DSAE 1415 Exam 1 Study Materials with Key Terms and Definitions
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Anaechoic
These areas appear black on ultrasound because they do not send back any sound waves.
Hypoechoic
structure appears darker than surrounding structures.
Hyperechoic
These areas bounce back many sound waves. They appear as light gray on the ultrasound.
focus
Adjusts shape and width of the ultrasound.
Narrower width results in better lateral resolution
Automatic and manual settings
Total gain/TGC
adjusts brightness of the image equally through out the Frame of view
zoom provides:
better resolution
Frame rate
changes sector size.
makes the image more narrow, the more narrow the better the details
Decrease depth, decrease sector size, decrease number of focal zones, use preprocessing zoom.
Medical ultrasound frequency:
2 MHz to 20 MHz
Adult transthorasic echo (TTE) transducer frequency range:
2 - 5 MHz
transducer frequency range for TTE
2-12 MHz
Pediatric TTE
3.5 to 5.0 MHz
Neonates TTE
7.0 MHz or higher
Motion mode echocardiography (M-mode)
one dimensional view.
curser lines passes through and displays on a graph
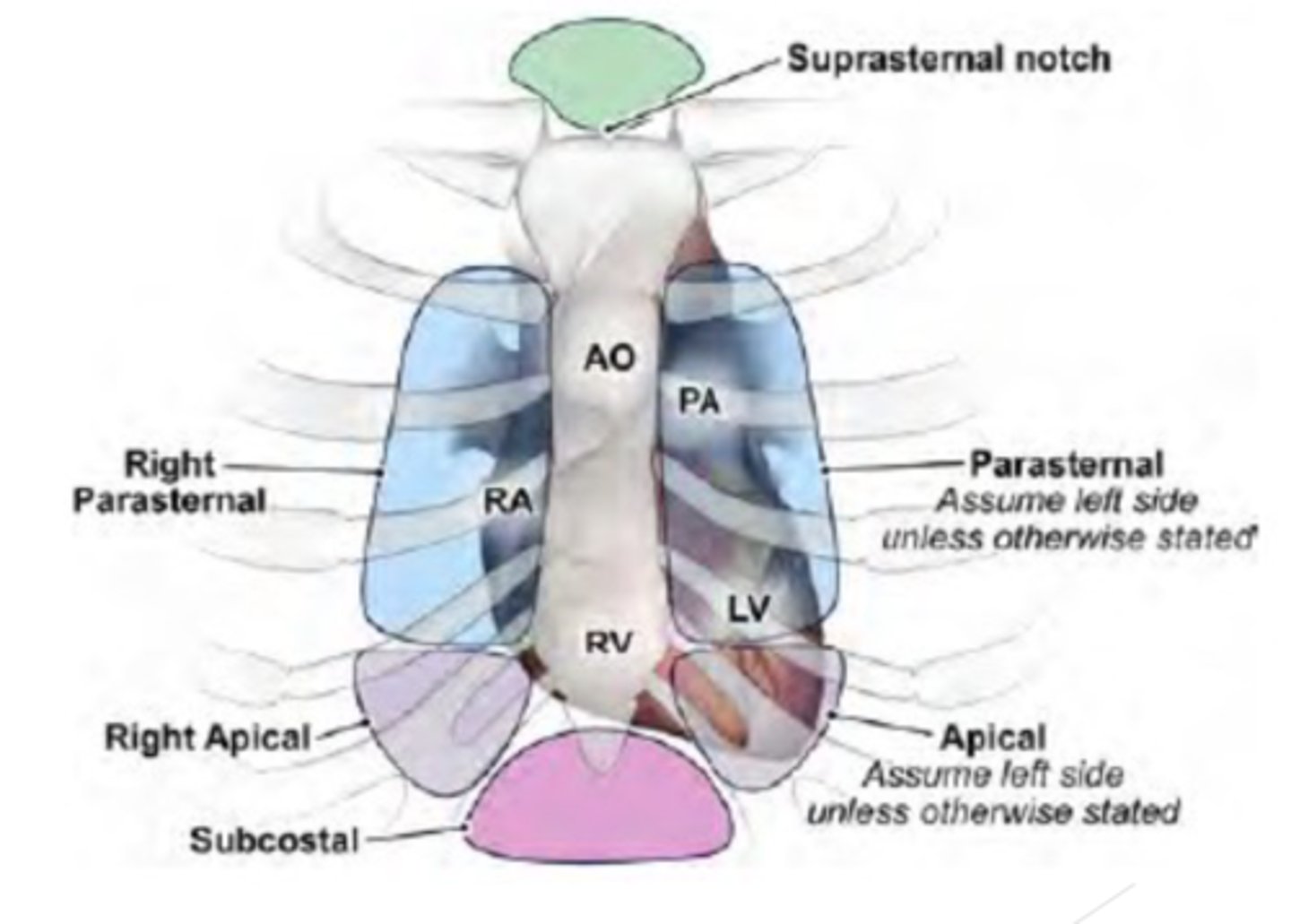
Acoustic Windows
