Skull Positioning/Projects Worksheet & Facial Bones, Sinus, and Orbits Projections Worsheet
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are the routine projections for the skull series (not Method!)?
AP Axial, bilateral laterals, PA or PA Axial
What is the degree difference between the OML and IOML?
7 degrees
Is it more ideal to have the OML or IOML perpendicular to the IR for a Towne's Method?
OML, less tube able/distortion
For the AP Axial Skull, you angle _____ degrees if the OML is perpendicular and _____ degrees if the IOML is perpendicular?
30, 37
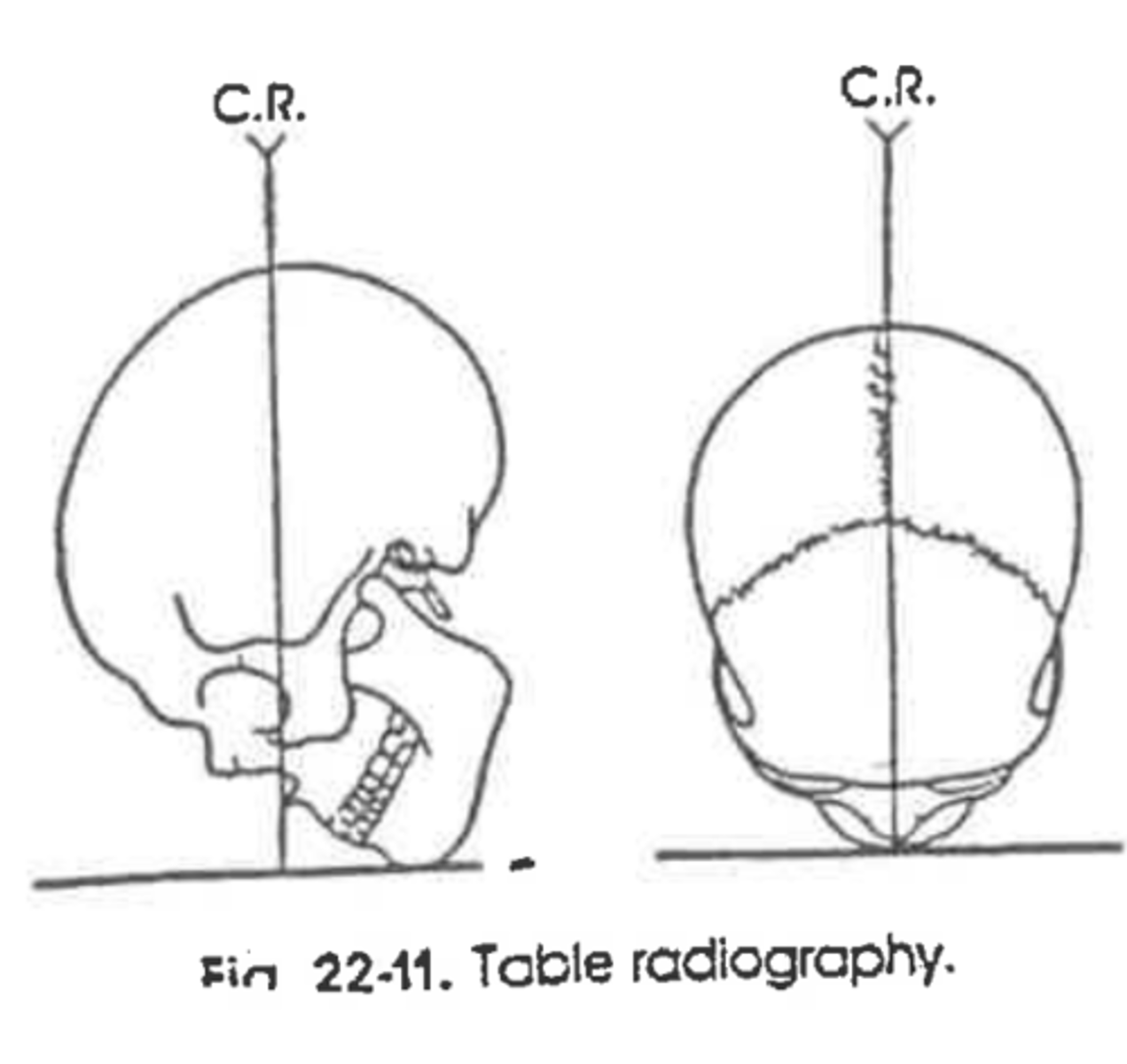
What is the criteria for an AP Axial/Towne's Method?
