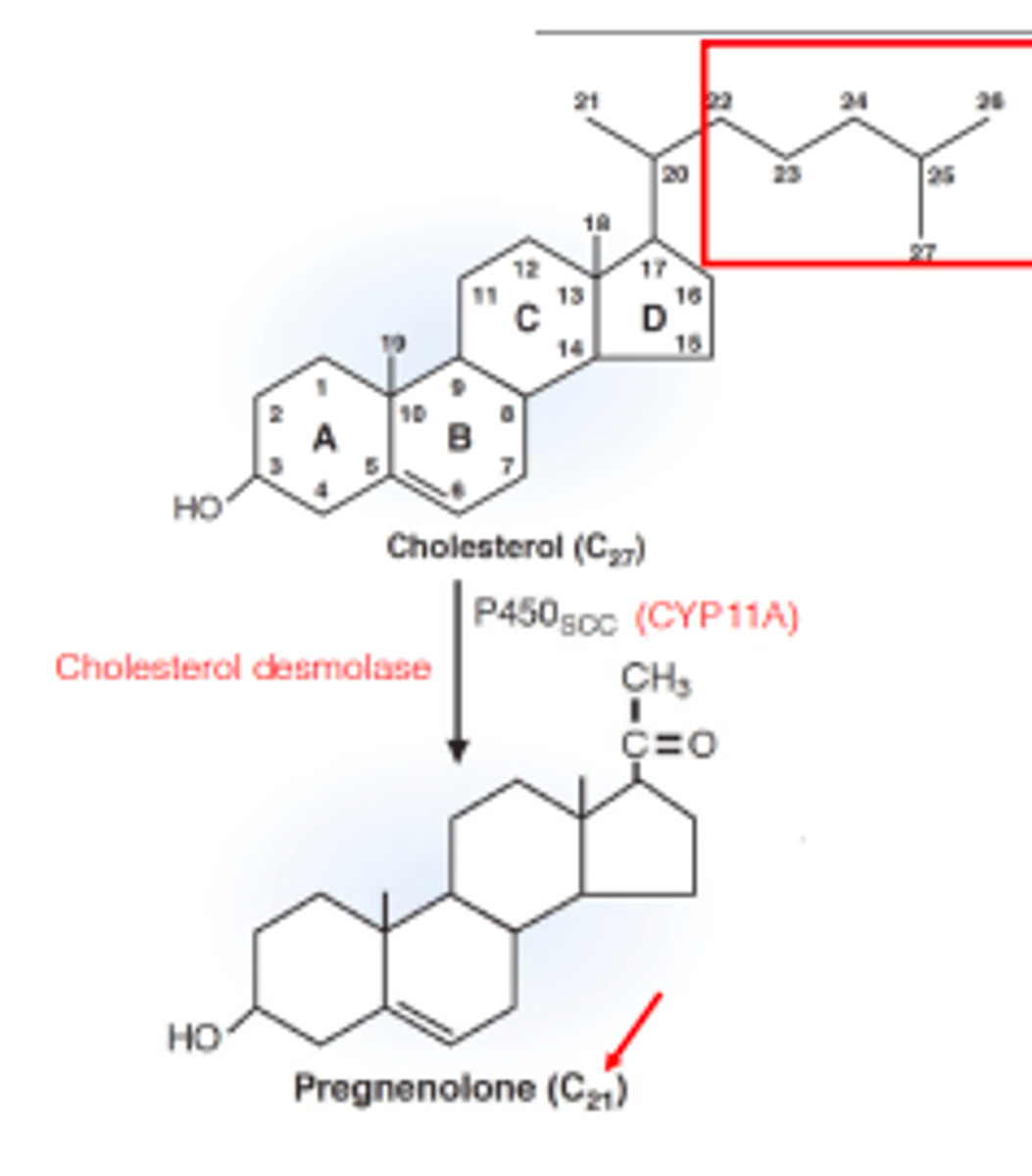
what 4 hormones are derived from pregnenolone?
aldosterone (controls water balance), cortisol, testoterone, estradiol
what intracellular organelle allows pregnenolone to form different steroid-specific molecules?
pregnenolone travels to smooth ER, where different enzymatic processes produce different specific steroid molecules
what is needed to make amine hormones?
proteins
which two amine hormones are derived from tyrosine?
catecholamines and iodothyronines
which amine hormones are derived further from catecholamines?
dopamine, norepinephrine + epinephrine (fight or flight)
which amine hormones are derived further from iodothyronines?
thyroxine and triiodothyronine
what amine hormone is derived from tryptophan?
melatonin
what are two examples of peptide/protein hormones consisting of amino acids?
gonadotropin-releasing hormone and insulin
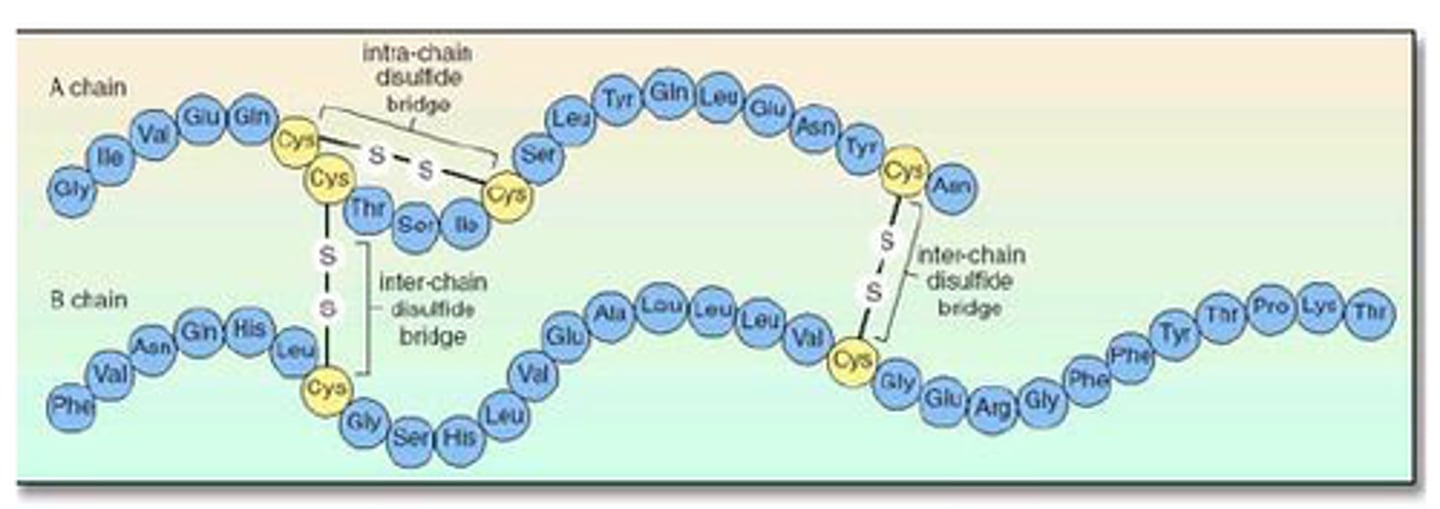
how are the chains of amino acids connected in insulin?
disulfide bonds
what occurs in the lumen of the rough ER in insulin systhesis?
