Chem 107 Final Review - SELU John Waggenspack
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
250 Terms
Chemistry
The study of matter and its properties
Kilo (k)
10^3
Mega (M)
10^6
Giga (G)
10^9
Tera (T)
10^12
Peta (P)
10^15
Deci (d)
10^-1
Centi (c)
10^-2
Milli (m)
10^-3
Micro (µ)
10^-6
Nano (n)
10^-9
Pico (p)
10^-12
Femto (f)
10^-15
Scientific Notation
Conveniently represents any number large or small
Express the number 180,000,000 g in scientific notation.
1.8 x 10^8 g
Express the number 0.000006 g in scientific notation.
6 x 10^-5 g
Express the number 751,000 g in scientific notation.
7.51 x 10^5 g
Express the number 0.1590 m in scientific notation.
1.590 x 10^-1 m
Express the number 45,000,000 in scientific notation.
4.5 x 10^7
How many significant figures are in the number 1.23?
3
How many significant figures are in the number 0.123?
3
How many significant figures are in the number 0.00123?
3
If a number is greater than 1,
All zeros to the right of the first decimal point are significant
If a number is less than 1,
All zeros to the right of the first significant figure are significant
How many significant figures are in the number 2.000?
4
How many significant figures are in the number 0.020?
2
Trailing zeros (No decimal place)
May or may not be significant
How many significant figures are in the number 100?
1
How many significant figures are in the number 100.?
3
How many significant figures are in the number 100.00?
5
What should the number of decimal places be equal to when adding or subtracting?
-The number of decimal places in the quantity with the fewest places
-Ex. 0.12 + 1.6 + 10.976 = 12.696 = 12.7
What should the number of significant figures in the answer be in multiplication and division?
-The same as the quantity with the fewest significant figures
-Ex. 0.01208/0.0236 = 0.512
How many significant figures do exact numbers and defined quantities have?
Infinate
Area (Square centimeters)
cm^2
Volume (Cubic centimeters)
cm^3
Cubic Centimeter (cc) and Milliliter (ml)
Are used interchangebly
1 cm^3 (Cubic centimeter) =
1 ml (Milliliter)
What is the basic unit of volume in the metric system?
Liter (L)
1 Liter = 1,000 cm^3 =
1,000 ml
Displacement
Final volume - Initial volume
Mass
A fundamental measure of the quantity of the matter in that body (Consistent/Does not change)
Weight
The weight of a body depends on the mass of that body and another body. It is the gravitational force of one body on another. It would/will change in space.
What is the SI unit for mass?
Kilogram (Kg)
In the laboratory, what are masses generally expressed in?
Grams (g) and milligrams (mg)
Density
Mass of substance/volume of substance
Mass
Density of substance x volume of substance
Volume
Mass of substance/density of substance
Temperature
A measure of the thermal energy of a substance
What are the 3 units used to measure temperature?
Fahrenheit, celsius, and kelvin
Celcius
Degrees F - 32/1.8
Fahrenheit
1.8 Degrees C + 32
Kelvin Scale
T(K) = Degrees C + 273 (Or 273.15)
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
What is the atomic theory of matter?
The idea that matter is made of discrete units (I.e. particles)
Atom
-Basic unit of matter
-One complete particle of an element
Proton (P+)
-Has a charge of +1
-Has a mass of 1 amu
Neutron (n^0)
-Has no charge, 0
-Has a mass of 1 amu
Electron (e-)
-Has a charge of -1
-Has a mass of 1/1867
Valence Electrons
-Occupy the outermost regions of the atom
-Electron dot or Lewis are used to keep track of valence electrons
-The number of valence electrons is equivalent to the group number of the element
What are the dots used to represent in an electron-dot structure of an element?
The valence electrons
Protons and electrons carry electric charges. What do like charges do? Unlike charges?
Repel, attract
Where are protons and neutrons located?
In the nucleus of atom
Where are electrons located?
Outside the nucleus of atom in shells or orbitals
Elements
Defined by the number of protons in the nucleus
Atomic Number
-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Given the symbol Z.
-Elements can only have one atomic number
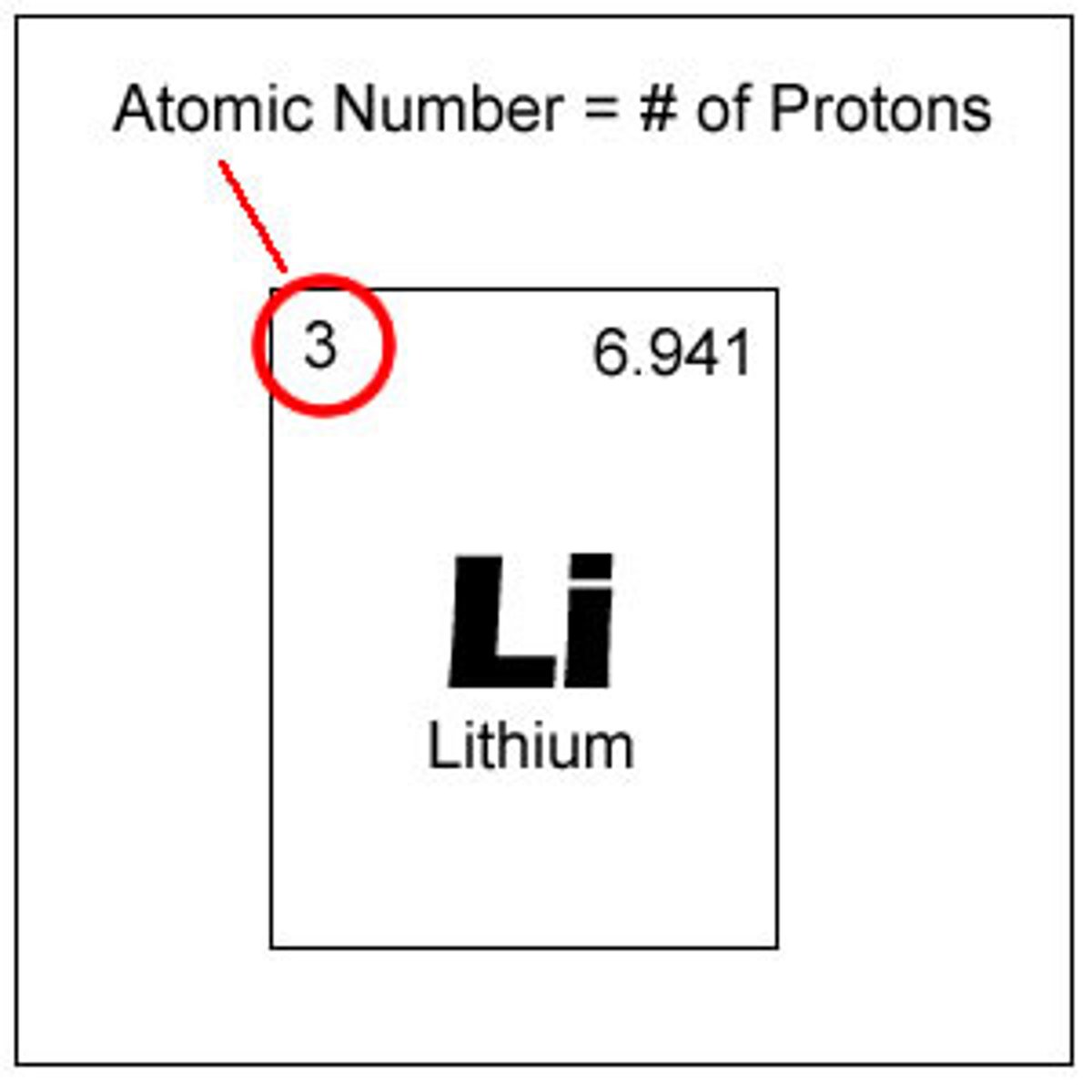
Atomic Number, Chemical Symbol, Chemical Name, Atomic Mass Number
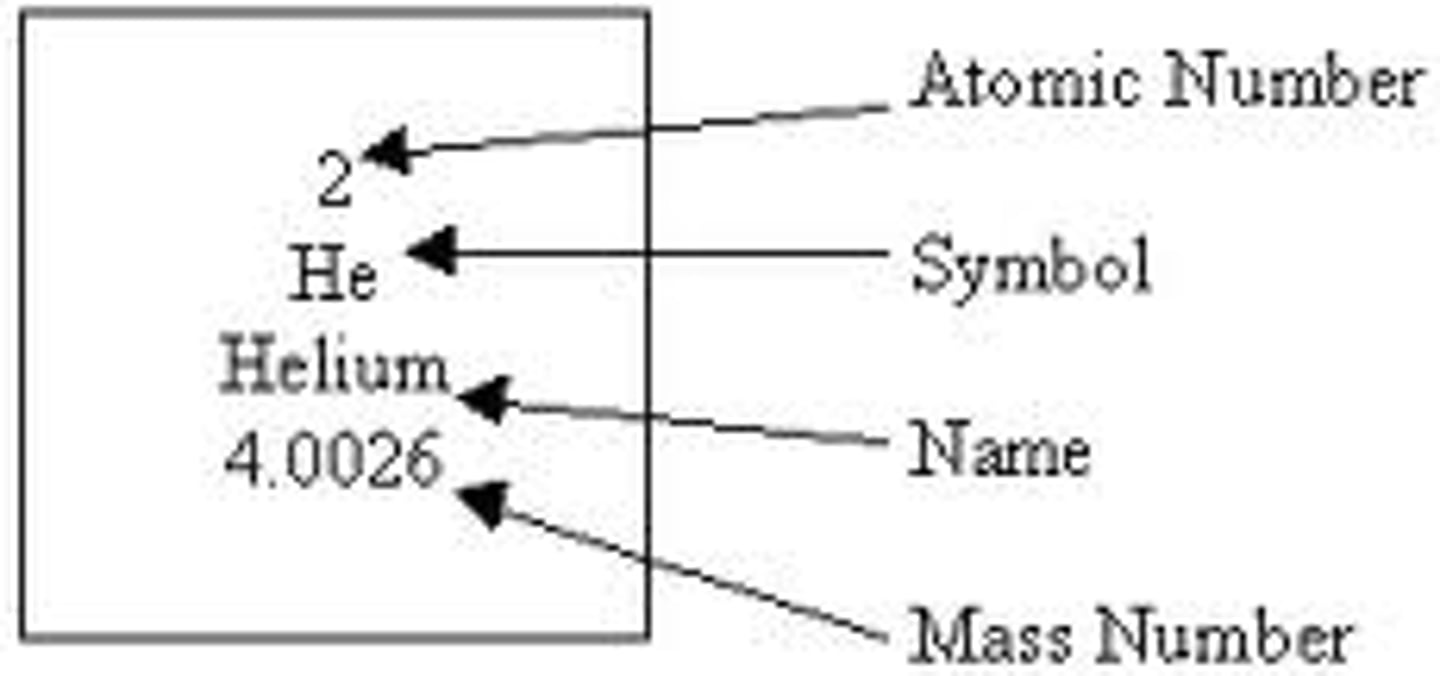
Atomic Mass Number
-The sum of masses of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Given the symbol A.
-Elements can have more than one mass number

Periodic Table
-Each horizontal row in the periodic table is a period
-Each vertical column on the periodic table contains a group
-Group 1A- Alkali Metals
-Group 2A- Alkali Earth Metals
-Transition Elements
-Group 7A- Halogens
-Group 8A- Noble Gases
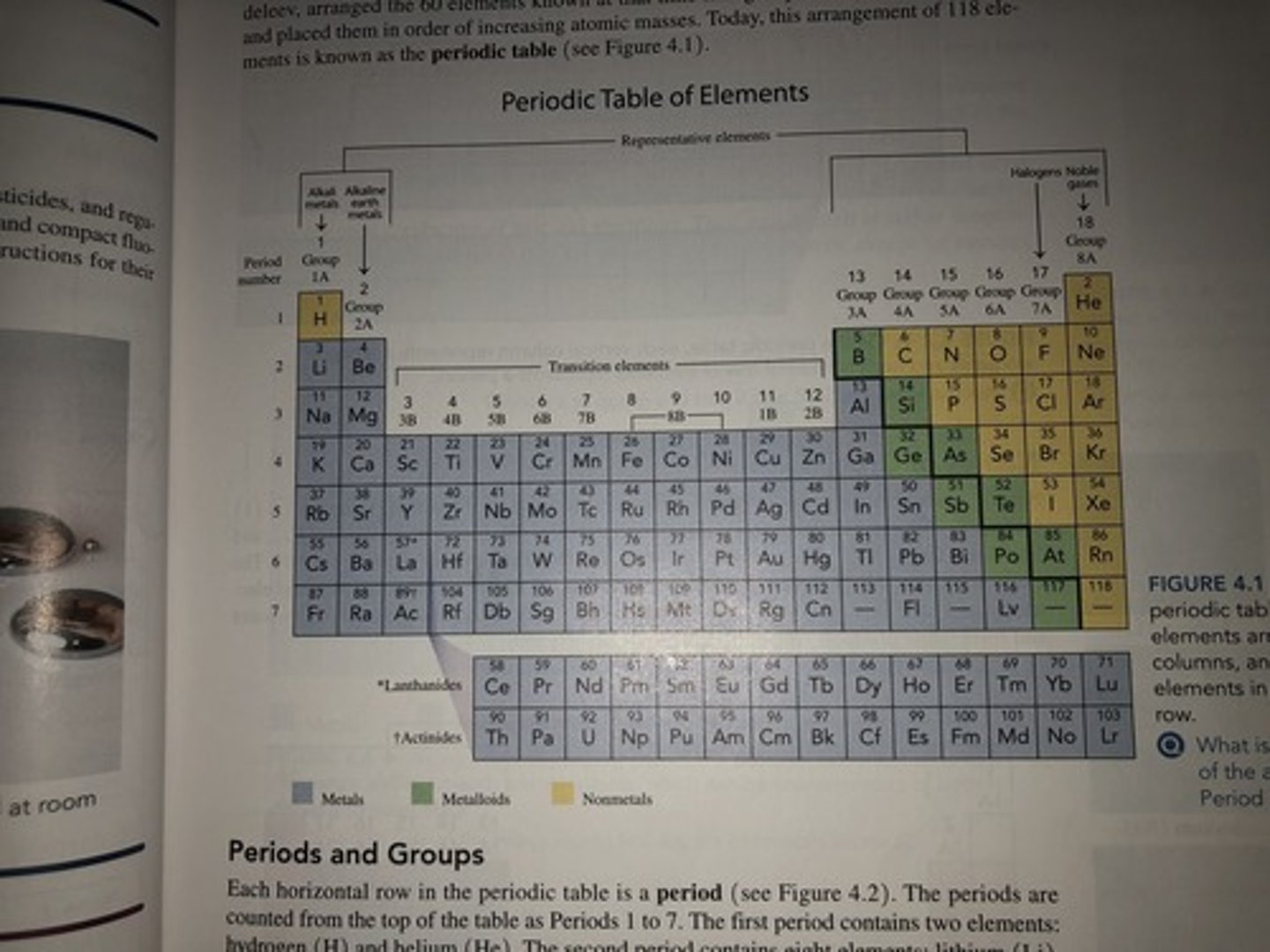
Names of Groups

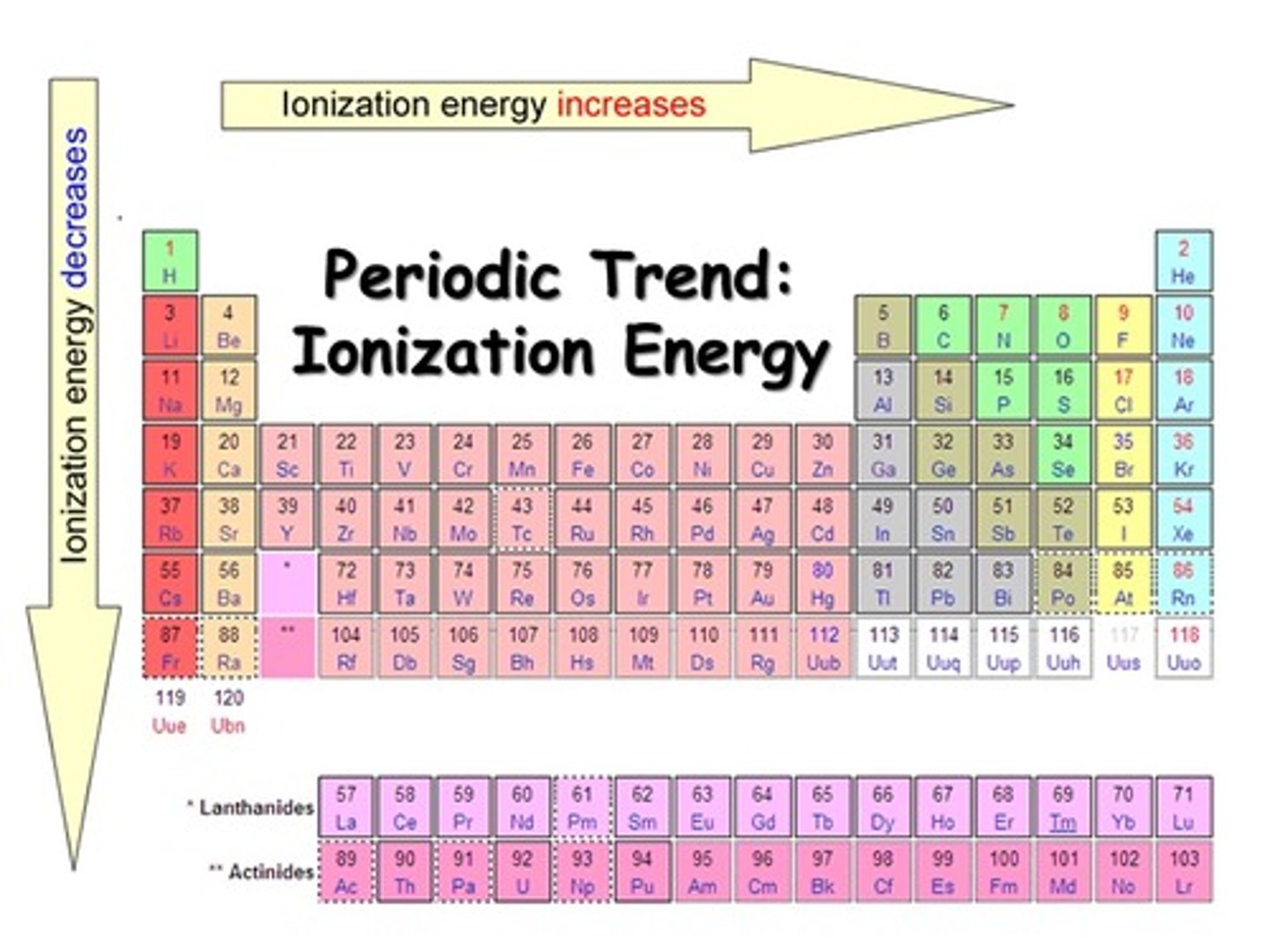
Atomic Size Periodic Trend
-Left to right atomic size decreases
-Top to bottom atomic size increases

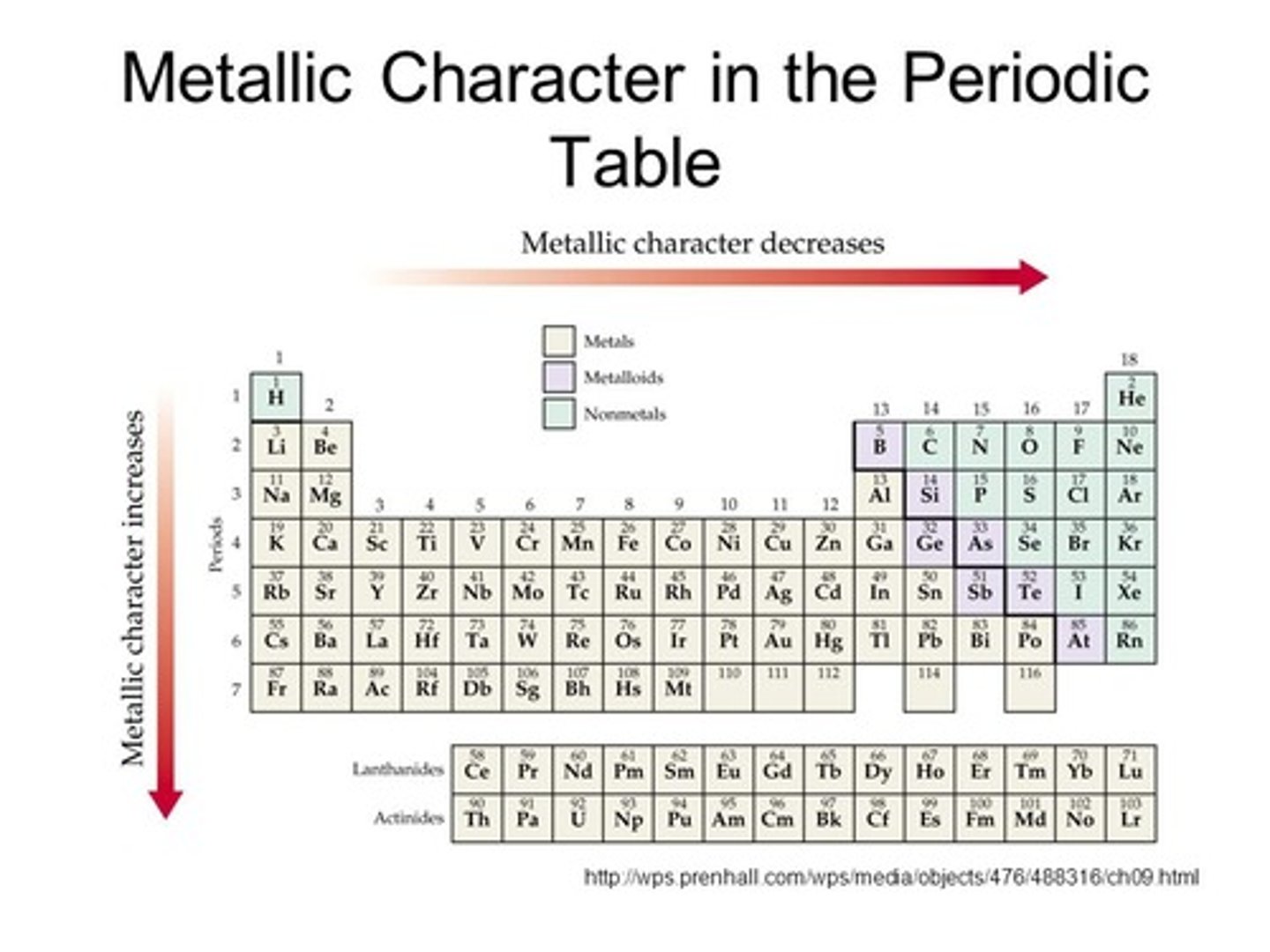
Metallic Character Periodic Trend
-Left to right metallic size decreases
-Top to bottom metallic size increases
Ionization Energy Trend
Energy needed to remove an electron from a metal atom
Compound
-A combination of atoms in a ratio of small whole numbers
-Matter consisting of identifiable units containing elements combined in specific ratios. All of the units are identifiable.
-Ex. Salt, sugar
Molecule
-Smallest unit of a compound
-Composition of a molecule can be represented by a chemical formula (Molecular formula)
-Identifying units of matter consisting of two or more atoms combined in a definite ratio
Molecule of Water
-H2O- Composed of 3 atoms
-2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom
In a chemical formula (Molecular formula), what does the subscript to the right of the elements symbol indicate?
-The number of atoms of that element in the molecule
-Ex. One molecule of PB3 is composed of 4 atoms- 1 atom of phosphorous, 3 atoms of bromine
Metals
Solid
Non-metals
May be solid, liquid, or gas
Diatomic Molecules
-Exist as two atom entities
-Ex. Hydrogen- H2, nitrogen- N2, oxygen- O2, and the halogens
Chemical Bond Formation
Result of the loss, gain, or sharing of electrons between atoms
What will atoms do in order to form a noble gas configuration?
Lose, gain, or share electrons
Ionic Bonds
-Bonds resulting from the attraction between a cation (+) and an anion (-)
-Valence electrons of atoms of a metal are transferred to atoms of non-metals
-Ex. NaCl
-Ex. AlN
Covalent Bonds
-Bonds resulting from the sharing of electrons between two non-metals
-Atoms of non-metals share valence electrons
-Ex. Cl2
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond
Ionic Compounds
-Compounds formed from a metal and one or more non-metals
-Metals lose electrons to form ions with a positive charge (Cation)
Ca+2
Means the Ca lost 2 electrons
F-
Means the F gained 1 electron
Naming Positive Ions
-Name of metal plus the word ion
-Ex. Al+3 - Aluminum ion
-Ex. Na+ - Sodium ion
Naming Negative Ions
-Monotomic negative ions are named by adding the suffix -ide to the stem of the name of the non-metal
-Ex. O-2 - Oxide ion
-Ex. Cl- - Chloride ion
Polyatomic Ions
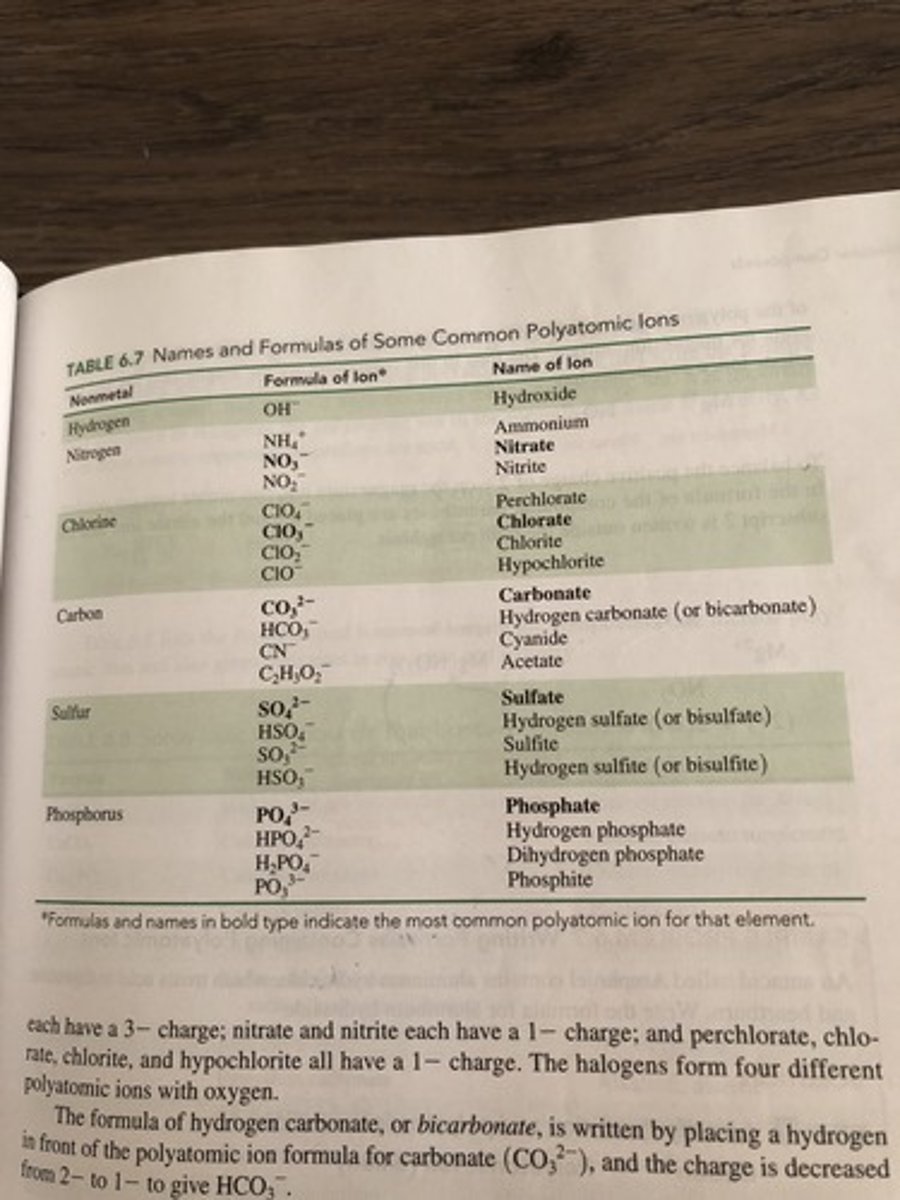
Oxyanions
Polyatomic ions containing oxygen with the greatest number of oxygen atoms are given the -ate suffix. The small number gets -ite.

Covalent Compound
Molecules that are combinations of non-metals
What type of compound has no ions?
Covalent compound
Naming Covalent Compounds
-The first non-metal in the formula is named by its elemental name
-The second non-metal is named by its elemental name with the ending -ide
-The number of atoms of the given element is designated with a prefix such as di, tribute, tetra, penta
-Ex. NF3 - Nitrogen trifluoride
-Ex. N2O - Dinitrogen oxide
Polar Covalent Bonds
-Shared electrons between atoms are not equally shared
-Occurs when one atom has a higher electronegativity than the atom it is sharing with
-Dipole
Non-polar Covalent Bonds
Atoms share their electrons equally
Electronegativity
-Ability of an atom (Within a molecule) to draw electron density to itself
-The greater the electronegativity the greater the ability of atoms to draw electrons to themselves
What can be used to determine if an element is polar or non-polar?
Electronegativity
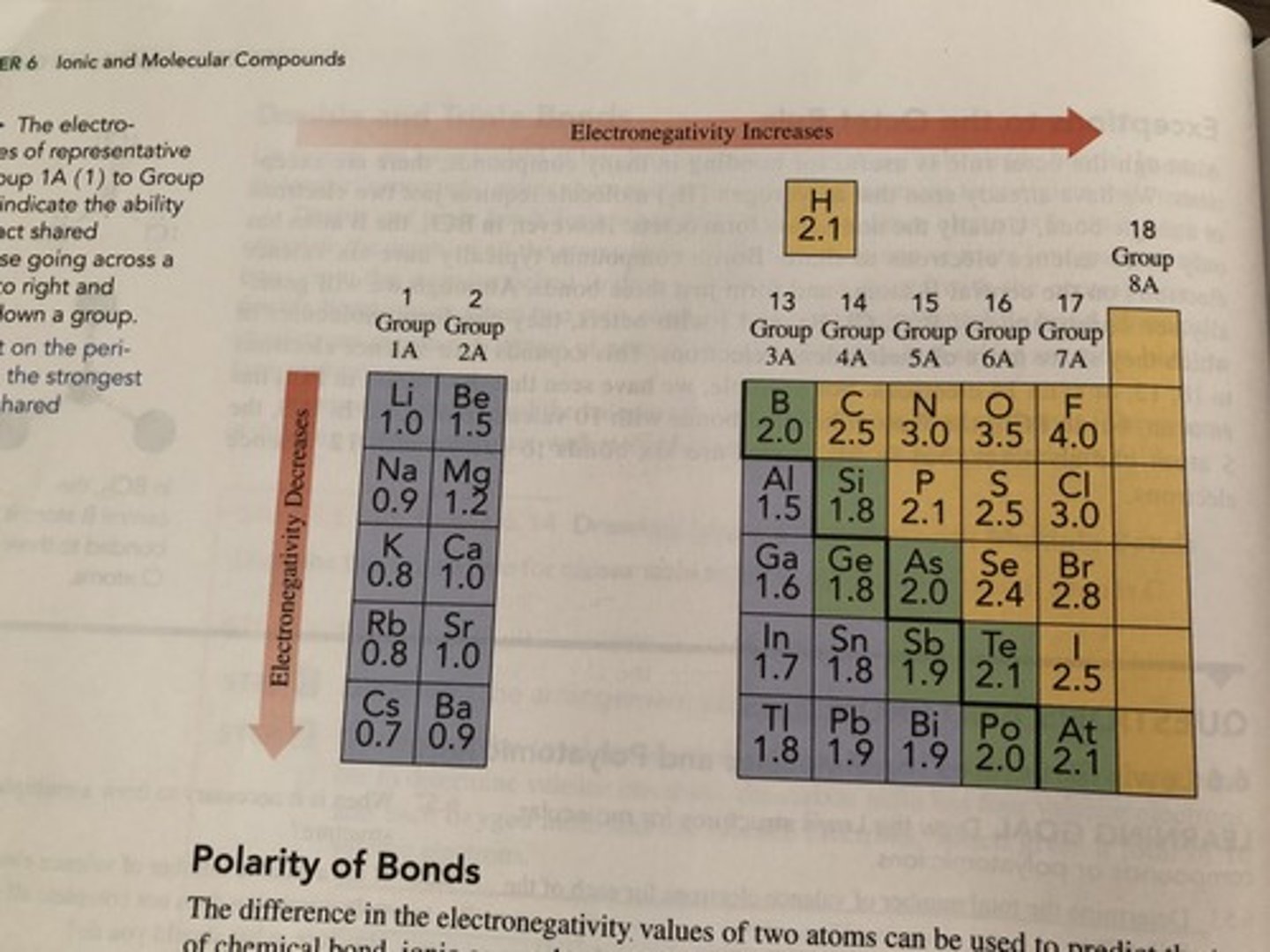
Between 0-0.4
Non-polar covalent bond
Between 0.4-1.7
Polar covalent bond