Dorsum sellae and post clinoids in foramen magnum
How do we choose which lateral to perform for our competency?
Patient side affected
Is the IOML parallel to the IR or perpendicular to the IR when performing a lateral skull?
Parallel
What three positioning lines do we use for a lateral skull projection?
IP, IOML, MSP
What is the criteria for a lateral skull?
Sella in profile, superimposed orbital plates, rami, and clinoids
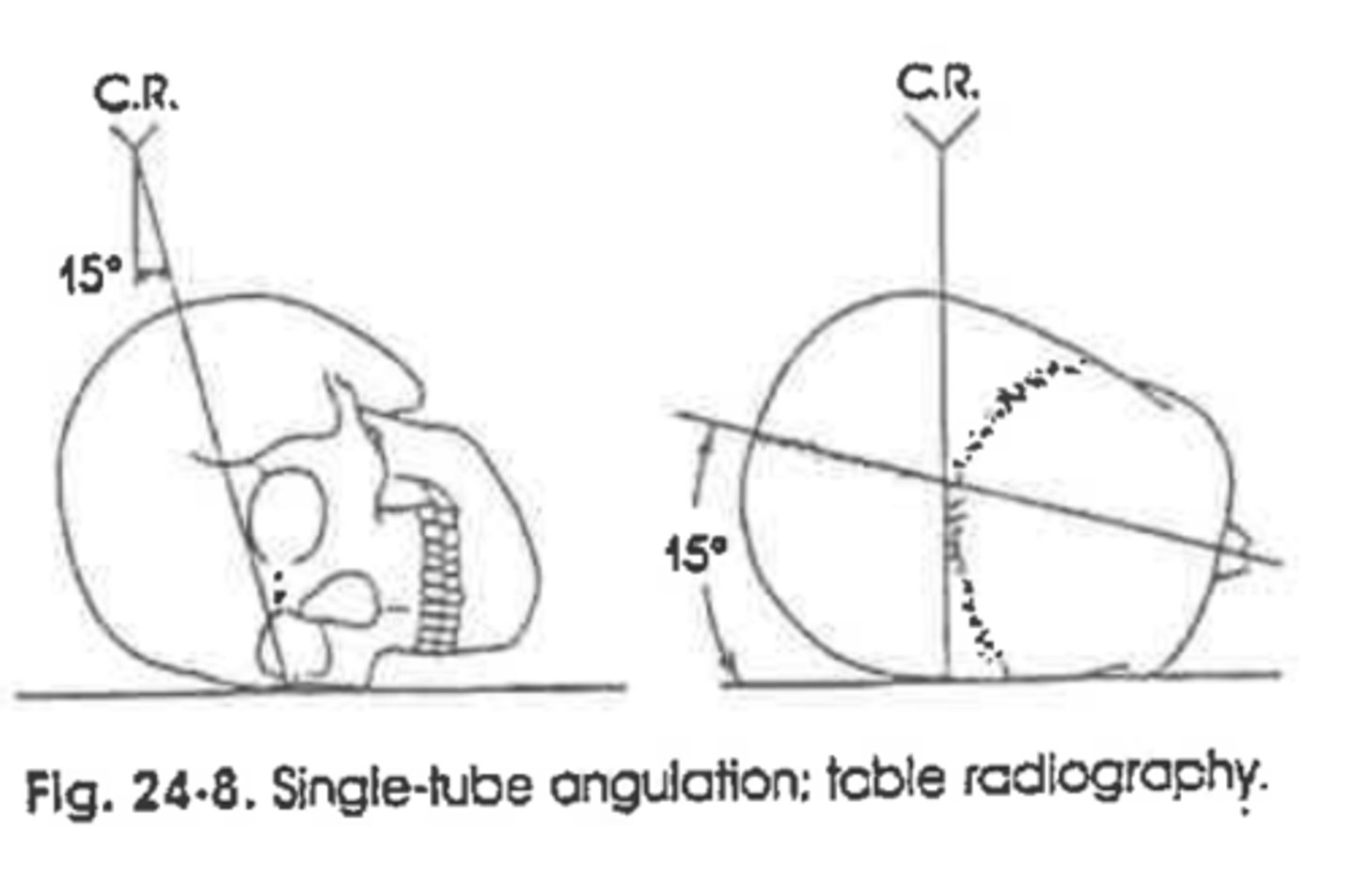
What tube angle is placed on the tube for a PA Axial projection of the skull?