enzymes in the ER cleave the P segment to produce proinsulin
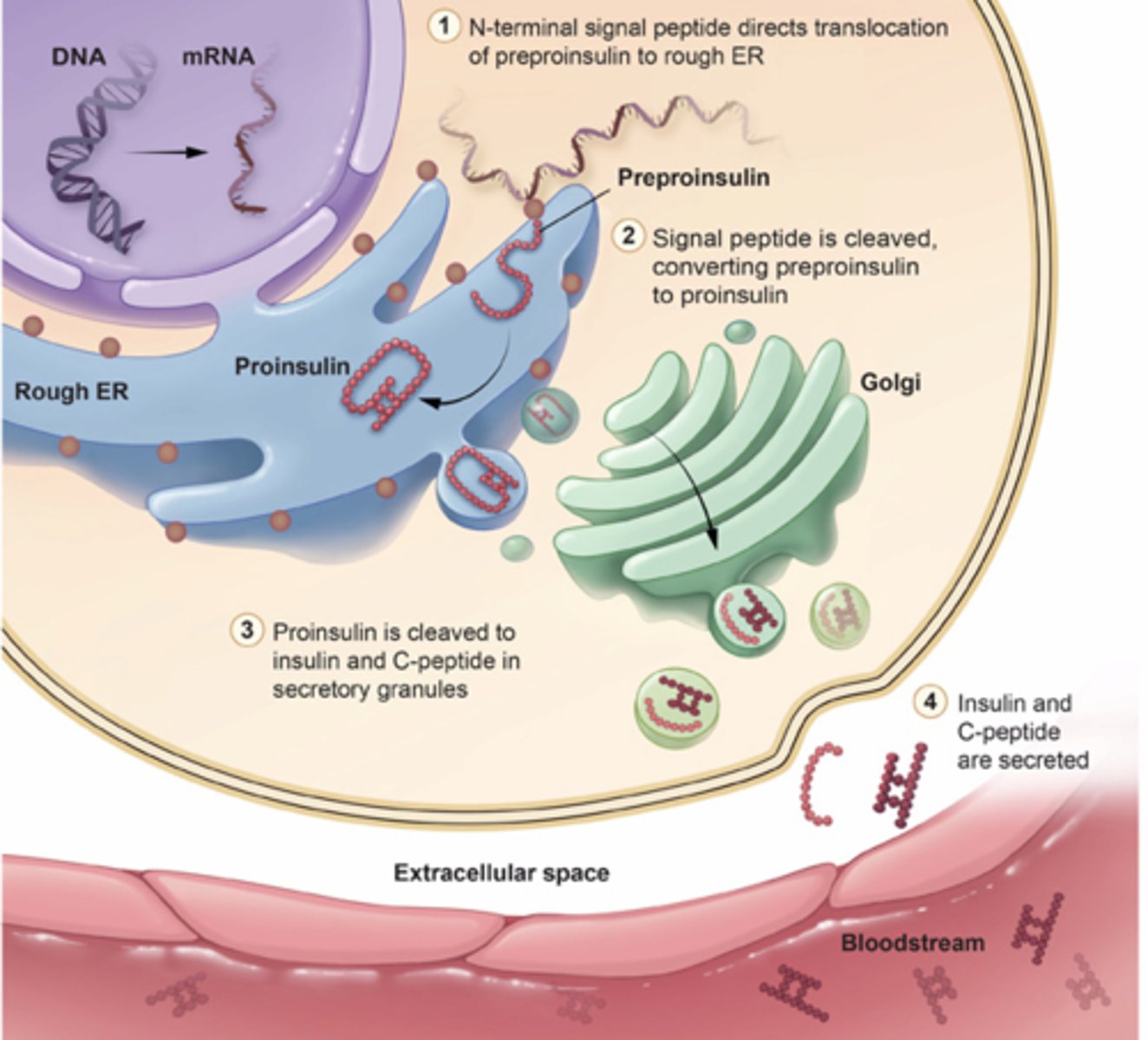
what occurs in the golgi apparatus in the proinsulin molecule?
three disulfide bonds fold the proinsulin molecule and link the A and B regions
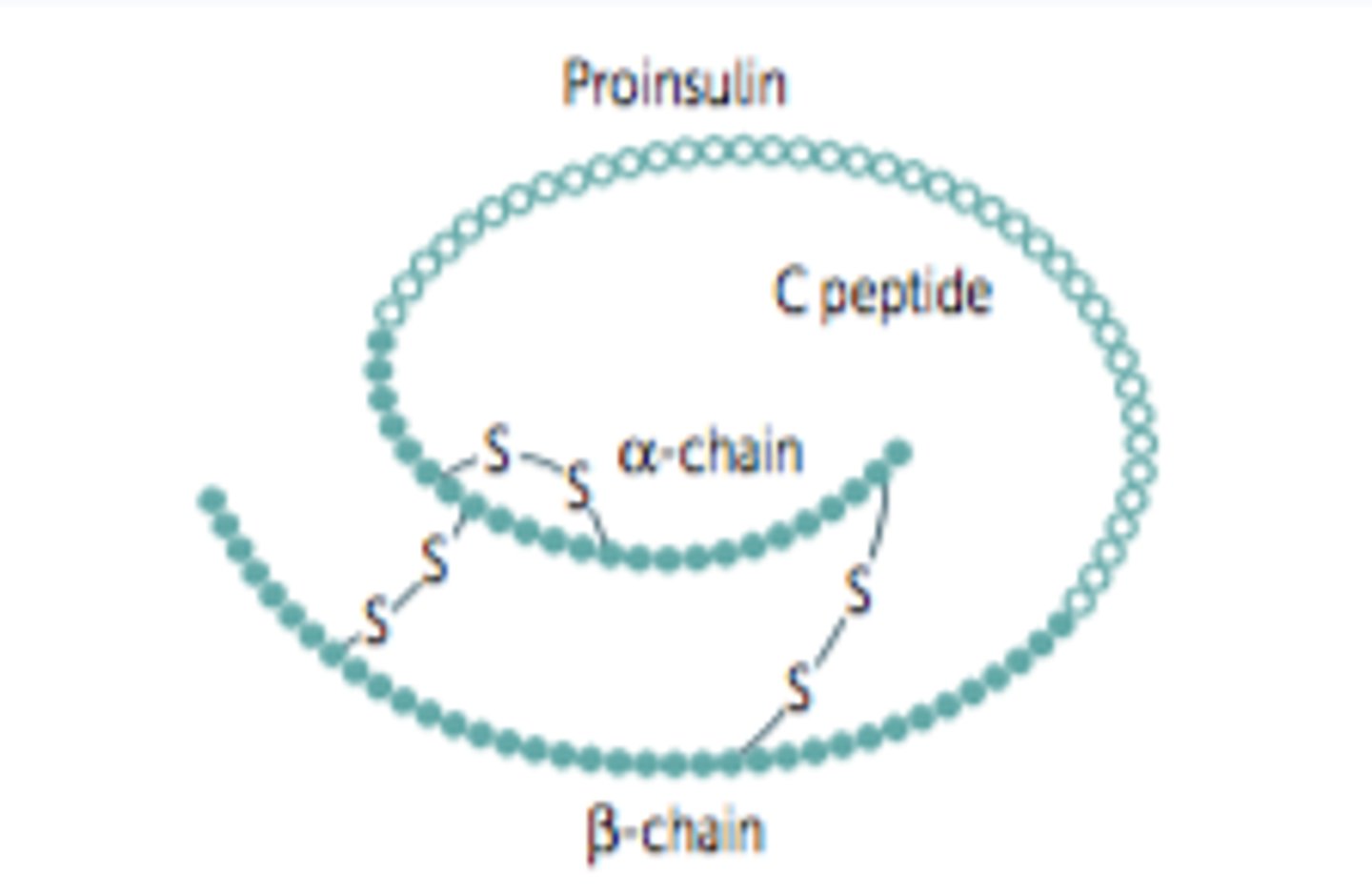
what is contained in the vesicles that the golgi apparatus buds off?
