E2- pulmonology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
what is the cause of pyriform aperture stenosis?
bony overgrowth at the anterior bony opening of the nose
which condition has clinical features of respiratory distress that worsens with feeding and improves with crying, craniosynostosis, pituitary abnormalities and the 2 front teeth combine into one big one?
pyriform aperture stenosis
treatment for pyriform aperture stenosis?
nasal stenting
tracheostomy
what should you suspect ff a child has unilateral foul-smelling nasal discharge?
nasal foreign body
if a child has nasal polyps, what disease should you be thinking of?
CF
treatment for nasal polyps?
steroids
restriction of tongue movement caused by a prominent lingual frenulum that is more common in males, can exacerbate/cause mouth breathing and sleep issues
lingual ankyloglossia (tongue tie)
treatment for lingual ankyloglossia?
frenotomy
failure of thyroid tissue to descend into the neck (remains at the base of the tongue) causing airway obstruction
lingual thyroid
treatment for lingual thyroid?
surgery if severe
lifelong thyroid hormone replacement
what condition has clinical features of:
- inspiratory stridor
- hoarseness
- aphona
- feeding disorders
laryngeal lesions
if a child has expiratory stridor, what should you be thinking?
tracheal anomalies
what condition is caused by the collapse of the supraglottic structure during inspiration (omega shaped) causing clinical features of inspiratory stridor that is worse when crying/feeding/supine and progresses over week to months?
laryngomalacia
what is the MC congenital anomaly of the larynx?
laryngomalacia
treatment for laryngomalacia?
self limiting → resolves by 12-18 months
if severe → refer to ENT
narrowing of the cricoid lumen that is either congenital or acquired (from trauma) and has clinical features of recurrent croup and biphasic stridor
subglottic stenosis
diagnostic testing for subglottic stenosis?
direct visualization only for symptomatic pts
what condition causes complete upper airway obstruction, presents with asphyxia at birth and requires emergent tracheostomy?
laryngeal atresia
rare congenital anomaly resulting in incomplete separation of the vocal cords and presents in infancy with respiratory distress and an unusual cry
laryngeal webs → tx is surgery
how does tracheal atresia present?
respiratory distress and die soon after birth
complete or nearly complete rings of cartilage that presents with sternal retractions, dyspnea, stridor, monophonic wheeze that doesnt respond to bronchodilators
tracheal stenosis
what is the diagnostic test and treatment for tracheal stenosis?
dx → bronchoscopy
tx → surgery
what condition is caused by abnormal flaccidity of the trachea during breathing leading to abnormal collapse on expiration and has clinical features of expiratory stridor at birth?
tracheomalacia
treatment for tracheomalacia?
self resolves in 6-12 mos
CPAP
surgery
what condition is caused by weak cartilage in the walls of the bronchus on expiration and causes features of recurrent infections and in severe cases, respiratory distress?
bronchomalacia
what are the 2 types of bronchomalacia?
primary → congenital absence of cartilaginous rings
secondary → extrinsic compression from enlarged vessel or cyst
a developmental anomaly of the lower respiratory tract characterized by hyperinflation of one or more of the pulmonary lobes (MC L upper lobe) that causes progressive respiratory distress of tachypnea, cyanosis and wheezing
congenital lobar emphysema
what is the diagnostic test for congenital lobar emphysema?
CXR → distention of affected lobe + mediastinal shift, compression and atelectasis of non-affected lung
treatment for congenital lobar emphysema?
lobectomy
uncommon condition characterized by incomplete development of the lungs that leads to respiratory distress, hypoxia, hypercarbia and sometimes neonatal death
pulmonary hypoplasia
what is a risk factor for pulmonary hypoplasia?
premature rupture of membranes and premature delivery
treatment for pulmonary hypoplasia?
extracorporeal membrane oxygen or mechanical vent until adequate lung growth
abnormal fistula between pulmonary arteries and veins that creates a pathologic intrapulmonary R→L shunt and impairs gas exchange
pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
which condition has clinical features of:
- dyspnea
- hemoptysis
- exercise intolerance
- associated with hemorrhagic hereditary telangiectasia (aka Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome)
pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
treatment for pulmonary arteriovenous fistula?
ablation by angiography or surgery
an uncommon anomaly characterized by non-functioning mass of lung tissue that lacks normal communication with the tracheobronchial tree and receives its arterial blood supply from the systemic circulation
bronchopulmonary sequestration
what are the 2 types of bronchopulmonary sequestration?
interlobar → contained w/in the normal lung parenchyma (MC)
- tx is lobectomy
extralobar → separate from normal lung parenchyma & visceral pleural, has its own pleural covering
- diagnosed in utero
- tx is resection
what condition is characterized by excessive curvature of the thoracic spine with several lateral curvature causing rib distortion?
kyphoscoliosis
what are clinical features of kyphoscoliosis > 50 degrees?
restrictive changes on PFTs → hypoventilation
what are clinical features of kyphoscoliosis > 90 degrees?
cardiopulmonary compromise
treatment for pectus excavatum/carinatum?
surgery (cosmetic)
what condition does the bowel herniate through the diaphragm into the chest, causing arrest of lung development (pulm hypoplasia)?
congenital diaphragmatic hernia → posterolateral defect MC
what condition is common in the fall/winter months and daycare/school and is caused by viruses rhinovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus or coxsackie virus?
upper respiratory infection → fever, rhinorrhea, cough, congestion peaking at 2-7 days
what are complications of upper respiratory infections?
AOM
sinusitis
asthma exacerbation
PNA
are antihistamines recommended for treating upper respiratory infections?
NO! they cause ↓ in ciliary motility and ↓ mucus clearance
what condition is caused by inflammation of the tracheobronchial tree and results in features of rhinorrhea, cough (dry to productive), malaise and rhonchi on auscultation?
acute bronchitis → self-limiting, associated w recent viral URI
what is seen on labs (CBC, PFT and CXR) of acute bronchitis?
CBC → WBC normal or viral shift
PFT → airway obstruction
CXR → increased pulm markings
treatment for acute bronchitis?
symptomatic → saline sprays, nasal suctioning
frequent position changes in young infants
persistent cough lasting > 4 wks caused by asthma, CF, bronchectasis, foreign body aspiration, or cigarette smoke exposure
chronic bronchitis
viral infection that affects the lower respiratory tract (bronchioles) most commonly caused by RSV and seen in < 18 mos of age
acute bronchiolitis
what condition has features of:
- fever
- respiratory distress → tachypnea, retractions, nasal flaring, cyanosis
- auscultation → wheezing, crackles
- breathing pattern shall w rapid respirations
acute bronchiolitis
what are risk factors for acute bronchiolitis?
- gestational age < 36 wks
- age of infant in distress < 12 wks
- chronic pulmonary disease
- congenital anatomical defect
- CHD
- immunodeficiency
what is seen on CXR of acute bronchiolitis?
hyperinflation of the lungs
↑ AP diameter on lateral view
areas of consolidation → atelectasis 2* to obstruction/inflam
if a pt is diagnosed with acute bronchiolitis, what other diagnoses should you be thinking of?
asthma
CF
CHF
pertussis
foreign body
treatment for acute bronchiolitis?
saline sprays & nasal suctioning
albuterol in office
admit to hospital if in distress
what is the discharge criteria for acute bronchiolitis?
pt stable on room air w adequate oral intake
< 6 mos → < 60 breaths per min
6-11 mos → <55 breaths per min
> 12 mos → < 45 breaths per min
what is the prevention for acute bronchiolitis?
Synagis vaccine
MCC of PNA in children < 5?
viral → RSV
bacterial → S. pneumo, S. aureus, S. pyogenes
MCC of PNA in children > 5?
S. pneumo (MC)
mycoplasma pneumo
C. pneumo
if a pt has PNA and has a WBC > 15-20K, what should you be thinking?
bacterial cause
for those < 2 y/o, what should you suspect if:
- fever + cough
- resp distress → tachypnea, subcostal retractions, cough, crackles, ↓ breath sounds
PNA
what type of PNA:
- rhinorrhea, nasal congestion
- low grade fever
- nonproductive cough
- tachypnea with wheezing or crackles
- CXR → perihilar & parenchymal infiltrates
viral PNA (caused by RSV)
treatment for viral PNA?
supportive
rehydration
what is the tx for this PNA:
- MCC of "typical" PNA
- abrupt infection w fever, cough, tachypnea, malaise and emesis
- ↓ breath sounds, localized crackles
S. pneumo PNA → tx w amoxicillin
what is the tx for this PNA:
- PNA usually after rash disease
- complications are abscess and empyema
S. pyogenes PNA → PCN
what is the tx for this PNA:
- pts have recent URI (influenza)
- fever, cough, tachypnea
- CXR → pneumotoceles
- complications of pneumotoceles, PTX, abscess and empyema
S. aureus PNA → naficillin or vanco
what is the tx for this type of PNA:
- common in children > 5 y/o
- fever, malaise, HA
- sore throat, nonproductive cough
- extrapulmonary manifestations → splenomegaly, bullous myringitis, pharyngitis, confusion
mycoplasma PNA → azithro (alt tetracycline)
what is the tx for this type of PNA:
- seen in children > 5 y/
- presents WITHOUT a fever
- sore throat 2-3 wks before onset of PNA
Chlamydophila PNA → azithro
true or false:
neonates are at higher risk for TB meningitis, pleural TB and pericardial TB
true
what type of TB are < 10 y/o at risk of?
clinically silent or latent TB → +CXR but - sxs
what condition has features of:
- chronic, unremitting cough > 3 wks
- fever > 100.4 for > 2 wks
- weight loss
TB
what is the screening criteria for TB?
recently immigrated → 8-12 wks after immigration & repeat in 6 mos
no risk factors = no screening
how many negative TB screenings does a recently immigrated individual need to be considered "negative" for TB?
2
what are the diagnostic tests for TB?
tuberculin skin test (TST) aka PPD
IGRA (quantiferon TB gold)
CXR → isolated hilar/mediastinal LAD
what are the measurements of induration during a PPD test to be considered positive for TB?
15 mm for individuals w/o risk
10 mm for members of high-incidence population
5 mm for HIV+ & the immunosuppressed individuals
treatment for TB? (we should know this by now)
6 mos regimen = RIPE x 2 months then RI x 4 months
or
4 mos regimen = RIPE x 2 months then RI x 2 months (for non-severe pulm TB in ages 3m-15y)
a highly contagious acute respiratory illness transmitted via respiratory droplets that occurs in 3 phases:
- catarrhal
- paroxysmal
- convalescent
pertussis (whooping cough)
what occurs during each phase of pertussis?
catarrhal → sneezing, coryza, night cough, injected conjunctiva
paroxysmal → paroxysmal cough followed by high-pitched whoop
convalescent → ↓ in frequency & severity of cough
how is pertussis diagnosed?
bacterial culture, PCR and serology
if a pt < 4 months old has a cough that is not improving, rhinorrhea, vomiting, cyanosis, poor weight gain and labs show leukocytosis with lymphocytosis, what should you be thinking?
pertussis
if a pt > 4 months old has a paroxysmal nonproductive cough > 7 days, rhinorrhea that remains watery, posttussive vomiting and sweating between paroxysms, what should you be thinking?
pertussis
what is the treatment and prevention of pertussis?
tx → macrolides (alt = bactrim only if > 2 mos old)
prevention → DTaP in infancy + booster Tdap at age 13
what are cautions of using macrolides and bactrim for treatment of pertussis?
macrolides ↑ risk of infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
bactrim îs not indicated younger than 2 mos d/t SE of kernicterus
when do you hospitalize a pt with pertussis?
< 4 months old
CBC → WBC > 30K
abnormal dilation associated w chronic lung infections and inflammation MCC is obstruction of airway & poor drainage from CF
bronchiectasis
what condition has features:
- persistent, productive/wet cough that is worse w exercise or changes in position
- dyspnea on exertion
- moist crackles/rales and rhonchi
- digital clubbing
- hemoptysis
bronchiectasis
what diagnostic tests should be done for bronchiectasis?
CXR → ↑ bronchovascular markings, atelectasis
- CT is more sensitive
sweat chloride test
PFT → obstructive pattern
treatment for bronchiectasis?
chest physiotherapy → clear airway
inhaled mucolytics (hypertonic saline)
flu/PNA vaccine
ABX for acute exacerbations
what condition is this:
- inherited disease of exocrine gland caused by mutation of chromosome 7 (CFTR gene)
- delayed meconium (aka meconium ileus)
- abnormal thick, viscous secretions that can lead to PNA or pancreatic obstruction
- abnormally high Na in sweat → salty tasting skin
- excessive appetite but poor weight gain
- nasal polyps
- greasy/bulky stools
- clubbing of nails
cystic fibrosis (CF) → >60 on sweat chloride test is positive
treatment for CF?
chest physiotherapy → vigorous clapping on chest & back to dislodge phlegm
inhaled hypertonic saline
CFTR modulator therapy (> 6 y/o)
what condition is this:
- nocturnal cough, cough that recurs seasonally or in response to specific exposures
- wheezing
asthma
- if cough is > 3 wks you should suspect asthma!
what is the severity of asthma:
- sxs < 2x/wk
- nighttime sxs < 2x/month
- < 2 days/wk use of inhaled SABA
- no interference w normal activity
- FEV1 > 80%
intermittent
what is the severity of asthma:
- sxs > 2x/wk but not daily
- nighttime sxs 3-4x/month
- > 2 days/wk use of SABA
- minor limitation of normal activty
- FEV1 > 80%
- exacerbation > 2x/yr
mild persistent
what is the severity of asthma:
- sxs daily
- nighttime sxs > 1x/wk but not daily
- daily use of SABA
- some limitation of normal activity
- FEV1 60-80%
- exacerbation > 2x/yr
moderate persistent
what is the severity of asthma:
- daily sxs
- nighttime sxs every night of the wk
- several times a day use of SABA
- extremely limited normal activity
- FEV1 < 60%
severe persistent
review of short acting relief vs long acting control names
short acting relief:
- albuterol, Xopenex, ipratropium, systemic steroids
long acting control:
- inhaled steroids (Advair), salmeterol, theophylline, montelukast
who is long term asthma therapy recommended in?
- > 3 episodes of wheezing in 12 month period
- lasting more than 1 day
- affects sleep
- risk factors → parent hx of asthma, atopic triad
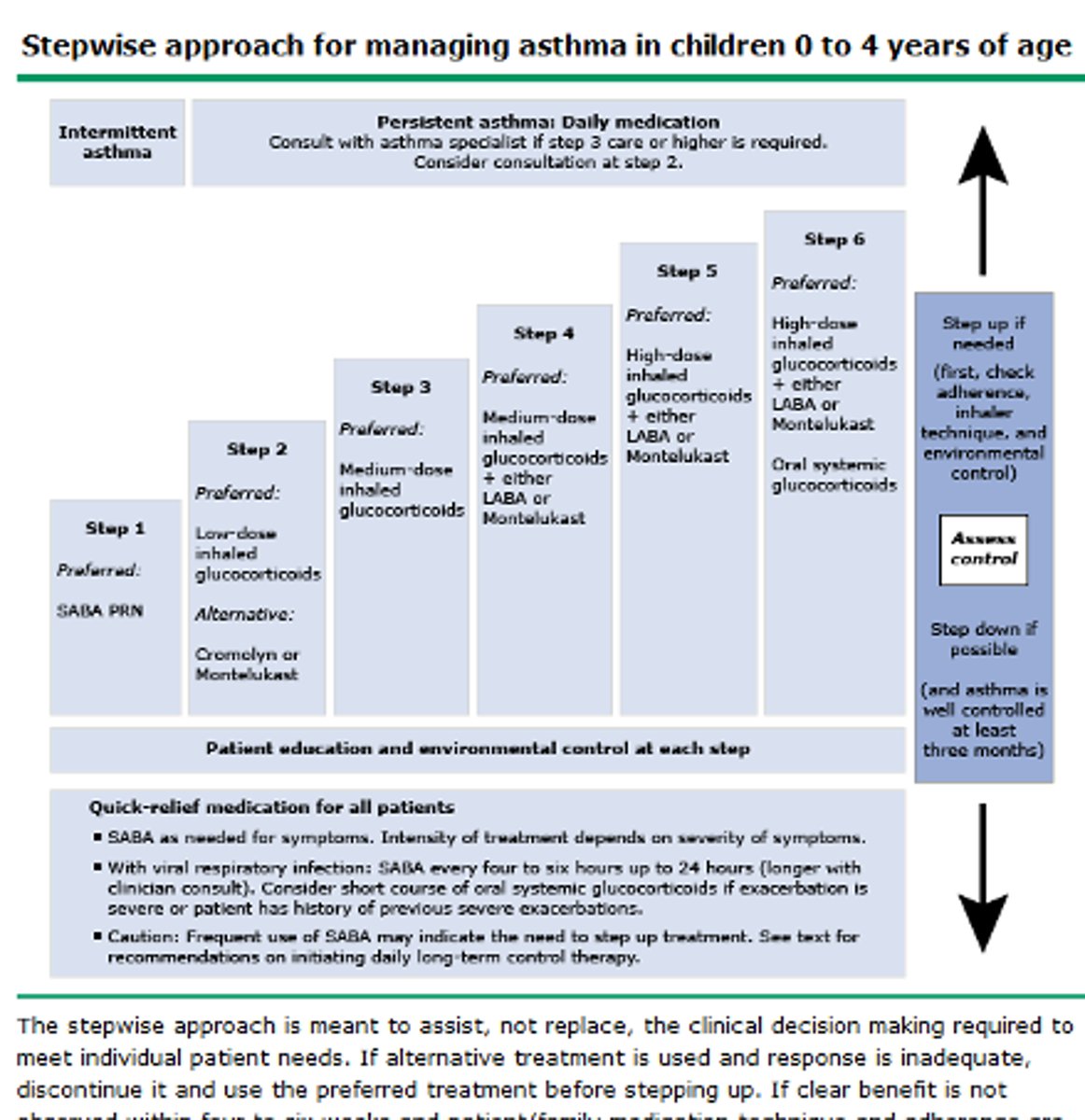
review asthma treatment step ladder for 0-4 y/o
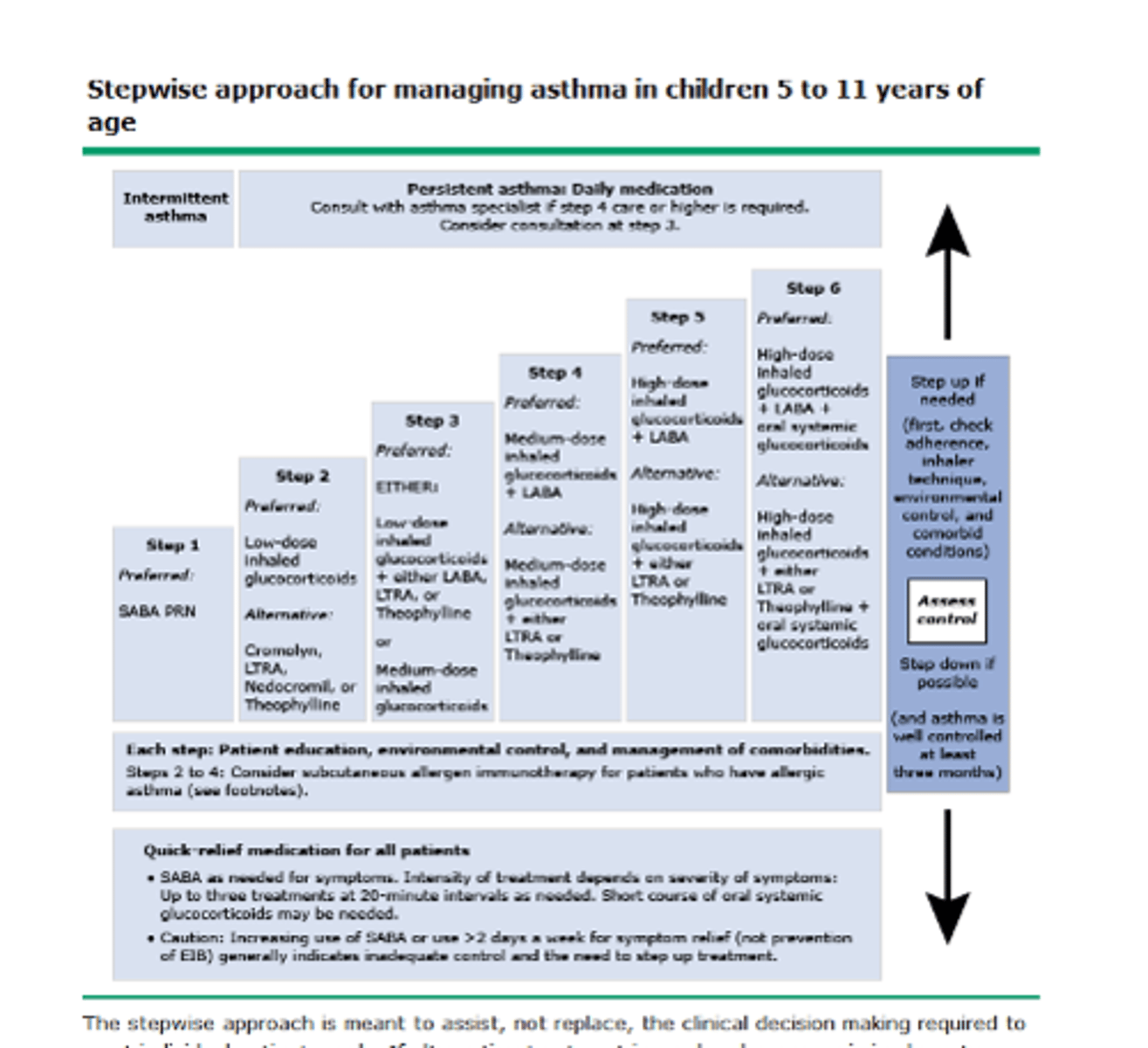
review asthma treatment step ladder for 5-11 y/o
what condition is described:
- fever/chills, hematuria, telangiectasia, clubbing
- MCC is infection, foreign body and bronchiectasis
hemoptysis