Math Finals Year 9
1/104
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
○
greater than/less than
●
greater than/less than or equal to
What happens when we multiply or divide both sides of an inequality by a negative number?
The inequality symbol is reversed
What happens if we swap the sides of an inequality?
The inequality symbol is reversed too
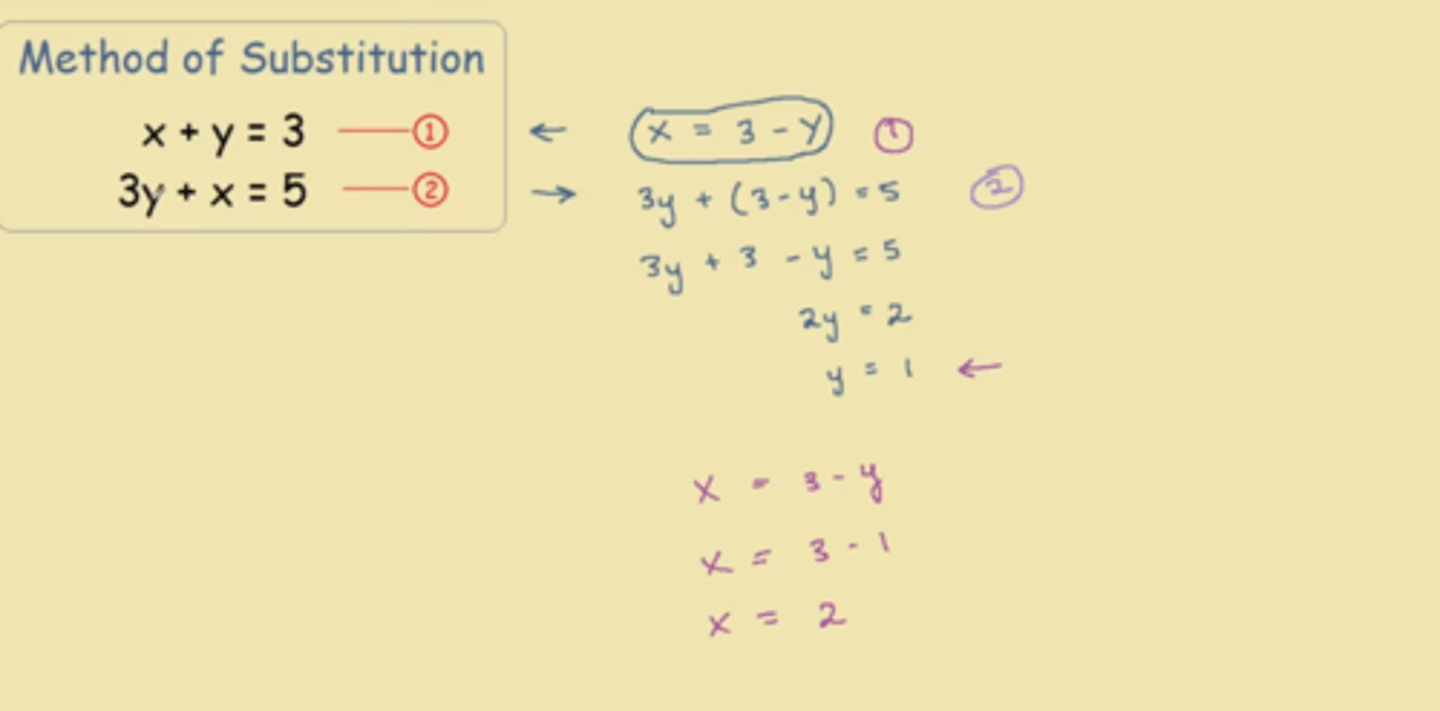
Substitution
Substitution can be used to solve simultaneous equations. It is used when at least one of the equations has a single variable as the subject. For example, y is the subject in the equation y = 3x + 1

Solving a simultaneous equation using substitution
1 Substitute one equation into the other, using brackets.
2 Solve for the remaining variable.
3 Substitute to find the value of the second variable.
Elimination method
when you add or subtract two equations to eliminate one of the variables, sometimes, this could require you to multiply or divide to create a matching pair
