SBI3U Unit 1
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
facultative anaerobe
grows with or without oxygen
archaea
not pathogenic
methanogens
archaea that live in digestive tract of many animals where they produce methane
extremophiles
lovers/tolerates extremes.
thermophile
heat lover
halophile
salt lover
acidophile
acid lover
bacteria
second oldest life forms
very adaptable—found in all of earth's ecosystems.
most abundant life form
shapes
cocci, bacilli, spirillium
form aggregations
diplo-, strepto-, staphylo-
diplo-
pairs
strepto-
chains
staphylo-
clusters
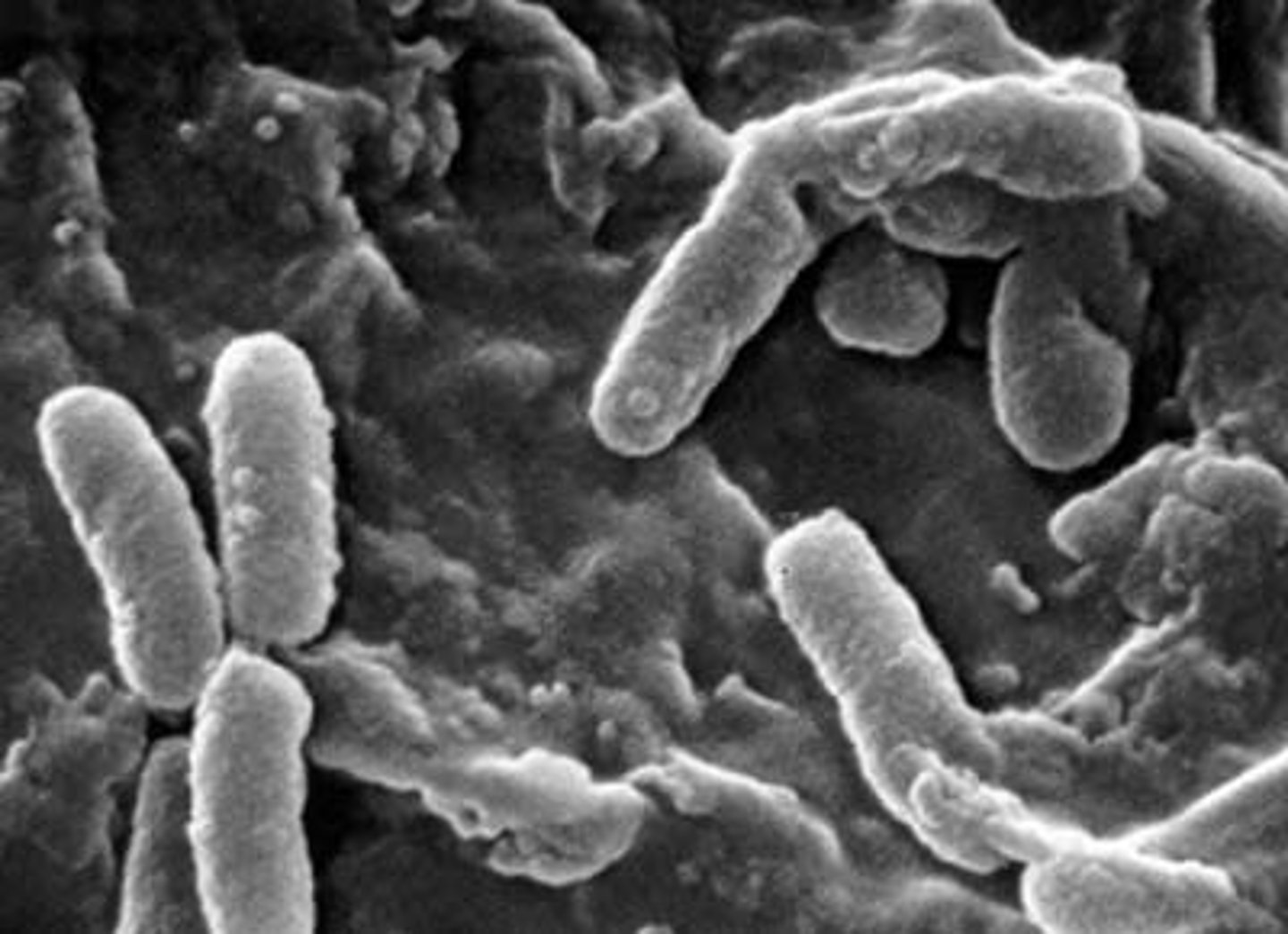
cocci
spherical
spirillium
spiral
bacillus
rod shaped
autotroph
self feeding
photosynthesis
cyanobacteria
cyanobacteria
photosynthesize
may have been responsible for adding oxygen to early earth, changing atmosphere and direction of evolution
powers food chain.