15 degrees cuadal
What two structures are placed against the IR to begin the Caldwell Method?
Nose and forehead
Where should the PP lie in a PA Axial skull projection?
Lower 1/3 of orbit
Where should the PP lie in a PA skull projection?
Fill orbit
What is the exit point for the PA projection of the skull?
Glabella
Will the PP be lower in a 30-degree caudal or 15-degree caudal image, PA Axial projection?
30
Where should the mandibular condyles lie in an SMV projection of the Skull?
Anterior to PP
How could you locate the sella turcica?
3/4 inch anterior and 3/4 inch superior to EAM
A radiograph of an AP Axial projection of the skull reveals the PP are not symmetrical What positioning error is present on this radiograph?
Rotation of the skull. MSP effected
A radiograph of a 15-degeee PA axial projection of the skull indicated the PP are projected below the IOM. What positioning error led to this radiographic outcome?
Too much angle or too much extension
A radiograph of a PA axial skull indicates the lateral borders of the orbit and the lateral margins of the skull are not symmetrical. What positioning error is present?
Rotation of skull, MSP
A radiograph of an SMV projection of the skull reveals the mandibular condyles are within the PP. What positioning error led to this radiographic outcome?
Insufficient extension, IOML not parallel to IR
A radiograph of the lateral skull reveals the orbital plates are not superimposed. One lies superior to the other. What positioning error led to this outcome?
Tilt, MSP
A lateral skull reveals that the mandibular rami are not superimposed. One lies posterior to the other. What positioning error led to this outcome?
Rotation, MSP
An AP Axial radiograph of the skull demonstrates the posterior arch of C1 within the foramen magnum. What positioning error occurred?
Over angulation or over flexion
A patient enters the ER with a possible fracture of the right parietal bone. What single projection would best demonstrate this injury?
Right lateral
What are the routine projections for a facial bone series?
Lateral, Waters, 15 degree PA Axial
Where should the PPs be located in relation to the orbits when performing a Water's method?
Below Maxillary Sinus
Do you need to visualize the entire skull when performing a lateral projection of the facial bones?
No
In a parietoacanthial projection, the x-ray beam enters ________ and exits __________.
Parietal, Acanthion
What degree angle is formed between the OML and the film when positioning for a Water's?
37
What is a nasal bone routine?
Waters, Lateral (bilateral)
Will you utilize a low or high kVp for zygomatic arches in an SMV projection?
Low, don't need to penetrate the skull
For an axiolateral projection of the mandible, the CR is angled _________.
25
How many degrees is the patient rotates in order to visualize the following:
Ramus __________
General Survey _________
Body __________
Mentum _________
0
10-15
30
45
What is a panorex?
Image of the entire mandible
What are the routine projections/methods for a sinus series?
Waters, Caldwell, Lateral
What is the benefit of doing a sinus series erect?
Air fluid levels
What is visualized in an open mouth waters that is not seen in a Water's?