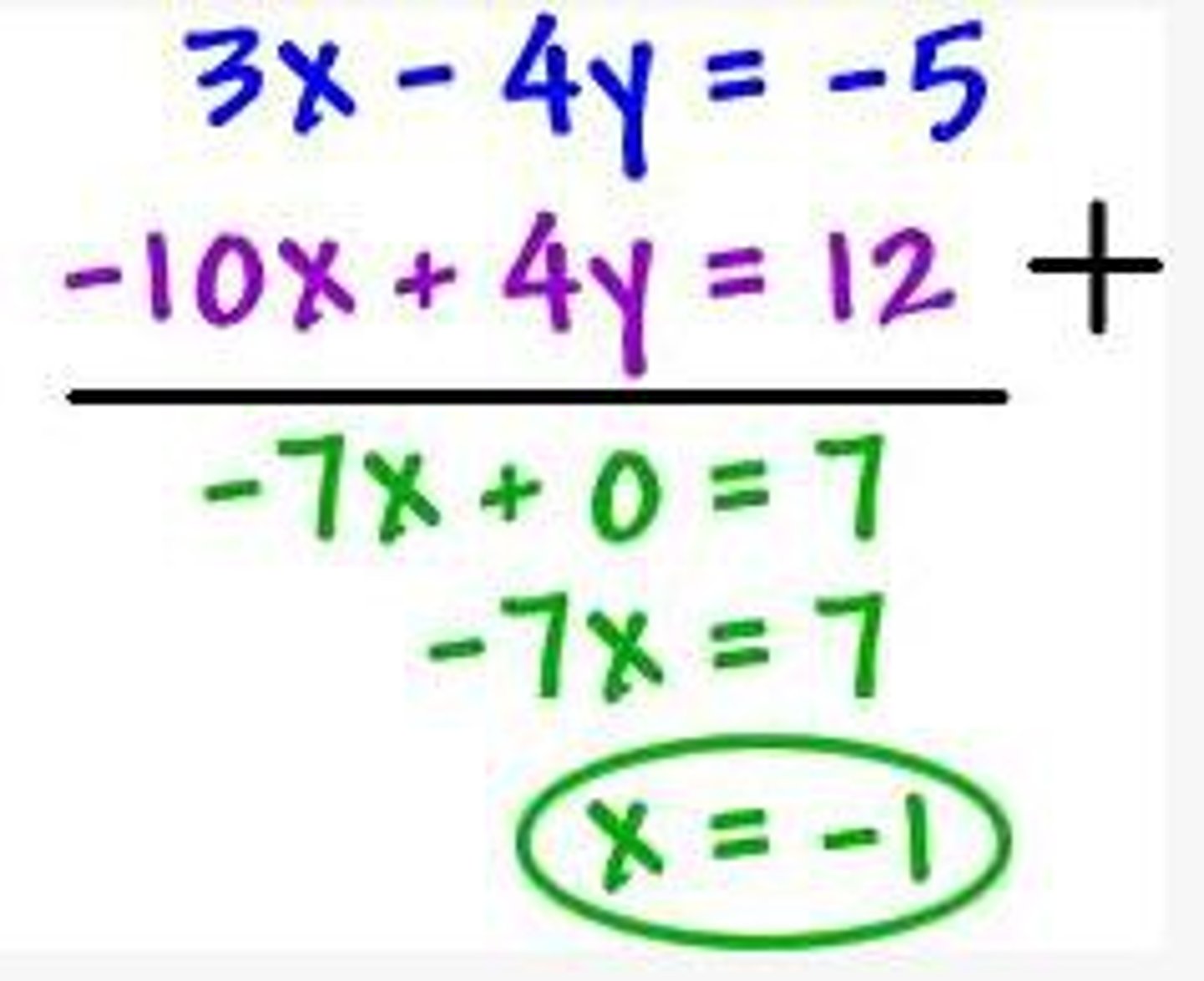
Add equations to...
Eliminate opposite signs
Subtract equations to...
Eliminate opposite signs
y=mx+c
y= y point
m= gradient
x= x point
c= y intercept
How to graph a straight line.
Two points are required to sketch a straight
line graph. Often these points are the axes
intercepts.
Gradient Formula
y2-y1/x2-x1
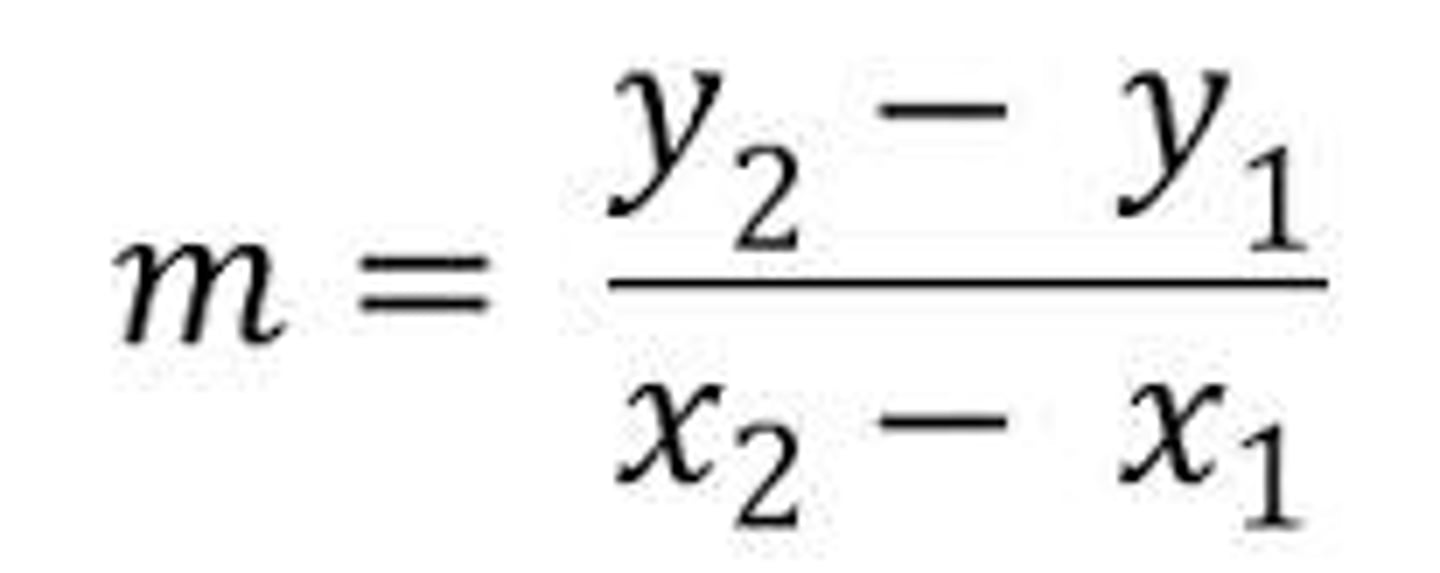
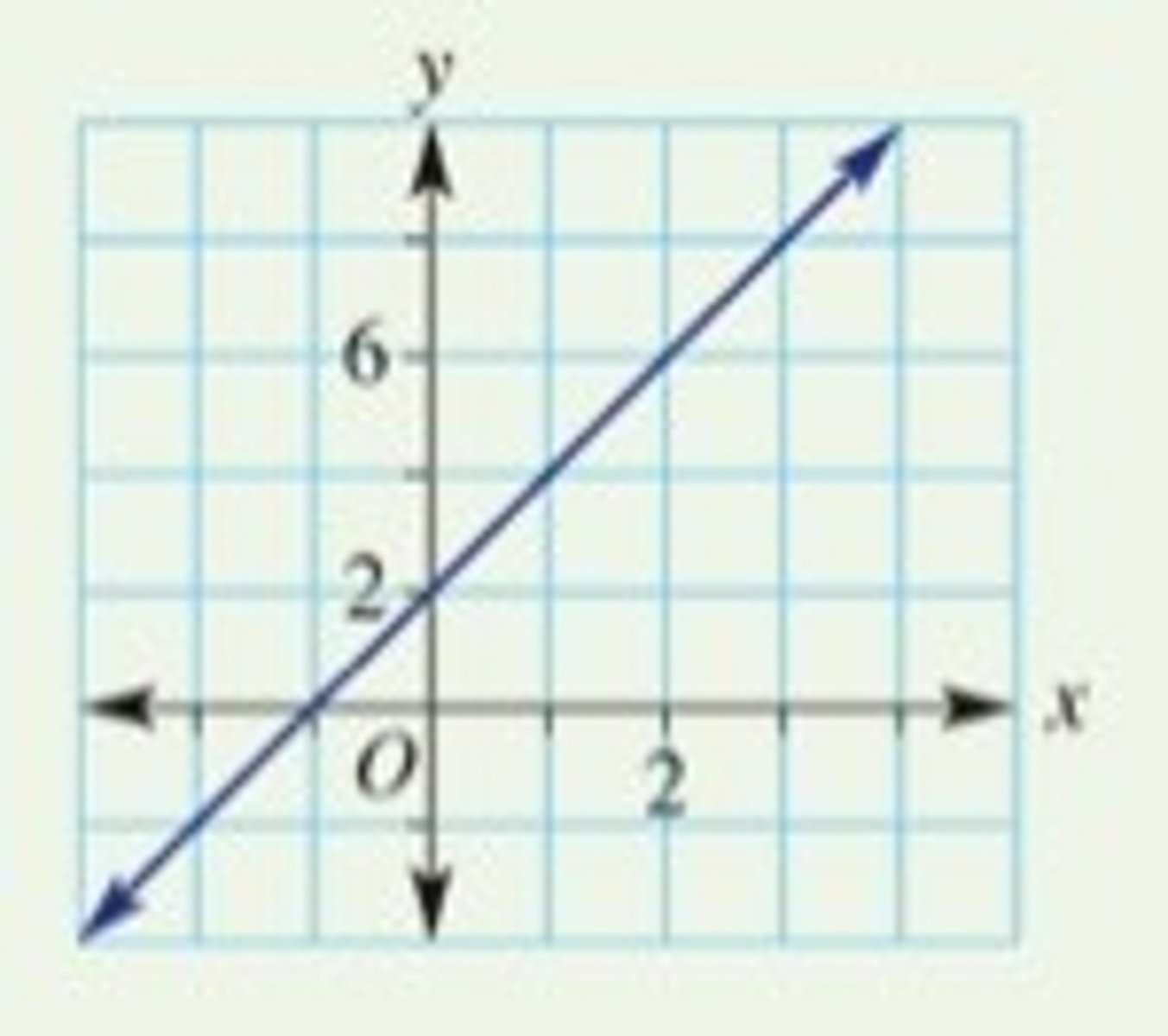
Positive Gradient
a line that goes up from left to right
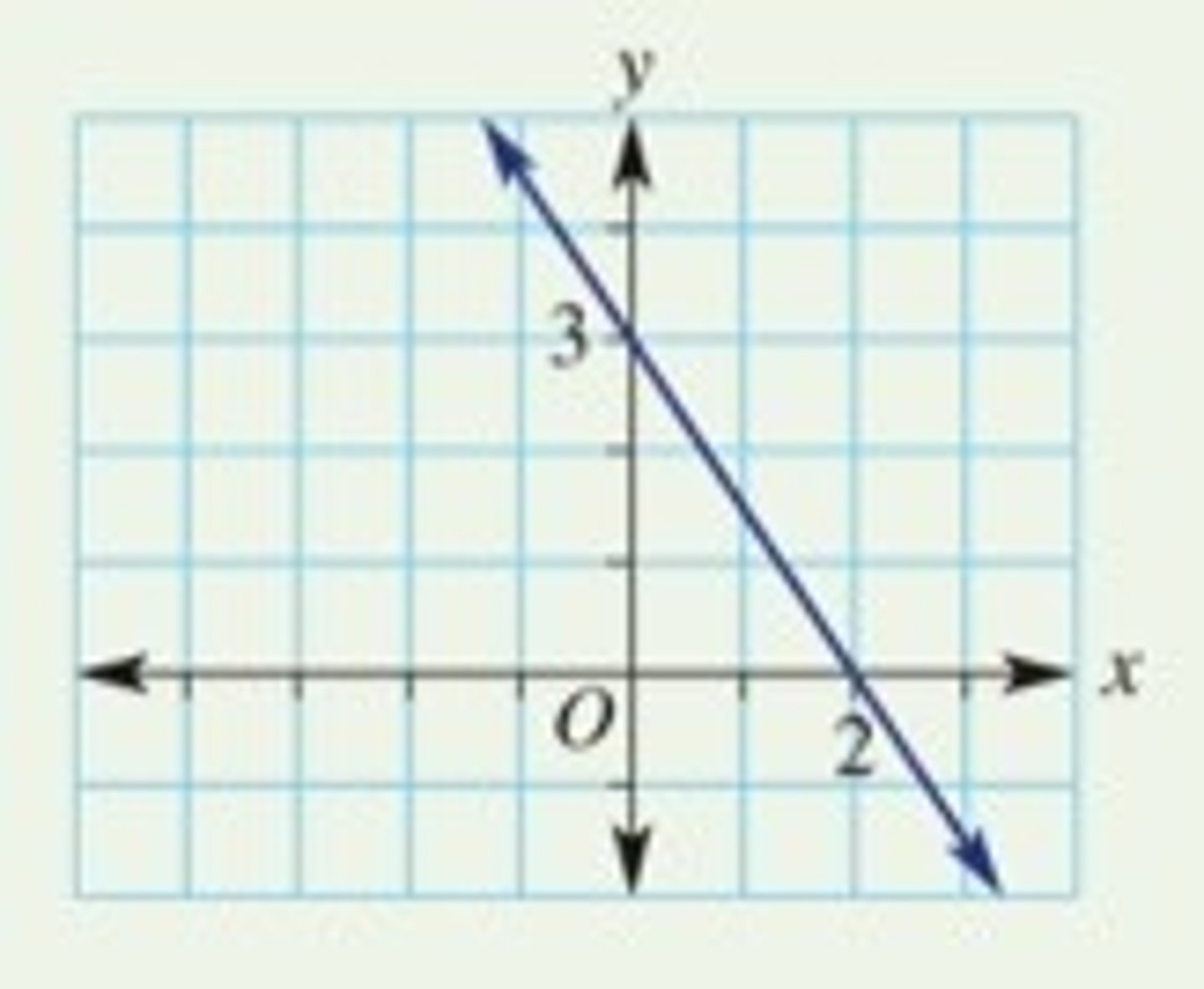
Negative Gradient
a line that goes down from left to right
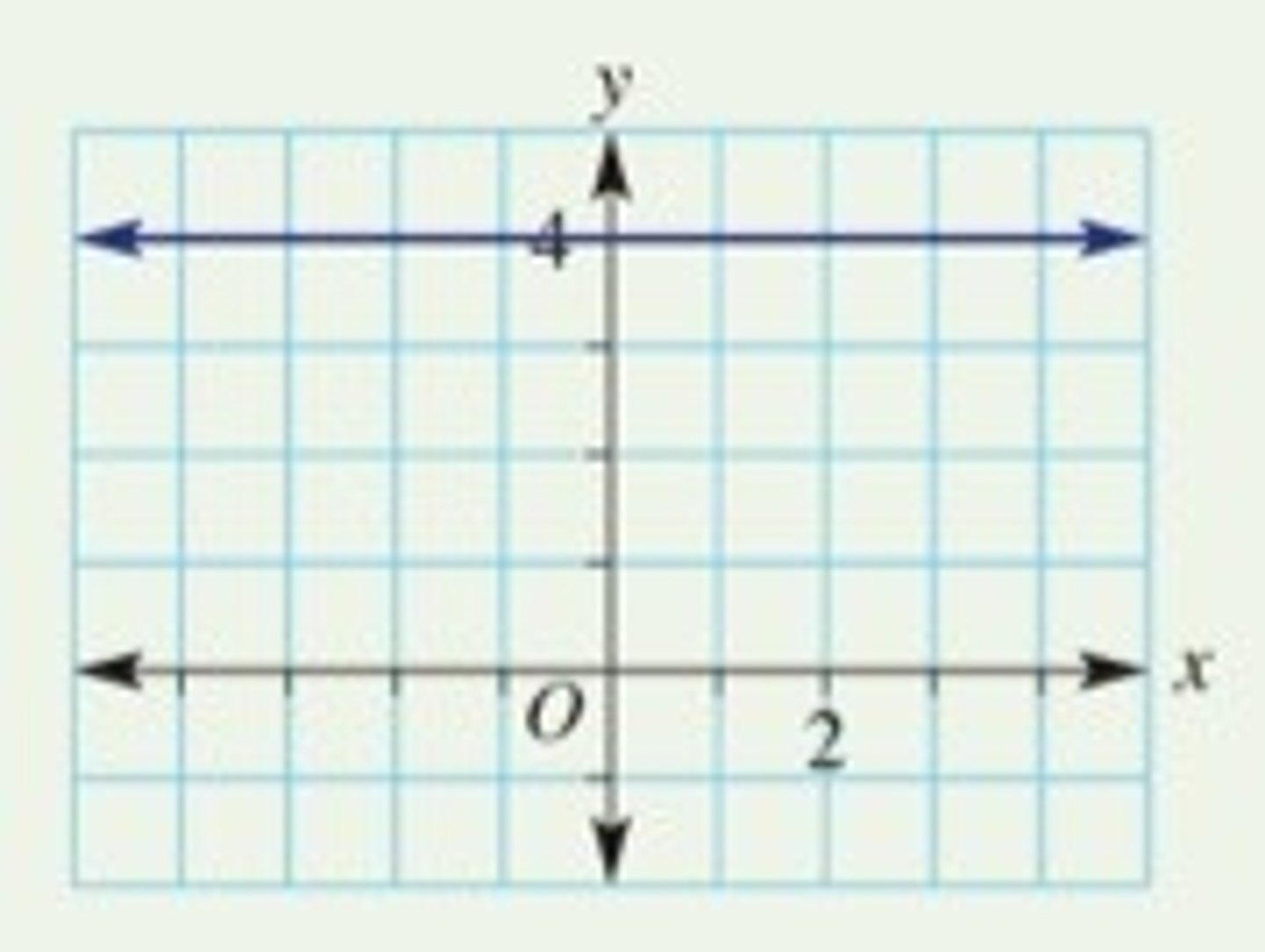
Zero Gradient
horizontal line
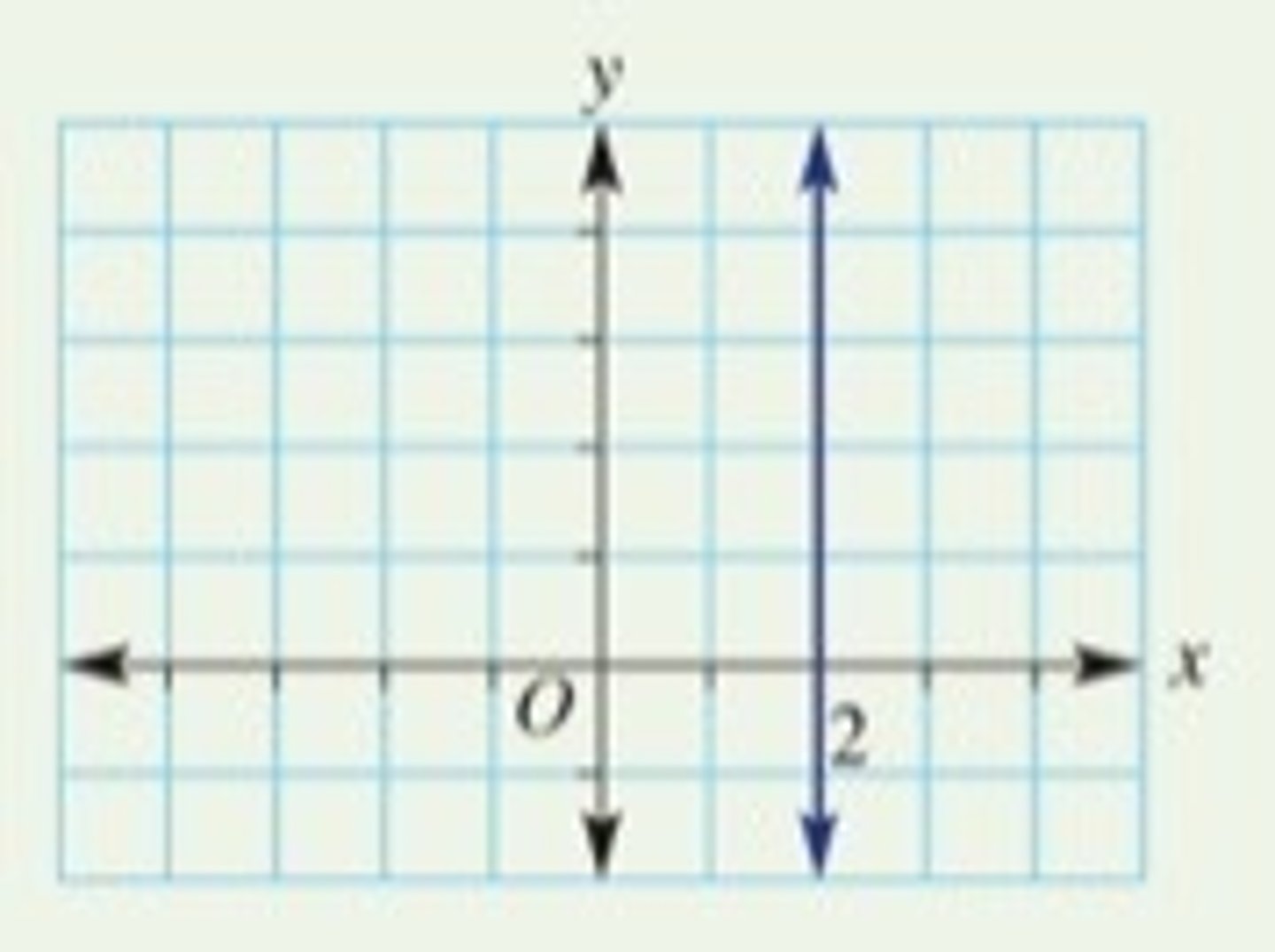
Undefined Gradient
a line that goes vertical
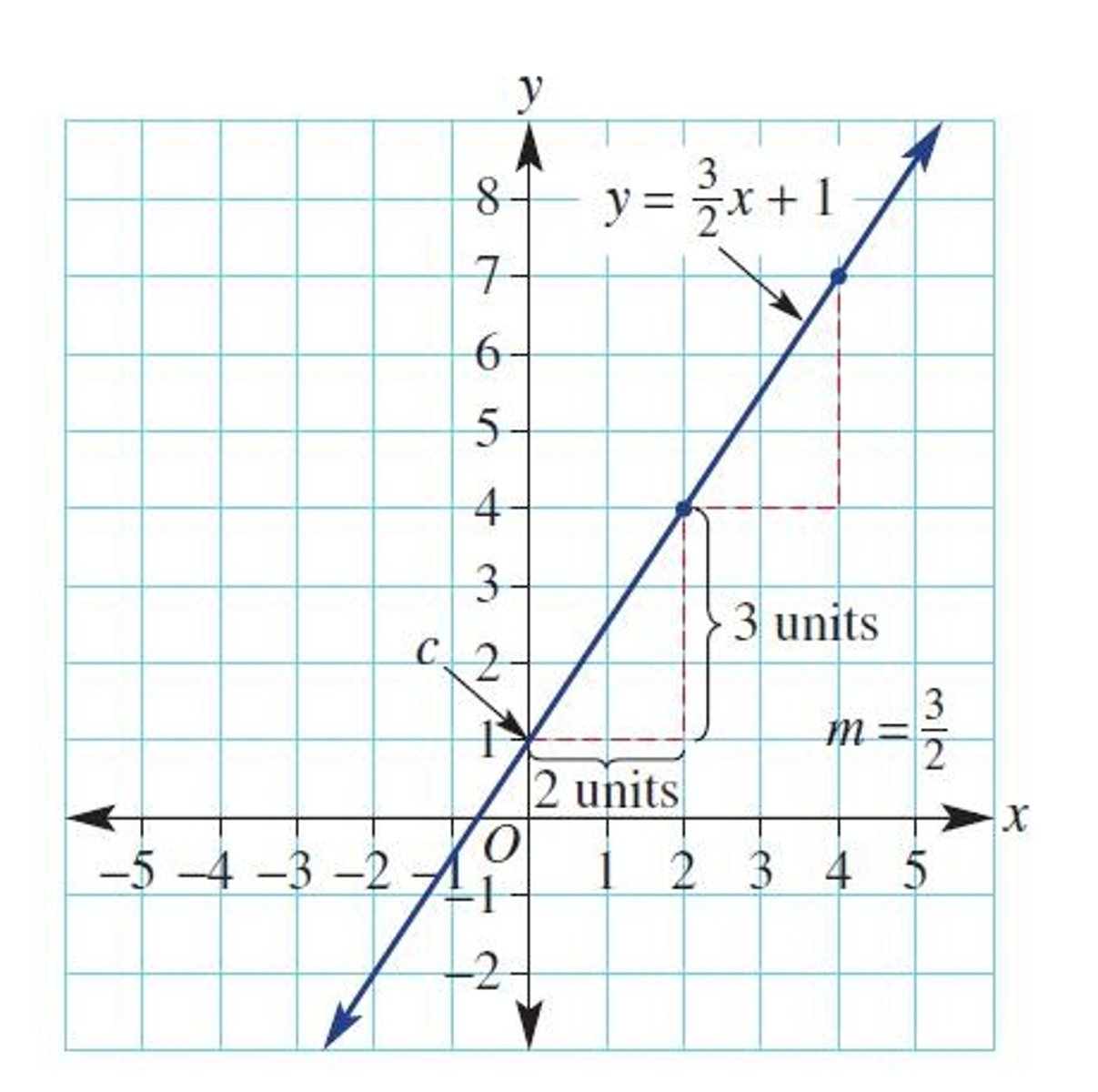
Gradient Intercept Form
To sketch a graph using the gradient-intercept method, locate
the y -intercept and use the gradient to find a second point.
Distance of a line segment formula
d = √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²
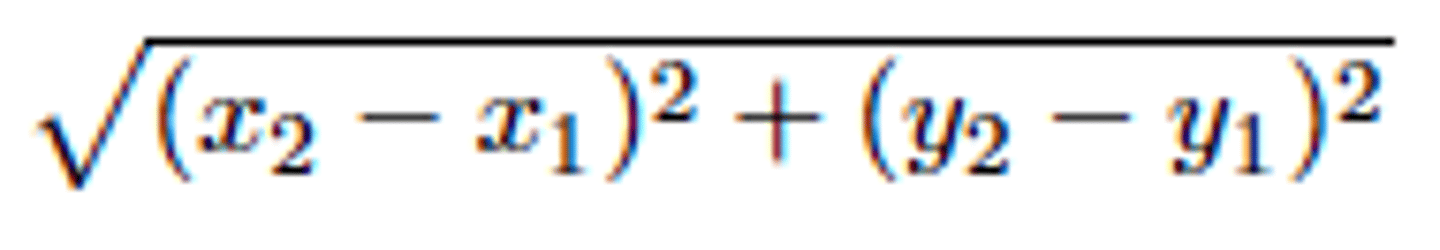
Complement
a probability of something not happening
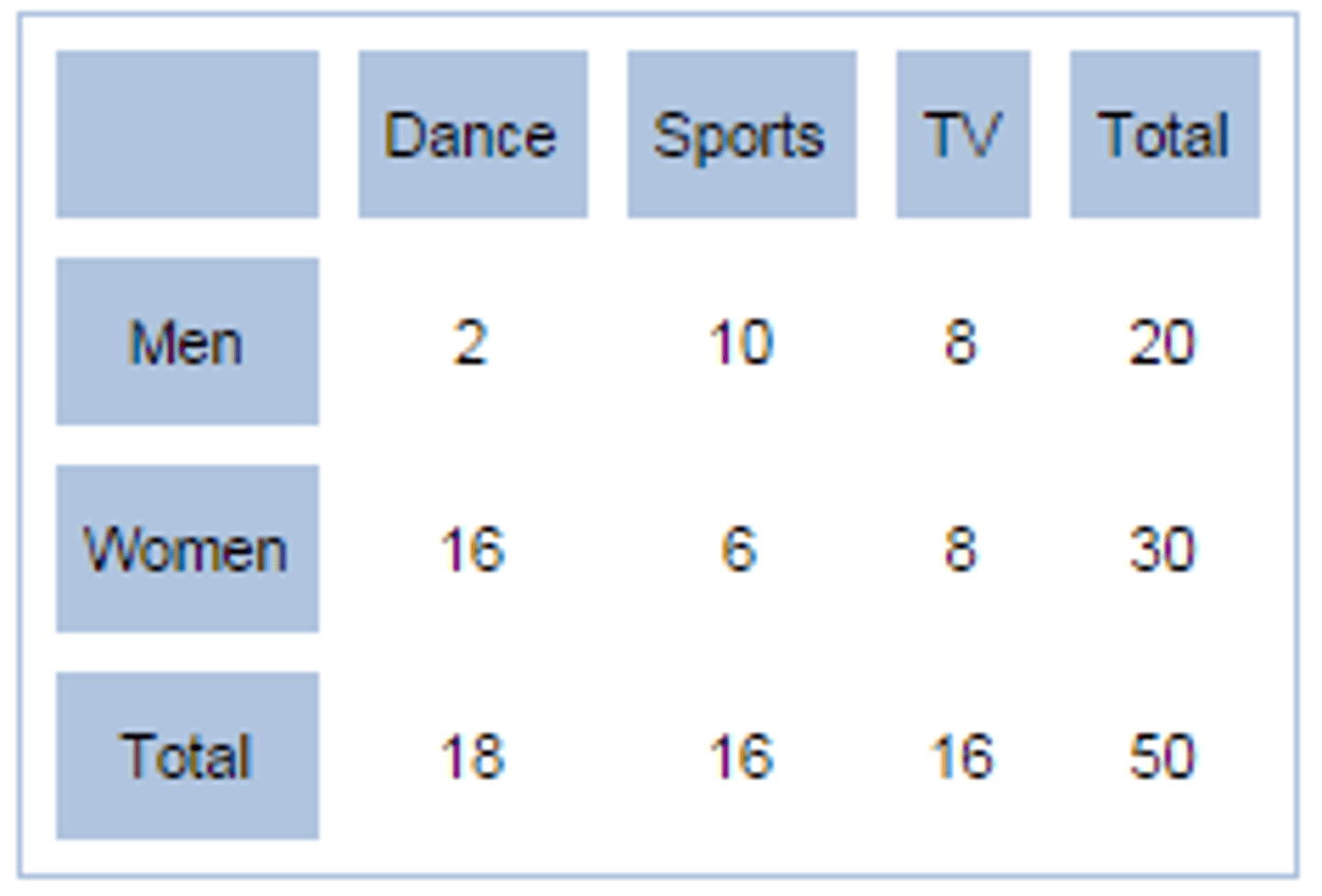
Two way tables
Describes two categorical values according to a row variable and a column variable.
Ω
Sample space
⊂
Subset. A particular part of a sample space
∈
an element of a set
∅
Empty set
n(A)
cardinal number
∪
Union, either A or B
∩
intersection - middle
A
only elements of A
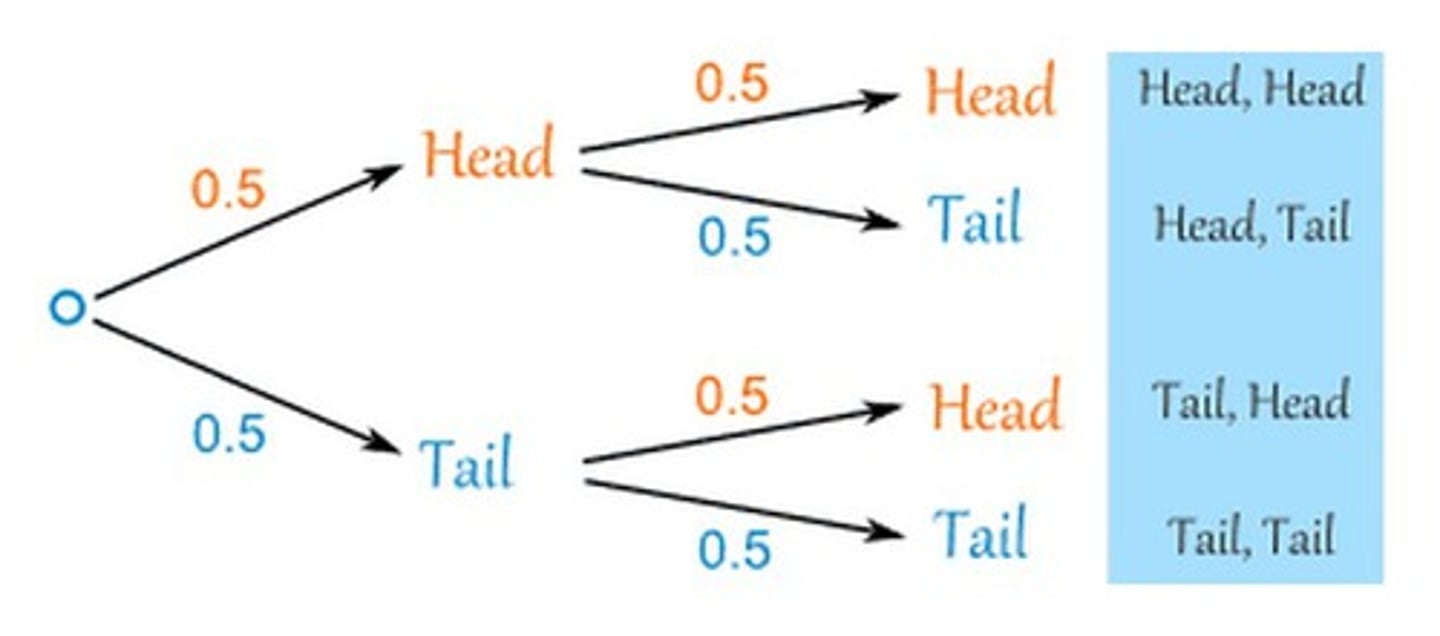
Tree diagrams
A diagram that is shaped like a tree and is used to show the outcomes of a situation or experiment.
Relative Frequency/Experimental Probability
number of outcomes/total trials
Long-run proportion
The experimental probability for a sufficiently large number of trials
Expected number of occurance
probability x number of trials
Mode
the most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
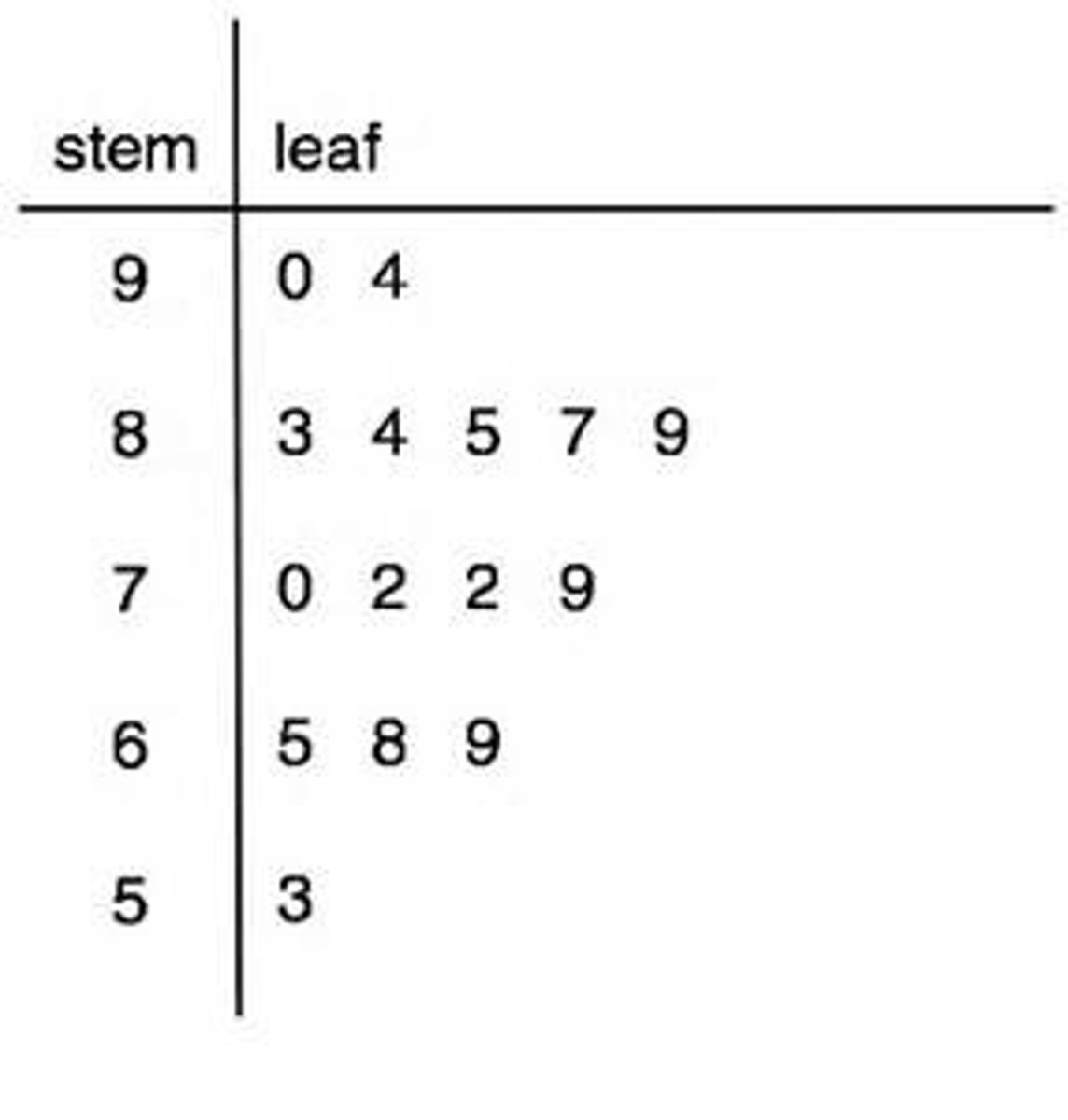
Stem and leaf plots
best suited for small sets of data and are especially useful for comparing 2 sets of data
Rule for finding the median
N+1/2
Skewed
not straight, crooked, slanting
Symmetrical
Well proportioned; balanced; the same on both sides
Categorical Nominal
No order required in a category eg. colours
Categorical Ordinal
Categories have a logical order eg. high, medium, low
Numerical DIscrete
data with a limited amount of numbers eg. children in a family
Numerical Continuous
Data can take any value in a given range eg. time taken to complete a race
How much is a quartile?
25%
What is a quartile?
A division of the total into four intervals, each one representing one-fourth of the total.
What does the second quartile represent?
Median
Simple random sampling
every member of the population has an equal probability of being selected for the sample
Systematic Sampling
Every nth item in the target population is selected, regular intervals.