chemosynthesis
food from chemicals.
chemosynthesis details
like photosynthesis, instead powered by chemicals.
used deep underground where there is no sunlight.
methane and sulfides which burst through earth's crust through hydrothermal vents are used by chemo-synthesizing bacteria.
organisms either eat the bacteria or provide a home for them and use their energy.
heterotroph
eat other things
decompose other organisms
cell wall
made up of peptidoglycan (achilles heel): combination of protein and polysaccharides (sugar)
give them strength and rigidity
gram stain test
bacteria are stained with a dye called crystal violet
gram positive bacteria
purple--thicker cell wall: peptidoglycan retains stain, no extra membrane.
cons of gram stain test
acid-fast and gram-variable bacteria do not respond to gram staining.
acid-fast bacteria
have a cell wall which retains stain well.
gram-variable bacteria
appear pink and purple.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT FOR DOCTORS TO KNOW WHAT TYPE OF GRAM BACTERIA YOU ARE INFECTED WITH?
help them know what type of infection you have
what antibiotics to treat it with
pili
tiny hair-like structures found in bacteria
helps bacteria stick to surfaces and form conjugation bridges
membrane
inhibits the uptake of antibiotics
helps stabilize inner membrane (less need for cell wall)
chromosome
a single loop of DNA that is folded on itself
controls cell's function
genophore
Nucleoid
not an actual nucleus!!!!!!!!
just the region where dna is found
Plasmid
small loop of DNA outside nucleoid
responsible for: conjugation, antibiotic resistance
capsule
found outside some bacteria
protects bacteria from external environmental conditions and stores nutrients.
layer of polysaccharide
outer membrane
protects cell wall in Gram negative bacteria
cell membrane
controls flow of nutrients between cell and environment
ribosomes
do protein synthesis
flagellum
rotate by means of a "motor" in cell envelope.
allow for motility
sensory purposes
storage granule
stores nutrients
binary fission
asexual reproduction
parent cell —> two identical daughter cells
reproduction, cell lacks a nucleus
occurs quickly under ideal conditions ~20 minutes
mitosis
growth in multicellular organisms, cell has a nucleus.
binary fission stages
1. cell grows, bacteria copies its chromosome
2. cell elongates, chromosomes separate, septum begins to form
3. septum complete and cells divide
conjugation
one cell links to another by a pilus (pilli) and transfers a copy of all or some of its chromosomes
not sexual reproduction
results in new genetic combinations
why is conjugation bad
bacteria with a genetic resistance to antibiotics can pass its DNA to another bacteria
bacteria: role in ecosystem
decomposers, nitrogen fixation, producers
CHNOPS
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur
bacteria as decomposers
recycle nutrients back to environment from dead organisms
no decomposers = elements would have remained in dead organisms and life would have ceased
nitrogen fixation
bacterial enzymes allow them to convert nitrogen from air into a useable form
bacteria as producers
form basis of food chain
Symbiotic bacteria
help host organisms
guts of herbivores: aiding digestion of cellulose
guts of humans: aid digestion and produce vitamins
Pathogenic bacteria
organisms that cause disease caused by toxins released by bacteria
commensal relationship
live in us but don't harm us
streptococcus (some)
mutualistic relationship
live in us and help us
parasitic relationship
live off of our nutrients
Antibiotics
chemicals that kill bacteria or prevent reproduction (infection)
revolutionized how we treat diseases (in a good and bad way)
we need to control the use of existing antibiotics, create new ones, combat bacterial resistance
antibiotics cons
overuse + misuse of antibiotics = more resistant bacteria
antibiotics overuse/misuse examples
antibiotics being used to attack viruses (doesn't work because viruses have a protein coat)
use of antibiotics in agriculture: helps livestock grow faster
why its important to finish antibiotics?
