vygotsky theory of cognitive development
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
V____ (1934) was a R______ p__ who was influenced by Piaget's work.
They agreed on many of the b____ of c______ d______.
Most importantly that children's reasoning abilities develop in a p____ s____, and that such abilities are q____ d____ at different ages, with a child typically capable of particular l____ at particular ages.
The major difference is that Vygotsky saw cognitive development as what ?
Knowledge is first i______, (between the m____ and less e___ individual)
knowledge then becomes intramental - what does this mean?
Vygotsky also saw l_____ as a much more i_____ part of c______ d______ than Piaget did.
Vygotsky (1934) was a Russian psychologist who was influenced by Piaget's work.
They agreed on many of the basics of cognitive development.
Most importantly that children's reasoning abilities develop in a particular sequence, and that such abilities are qualitatively different at different ages, with a child typically capable of particular logic at particular ages.
The major difference is that Vygotsky saw cognitive development as a social process of learning from more experienced others ('experts').
Knowledge is first intermental, (between the more and less expert individual)
knowledge then becomes intramental, within the mind of the less expert individual.
Vygotsky also saw language as a much more important part of cognitive development than Piaget did.
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
children acquire reasoning abilities of particular people - why?
This means that there may be cultural differences in cognitive development - why
These mental tools include things like what
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
children acquire reasoning abilities of particular people as reasoning abilities are acquired from the more experienced individuals who the child has contact with e.g parents