transduce placement on special positions on the chest to image the heart through the chest wall
what are the Main acoustic windows:
Parasternal (right & Left)
Apical
Subcostal
Suprasternal
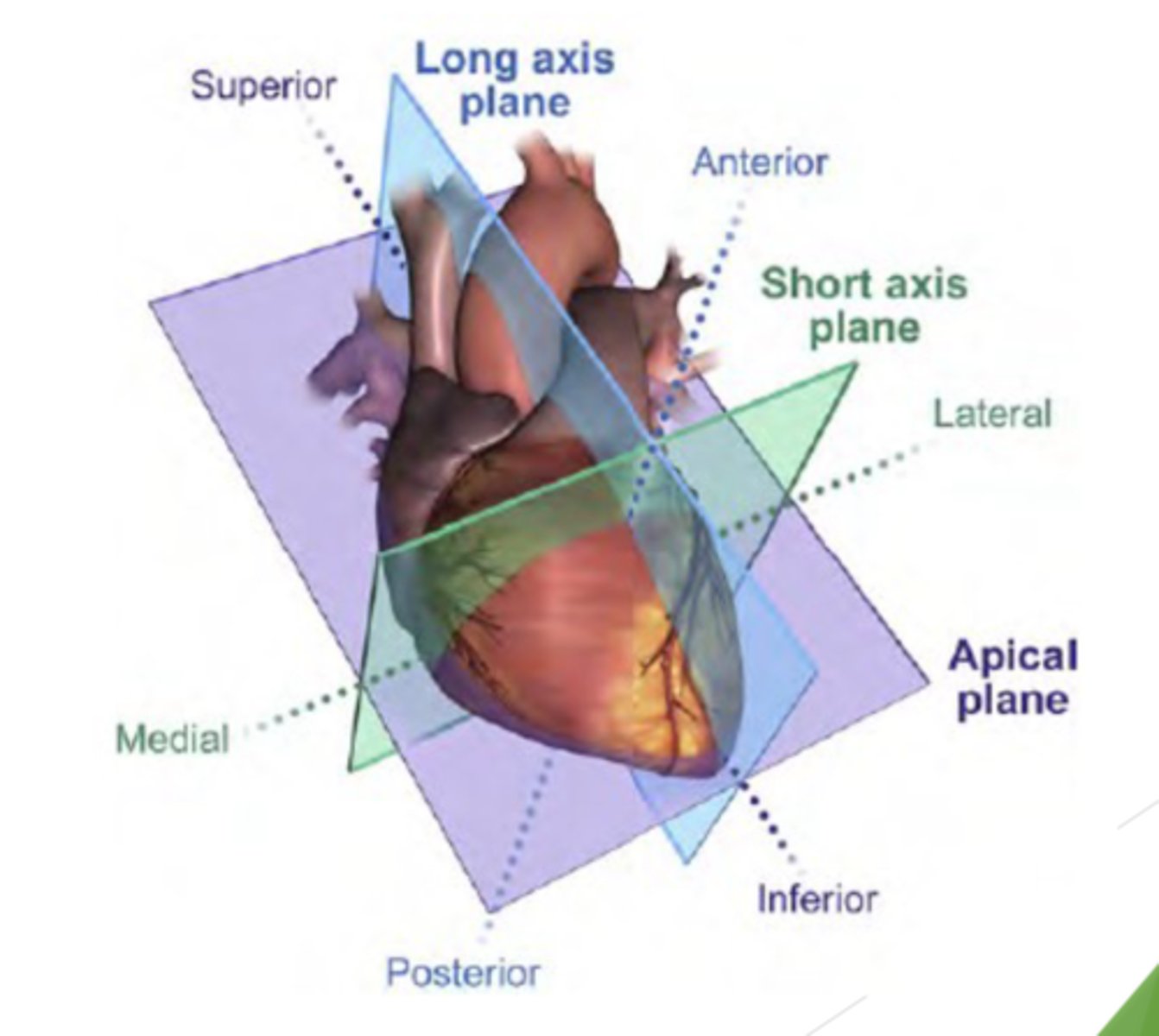
Three imaging planes:
Long axis plane (LAX) divides the heart into left and right
Short axis plane (SAX) divides the heart into inferior and superior portion (perpendicular to above plane)
Apical or 4 chamber plane -runs parallel to anterior andposterior surfaces and divides the heart into four chambers
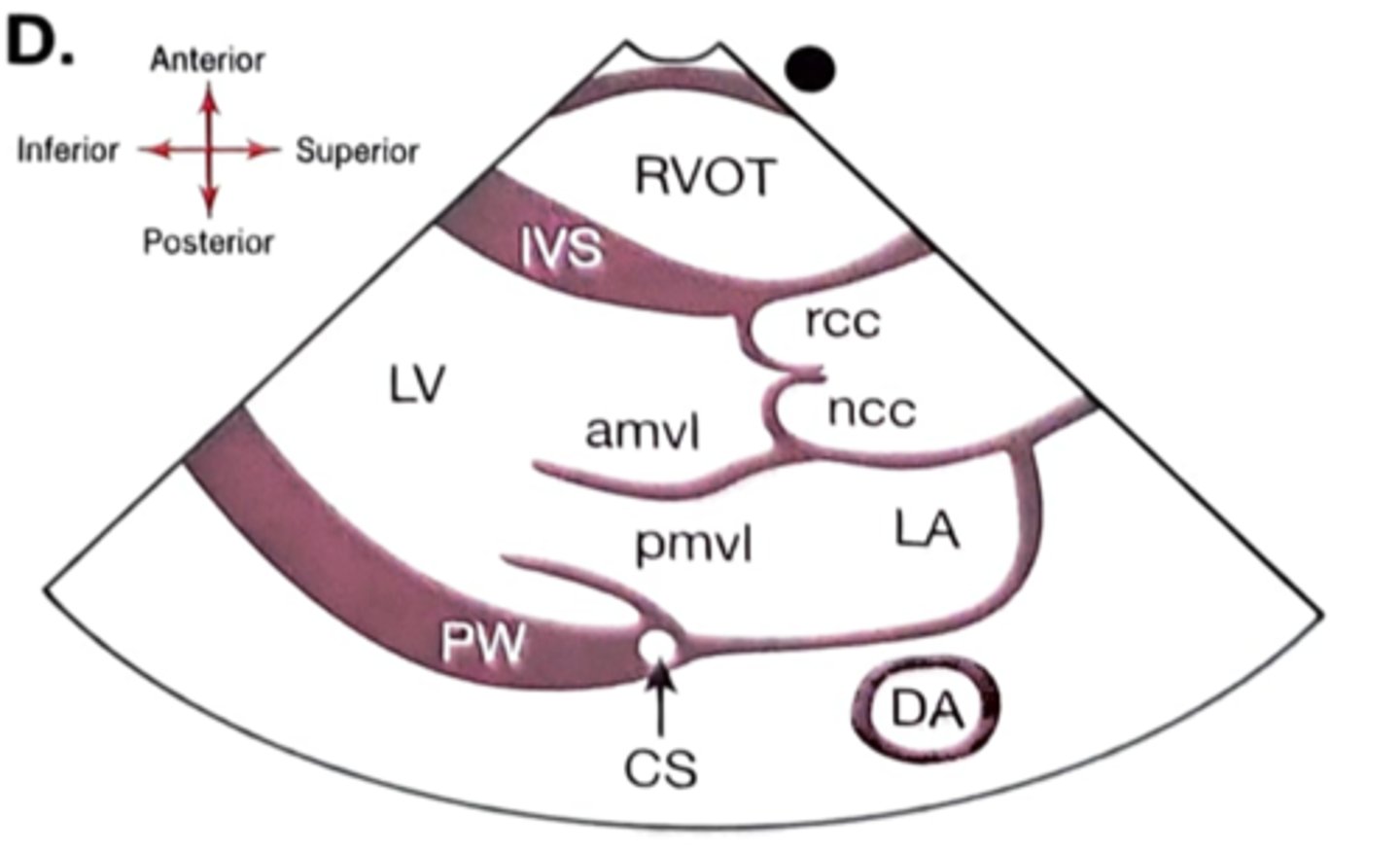
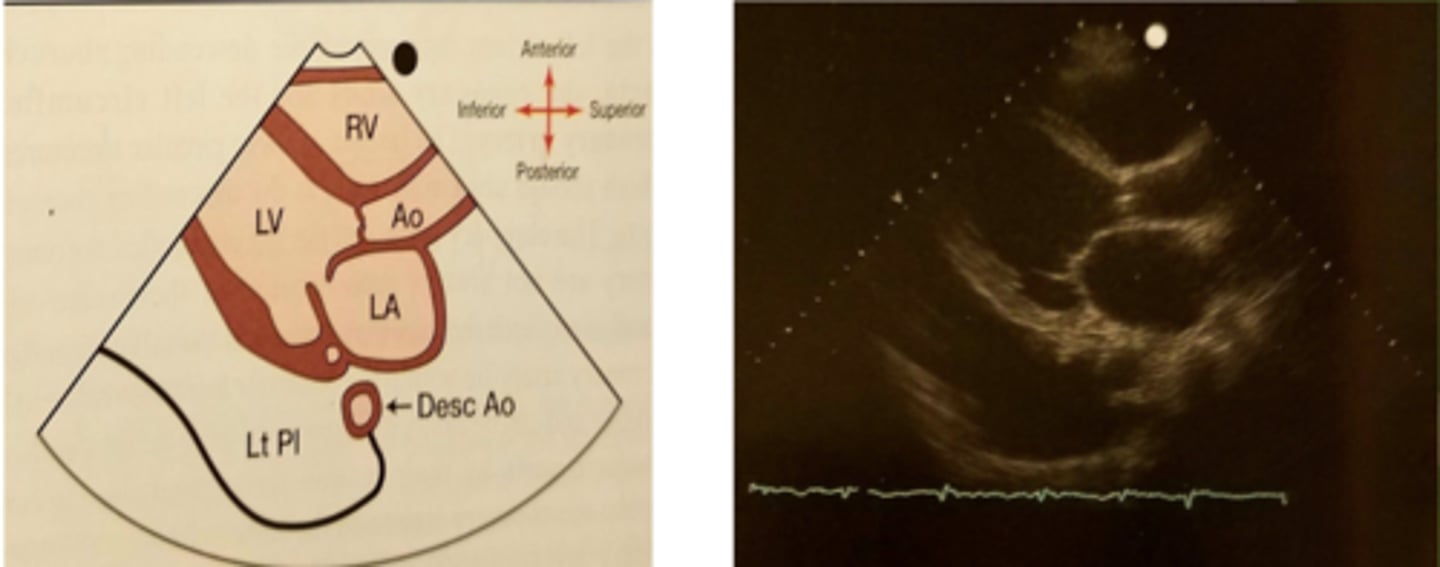
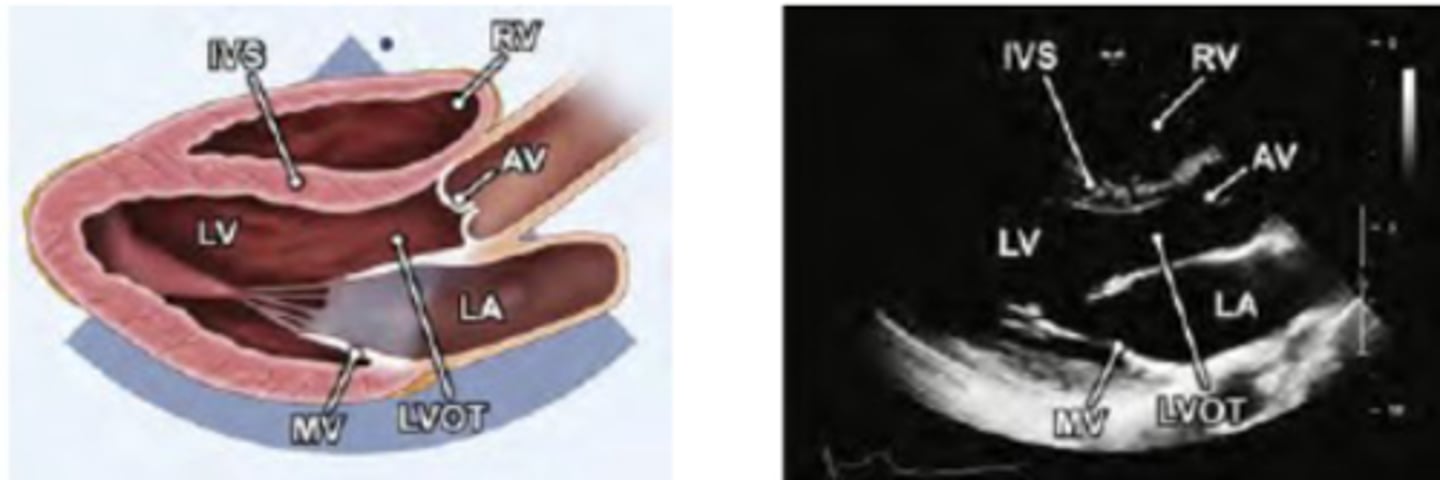
Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX) shows:
RV-right ventricle
LV-left ventricle
LA-left atrium
AV -aortic valve
MV-mitral valve
LVOT-left ventricular outflow tract
AO -aorta
IVS-interventricular septum
PW-posterior wall
DAO - Descending aorta
CS- Coronary sinus
PLAX optimized: Arties that can be seen
DA, CS and LCX
mostly the DA is seen
PLAX: Anterior structures are seen..
top of the image
ex: RA and chest wall
PLAX: posterior structures are seen..
seen at the bottom of the image
EX: posterior LV wall
PLAX: superior structures are seen..