so they are all killed and don't start multiplying again.
Similarities of archaea and bacteria
use conjugation for adaptation, similar shapes and form aggregations, asexual/binary fission
Differences of Archaea and Bacteria
important genetic differences and makeup of RNA
bacteria: peptidoglycan in their cell walls, create endospores,
archaea: unique enzymes allow archaea to live under extreme conditions, resistant to antibiotics because they lack peptidoglycan
obligate aerobe
grows with oxygen
obligate anaerobe
killed by oxygen
aerotolerant anaerobe
don't care about oxygen (don't need it for growth)
bacteria eyes?
no, but they have receptors on their cell surface which can detect changes in their environment.
staph
pimples, pneumonia
found on skin, nose, mouth
GOOD E. coli
digest food + make vitamins
BAD E. coli
in raw meat causes food poisoning
ingested anthrax
infected, undercooked meat.
inhaled anthrax
dried spores are inhaled, most dangerous form, must be treated early.
endosymbiosis
explains how eukaryotic cells evolved from symbiotic relationships between two or more prokaryotic cells.
cell organelles
aerobic bacteria —> mitochondria, cyanobacteria —> chloroplasts
endosymbiosis stages
1.start with two independent bacteria
2.one engulfs the other
3.one survives and lives inside the other now
4.internal bacteria are passed on from generation to generation
both bacteria benefit
endosymbionts benefit by getting safe home and nutrients
host cells benefit by getting some energy released by endosymbionts
evidence
mitochondria and chloroplasts: have separate circular DNA similar to prokaryote DNA, reproduce through binary fission
Eyepiece or ocular lens
First lens which you look through: 10x
Body Tube
Keeps the two sets of lenses the correct distance apart.
Revolving Nose Piece
Allows user to change objectives. Hold lenses.
Objective Lens
Increases magnification.
Low objective lens
4x
Medium objective lens
10x
High objective lens
40x
Stage
Where slide is placed.
Diaphragm
controls amount of light that hits slide.
Condenser Lens
focuses light hitting the slide.
Light
Provides a light source.
Fine Adjustment Knob
Sharpens the image. Slowly moves the stage.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Moves the stage quickly.
Stage Clips
Holds the slide in place.
Arm
Supports the body tube.
Base
Supports the microscope from the bottom.
microscope rules
Keep stage dry
Return to 4x objective.
Higher resolution = Fine adjustment knob.
Resolution
Measure of clarity.
classification
grouping organisms based on shared characteristics
organize and indicate evolutionary relationships.
biological species concept
If two organisms can mate naturally and produce fertile offspring, they are the same species.
biological species concept pros and cons
PROS
Simple, widely used
CONS
Can't apply to asexual and extinct organisms
biological species concept example
Donkey + Horse = Mule. Mule can't reproduce. therefore, donkeys and horses are different species.
morphological species concept
characterizes a species by body shape and other structural features
morphological species concept pros
Simple
Applied to asexual and extinct organisms
morphological species concept cons
Subjective: deciding how much variation is acceptable in a species.
Many organisms have similar characteristics.