proinsulin and enzymes
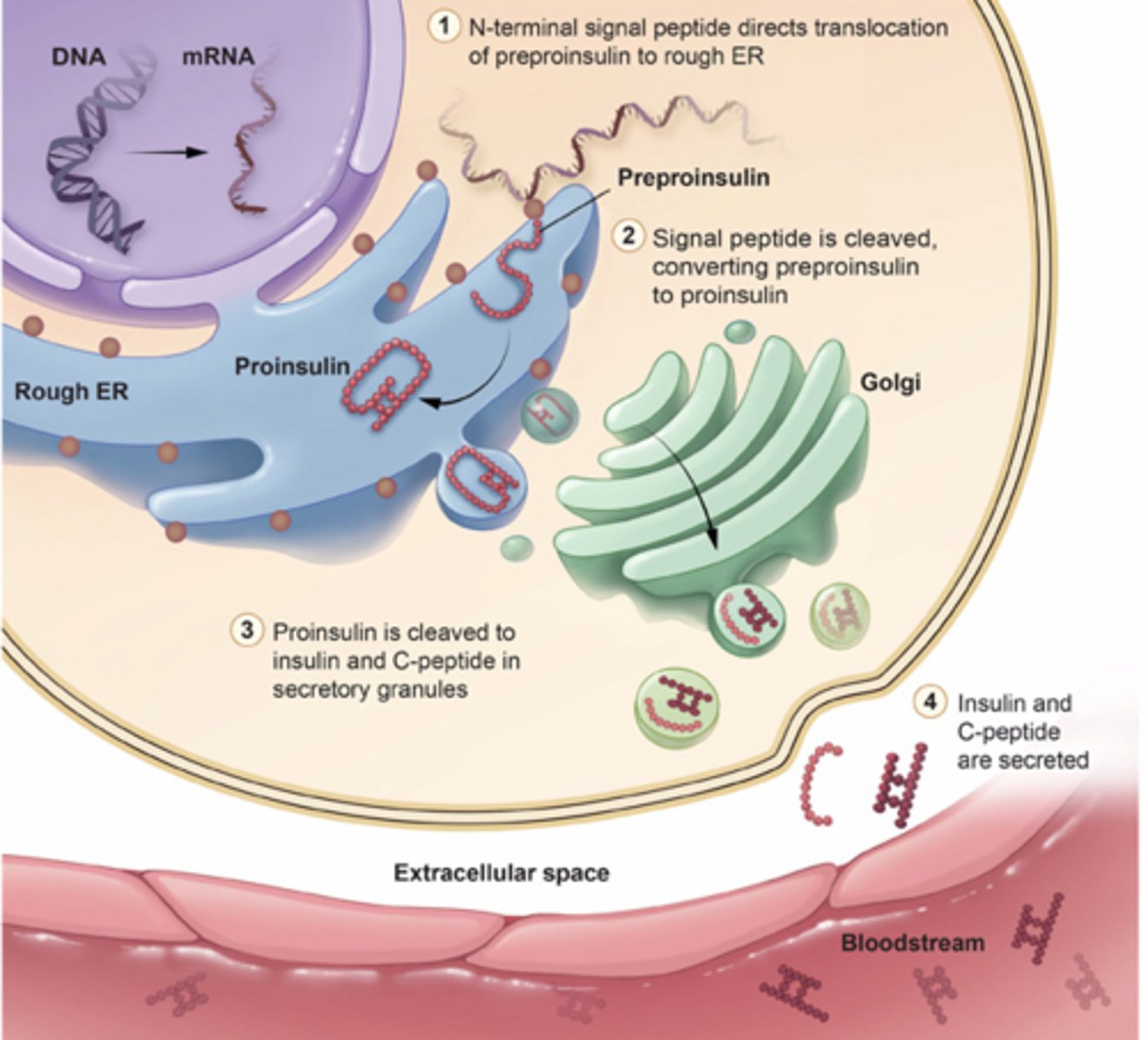
what do the enzymes in the vesicles do?
cleave the C-peptide from proinsulin to form mature insulin
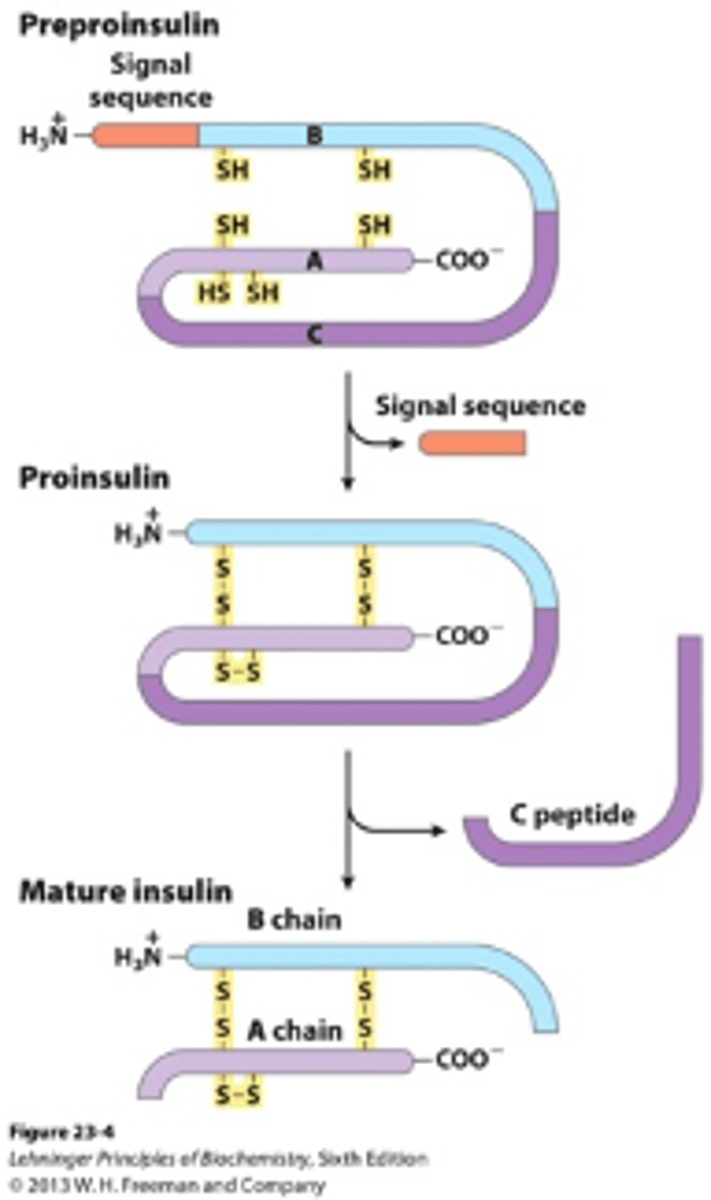
what occurs when the body senses food?