This means that there may be cultural differences in cognitive development as children pick up the mental 'tools' that will be most important for life within the physical, social and work environments of their culture.
These mental tools include the hand-eye co-ordination needed to hunt with a bow and arrow
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
Vygotsky put t______ e_____ on the role of learning through interaction with others.
He i_____ a gap between a child's current level of development, i.e. what they can u____ and do a_____, and what they can p_____ u_____ after interaction with more expert others.
This gap is known as what?
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
Vygotsky put tremendous emphasis on the role of learning through interaction with others.
He identified a gap between a child's current level of development, i.e. what they can understand and do alone, and what they can potentially understand after interaction with more expert others.
This gap is known as the zone of proximal development (or ZPD)
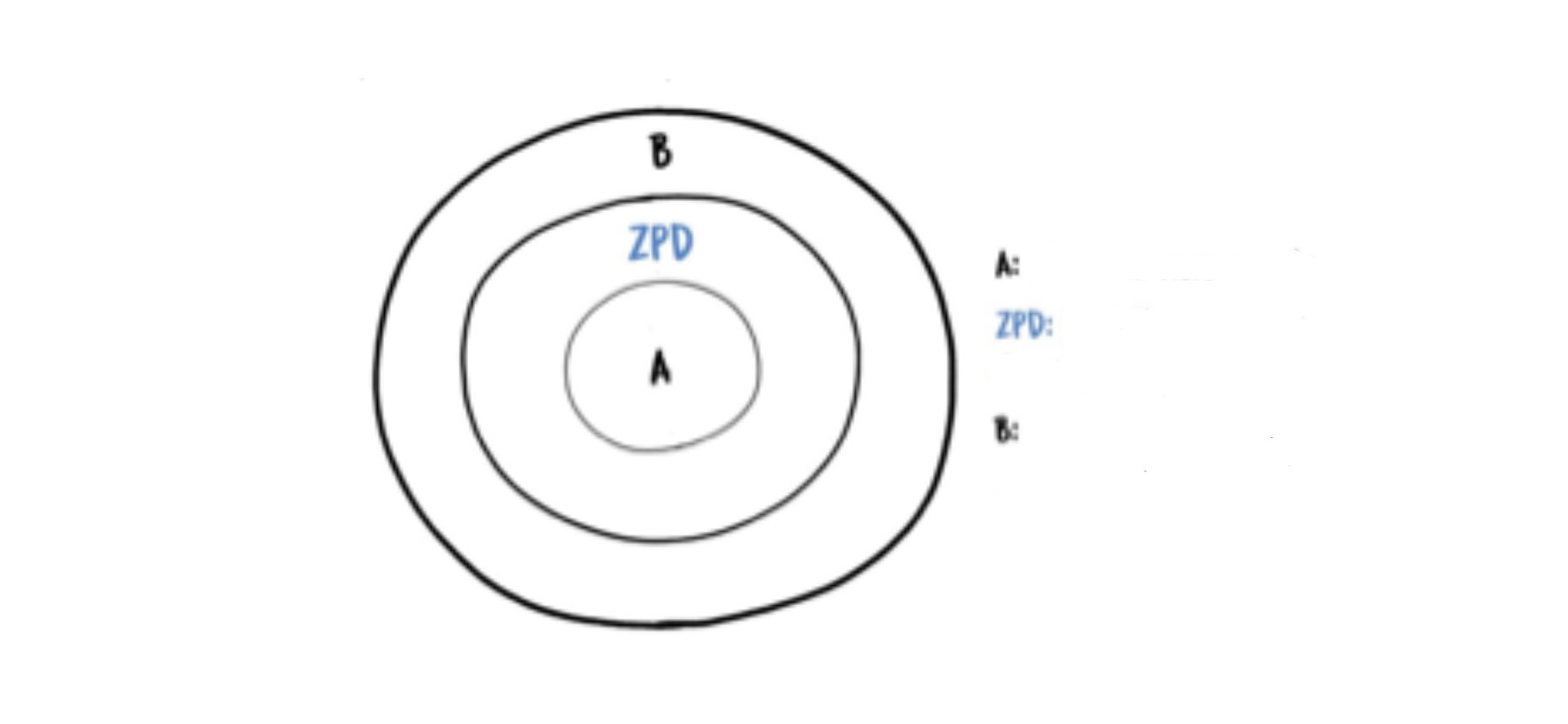
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
fill in the gap for the zone of proximal development
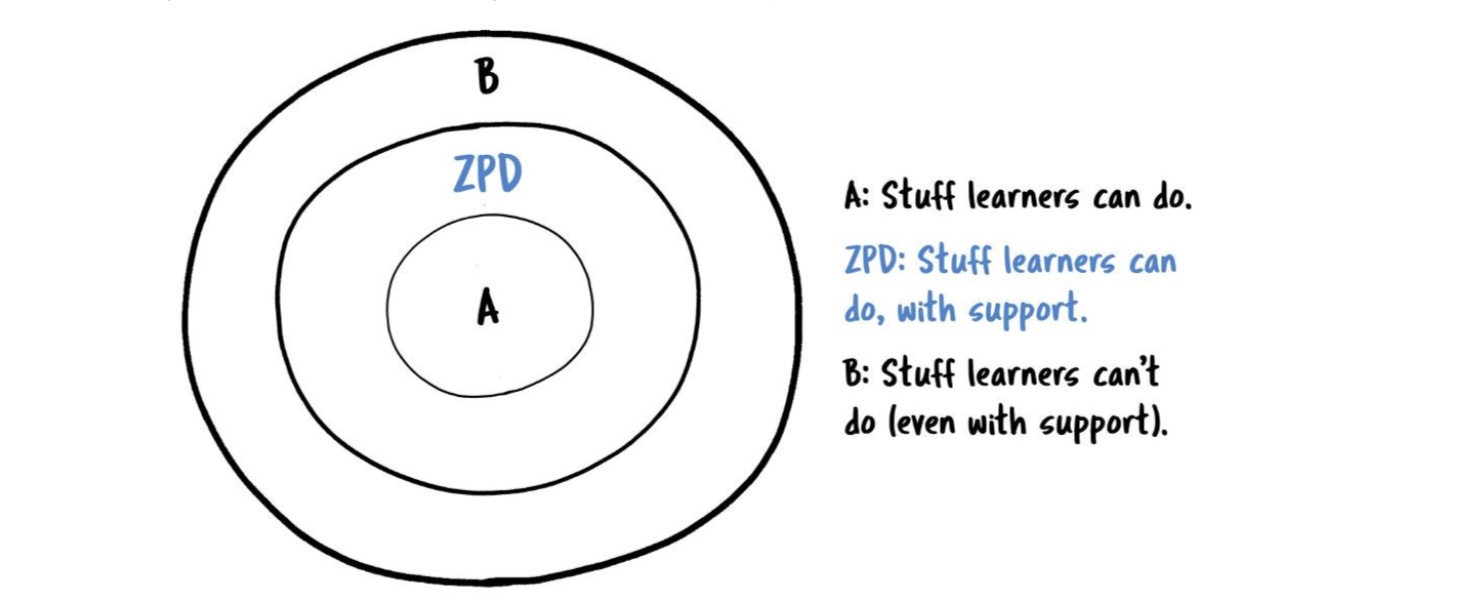
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
E_____ a____ allows a child to cross the ZPD and understand as much of a subject or situation as they are capable - children are still to some extent l____ by their d____ s____
what did Vygotsky believe as opposed to through individual exploration of the world (who’s idea)
Cultural differences in cognitive abilities
Expert assistance allows a child to cross the ZPD and understand as much of a subject or situation as they are capable - children are still to some extent limited by their developmental stage.
Vygotsky believed that children develop a more advanced understanding of a situation and hence the more advanced reasoning abilities needed to deal with it by learning from others, as opposed to through individual exploration of the world. (Piaget)
Vygotsky believed that higher mental functions such as formal reasoning could only be acquired how?
Vygotsky believed that higher mental functions such as formal reasoning could only be acquired through interaction with more advanced others
Scaffolding
what is scaffolding?
what we know about scaffolding isn’t directly Z_____ but from other psychologists i____ by his theory, such as J_____ B____ and colleagues, so this approach is sometimes called what?
Scaffolding
scaffolding is when adults/more advanced peers give a child to help them to cross the zone of proximal development.
what we know about scaffolding isn’t directly Zygotsky but from other psychologists influenced by his theory, such as Jerome Bruner and colleagues, so this approach is sometimes called 'the Vygotsky-Bruner model':
Scaffolding
W____, B_____ and R____ (1976) identifies five aspects to scaffolding which are ways an e____ a_____ can help a child better understand and perform a task : what are these 5 aspect + example?
In general, as a learner crosses the zone of p_______ d_____, the level of help given in scaffolding declines from level 5 (most help) to level 1 (least help)
. An adult is more likely to use a high level of strategies when?, then to gradually withdraw the level of help when?
Scaffolding
Wood, Bruner and Ross (1976) identifies five aspects to scaffolding which are ways an expert adult can help a child better understand and perform a task : demonstration, preparation, indication, specific verbal instructions, general prompts
Level of help | Nature of prompt | Example |
5 | Demonstration | Adult draws an object with crayons. |
4 | Preparation for child | Adult helps child grasp a crayon. |
3 | Indication of materials | Adult points to crayons. |
2 | Specific verbal instructions | Adult says 'How about the green crayon?" |
1 | General prompts | Adult says 'Now draw something else. |
In general, as a learner crosses the zone of proximal development, the level of help given in scaffolding declines from level 5 (most help) to level 1 (least help)
. An adult is more likely to use a high level of strategies when first helping, then to gradually withdraw the level of help as the child grasps the task.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength of Vygotsky's theory is research support for the what?
There is evidence to show that there is indeed a gap between what?
An example of such a study comes from R____ and B_____ (1998).
Children aged _-_ years were to estimate what?
what were the 2 conditions?
Most children working a____ f___ to give a g___ estimate (one that was close to the an____ answer). In the e___ h____ condition the older (expert) children were observed to offer p____, pointing the younger children in the r____ d___ to work out how to arrive at their e____.
Most ___-___ -year-olds receiving this kind of help successfully m____ the task.
This shows that children can develop what? when working with a more e____ individual.
This in turn suggests that the zone of proximal development is a valid concept.
EXTENSION:
In schools, this can be applied through s____ and s___-g____ work, where children are d_____ into a___-b___ g___ to receive t____ support from teachers/more capable peers.
This allows pupils to improve u____ and c_____ before s___ is g____ r____.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength of Vygotsky's theory is research support for the ZPD.
There is evidence to show that there is indeed a gap between the level of reasoning a child can achieve on their own and what they can achieve with help from a more expert other.
An example of such a study comes from Roazzi and Bryant (1998).
Children aged 4-5 years were to estimate the number of sweets in a box.
In one condition the children worked alone and in another they worked with the help of an older child.
Most children working alone failed to give a good estimate (one that was close to the actual answer). In the expert help condition the older (expert) children were observed to offer prompts, pointing the younger children in the right direction to work out how to arrive at their estimate.
Most 4-5-year-olds receiving this kind of help successfully mastered the task.
This shows that children can develop additional reasoning abilities when working with a more expert individual.
This in turn suggests that the zone of proximal development is a valid concept.
EXTENSION:
In schools, this can be applied through scaffolding and small-group work, where children are divided into ability-based groups to receive targeted support from teachers/more capable peers.
This allows pupils to improve understanding and confidence before support is gradually reduced.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength Vygotsky's theory is research support for scaffolding.
Research shows that the level of help given by an expert partner d___ during the p____ of l_____, as predicted by the p____ of s____.
For example C____ and C____ (2003) used a longitudinal procedure to follow up ___ children, o____ them engaged in p____-s____ t____ with the help of their mothers at ___,___ , and ___ months.
Distinctive changes in help were observed over time - like what?
Mothers also increasingly offered h____ when it was needed rather than c____
This means that a____ a____ with children's learning is well described by the concept of scaffolding.
EXTENSION
Evaluation of Conner and Cross (2003) methodology- is it reliable? and how is this beneficial?
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength of Vygotsky's theory is research support for scaffolding.
Research shows that the level of help given by an expert partner declines during the process of learning, as predicted by the principle of scaffolding.
For example Conner and Cross (2003) used a longitudinal procedure to follow up 45 children, observing them engaged in problem-solving tasks with the help of their mothers at 16, 26, 44 and 54 months.
Distinctive changes in help were observed over time - the mothers used less and less direct intervention and more hints and prompts as children gained experience.
Mothers also increasingly offered help when it was needed rather than constantly.
This means that adult assistance with children's learning is well described by the
concept of scaffolding.
EXTENSION
Evaluation of Conner and Cross (2003) methodology- the research design is reliable as participant variables are reduced using the longitudinal method and the same participants
This is beneficial as this means changes in scaffolding are more likely due to children’s cognitive development rather than individual differences, which increases the study’s internal validity.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength of Vygotsky's theory is p____, r____-w___ application in education.
Vygotsky's ideas have been highly i___ in education in the 21st century.
The idea that children can learn more and faster with a_____ s____ has influenced social interaction in learning e,g through what?
these have all been used to s____ children though their ZPD.
There is evidence to suggest that these s_____ are e____.
For example V____ K____ and P____ V____ (2005) found that ___-year-olds tutored by ____-year-olds, in addition to their whole-class teaching, p____ further in reading than c_____ who just had s____ whole-class teaching.
also a review of the usefulness of what?(A____ et al. 2009) concluded that teaching assistants are very e____ at i___ the rate of learning in children.
This means that Vygotsky's ideas have v___ in real-world settings.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- strengths
✓- One strength of Vygotsky's theory is practical, real-world application in education.
Vygotsky's ideas have been highly influential in education in the 21st century.
The idea that children can learn more and faster with appropriate scaffolding has influenced social interaction in learning, through group work, peer tutoring and individual adult assistance from teachers and teaching assistants
these have all been used to scaffold children though their ZPD.
There is evidence to suggest that these strategies are effective.
For example Van Keer and Pierre Verhaeghe (2005) found that 7-year-olds tutored by 10-year-olds, in addition to their whole-class teaching, progressed further in reading than controls who just had standard whole-class teaching.
also a review of the usefulness of teaching assistants (Alborz et al. 2009) concluded that teaching assistants are very effective at improving the rate of learning in children.
This means that Vygotsky's ideas have value in real-world settings.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- limitations
✘- One limitation of Vygotsky’s theory is that it may overestimate what?
If Vygotsky was right about the process of interactive learning, we would expect what?
However, Howe (1992) found that what children actually learn varies considerably between individuals, even in group learning situations.
EXTENSION:
This limitation makes Piaget’s theory appear stronger, as it places greater emphasis on individual cognitive development and the child’s active role in constructing knowledge, which better explains why children can learn different things even when exposed to the same social environment.
evaluation of Vygotsky’s theory of cognitive development- limitations
✘- One limitation of Vygotsky’s theory is that it may overestimate the consistency of learning outcomes from social interaction.
If Vygotsky was right about the process of interactive learning, we would expect all children learning together to pick up very similar skills and a very similar mental representation of material.
However, H_____ (1992) found that what children actually learn v____ c___ between i____, even in g____ l_____ situations.
EXTENSION:
why does this limitation makes Piaget’s theory appear stronger?