Stratified Sampling
a variation of random sampling; the population is divided into subgroups and surveyed in that group
Histogram
a bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
Bar chart
a chart with bars whose lengths are proportional to quantities
a^n
1/a^n
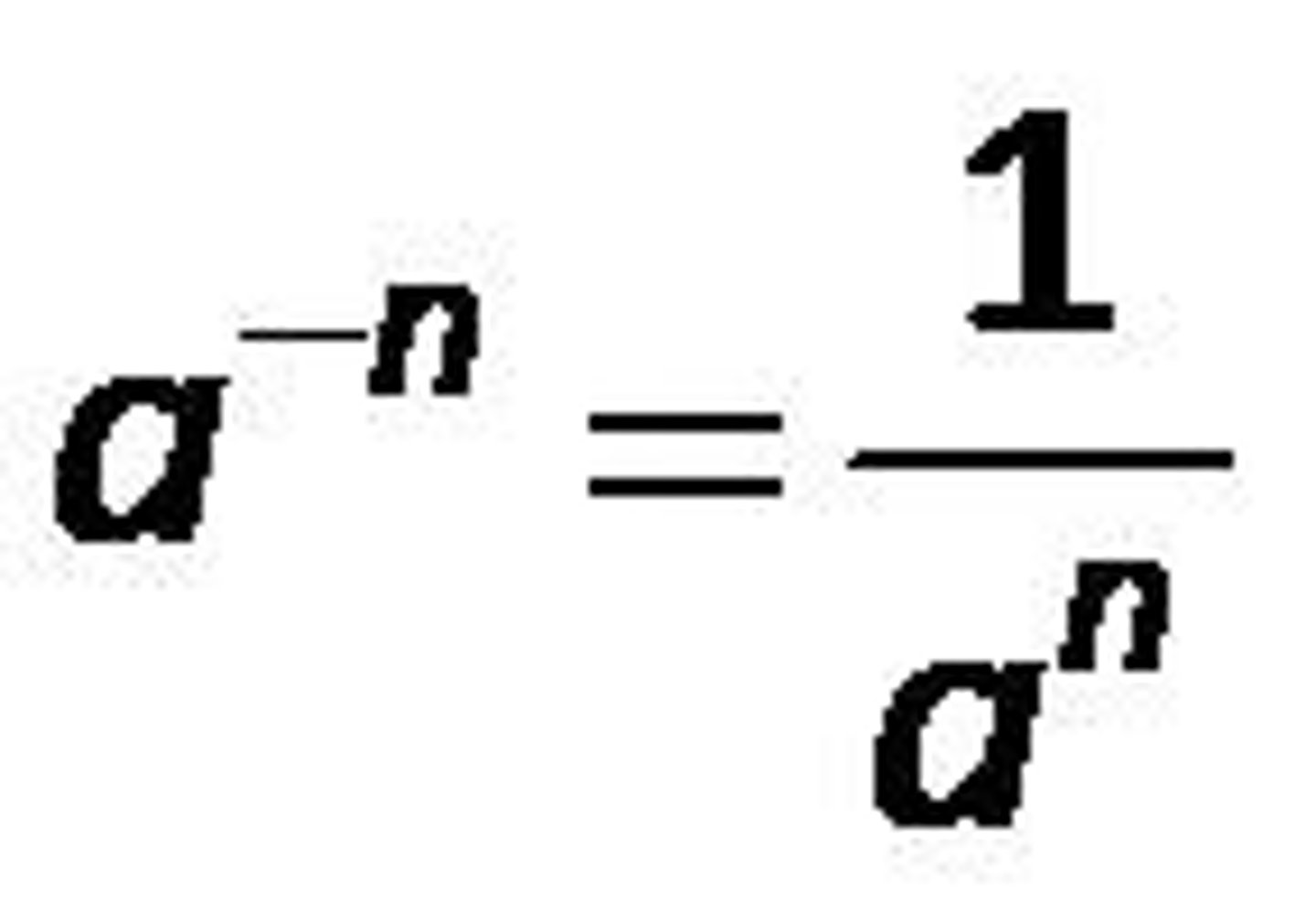
1/a^n
a^n
x^a/b
b√x^a
x^-a/b
1/x^a/b
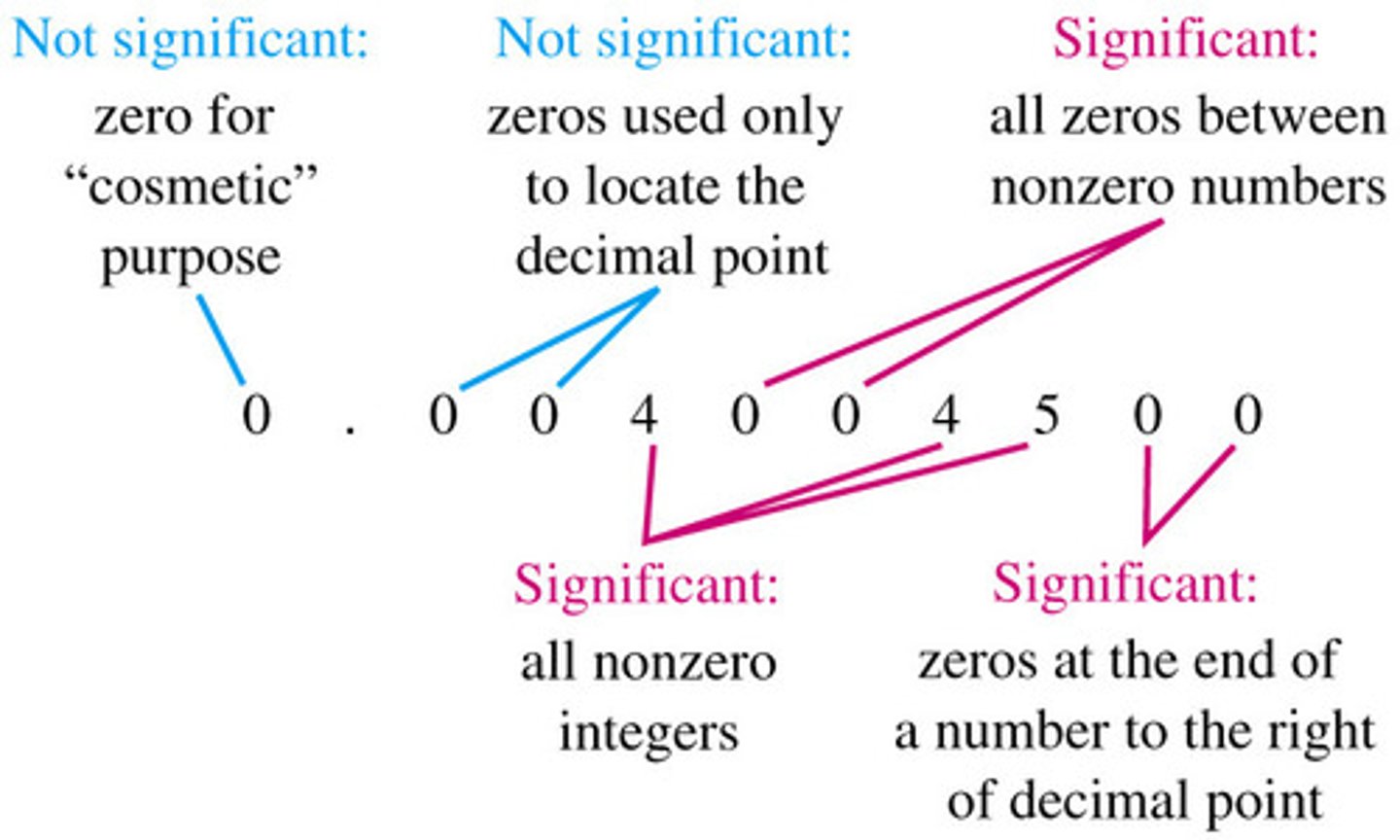
Significant numbers
any number that is not a 0, sandwiched 0s, trailing 0s when there is a decimal place; NOT trailing 0s without a decimal place and leading 0s.
Scientific notation
A method of writing or displaying numbers in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10.
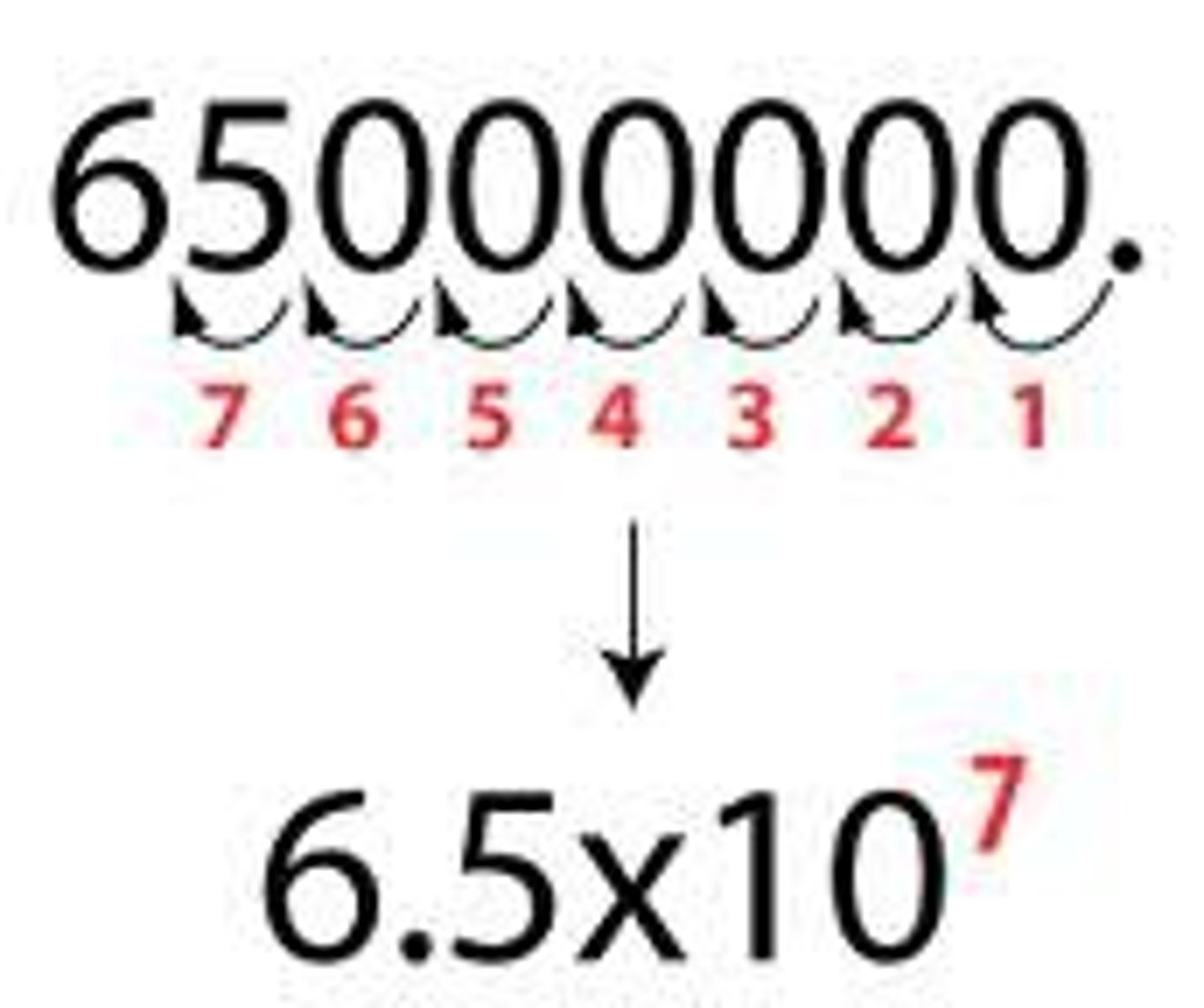
Negative scientific notation
A method of writing or displaying numbers in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10 with negative indice.
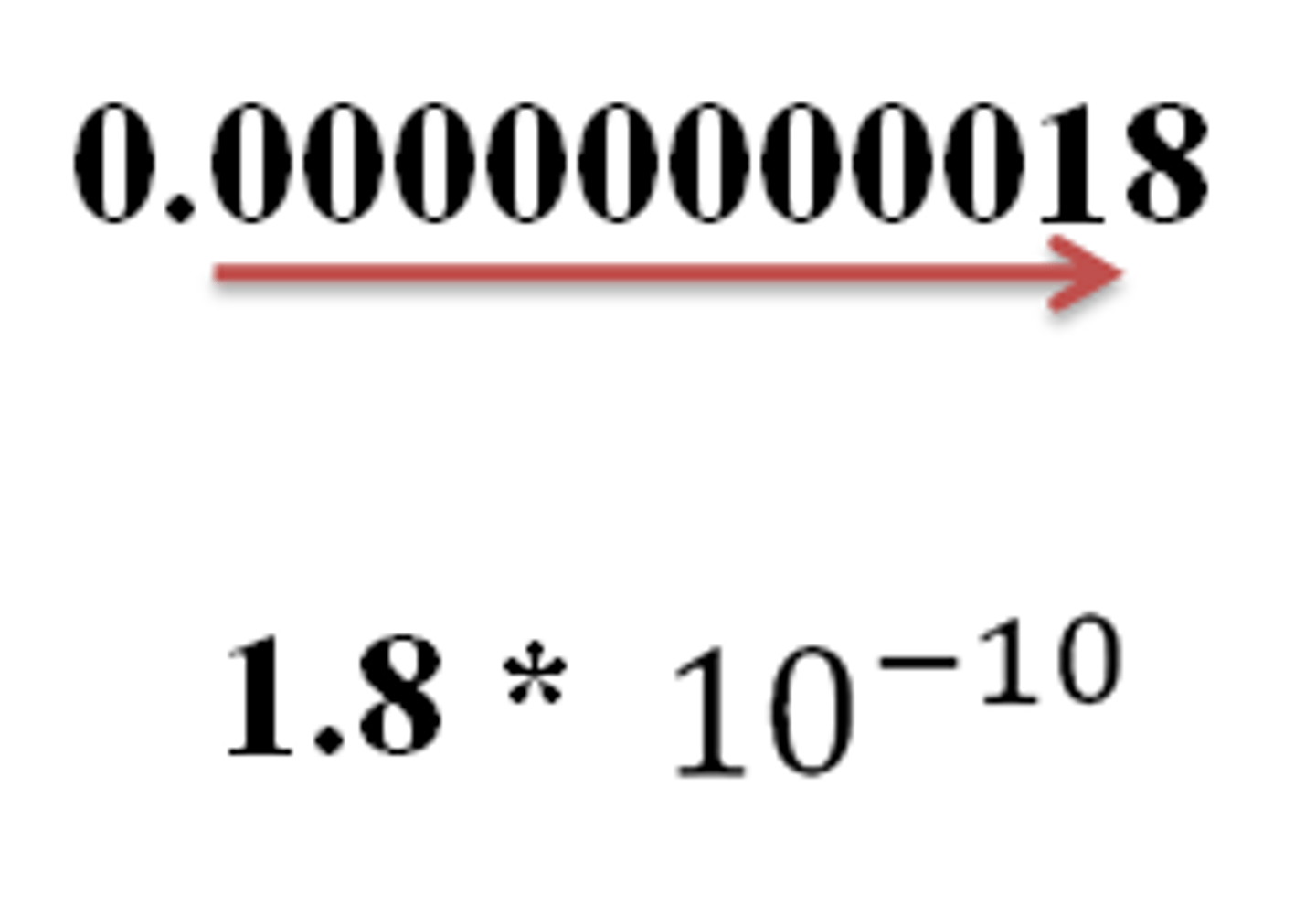
How to simplify surds
Find the common square number and pull that out.