Sphenoid Sinus
A radiograph of a parietoacanthial projection reveals that the distance between the midsagittal plane and the outer orbital margin are not equal. What positioning error is present on this radiograph?
Rotation, MSP not Perp
A patient with a clinical history of sinusitis comes to the radiology department for a sinuses study evaluation. The patient is quadriplegic and cannot be places erect. Which single projection demonstrates any air-fluid levels present in the sinuses?
Cross-Table Lateral
A patient with a possible fracture of the nasal bones enters the emergency room. The physician is concerned about deviation of the bony nasal septum along with possible nasal bones fracture. What radiographic routine would be best for this situation?
Waters, Lateral (Bilateral)
A patient with a possible blowout fracture of the right orbit enters the emergency room. In addition to the basic facial bone routine, what additional single projection would best demonstrate this type of injury?
Modified Waters
A radiograph of an axiolateral projection of the mandible is ordered and the body of the mandible is of interest. How should the technologist proceed?
Place body of mandible parallel to IR.
Requires 30-degree rotation toward the IR
What must be done to prevent the ramus of mandible from being superimposed over the cervical spine with an axiolateral projection of the mandible:
Extend the chin, use IOML
The axiolateral oblique projection of the TMJ's is commonly referred to as the _______________ method, which requires a __________ degree head rotation from lateral and a ____________ cuadad CR angle.
Modified Laws, 15, 15
What specific positioning error has been committed if both sides of the mandible are largely superimposed with an axiolateral projections?
Not enough cephalic tube angle
A radiograph of a parietocanthial (Waters) projection reveals that the petrous ridges are projected within the maxillary sinuses. Is this an acceptable image? If not, what must be done to improve the image during the repeat exposure?
No. MML not Perp. Head needs to be ecxtended. PP should be below maxillary sinus.
A radiograph of a PA axial (Caldwell) projection for sinuses reveals that the petrous ridges are projected into the lower half of the orbits and over the ethmoid sinuses. The technologist used a horizontal beam for the projection. Also the skull was positioned to place the OML at a 15-degree angle from the horizontal plane. What positioning modification is needed to correct this problem during the repeat exposure?
PP need to be lower 1/3 of orbit. OML not Perp or 15-degree angle not correct.
A radiograph of parietoacanthial projection reveals that the petrous ridges are projected just below the maxillary sinuses. What positioning error (if any) is present?
None. Image passes
A radiograph of a submentovertex projection for sinuses reveals that the distance between the mandibular condyles and lateral border of the skull are not equal. What positioning error is present on this radiograph?
Tilt of head. MSP not Perp to IR
A radiograph of a submentovertex (SMV) projection of the sinuses reveals the mandible is superimposed over an aspect of the ethmoid and maxillary sinuses. What modification is needed to improve this image during the repeat exposure?
IOML not parallel to IR. Extend head more.
A lateral radiograph of the facial bones demonstrates that the gonions of the mandible are not superimposed; one is about 1cm superior to the other. How would this be corrected on a repeat exposure?
Make IP Perp to IR, MSP Parallel. Head was tilted
What must be done to prevent the ramus of the mandible from being superimposed over the cervical spine with an axiolateral projection of the mandible:
IOML needs to be parallel to IR. Extend chin.
Which skull line is placed perpendicular to the image receptor for a PA or PA axial projection of the mandible?
OML, Also MSP
Which projection best visualizes the condyloid processes and the temporomandibular fossae?
Modifies Towne's, AP Axial
What angles should be used for the above-mentioned projection?
OML-35 degrees caudal
IOML-42 degrees caudal
Where should the CR exit for the parietoacanthial projection?