seen to the right of the image
EX: aorta and LA
PLAX: inferior structures are seen..
seen to the left of the image
EX: apex
PLAX: If the LV apex is seen, the probe is rotated too far clockwise or the probe is too low on the chest wall
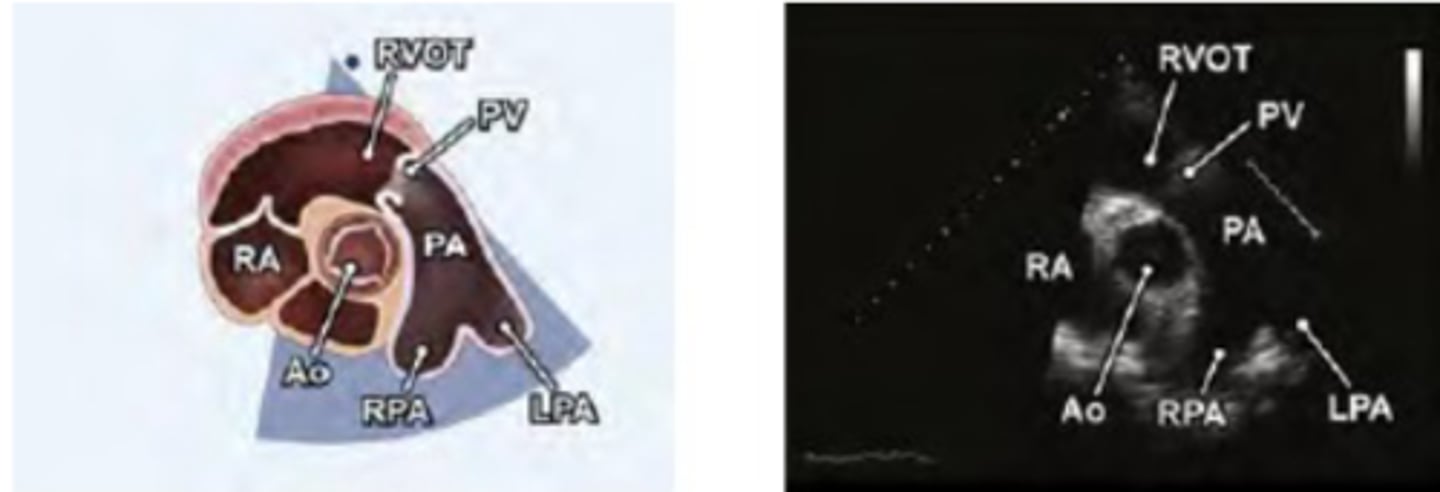
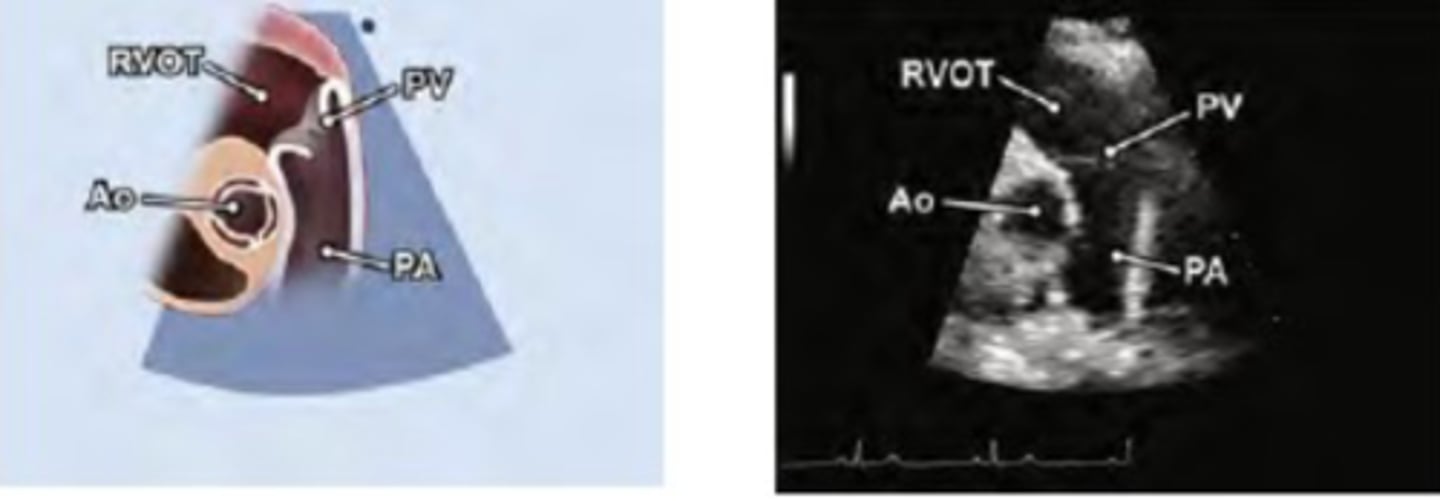
right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT)
PV-pulmonary valve (right and left leaflets)
PA-pulmonary artery.
*tilt face superior
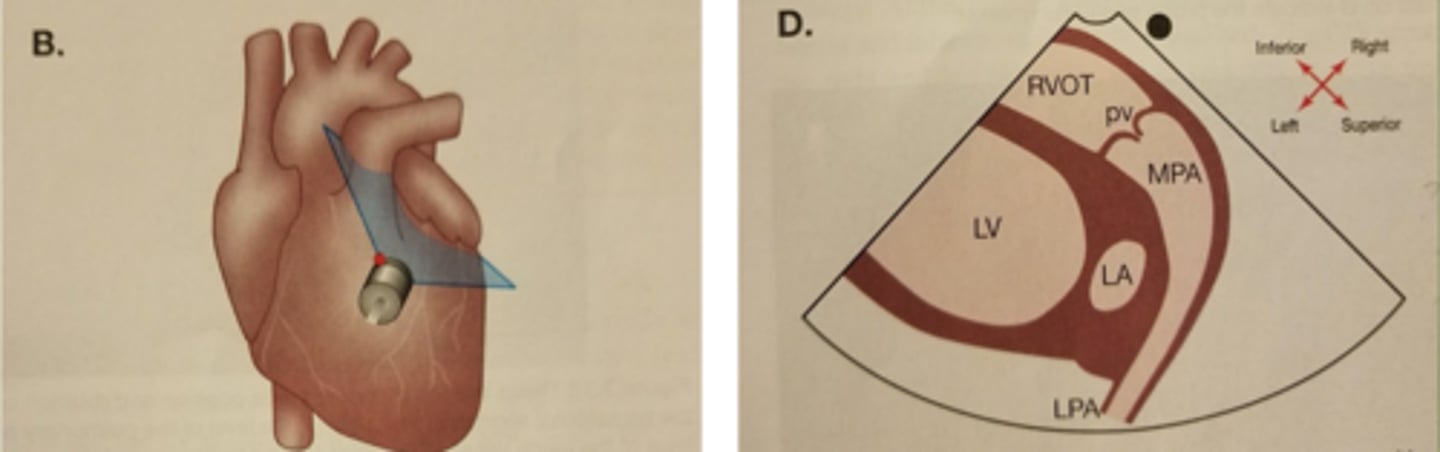
RVOT: inferior structure are seen..
towards the top left
EX: RVOT
RVOT: superior structures are seen..
towards the bottom right
EX: MPA
RVOT: right sides structures are seen..
top right
RVOT: left sides structures are seen...
bottom left
EX: LV
Right Ventricular Inflow Tract (RVIT)
TV- tricuspid valve (leaflets: ATVL & PTVL)
RV -right ventricle
MB-moderator band
RA-right atrium
CS-coronary sinus
IVC-inferior vena cava
ER- eustation ridge
*Tilt face inferior
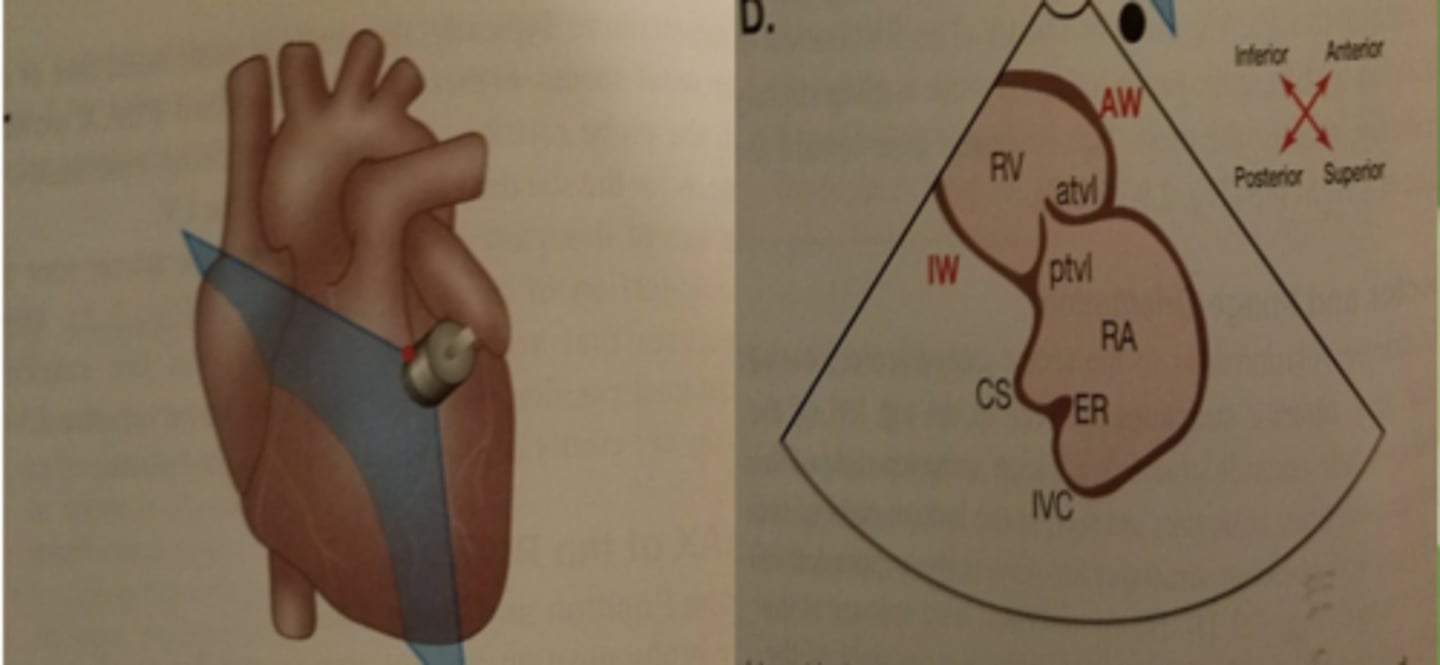
RVIT: inferior structure are seen..