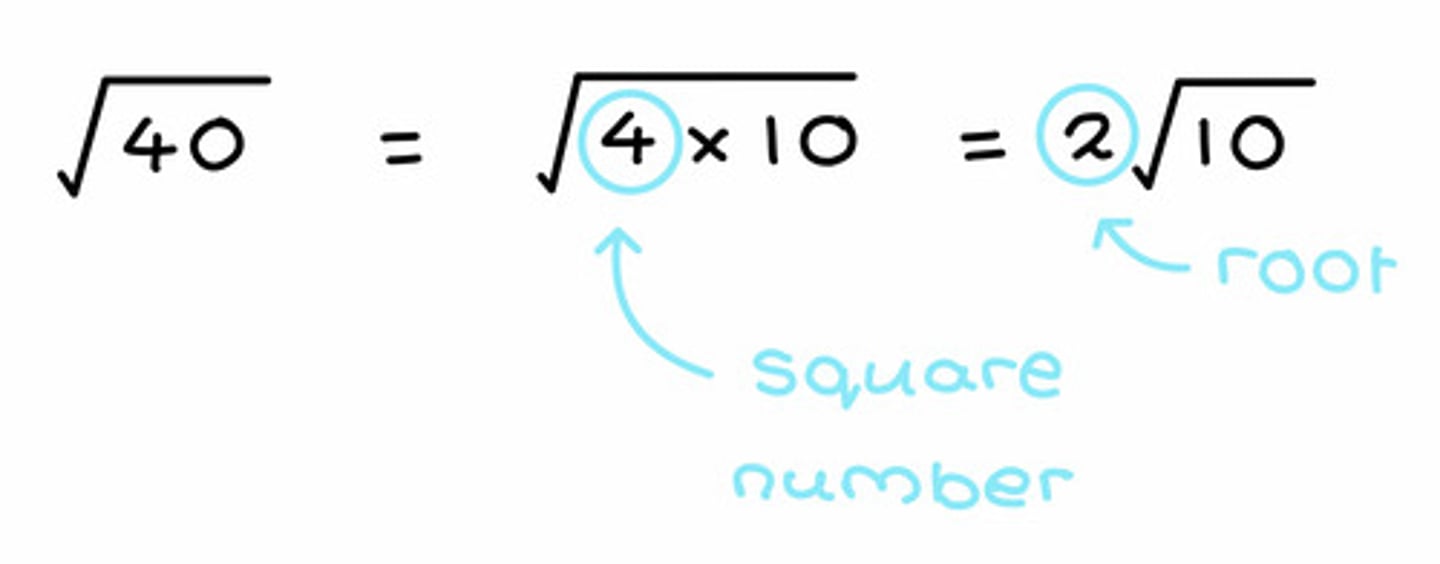
True of false: You can only add or subtract like surds
True
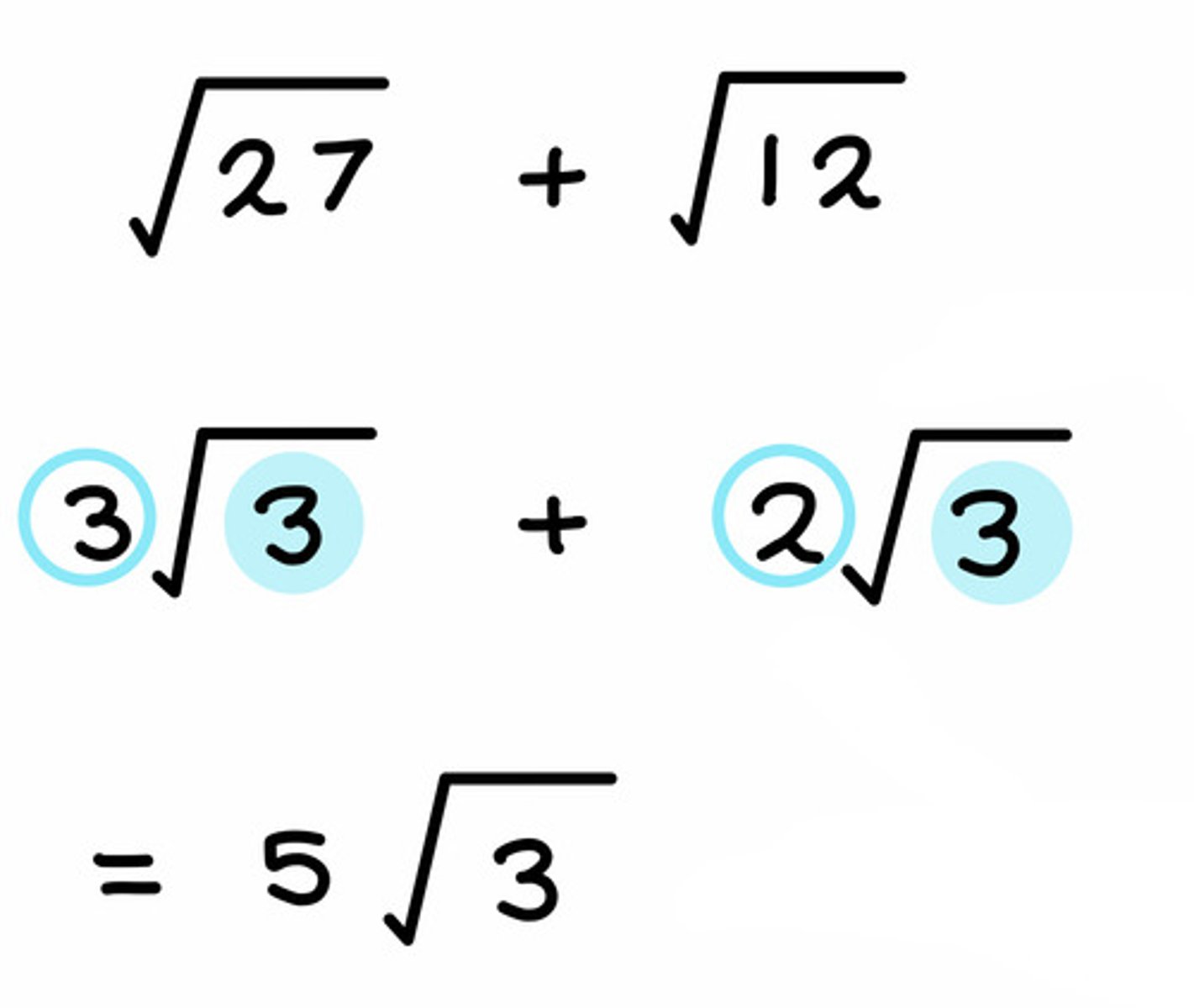
BIDMAS
Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction.
What is an error?
An incorrect measurement
Formula to find the error
Error=Measurement-Actual Value
Formula to find the percentage of an error
Percentage error = Error/Actual value x 100
Upper Limit for measurement
recorded measurement + 0.5 x smallest unit of measure
Lower Limit for measurement
recorded measurement - 0.5 x smallest unit of measure
Cross-section
What a shape is sliced, what shape appears?
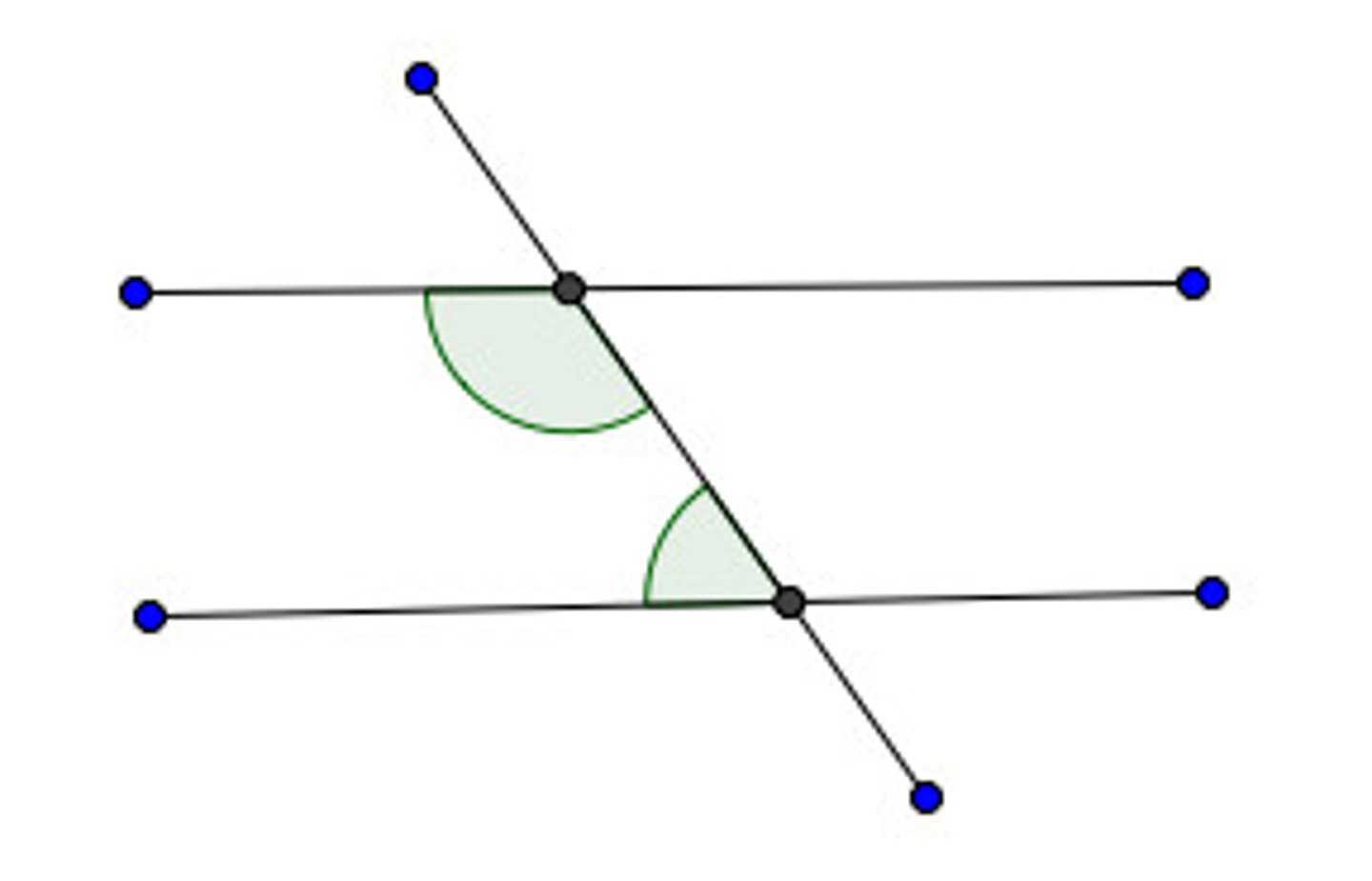
Corresponding Angles
Angles in the same place on different lines
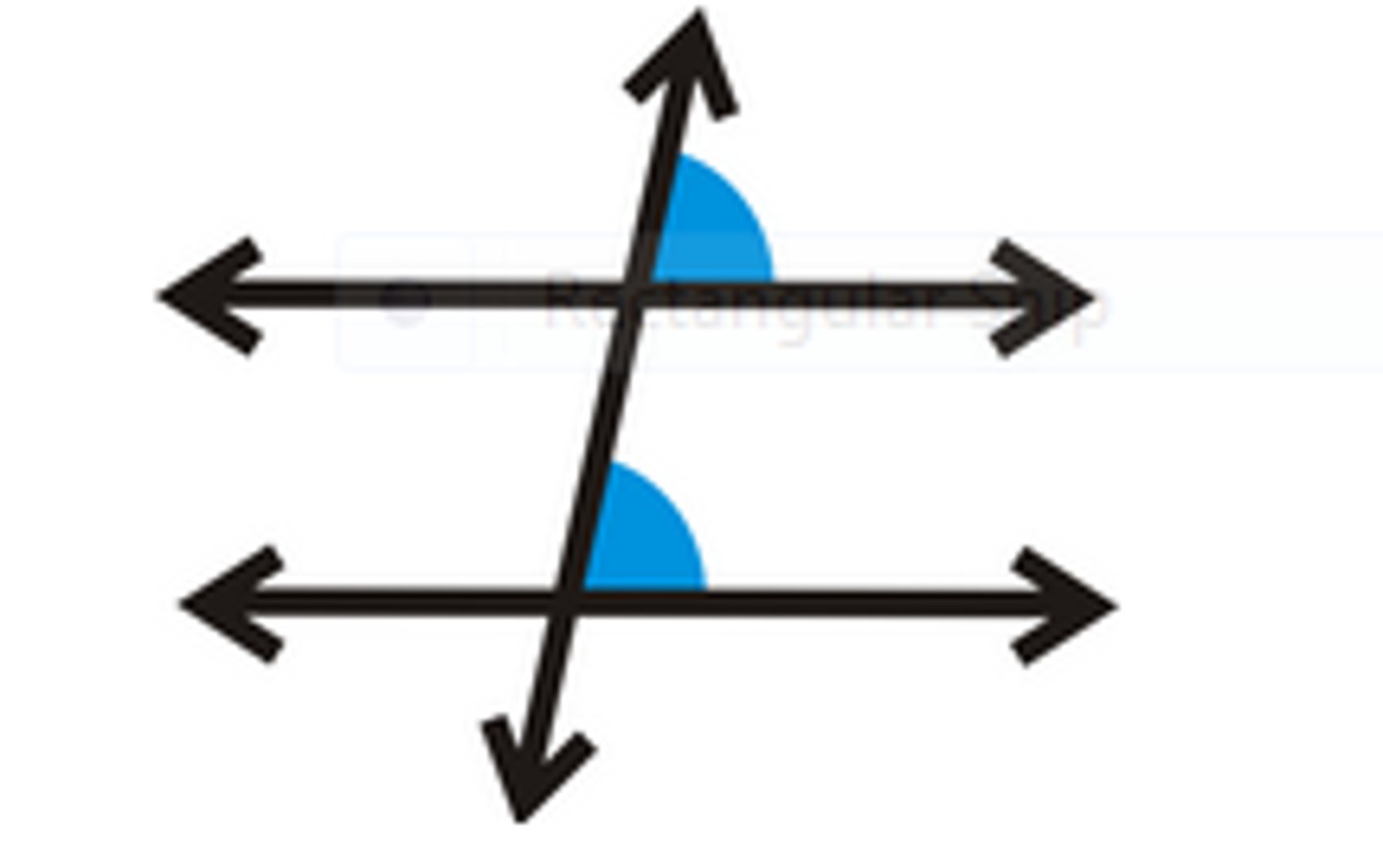
Alternate Interior
angles between 2 lines and on opposite sides of a transversal
Alternate Exterior
Angles that lie outside a pair of lines and on opposite sides of a transversal.
Co-interior angles
add to 180
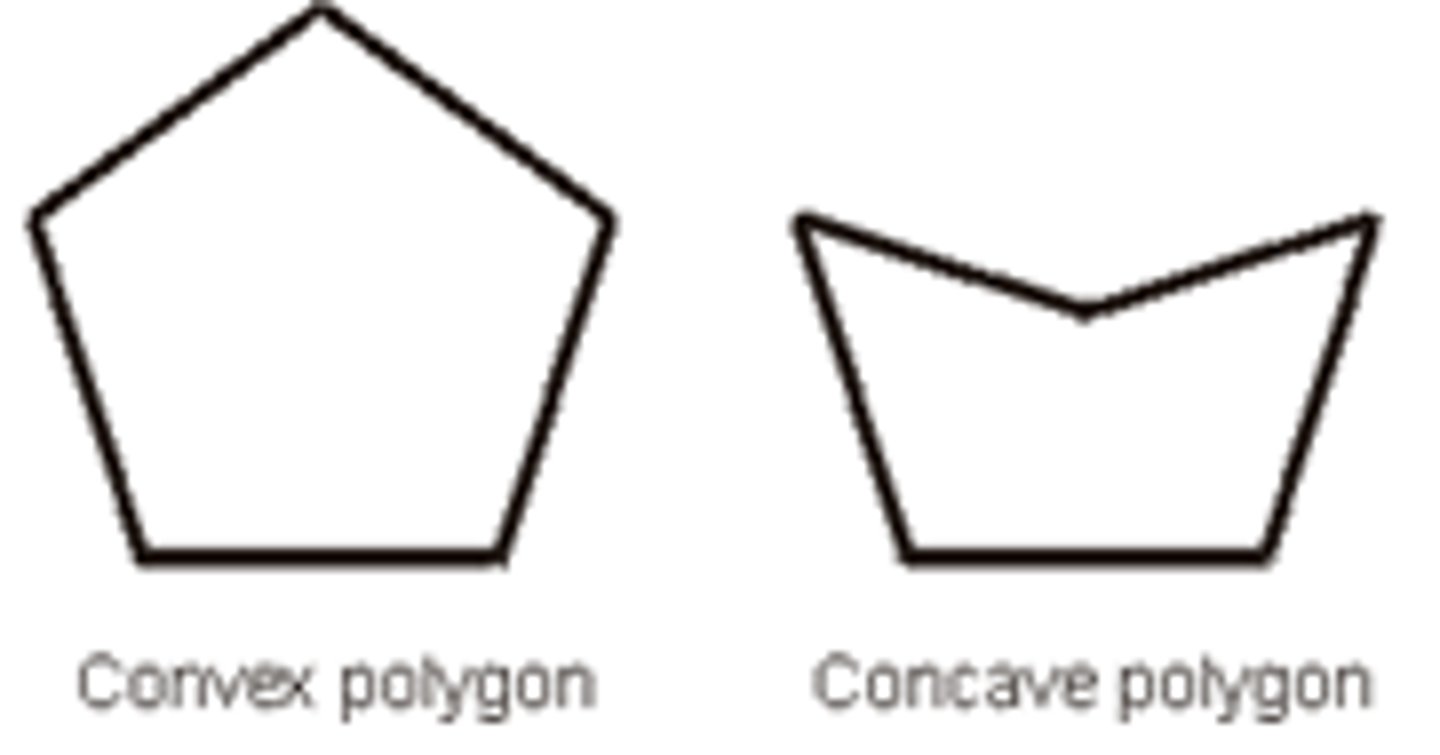
Convex polygons
A polygon in which each interior angle has a measure less than 180 degrees
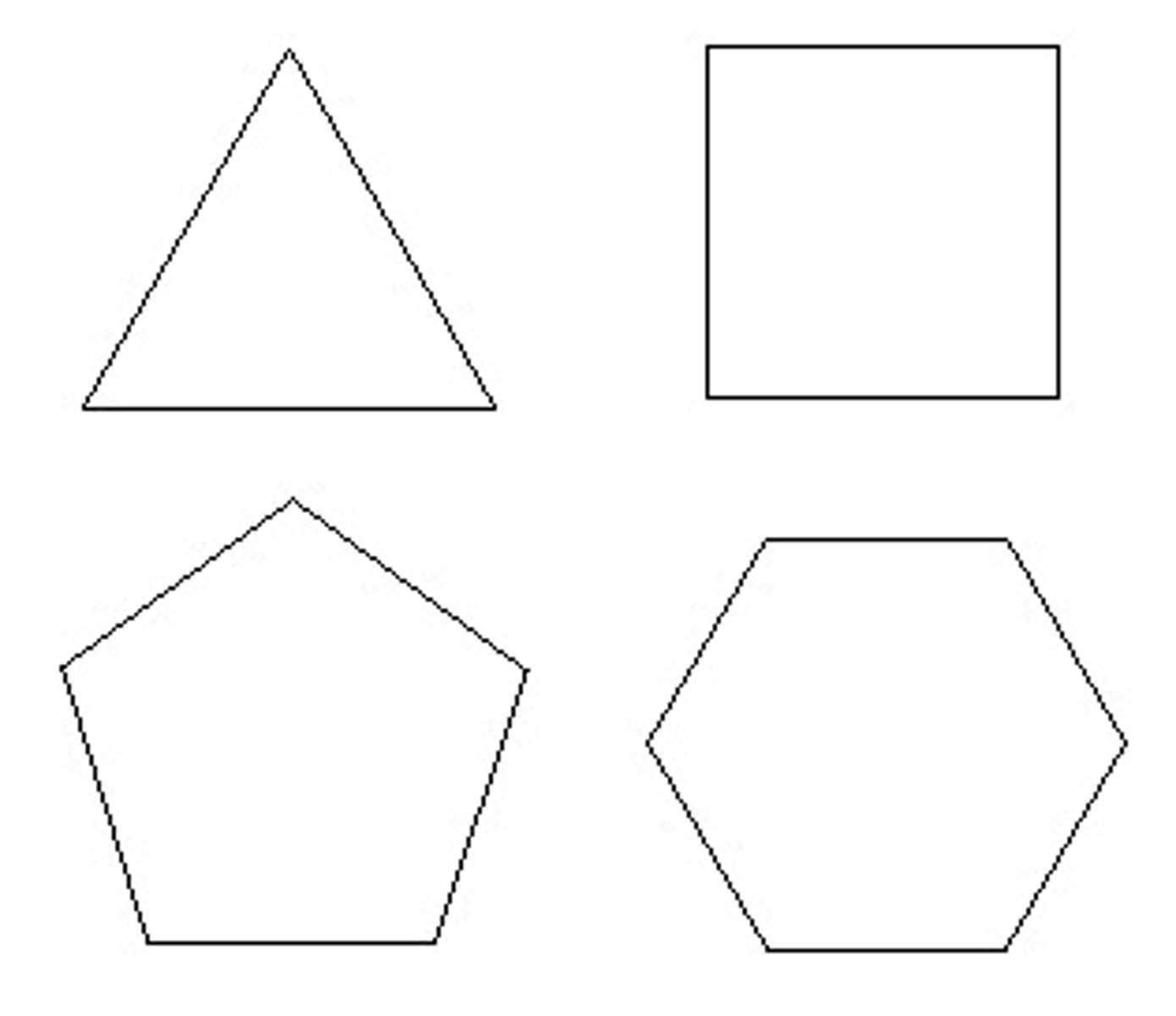
Non-convex polygons/concave
A polygon in which not all interior angles have a measure less than 180 degrees
Formula to find the degrees of a polygon
(n-2)x180
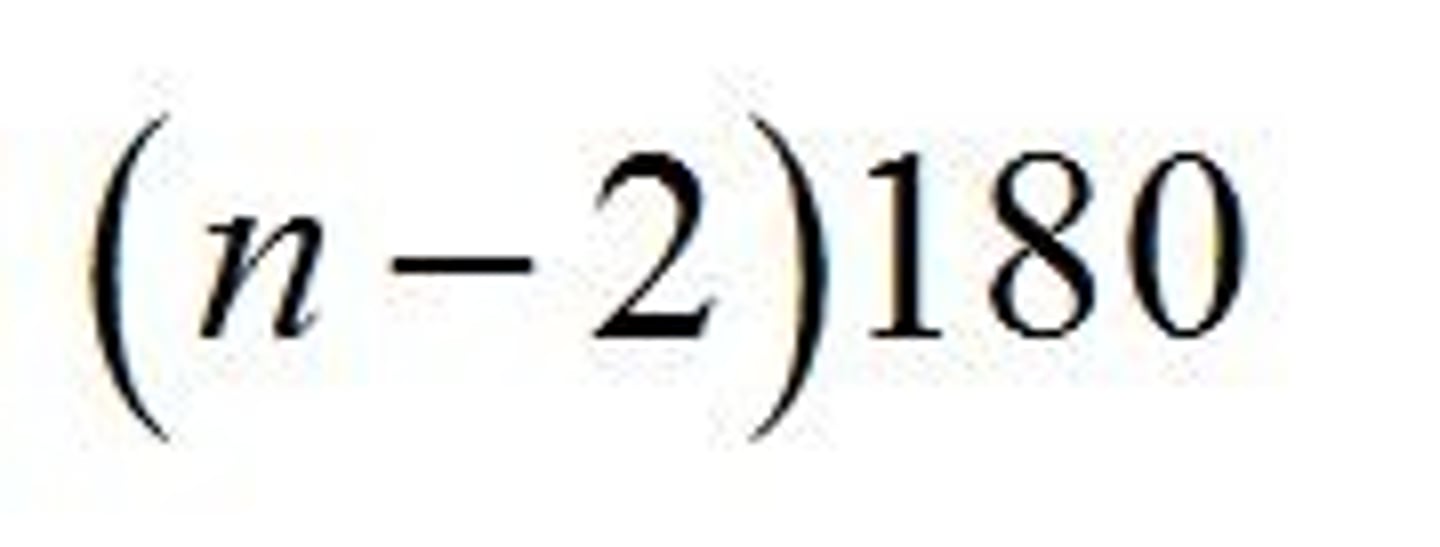
Congruent figures
Figures that have the same size and shape
SSS
side side side
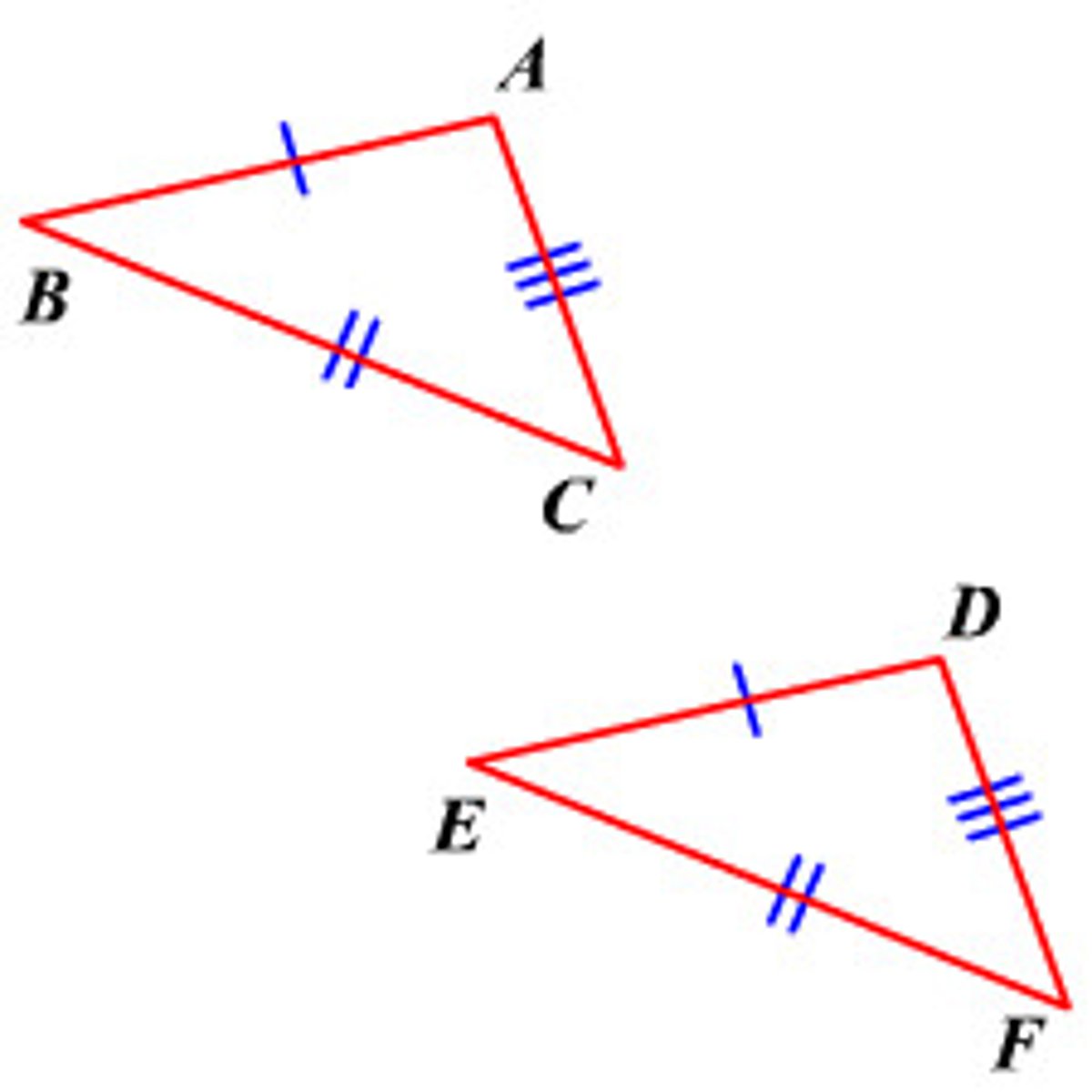
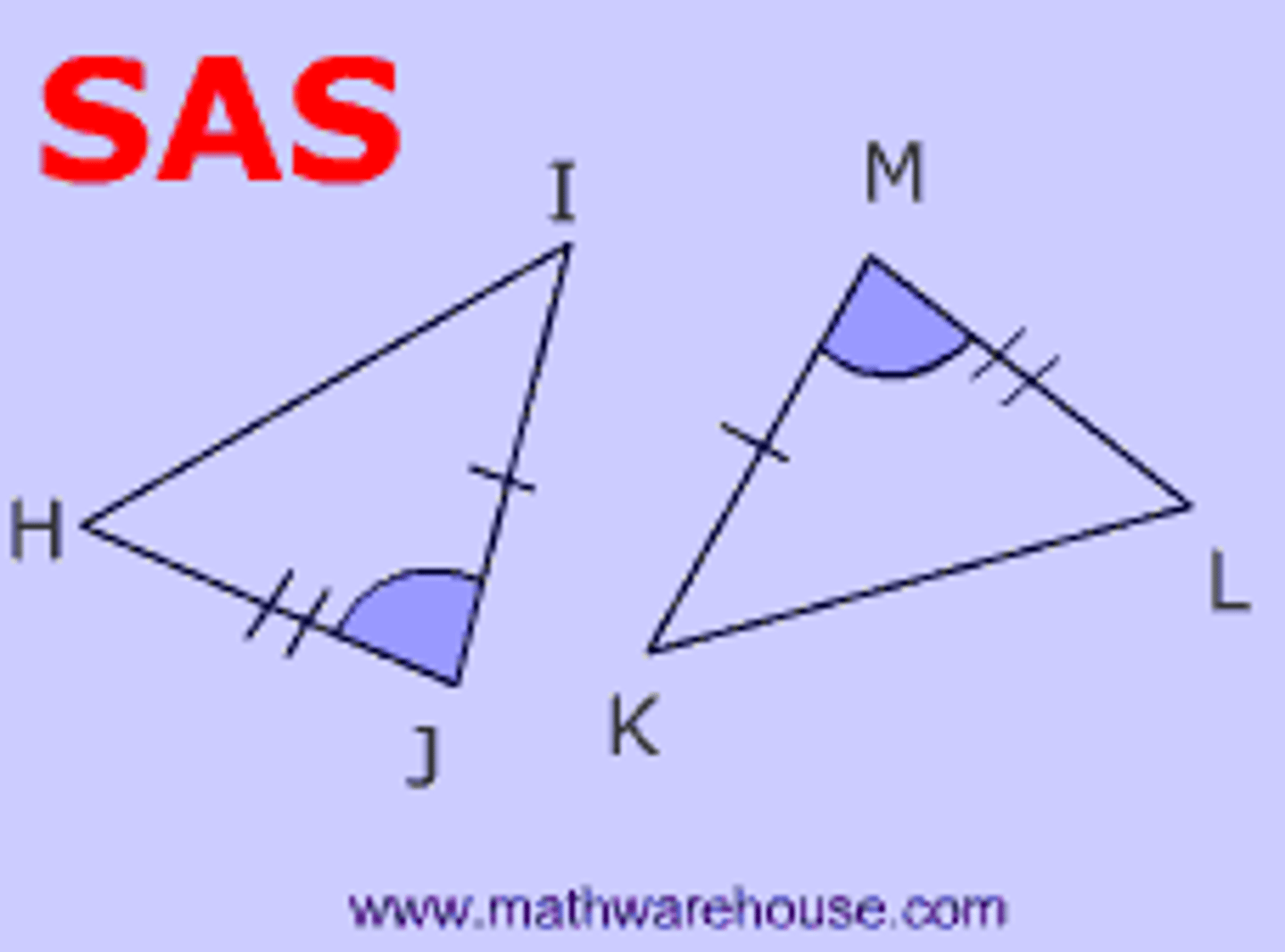
SAS
side angle side
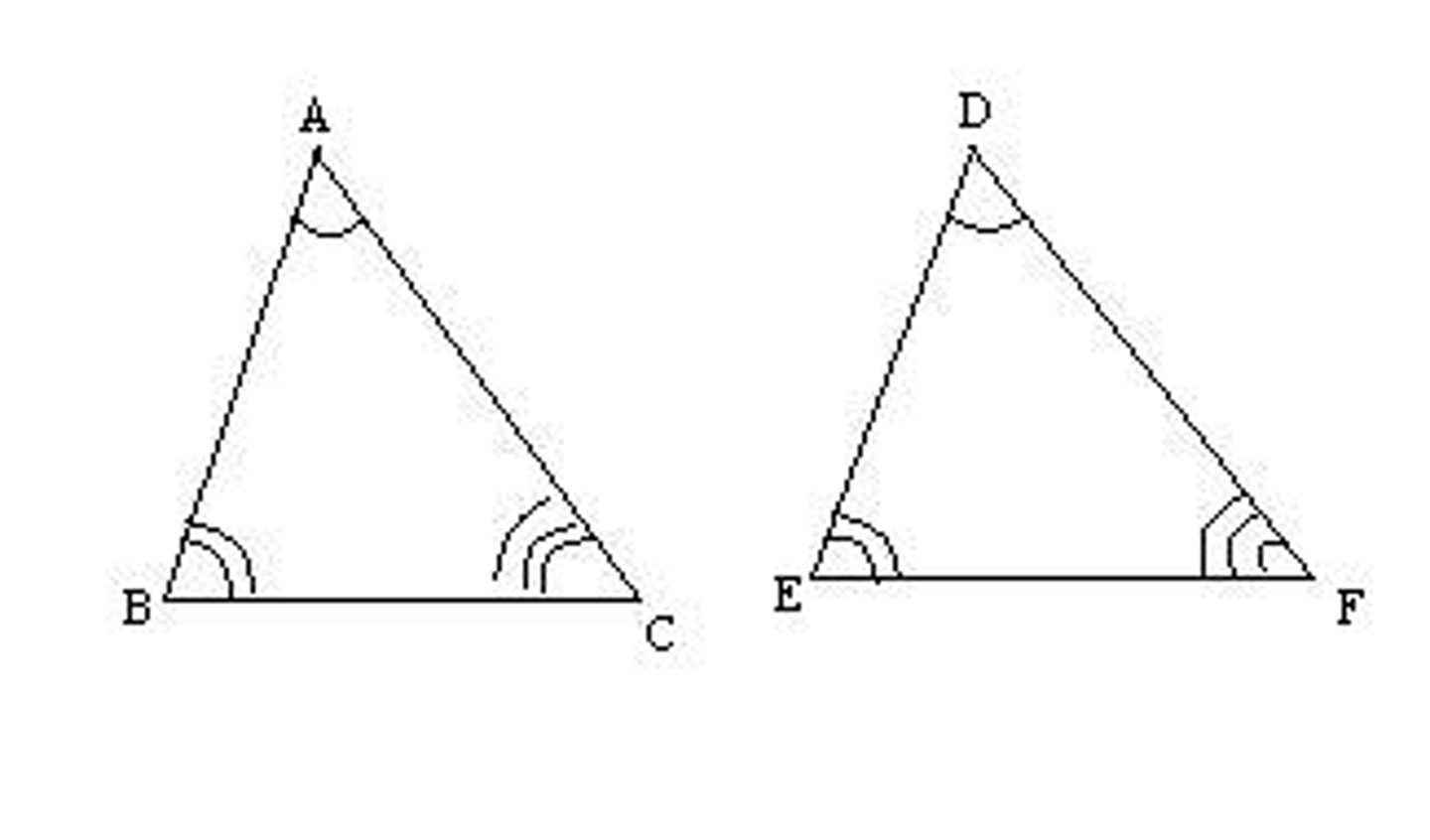
AAA
angle angle angle
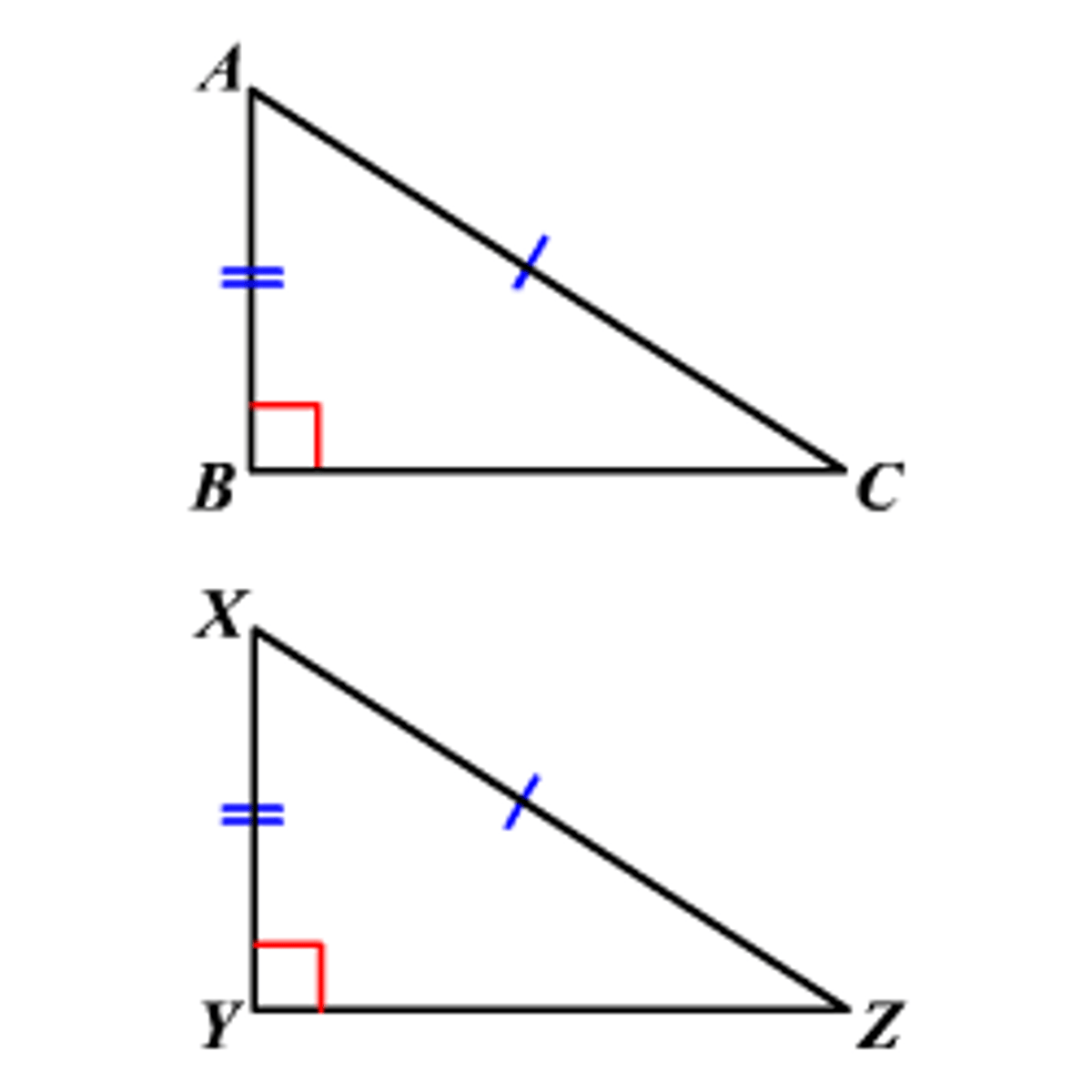
RHS
Right Angle, Hypotenuse, Side
Congruency symbol
≅
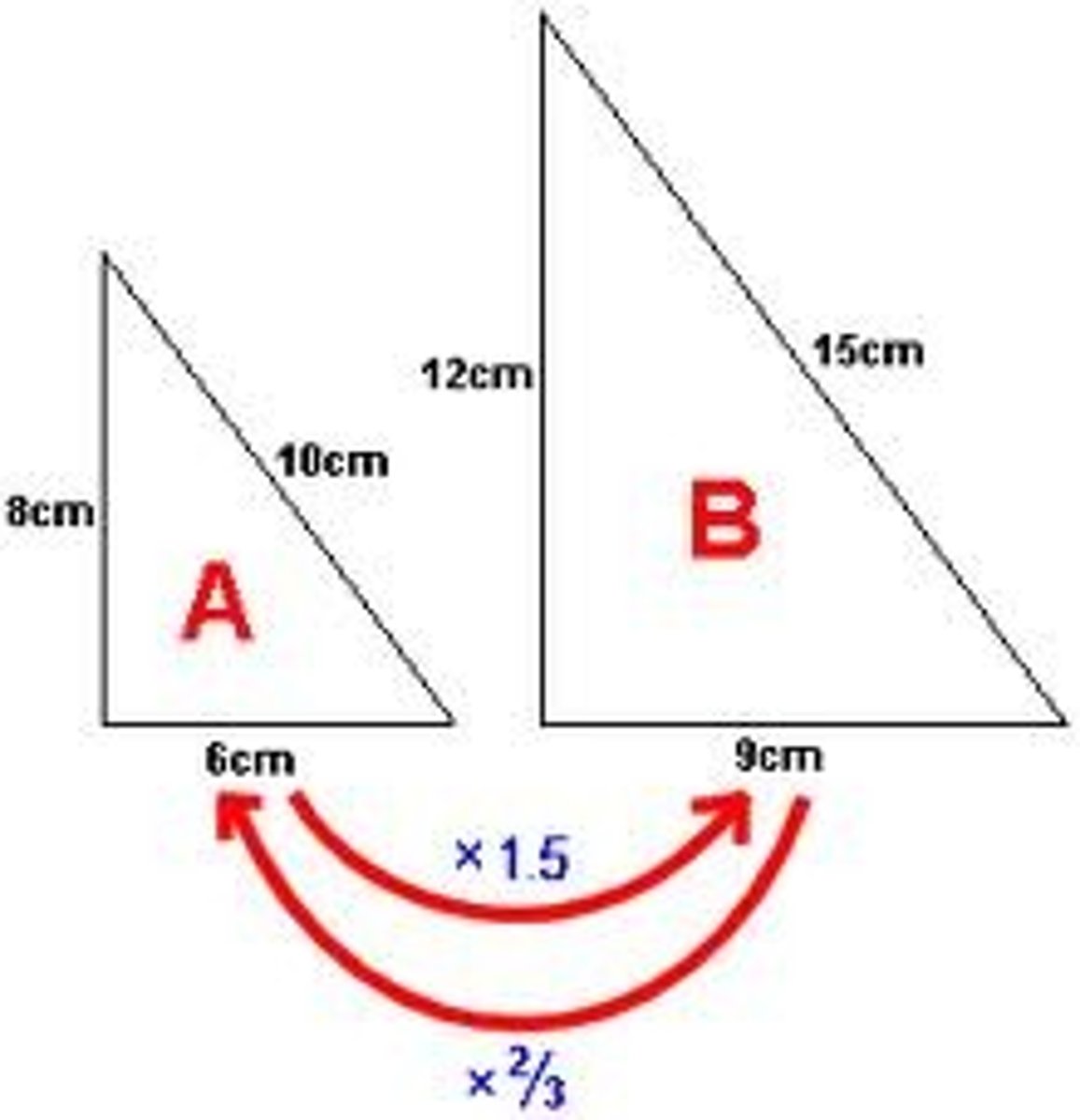
Scale factor
Image length/Original Length
Pythagoras Theorem- Hypotenuse
a²+b²=c²
Pythagorean Triad
A set of three numbers that make a right angled triangle.
Pythagorean Triads
3,4,5/6,8,10/12,16,20
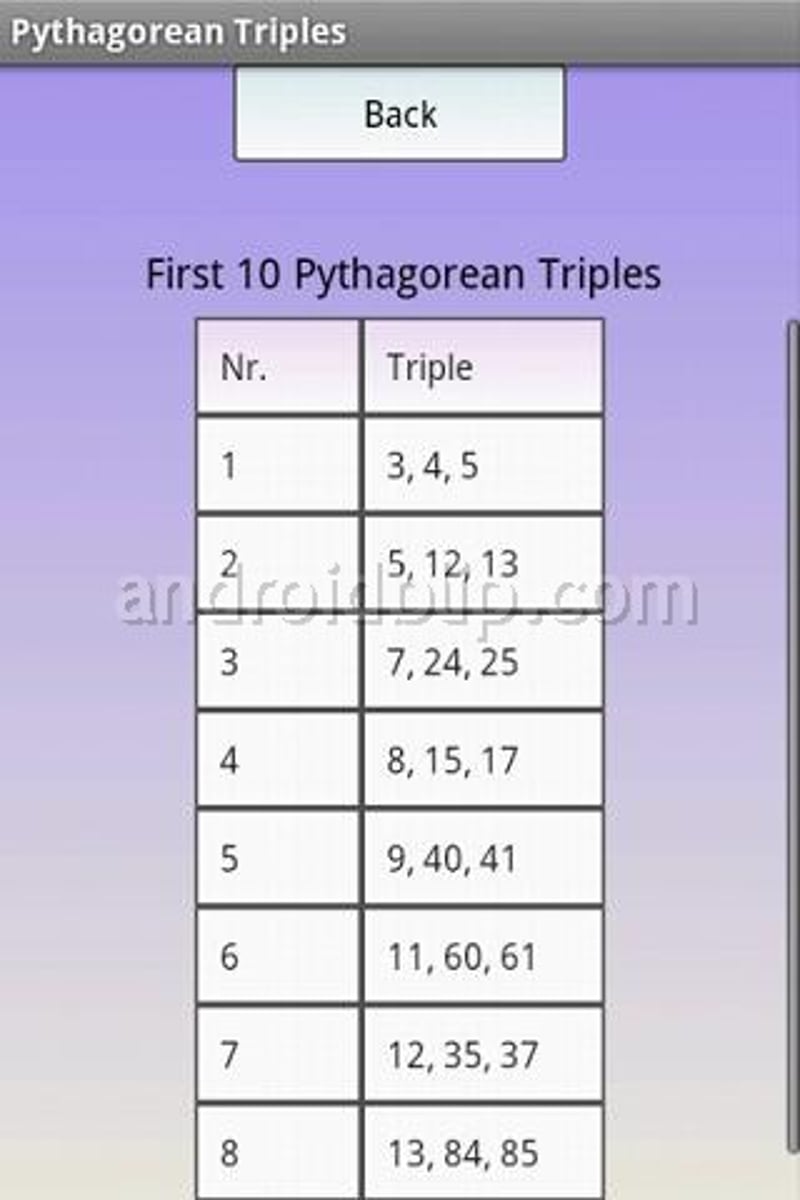
Pythagoras Theorem- Shorter Sides
c²-a²=b² or c²-b²=a²
How to find if a triangle is acute or obtuse
Find the third side and using Pythagoras theorem, if the predicted side is smaller than the other sides (acute) and if it is bigger (obtuse).
SOH-CAH-TOA
sin= opposite/hypo
cos= adjacent/hypo
tan= opposite/adjacent
How inverse trigonometry works
Inverse sine (sin−1) , inverse cosine (cos−1) and inverse tangent (tan−1) can be used to find angles in right-angled triangles.
Eg. sinθ=a/c means θ=sin⁻¹(a/c)
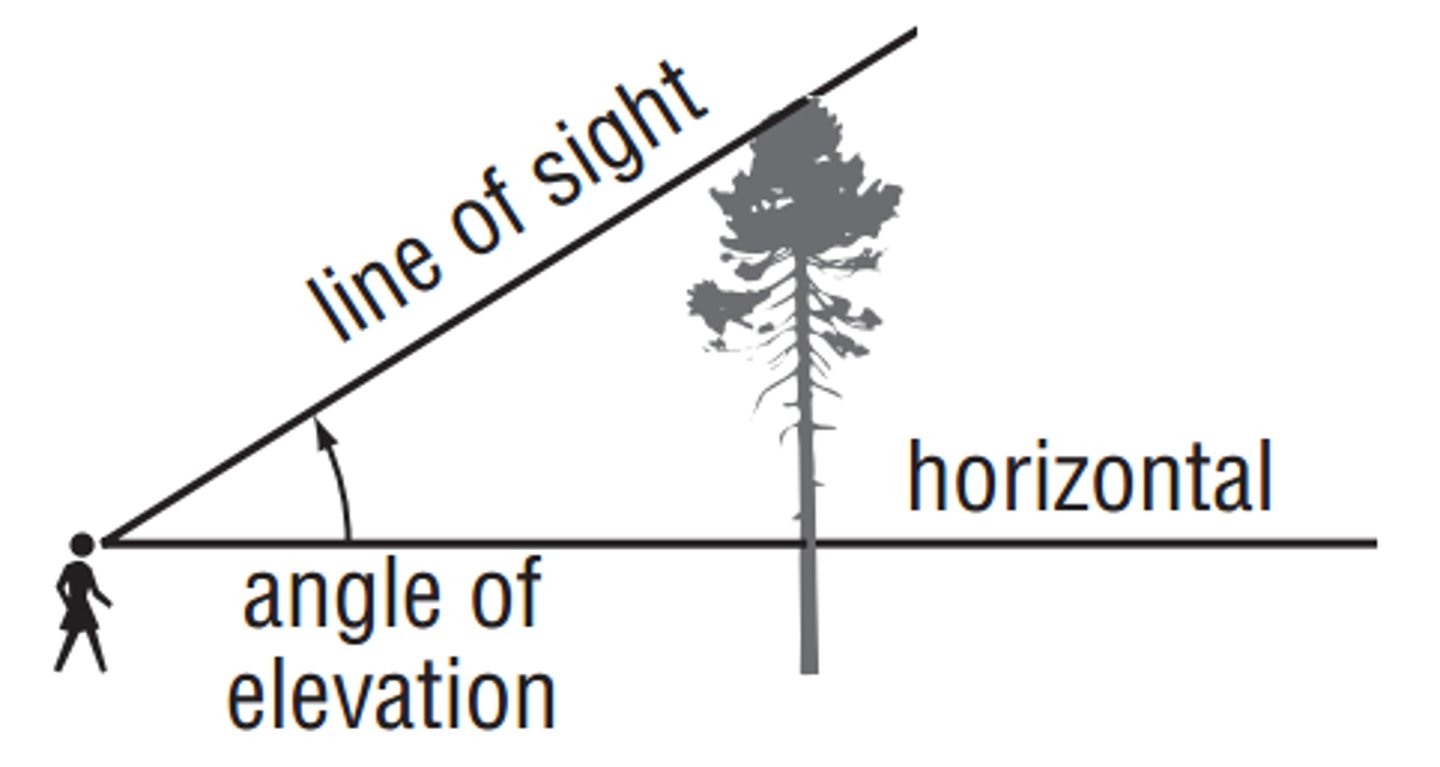
Angle of Elevation
Angle between horizontal line and the line of sight of the observer to an object above the observer.
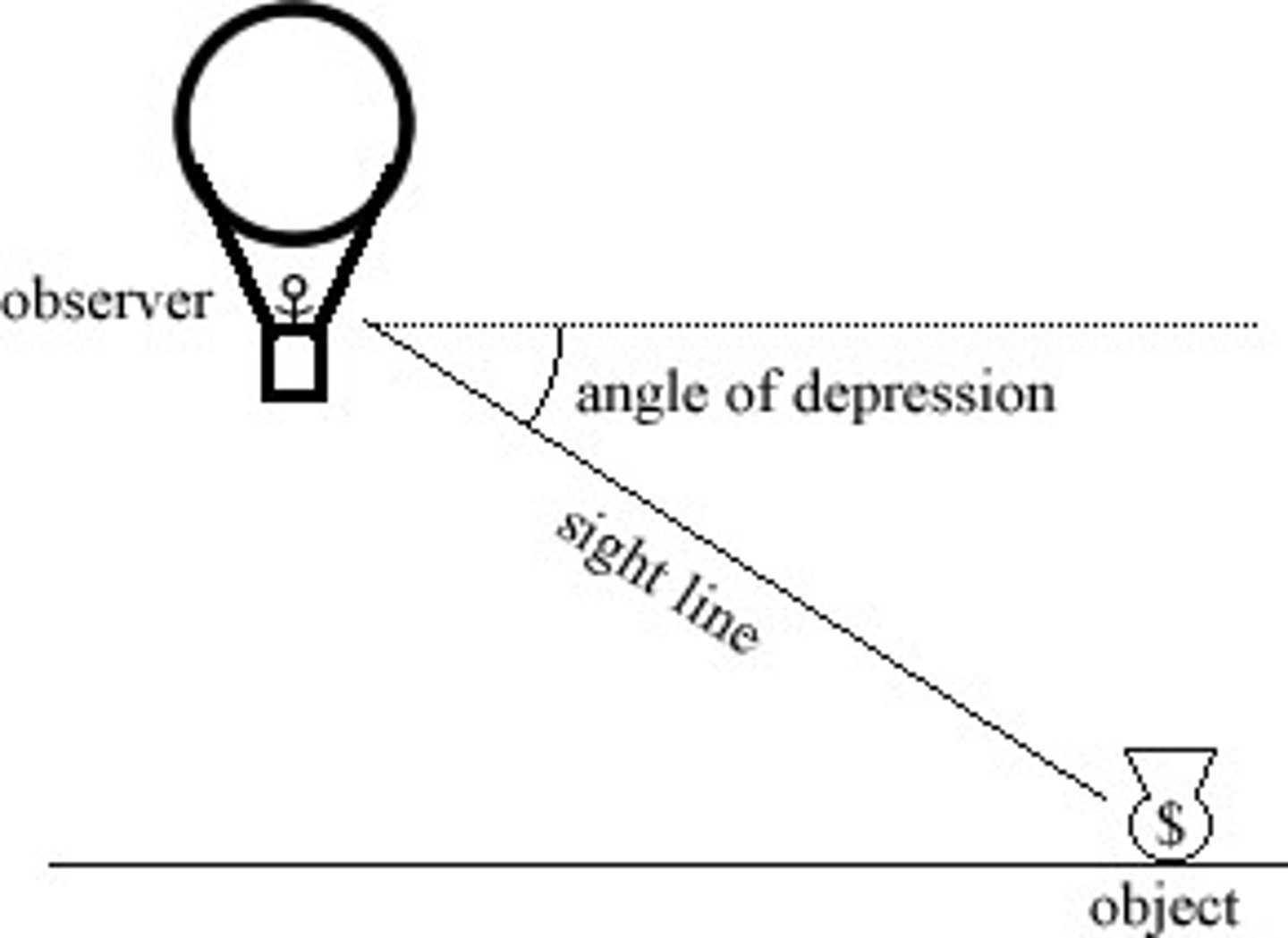
Angle of depression
Angle between horizontal line and the line of sight of the object to an object below the observer.
Where are angles of elevation measure from?
Angles of elevation or depression are ALWAYS measured from the horizontal!
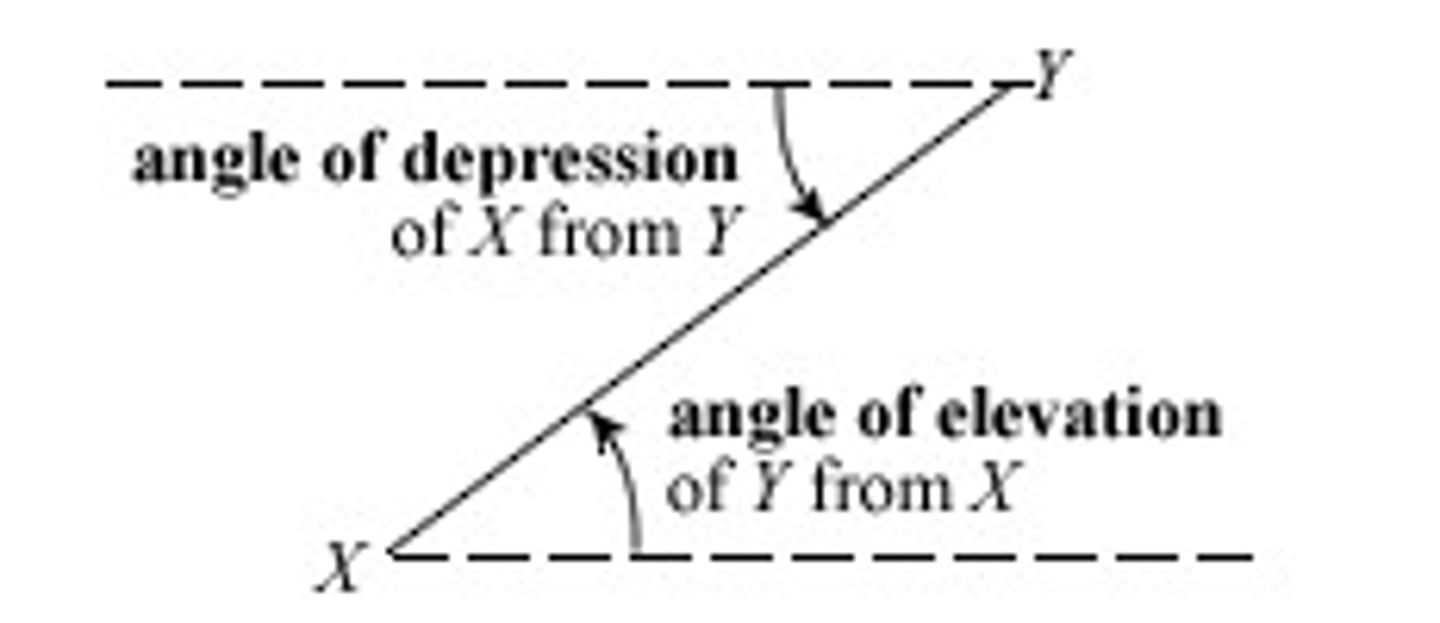
Elevation and Depression
In this diagram the angle of elevation of B from A is equal
to the angle of depression of A from B. They are equal
alternate angles in parallel lines.
How do you find if something is a Pythagoras Triad?
You try the Pythagoras theorem on it:
Eg. Find is 3,4,5 is a Pythagoras Triad
3²+4²=5²
9+16=25
How to find the coordinates of the x and y intercept in parabolas
Make the other term 0
How to find the axis of symmetry
(a+b)/2
How to solve a system of equations on cas
Menu-Algebra-Solve System Of Equations
How to graph linear equations on cas
Menu-Graphs-f1(x)
Dilation
When something is multiplied by a particular factor
Reflection
When something changes from concave up to concave down
Translation
Shifting every point horizontally and/or vertically
Vertex Form of Quadratic Equations
y=a(x-h)²+k
Circles Area
πxr2