depolarization of the cell membrane triggers release of the vesicle contents (mature insulin and C-peptides) by exocytosis into a blood vessel
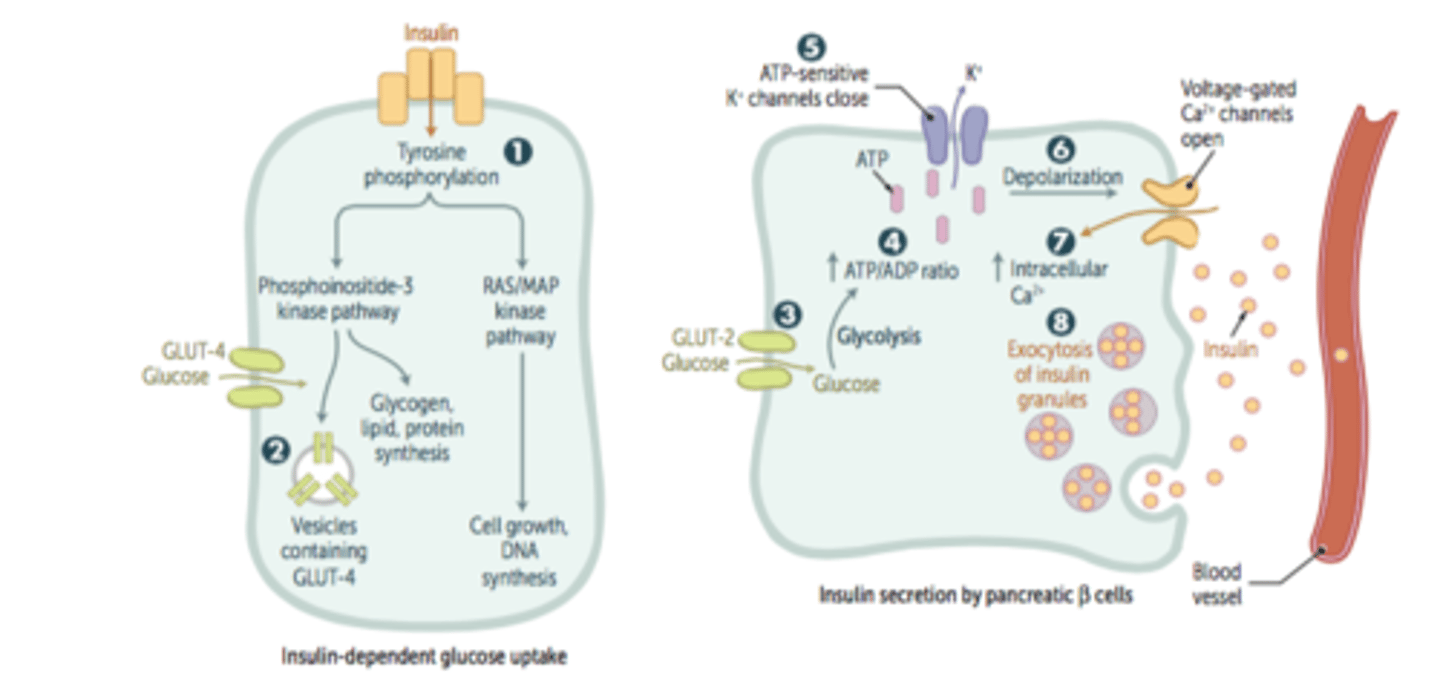
what is unique about the posterior pituitary?
it does not make its own hormones, it is just a storage unit for the hypothalamus
what two hormones are made by the hypothalamus?
oxytocin and vasopressin
how are oxytocin and vasopressin secreted?
by neurosecretory cells
what two places does the hypothalamus send information to?
anterior and posterior pituitary
what is unique about the anterior pituitary?
it makes its own hormones and secretes them
how to neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus work to release or inhibit hormones in the anterior pituitary?
neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones at capillaries of the median eminence, releasing/inhibiting hormones travel through the portal vessels to the anterior pituitary, they then stimulate or inhibit secretions by the anterior pituitary endocrine cells
what 6 hormones are released from the anterior pituitary?
thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropin, growth hormone, gonadotropins, prolactin, and MSH (in some animals)
function of thyrotropin
metabolism, growth
function of adrenocorticotropin
stress response, metabolic actions
function of growth hormone
growth of many tissues, metabolic actions (can be positive or negative feedback)
function of gonadotropins
sex hormones production and secretion, sperm production in males, follicle development and secretion in females
function of prolactin
growth during pregnancy, milk production, reproduction, water and ion balance, caring for young
function of MSH
skin darkening in amphibians, reptiles, and fish
function of glucocorticoids as derived from adrenocorticotropin
help in metabolism of foods and has anti-inflammatory properties
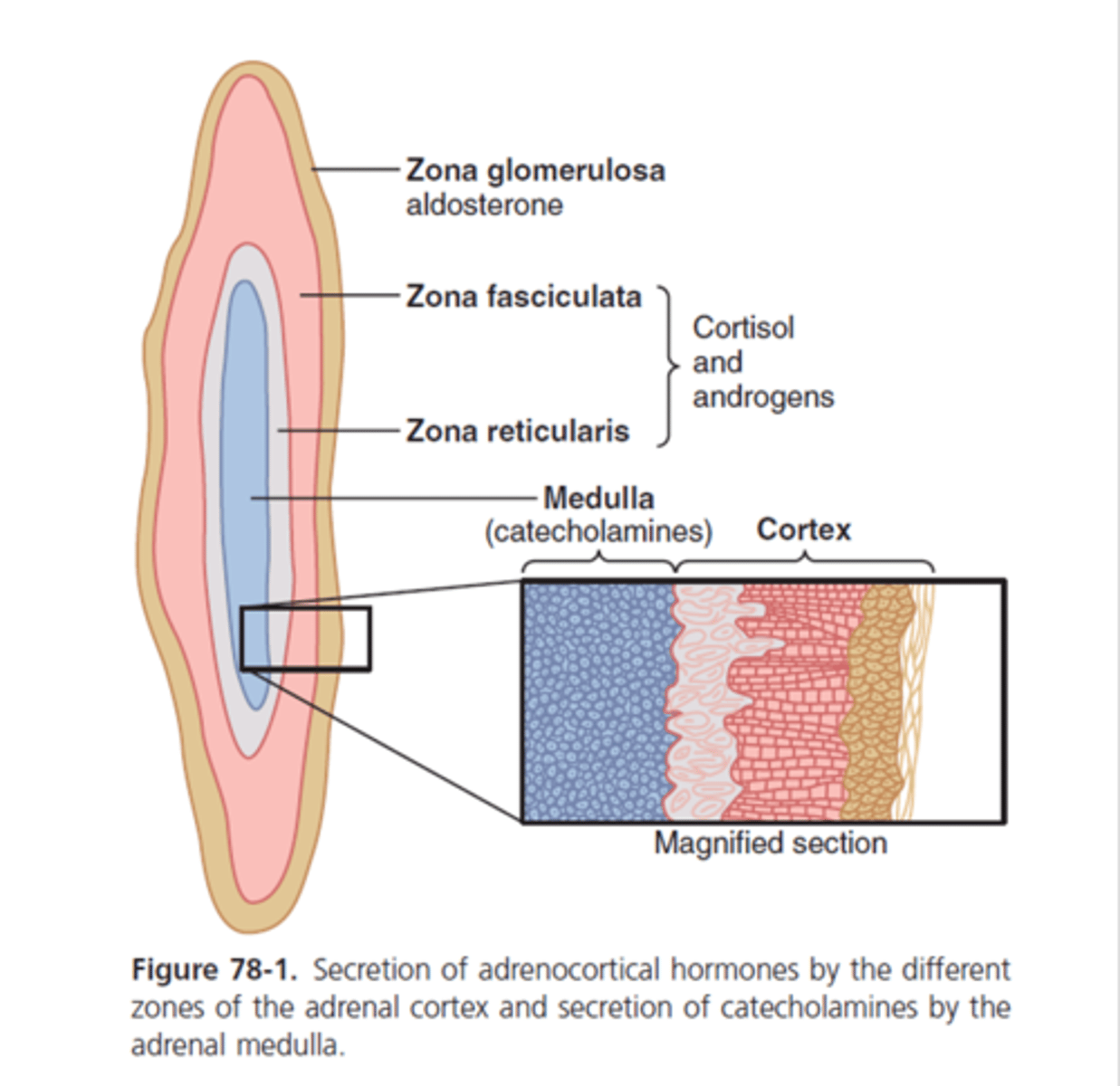
what does the zona reticularis secrete in the adrenal gland?
primarily adrenal androgens such as androstenedione (precursor for estrogen and testoterone)
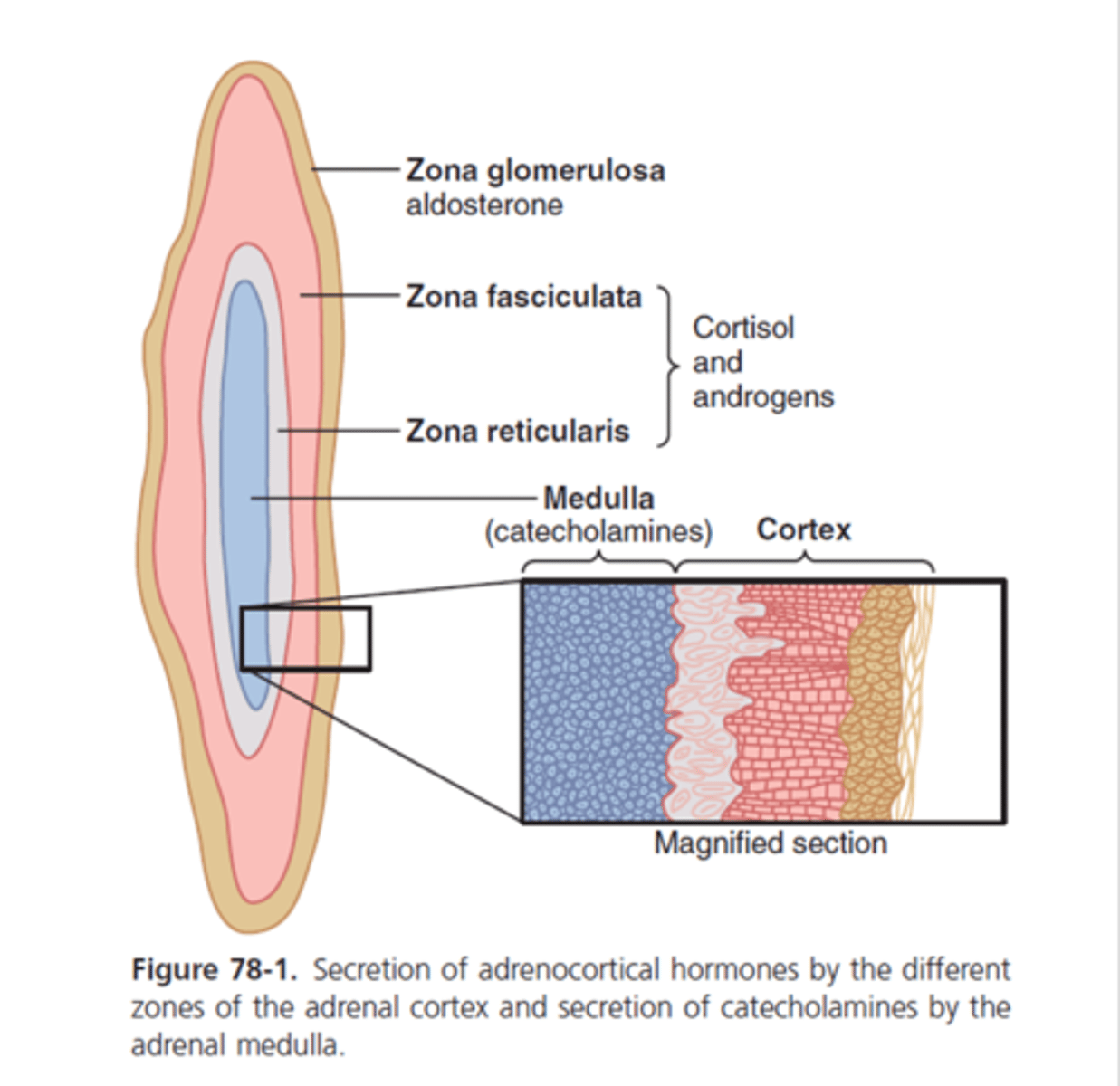
what does the zona fasciculata secrete?
primarily glucocorticoids such as corticosterone
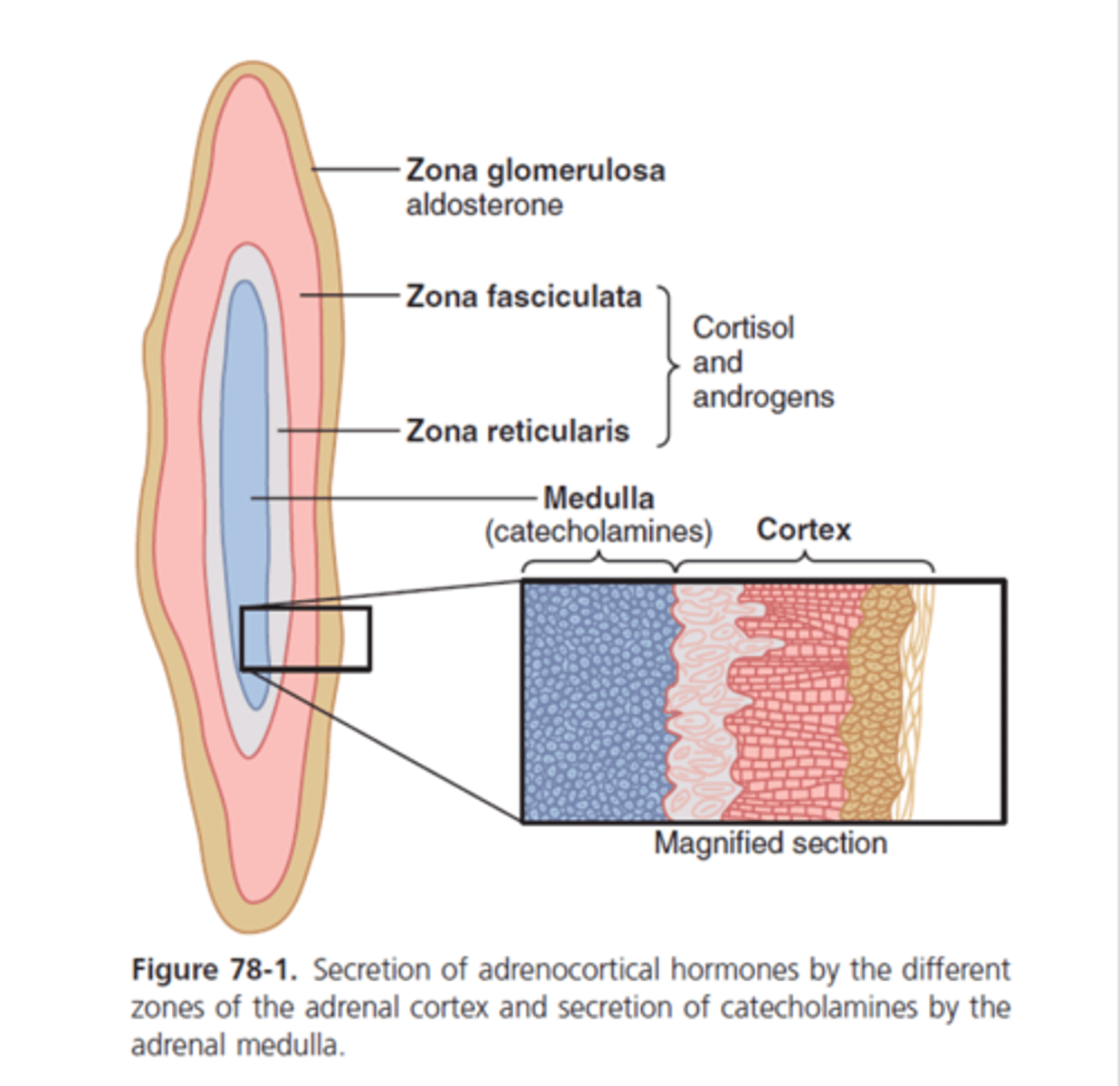
what does the zona glomerulosa secrete?
mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone
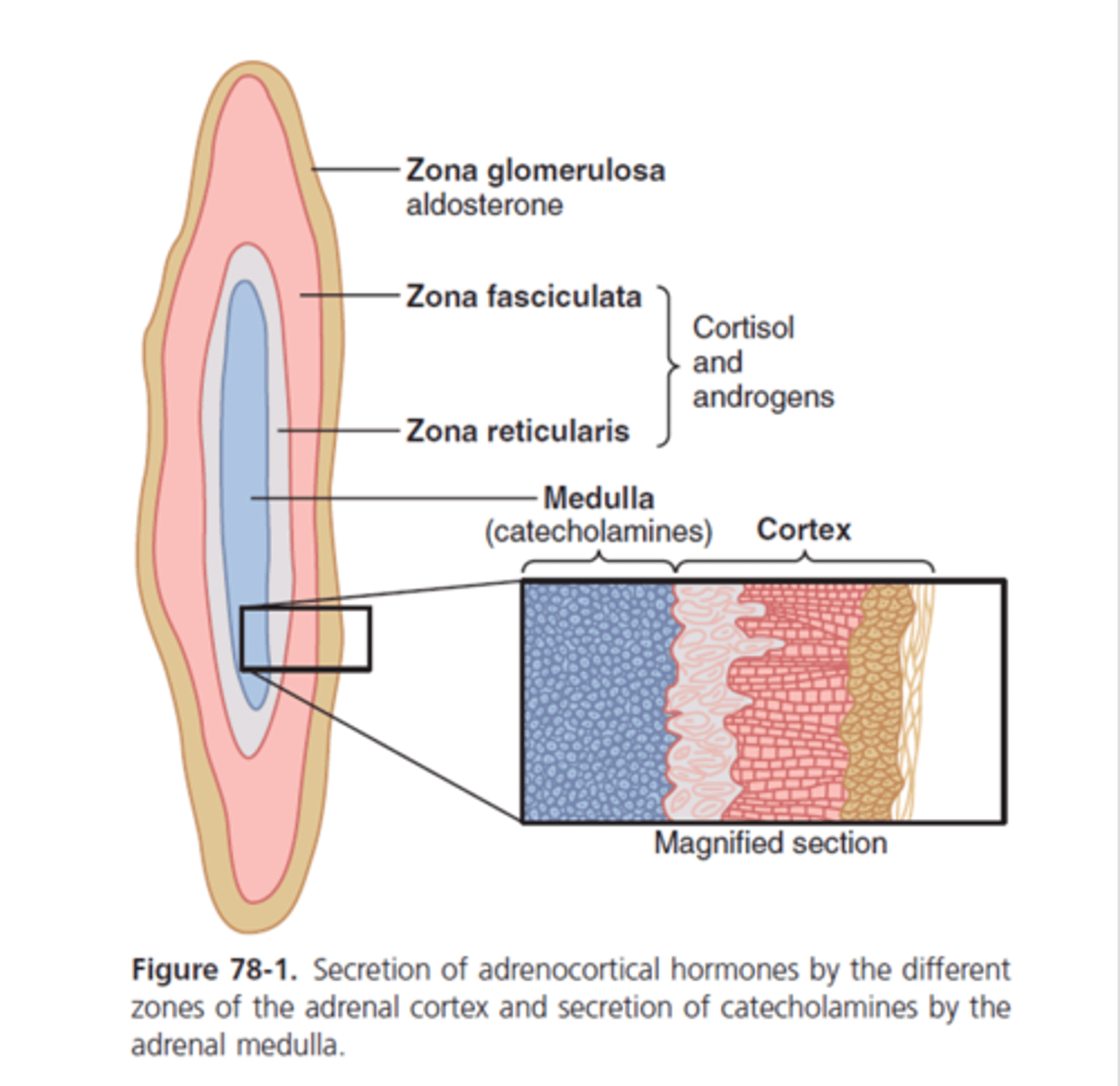
what does the adrenal medulla secrete?
catecholamines (dopamine, epinephren, norepinephren)
what increases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) production?
stress
what sets the daily rhythm of CRH secretions?
circadian clock
what do the parvocellular hypothalamic neurosecretory cells secrete? where does each hormone come from?
CRH (anterior pituitary)
vasopressin (posterior pituitary)
in the portal system, what does the hypothalamus tell the anterior pituitary after secreting CRH?
anterior pituitary corticotrophs secrete ACTH
in the general circulation, what does the adrenal cortex zona fasciculata cells secrete?
glucocorticoids
what effects do glucocorticoids have on target tissues?
protein catabolism in muscle+bone, glucogenesis in liver, fat catabolism in adipose tissue, decreased immune system function, permissive to catecholamine action on vasoconstriction (blood increases in system)
what does ACTH affect?
your ability to digest food
why are you unable to sleep when you're stressed?
stress can override circadian rhythm
what kind of feedback do glucocorticoids exert on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary?
in the general circulation, they exert negative feedback
what do glucocorticoids ensure you have?
enough energy requirements to override stress
early physiological effects of sympathetic activation of norepinephrine and epinephrine
increased heart rate, ventilation, vasoconstriction, glucagon, fat catabolism
decreased digestion, insulin
what two structures form memories from emotionally charged events?
amygdala and hippocampus
what do the immune cells create that is not only limited to the anterior pituitary?
ACTH (produced independently of CRH)
low levels of what two hormones stimulate the immune system in early stress responses?
glucocorticoids and catecholamines
what are produced by the immune cells?
cytokines
what is the significance of immune cells producing cytokines?
allows immune cells to send signal to the brain when CRH is needed since the immune cells can only produce ACTH
what are characteristics of the locus coeruleus?
place where many nerve endings meet, determine how long a stimulus is maintained, maintains attentions and responding to novel stimuli -> knows which stimuli to prioritize
what two hormones oppose the action of insulin?
glucagon and epinephrine
when is insulin secreted and what does it do?
secreted in response to food, stimulates cells to take up glucose to reduce glucose in the blood
what is the function of epinephrine?
prepares the body for fight or flight by breaking down glycogen, a FASTER way of breaking down glycogen
what is the function of glucagon?
exactly opposite of insulin, increases levels of glucose, SLOWER than epinephrine
what is the term for epinephrine and glucagon working at the same time?
synergism: both amplify each other in opposing the action of insulin
what is the level of glucose in the blood when insulin is opposed and synergism is occuring?
the glucose concentration remains high
what is the term for when epinephrine alone and glucagon alone oppose the action of insulin?
antagonism
is the glucose concentration higher in insulin+epinephrine or insulin+glucagon?
insulin+epinephrine
why do both insulin and glucagon spike even after a protein-only meal rather than carb?
both increase in response to food to prepare the body for whatever food is taken in --> since no glucose was taken in, the glucagon increases to maintain glucose levels after the insulin spike
what is released when wanting to increase blood pressure?
arginine vasopressin (AVP)
what do secondary signaling in the kidney signal for?
AVP binding to its receptor causes secondary signaling to allow storage vesicles to fuse with the membrane
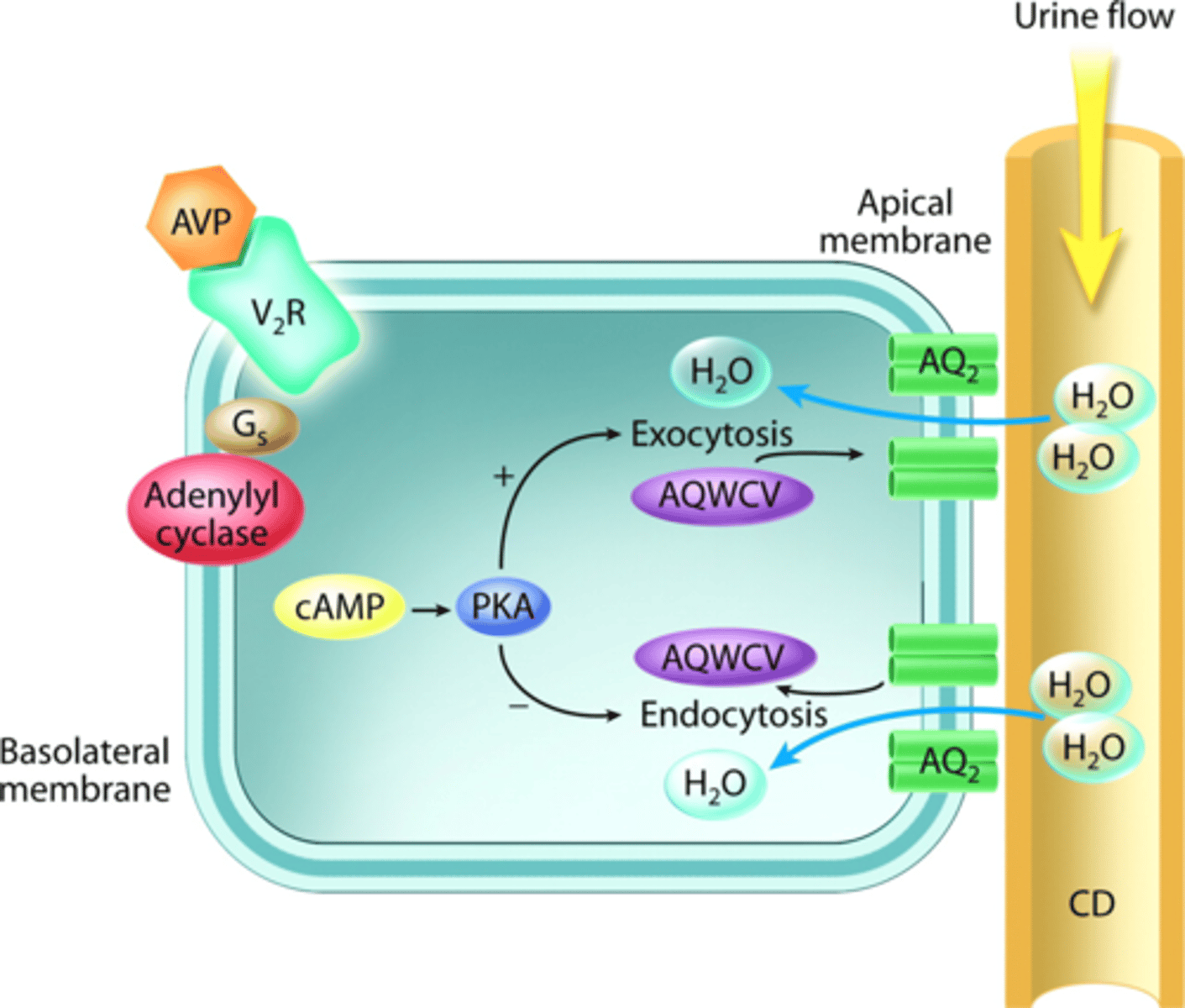
what type of channels are incorporated in the apical membrane from the storage vesicles?
AQP-2
what flows through the AQP-2 channels?
water from the body that would have been released but is being reabsorbed instead
where does the water travel after flowing through AQP-2 membranes?
into the extracellular fluid through permanent AQP-3 channels
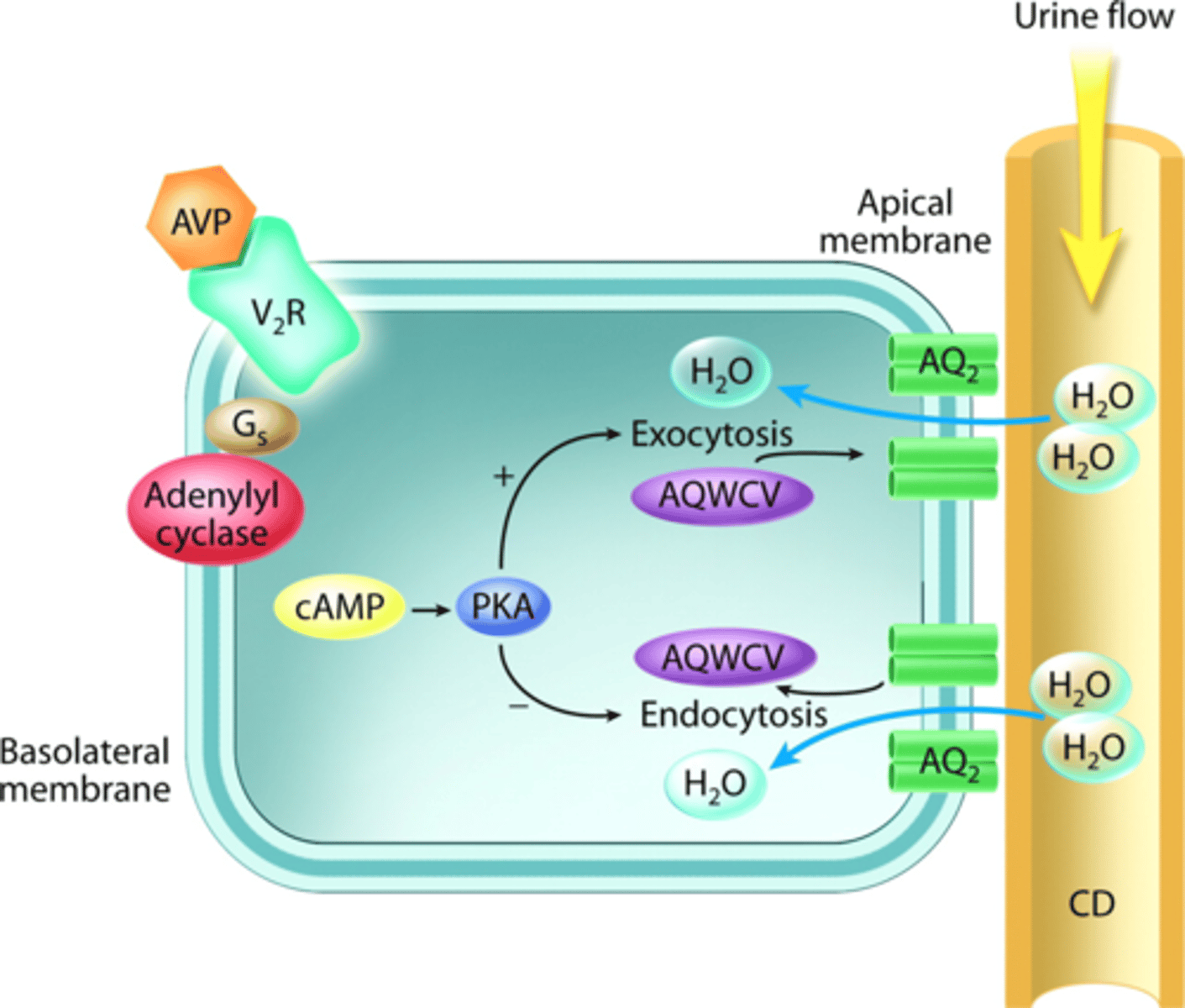
after entering extracellular fluid, how does the water enter the blood?
spaces between capillary endothelial cells
how is the adrenal cortex involved in fluid retention?
an increase in aldosterone causes an increase in Na+ reabsorption in the kidney which causes an increase in fluid retention, increase in blood volume, and increase in blood pressure
what is secreted by juxtaglomerular cells when blood pressure is low?
renin
what is secreted by the heart muscles in response to an increase in blood volume?
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
what is released in response to low Ca2+ in the blood?
chief cells secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) when extracellular Ca2+ is low
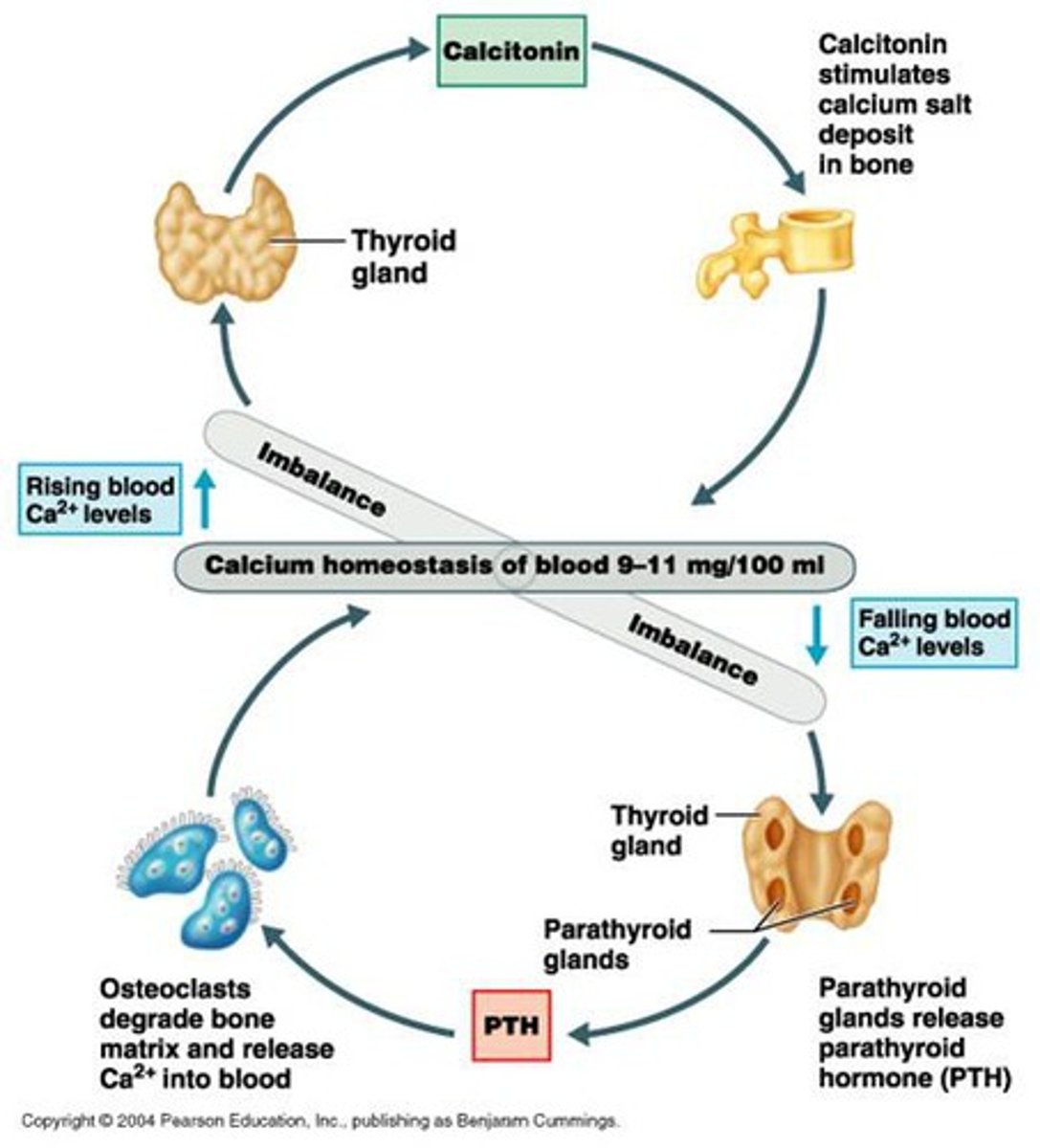
when is vitamin D active?
in response to low Ca2+ which is self-regulated by negative feedback --> causes intestinal Ca2+ absorption
what is secreted in response to high Ca2+?
calcitonin
what relationship does reducing Ca2+ absorption do to vitamin D?
reducing absorption reduces the production of active vitamin D, so intestinal Ca2+ absorption is decreased