Acanthion
Schueller's
Aniolateral
RT
Method:
Projection:
Side Vizualized:
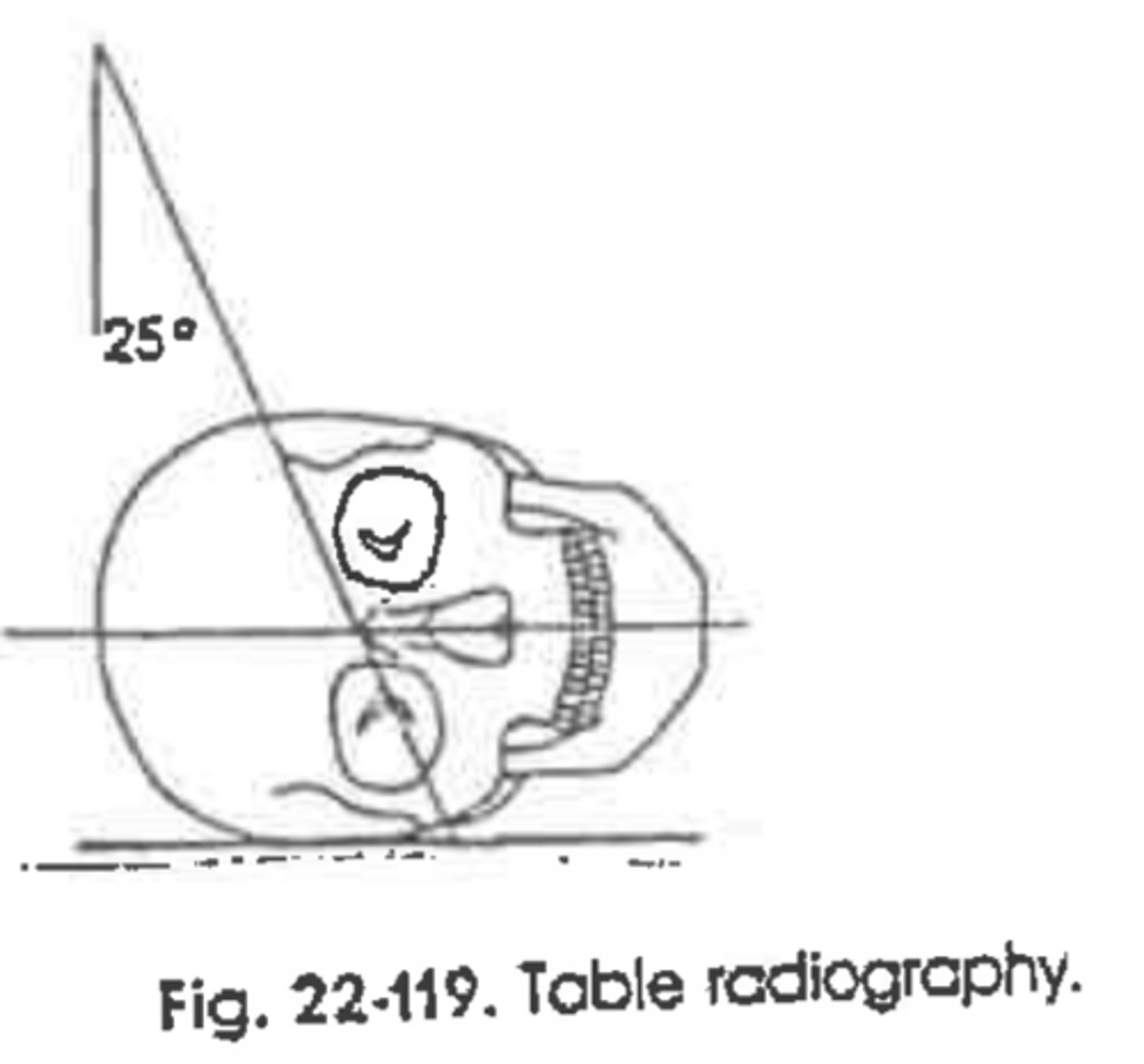
Modified Waters
Parietoacanthial
Method:
Projection:
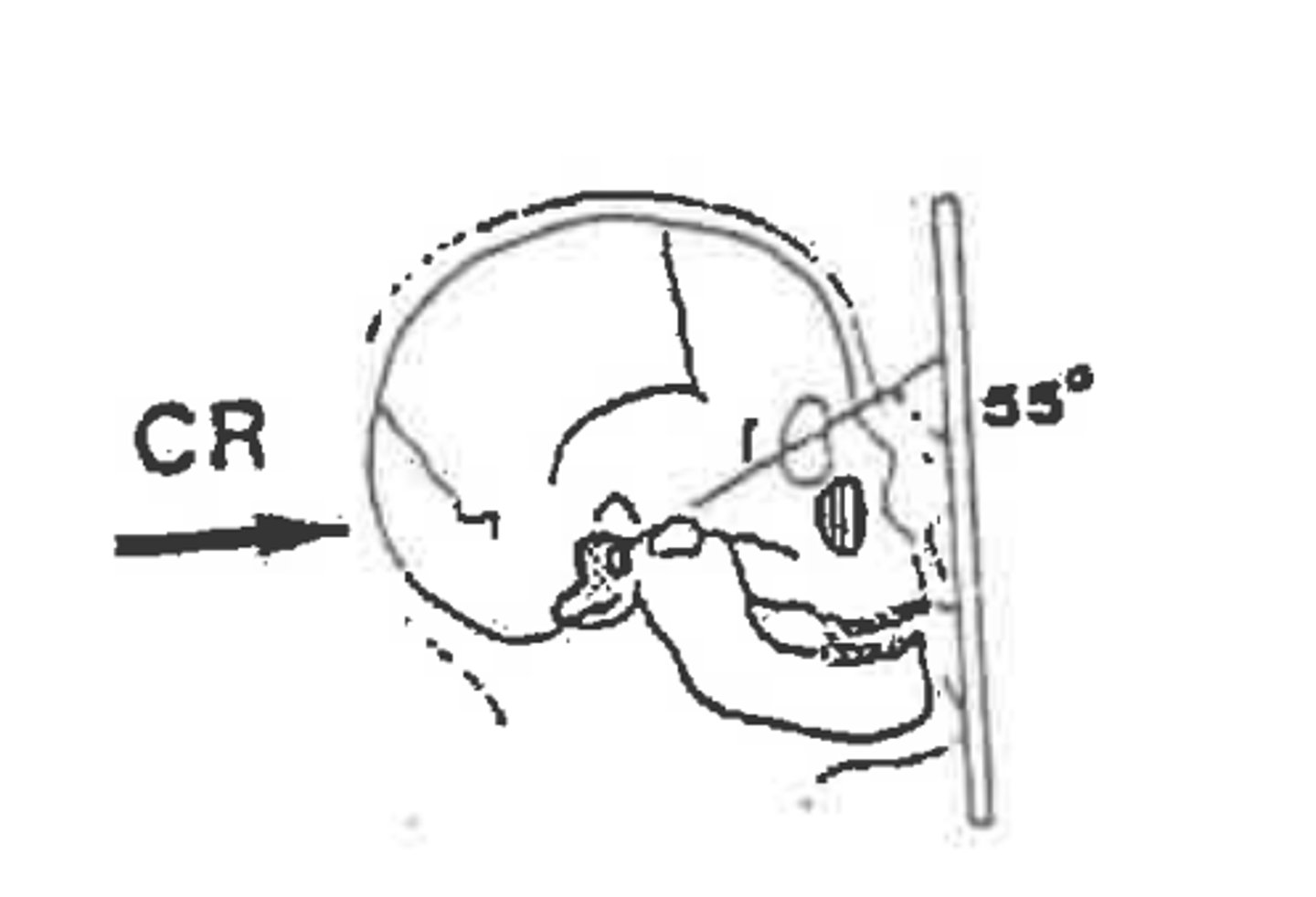
Waters
Parietoacanthial
Method:
Projection:
Modified Laws
Axiolateral Oblique
RT
Method:
Projection:
Side Visualized: