Human Anatomy Chapter 4- Tissues
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
1. Epithelia and Glands- Epithelia
the tissues that cover the external body surface (epidermis) lines its cavities and tubules and generally "marks off our inside from our outsides"
Epithelial membrane
Glands develop from__
interfaces between two different environments
Epithelia occurs at the ___
What are the functions of epithelia
1. protection
2. absorption
3. filtration
4. secretion
5. diffusion
6. sensory reception
Unique characteristics of Epithelia
1. Cellularity- composed almost entirely of cells
-mostly just cells
2. Special contacts- form continuous sheets held together by tight junctions and desmosomes
- how cells stick together) surfaces
3. Polarity- apical (upper free) and basal (lower attac
4. Supported by connective tissue- reticular and basal laminae (basement membrane)
-north and south
-deep to epithelium
5. Avascular but innervated- no vessels, has nerves
6. High regenerative capacity- rapidly replaces lost cells by cell division
-grows all the time
Epithelia are classified according to two criteria
1. arrangement- or relative number of layers (first name of tissue)
2. cell shape (last name of tissue)
Arrangement of epithelia
1. simple: consisting of one layer of cells attached to the basement membrane
2. stratified: consisting of two or more layers of cells
Types of epithelia- cell shape
1. squamous- cells wider than tall (plate like)
2. cuboidal- cells are as wide as tall (cube like)
3. columnar- cells are taller than they are wide (column like)
Stratified epithelia are named
according to the cells at the apical surface of the epithelial membrane, not those resting on the basement membrane
2 other types of epithelia
1. pseudostratified epithelium
- actually a simple columnar epithelium one layer of cells, but because its cells vary in height and the nuceli lie at different levels above the basement membrane it gives a false appearance of being stratified. (this epithelium is often ciliated)
2. Transitional epithelium
-Stratified squamous epithelium are formed of rounded or plump cells with the ability to slide over one another to allow the organ to be stretched.
ONLY found in urinary systems e.g. bladder
What type of epithelia is only found in the urinary system?
Transitional. the shape at the top is domed because it stretches.
What type of epithelia is always ciliated?
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium (technically only has one layer)
function
The structure of epithelium reflects its ___
1. Simple squamous epithelium
a single layer of flat cells with disc shaped nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
Function- Simple squamous epithelium
Passage of materials by passive diffusion and filtration and secretes lubricating substances in seorsae (membranes)
-expect things to pass through it such as gases
Special Types- Simple squamous epithelium
1. Endothelium (inner covering)- slick lining of hollow organs
2. Mesothelium (middle covering)- lines peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial caviites, covers visceral organs and those cavities
Location- Simple squamous epithelium
1. renal corpuscles
2. alveoli of lungs
3. lining of heart, blood and lymphatic vessels and ventral body cavity (serosae)
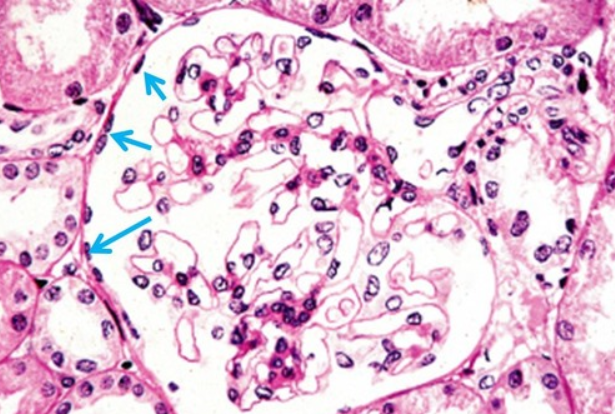
2. Simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube like cells with large, spherical central nuceli
Function- simple cuboidal epithelium
1. secretion
2. absorption
Location- simple cuboidal epithelium
1. kidney tubules
2. secretory portions of small glands
3. ovary surface
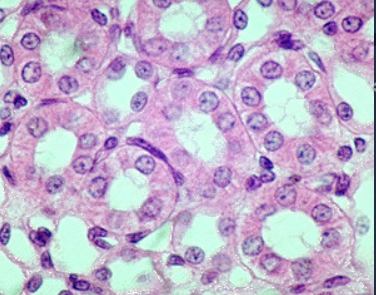
3. Simple columnar epithelium
single layer of column shaped (rectangular) cells with oval nuclei, some bear cilia at their apical surface, may contain golbet (mucus secreting) cells (absorption taking place)
Function- simple columnar epithelium
1. absorption
2. secretion of mucus
3. ion transport
4. ciliated type propels mucus or reproductive cells by ciliary action
Location- simple columnar epithelium
1. Nonciliated form- lines digestive tract, glallbladder, ducts of some glands
2. Cilated form- lines small bronchi, fallopian tubes, uterus
4. Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
all cells originate at basement membrane. only tall cells reach the apical surface; may contain goblet cells and bear cilia; nuceli lie at varying heights within cells (gives false impression of statification)
Function- Pseudostratified Ciloated Columnar Epithelium
1. Secretion of mucus, propulsion of mucus by cilia
Location- Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Non-ciliated form- is in ducts of male reproductive tubes and ducts of large glands
Ciliated form- lines the TRACHEA and most upper respiratory tract
What are cilia?
hair like projections that move mucus out.
2. Stratified Squamous Epithelium
many layers of cells, superficial layers are squamous on shape while deeper layers of cells appear cuboidal or columnar, thickest epithelial tissue, adapted for protection
Function- stratified squamous epithelium
1. protection- underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
Location- stratified squamous epithelium
Keratinized forms- epidermis (hardened cells)
Non-keratinized forms- lining of esophagus, mouth and vagina (mucus membrane)
- no fluid moving across
-main function of stratified is protection
2. Stratified cuboidal epithelium
generally two layers of cubed shaped cells
Function- stratified cuboidal epithelium
Protection
Location- stratifed cuboidal epithelium
1. forms largest ducts of SWEAT GLANDS
2. forms ducts of mammary glands
3. salivary glands
(typically glands)
3. Stratified columnar epithelium
Several layers; basal cells usually cuboidal; superficial cells elongated
Function- stratified columnar epithelium
1. protection
2. secretion
(coming out, not coming in)
Location- stratified columnar epithelium
1. Rarest tissue type, found in male urethra and large ducts of some glands
4. Transitional epithelium
basal cells usually cuboidal or columnar, superficial cells dome-shaped or squamous, undergoes transitions in shape
Function- transitional epithelium
1. stretching
2. permits distension of urinary bladder causing thinning
3. BLADDER that will stretch
Basal surfaces + fibers
What makes up the basement membrane?
Location- transitional epithelium
1. lines the ureters
2. urinary bladder *
3. part of urethra
(all stretch)
Epithelia: Gland
gland- many epithelia cells that make and secrete a product
The products of the gland are ___
aqueous fluids that usually contain a protein
What are epithelial cells highly specialized to do?
-remove materials from the blood and to manufacture them into new materials which they secrete
Every fluid is a filtrate from?
Blood
(glands get fluid from blood)
Glands are classified by?
1. The site of release: Endocrine (Internally releasing) vs. Exocrine (externally releasing)
2. The relative number of cells forming the gland
-Unicellular or Multicellular
Endocrine glands
lose their surface connection (duct) as they develop. this they are referred to as "ductless glands"
-when they release product it goes into the blood stream
Endocrine glands secrete
hormones directly into the blood or the lymphatic vessels (tissue fluid) that weave through the glands to specific target organs far from the site of release
Exocrine glands
-retain their ducts, and their secretion empty through these ducts to an epithelial surface (skin or body cavities)
- local activity: diverse group of cells (a lot of cells in ducts)
e.g. sweat glands
1. Unicellular
scattered within epithelial sheets
e.g. goblet cells
2. Multicellular
formed by invaginations or evaginations and usually have ducts (tube-like connections to epithelial sheets) that carry products of exocrine glads to epithelial surface
e.g. salivary glands
Basal surface feature- Basal lamina
the border between the epithelia and the underlying C.T.
2. Connective Tissue
found in all parts of the body as discrete structures or as part of various body organs
Functions- Connective tissue
1. protect
2. support (cartilage and bone)
3. bind together (tendons and ligaments) other tissues of the body
Examples of some Connective Tissue
1.Osseous tissue- connective tissue of bones
2.Areolar connective tissue- soft packaging material that cushions and protects body organs
3. Adipose (fat) tissue- provides insulation of the body tissues and a source of stored food
4. Hematopoietic tissue- replenished the body's supply of red blood cells
Four main types of adult connective tissue
1. connective tissue proper- fat tissue and fibrous tissue of ligaments
2. cartilage
3. bone tissue
4. blood
What are the 4 simple structural plans of connective tissue?
1. Embryonic origin
2. rich supply of blood vessels
3. many cell types
4. extracellular matrix
What component of the extracellular matrix hold the intersitial fluid?
Ground substance
2. Fibers
Provide support.
ex. collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
all made from a single cell called fibroblast
fibroblast
All fibers are made from a single cell called
2. Cartilage
Cells- chondroblasts, chondrocytes
Matrix- gel like ground substance
Fibers- collagen, elastic fibers
Function- cushion and support body structures
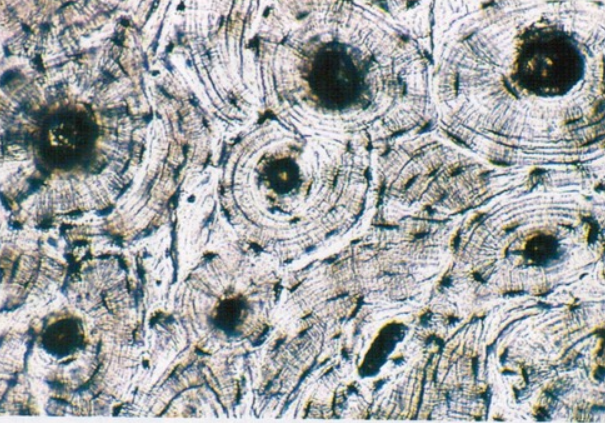
3. Bone Tissue
Cells- osteoblasts, osteocyte
Matrix- gel like ground substance calcified with inorganic salts
Fibers- collagen
Function- support
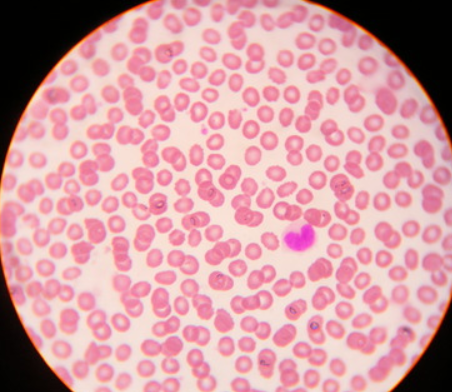
4. Blood
Cells- erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets
Plasma
No fibers
Function- to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide, nutrients waste and other substances
Areolar connective tissue
(most common)
- underlies almost all the epithelia of the body and surrounds almost all the small nerves blood vessels
Functions- Areolar connective tissue
1. support and binding of other tissues
2. holding body fluids
3. defending the body against infection
4. storing nutrients as fat
Fibers that provide support
1. collagen
2. reticular
3. elastic
1. collagen fibers
strongest and most abundant type
- allows connective tissue to WITHSTAND TENSION
- cross-linking of collagen fibers give collagen its strength
2. reticular fibers
bundles of special type of collagen
-cluster into NETWORKS (reticulum) that cover and support all structures bordering the CT
-allow more “give”
3. Elastic fibers
- long and thin. form wide networks within the ECM.
- made up of collagen but also contain elastin, which allows them to function like rubber bands. Stretch and recoil
Function of ground substance?
functions as a MEDIUM through which nutrients waste and other dissolved the substances can diffuse between the blood capillaries and cells
Connective tissue proper
1. loose connective tissue
-areolar
-adipose
-reticular
2. Dense (fibrous) connective tissue
-regular (tendon)
-irregular
-elastic (aorta)
Connective tissue proper- 1. Loose connective tissue
1. areolar
2. adipose
3. reticular
Loose connective Tissue- 1. Areolar CT
most common
contains elastic fibers, collagen fibers, fibroblast nuclei
functions- wraps and cushions organs
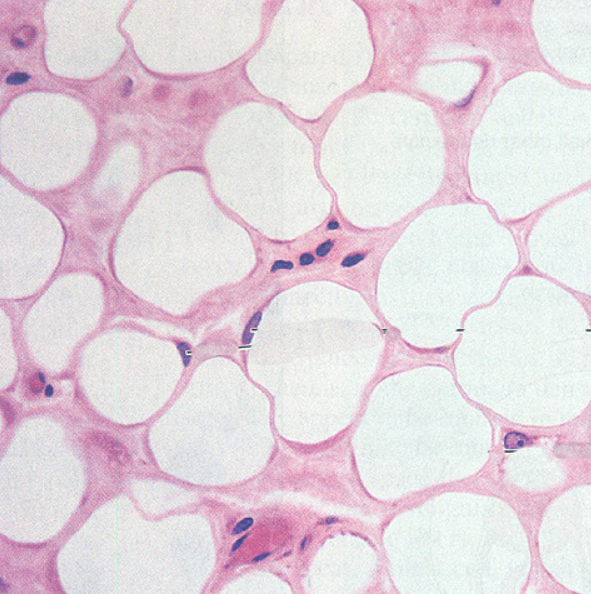
Loose connective tissue- 2. Adipose CT
1. 90% of mass consists of fat cells
2. highly vascularized
3. removes lipids from the bloodstream after meals and later releases them into the blood as needed
4. occurs in the HYPODERMIS and the MESENTERIES (sheets of serous membrane that hold the stomach and intestine in place)
Loose connective tissue- 3. Reticular CT
1. reasembles areolar tissue BUT THE ONLY FIBERS PRESENT in its matrix are RETICULAR FIBERS which hold many free cells
-found in the bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes (all have many free blood cells outside their capillaries)
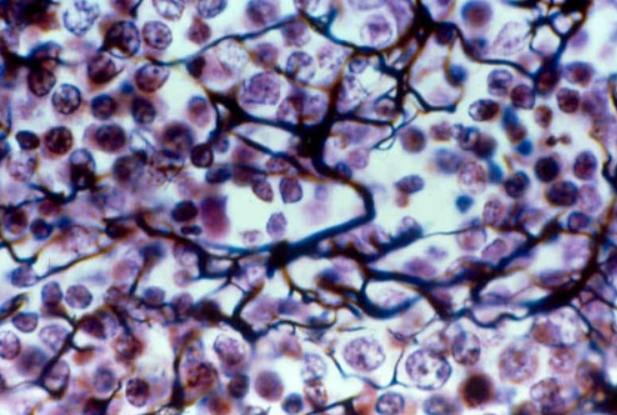
Dense Connective tissue
1. irregular CT
2. Regular CT
Dense connective tissue- 1. Irregular connective tissue
1. reasembles areolar tissue, but the COLLAGEN FIBERS ARE MUCH THICKER
2. collagen fibers run in different planes, allowing dense irregular CT to resist tensions from different directions
Dense connective tissue- 2. Regular connective tissue
1. collagen fibers run in the same direction parallel to the direction of pull
2. crowded between the fibers are rows of fibroblasts which continuously produce collagen fibers and scant ground substance.
3. unlike areolar, poorly vascularized, no fat or defense cells
Matrix
thin collagen, GROUND SUBSTANCE, lots of tissue fluid (cartilage consists of 80% water)
3 types of cartilage
1. hyaline cartilage
2. fibrocartilage
3. elastic cartilage
Connective tissue- Bone (osseous) tissue characteristics
1. calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers
2. osteoblasts (immature)- secrete collagen fibers and matrix
3. osteocytes- mature bone cells in lacunae
4. very well vascularized
Connective tissue- Bone (osseous) tissue function
1. supports and protects organs
2. provides levers and attachment sites for muscles
3. stores calcium, fat and minerals
4. marrow: site for blood formation
Connective tissue- Blood tissue
the fluid in blood vessels
1. the most ATYPICAL connective tissue DOES NOT bind things together or give mechanical support
Function of blood tissue
Blood functions as a transport vehicle for the CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM carrying nutrients waste respiratory gas and other substances throughout the body
Connective tissue- Muscle tissue
1 bring about most kinds of body movements
2. most MUSCLE CELLS are called MUSCLE FIBERS because they have an elongated shape and contract forcefully as they shorten
3. contain Myofilaments (combination of actin and myosin)
Muscle tissues- 1. Skeletal muscle
1. pull on bones to cause body movements
2. long large cylinders that contain many nuclei
3. appear striated due to the organization of myofilaments
nucleus located on the outside (multiple)
Where is the nucleus located on skeletal muscle?
Muscle tissues- 2. Cardiac muscle
1. occurs at the wall of the heart
2. contracts to propel blood through the blood vessels
3. like skeletal muscle, striated appearance
4. each cell just has one nucleus
5. cardiac cells branch and join at a special cellular junction called intercalated discs
intercalated discs
In cardiac muscles, cardiac cells branch and join forming
Muscle tissues- 3. Smooth muscle
1. no visible striations in its cell
2. spindle shaped and contain one centrally located nucleus
3. found in the hollow walls of the viscera
4. acts to SQUEEZE SUBSTANCE through these organs
Connective tissue- Nervous tissue
- the main component of the nervous organs: the brain, spinal cord, and nerves which regulate and control body functions.
Nervous tissue contains two types of cells
1. neurons
2. supporting cells (neuroglial cells)
1. neurons
1.are highly specialized cells that generate and conduct electrical impulses
2. they have extensions that allow them to transmit impulses over great distances within the body
2. supporting cells
1. are non conducting cells that nourish, insulate and protect the delicate neurons
(do not send signals, just help out neurons)