top left of the image
Ex: RV
RVIT: anterior structures are seen..
top right of the image
RVIT: superior structures are seen..
bottom right of the image
Ex: RA
RVIT: posterior structures are seen..
bottom left of the image
LAX views
views of the heart obtained from the parasternal and apical windows
decides the heart into left and right
SAX views
views of the heart obtained from the parasternal and subcostal windows
divides heart into inferior (lower) and superior (upper) sections
views of the heart obtained from the apical and subcostal windows:
4-chamber views of the heart
angulation: is:
side to side swinging of the probe on the chest
High Parasternal Window (high PLAX):
used To assess ascending aorta
Probe is positioned one or two intercostal space higher than the standard PLAX position
Aim is to demonstrate the aortic root and long axis of ascending aorta
Pericardial effusion
when excess fluid builds up in the pericardial sac around the heart
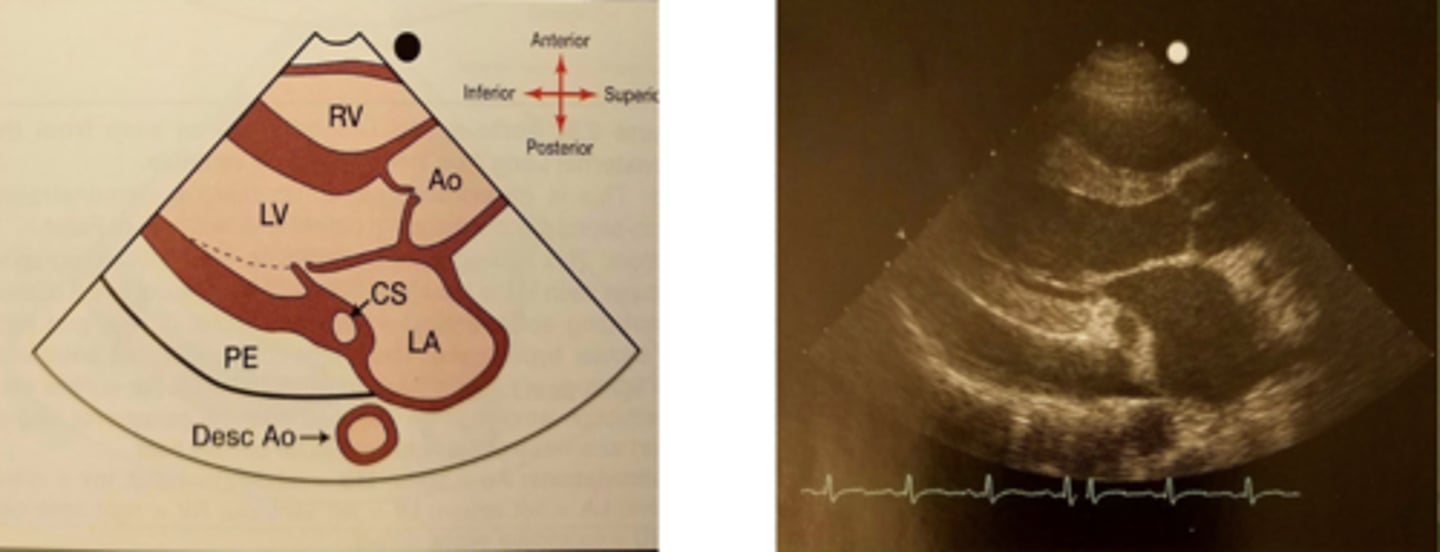
Pleural effusion
A buildup of fluid between the tissues that line the lungs and the chest.
RVIT
TV (anterior and Posterior leaflets)
*NO LV
Deep PLAX
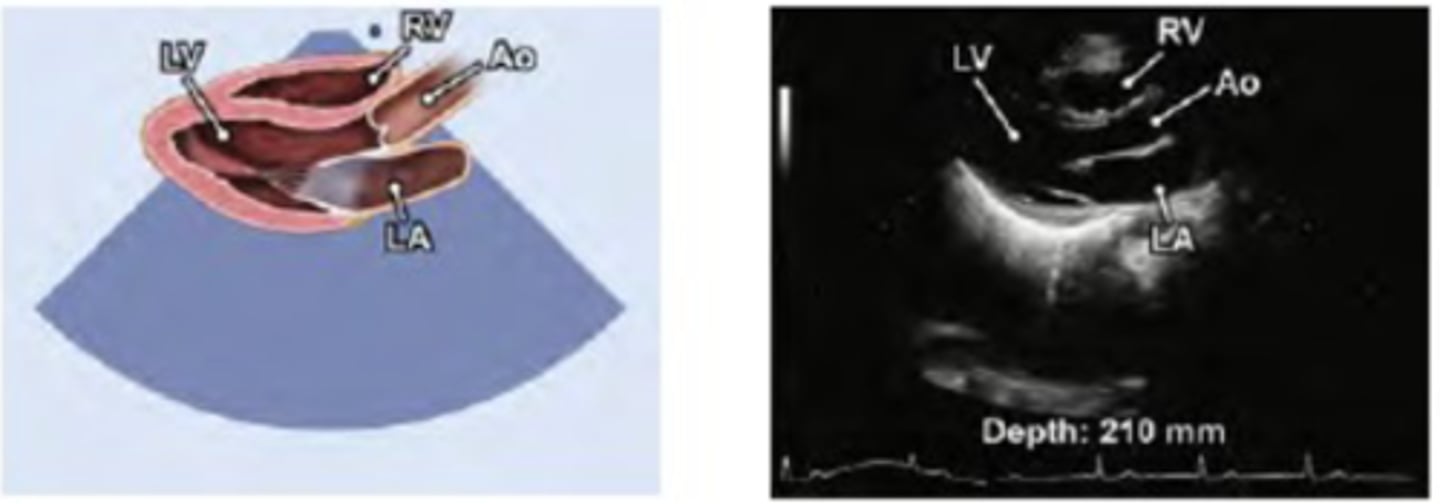
optimized PLAX
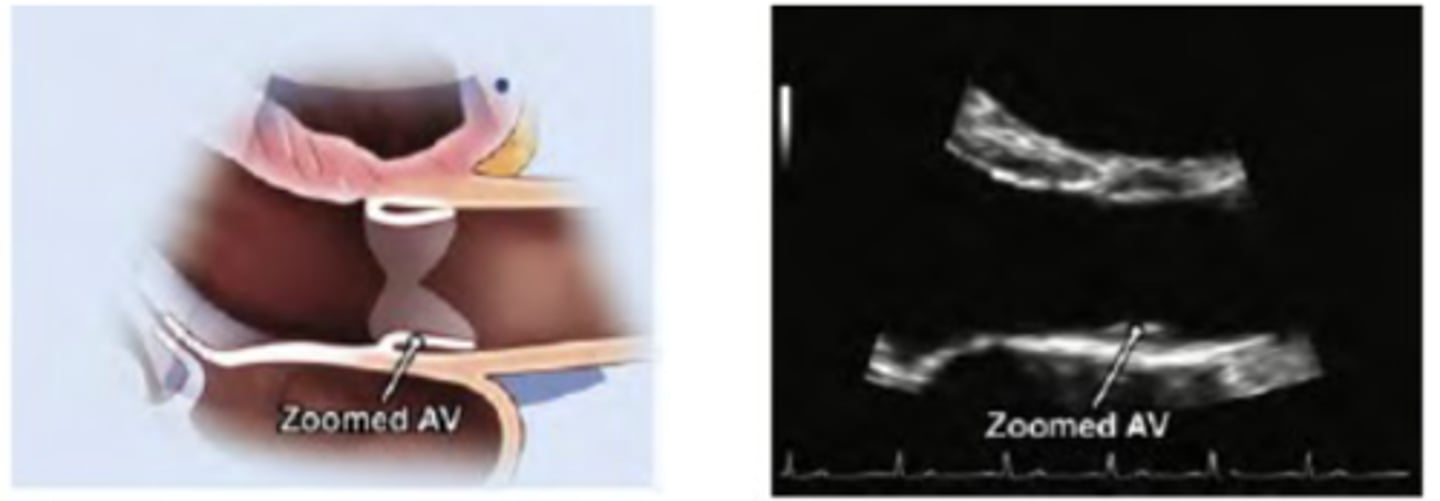
Zoomed AOV
be able to see AO root and arch
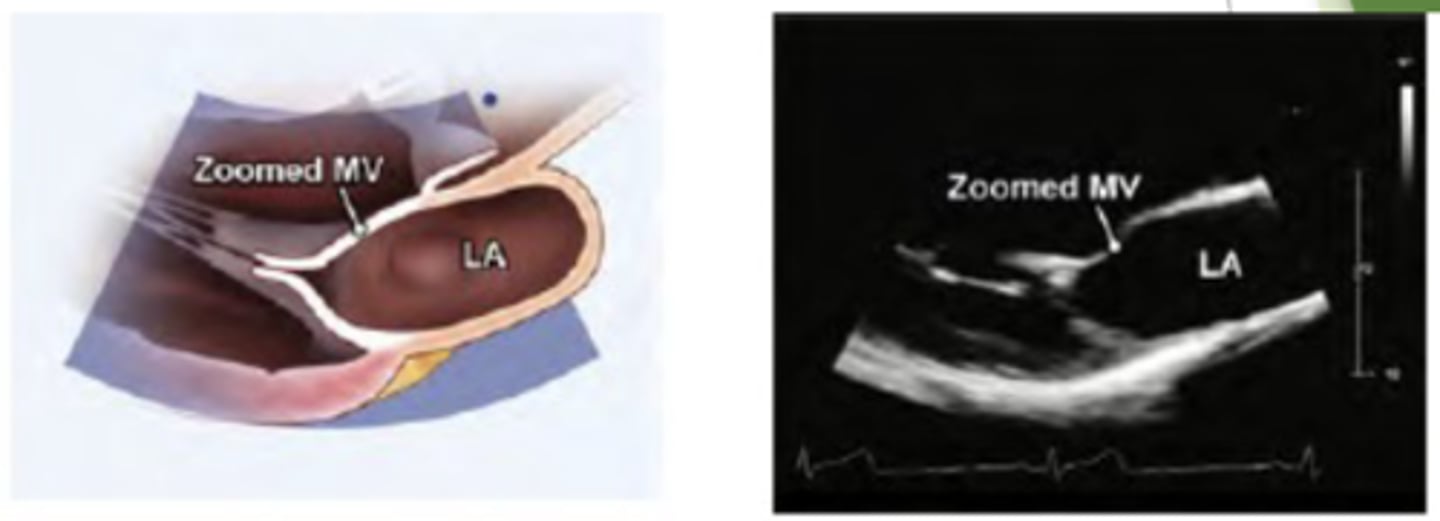
Zoom MV and AV
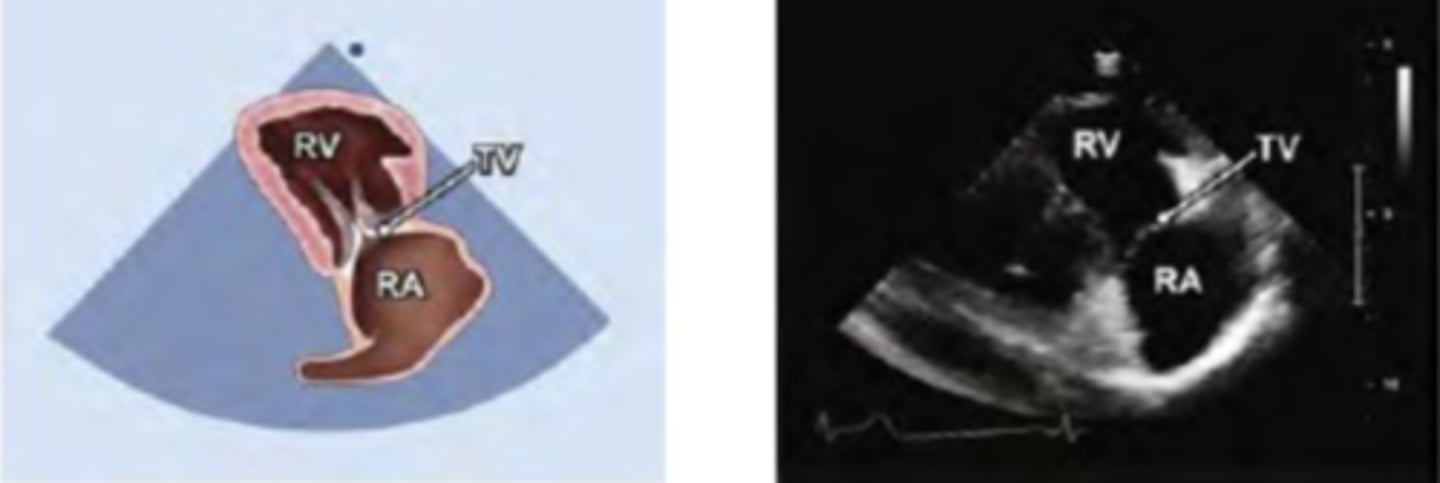
RVIT
RVIT
TV (anterior and Posterior leaflets)
*NO LV view should be in image
Why does echo not use a higher frequency when scanning?
a higher frequency = lower penetration
-produces a good resolution but cannot go through the body very well
When is high frequency used during echo?
a high frequency is used when scanning babies because of their small size
the sound waves do not have to penetrate through much (babies have small bodies)
low frequency transducer produces:
decreased resolution but improves depth
high frequency transducer produces:
increased resolution but decreases depth
low frequency yields
high penetration & bad resolution
newborns are scanned with
7 MHz transducer
sweep
Multiple movements are used to record a long video clip or showmultiple anatomic structures
modalities of echocardiogram
1. 2D echo
2. M-mode (motion mode) echo
3. Doppler echo (color flow and spectral)
4. 3D
5. 4D
depth
maximum distance into the body that an ultrasound system is imaging
TTE
transthoracic echocardiogram
two dimensional echo (2D echo):
real time
black and white
cardiac vessel and anatomy functions and dimensions
frame rate:
number of images per second
temporal resolution
systems ability to detect a structure has moved over time of distinguish between rapidly moving structures
harmonic imaging
the creation of an image from sound reflections at twice the frequency of the transmitted sound
helpful with obese patients
Parasternal Long Axis - Systole
AOV opens, blood flows LV-> AO
Parasternal Long Axis - Diastole
MV opens, blood flows LA -> LV
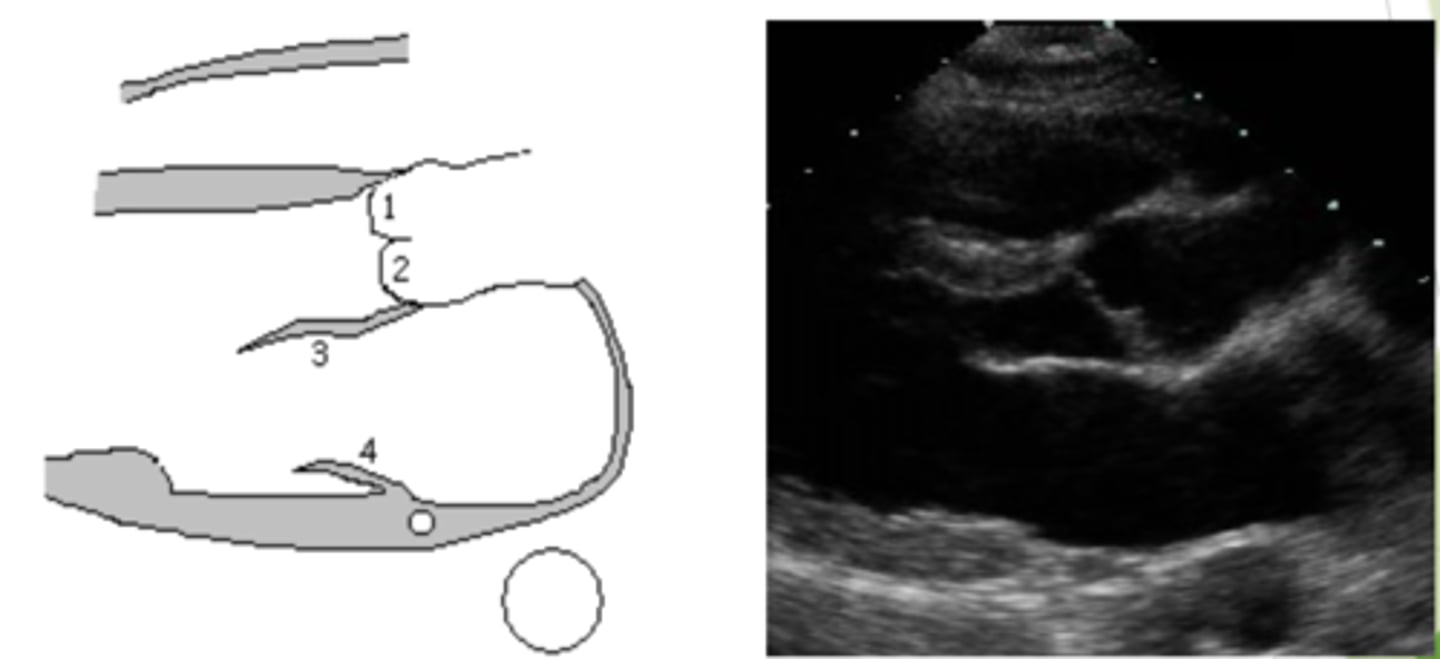
RVIT: chiari network
thin web-like fenestrated membrane off the IVC
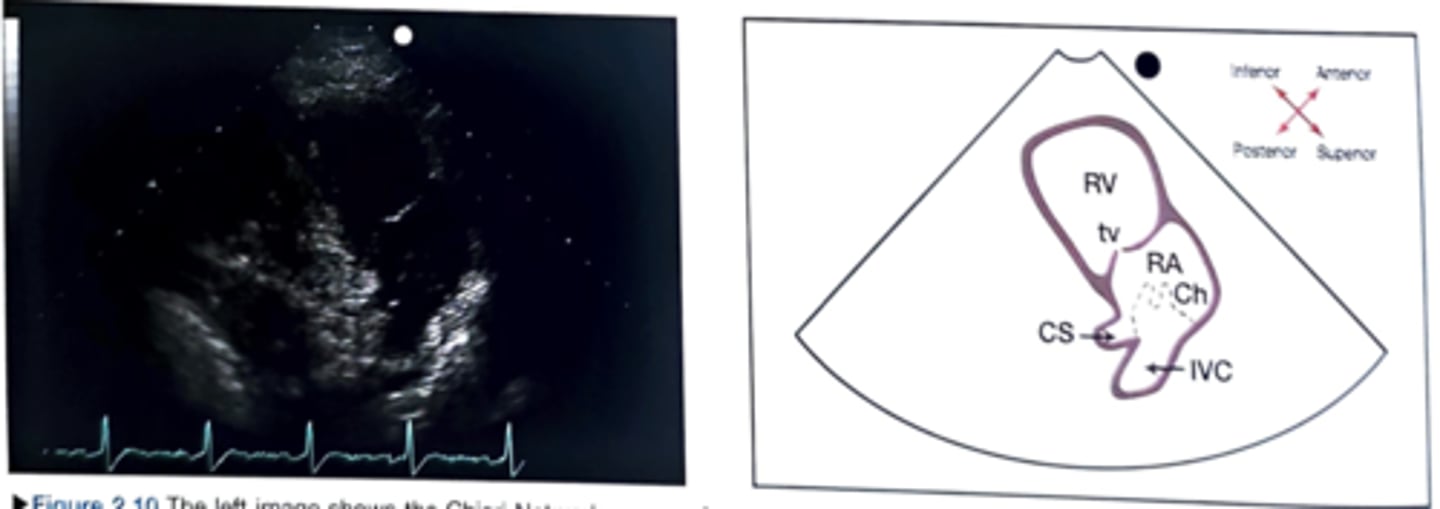

ONLY view to see posterior leaflet of TV
RVIT
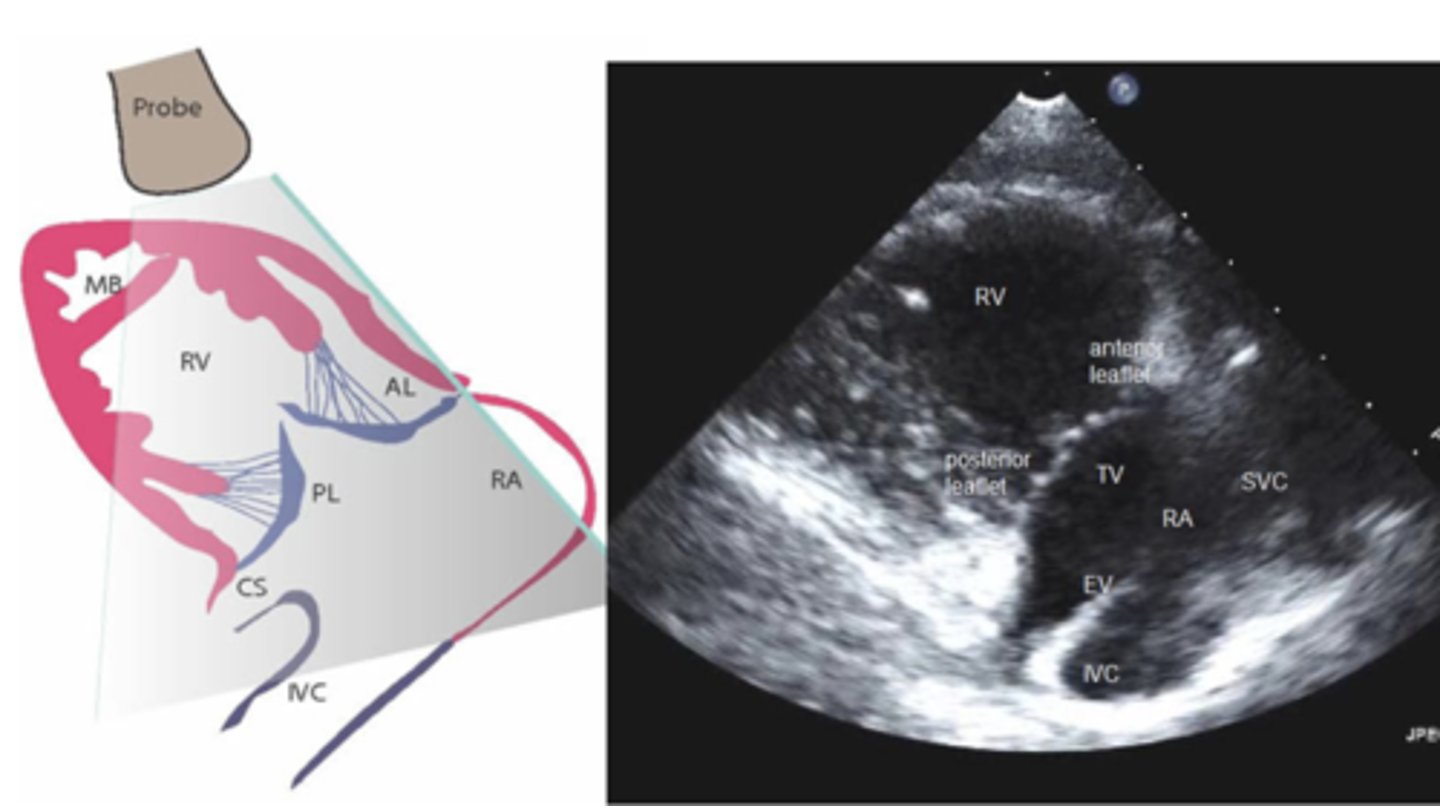
the index marker is pointing towards the patients left, subclavicular fossa (at 1 o clock)
PSAX orientation
5 PSAX images
1. PA
2. PSAX AV, LA
3. PSAX LV, MV
4. LV papillary muscles
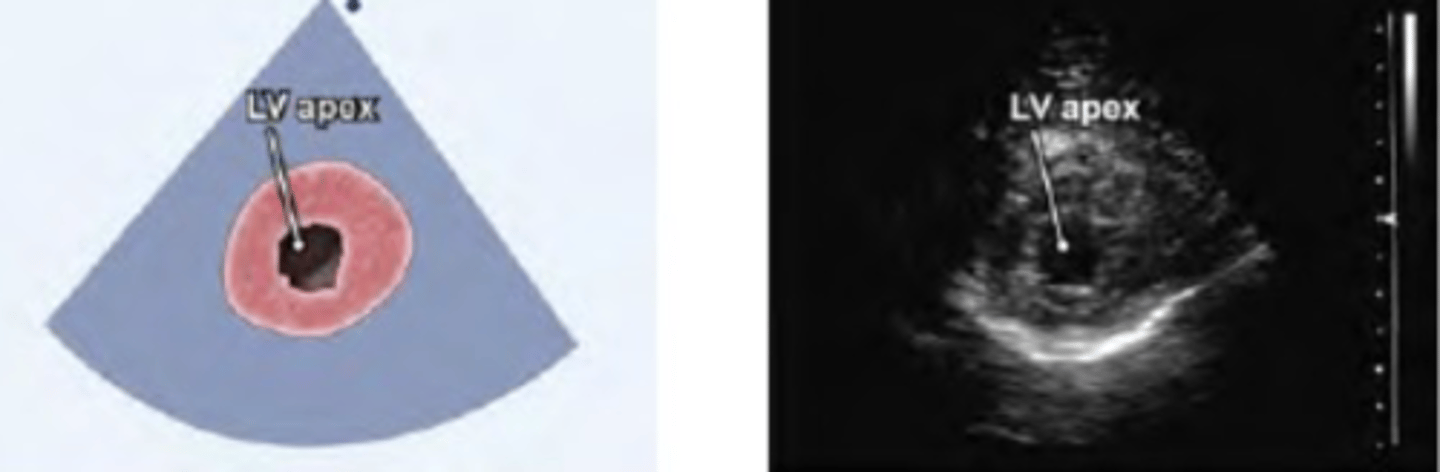
5. PSAX LV apex
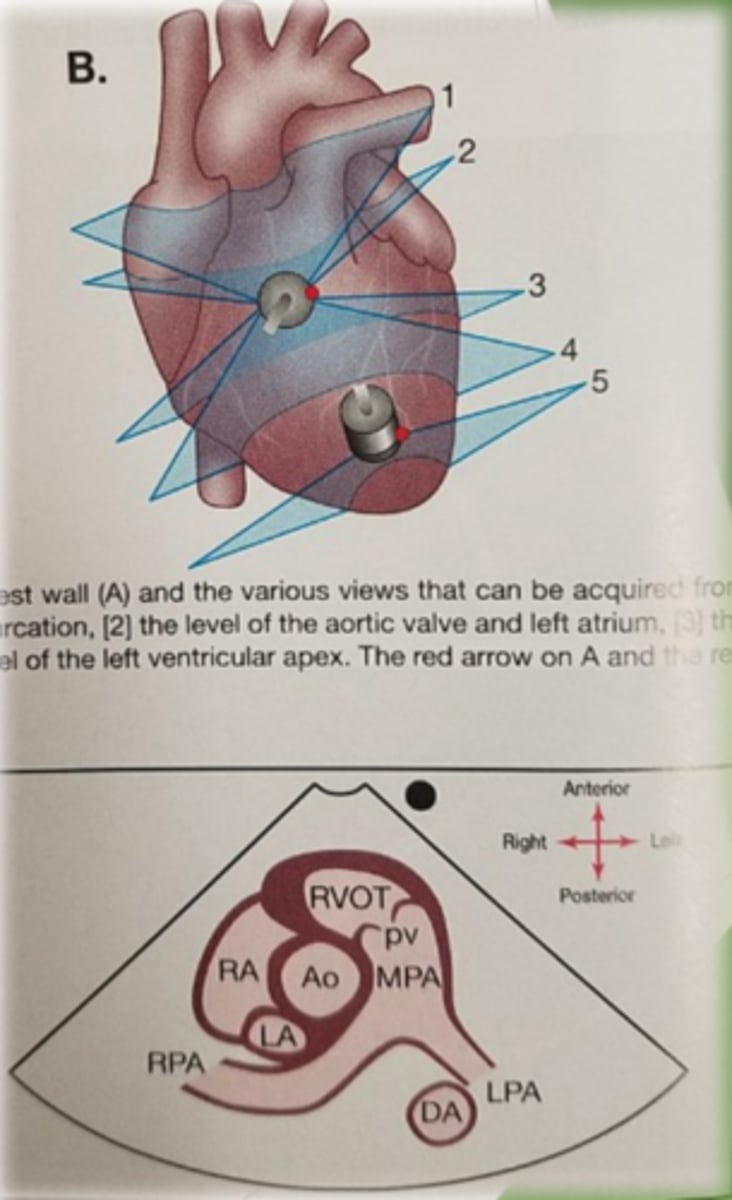
PSAX PA level
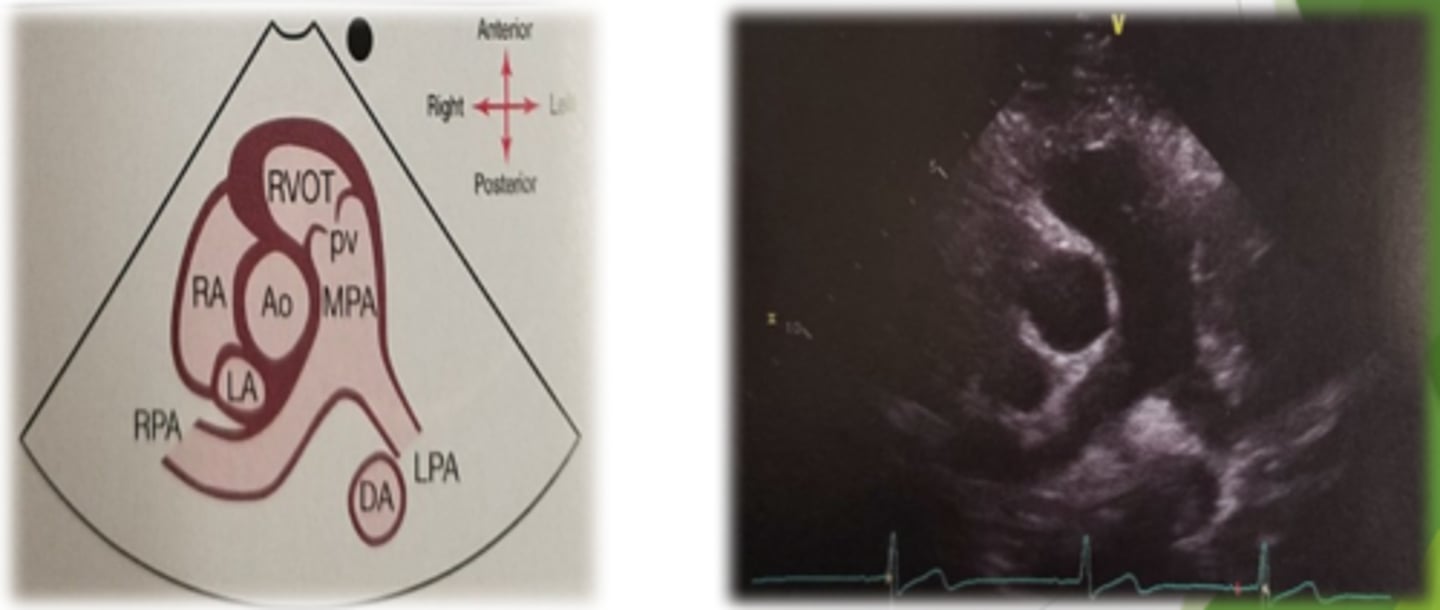
PSAX: aorta level structures
Aortic leaflets
Pulmonary leaflets
Main pulmonary artery
Tricuspid leaflets
IVC, coronary sinus
LA, LAA
Pulmonary veins
IAS (dropout artifact)
Descending aorta
PSAX at AV level
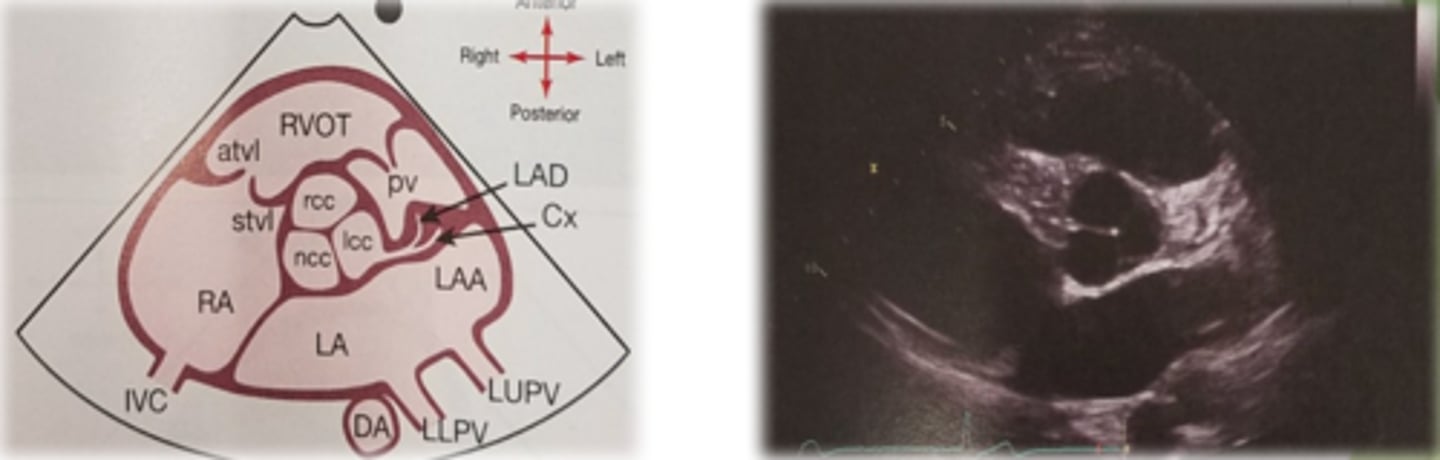
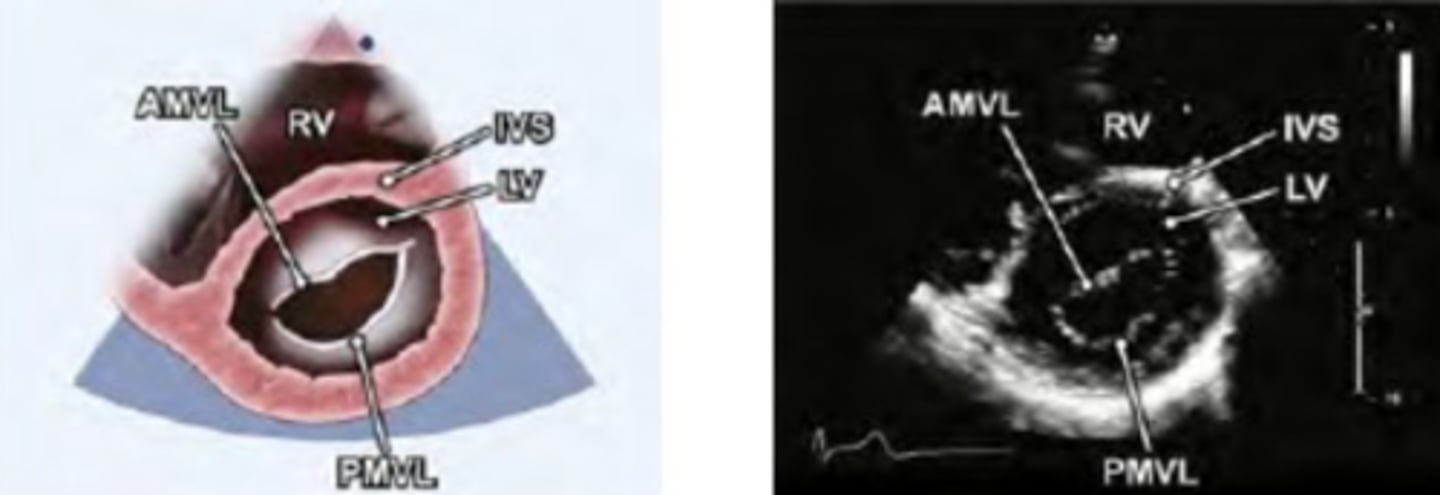
PSAX LV at mitral level
Portion of RV-crescent shaped
LV-identify the walls
Diastole and systole
AMVL, PMVL (fish mouth appearance, Commissures seen)
PSAX LV at mitral level
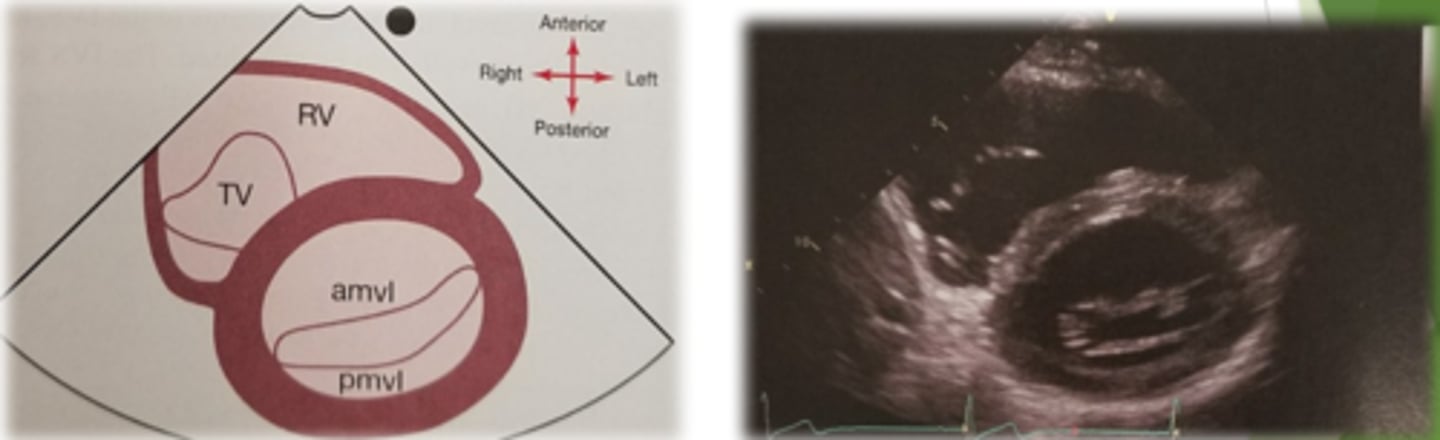
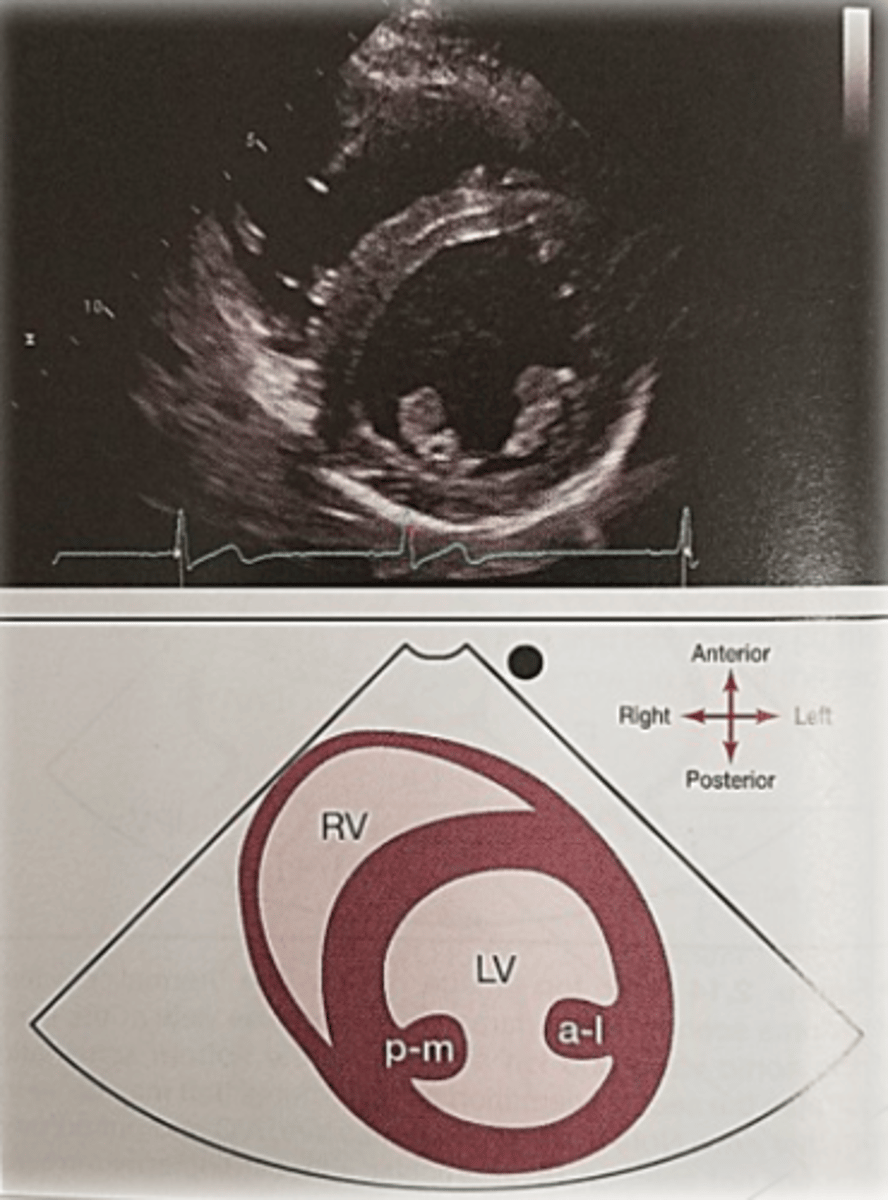
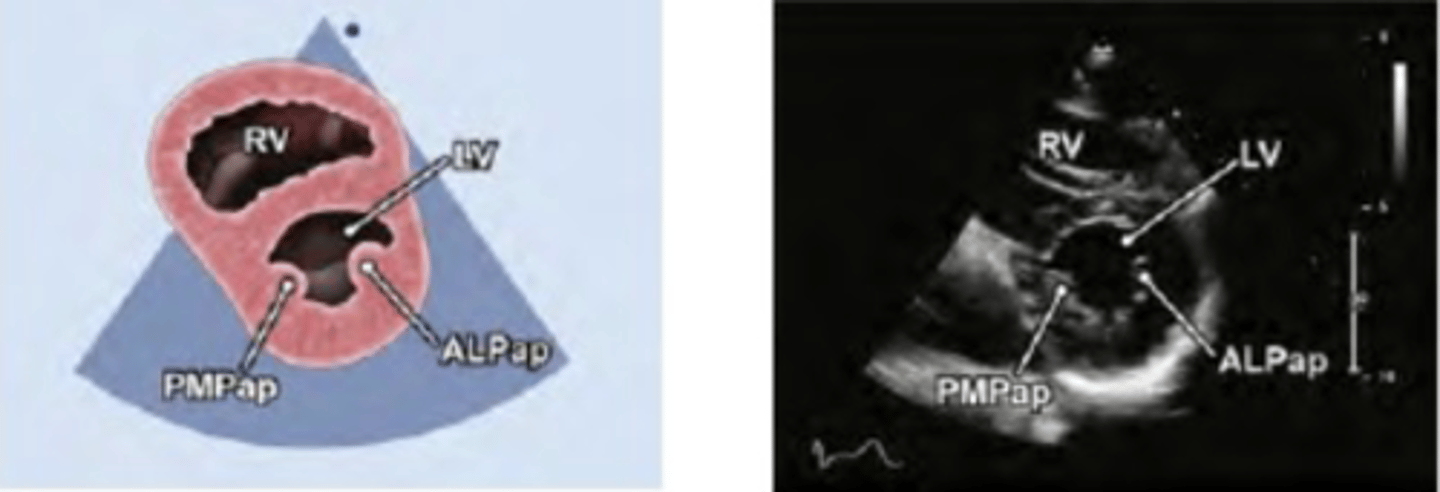
PSAX Papillary Muscle level
Middle segments of LV-IVS, anterior, lateral and inferior walls
PM- posterior medial
AL- anterior medial
* remember AL and PAM are a couple
PSAX LV papillary muscles 1
PM- posterior medial
PSAX LV papillary muscles 2
AL- Anterior lateral
PSAX LV at apical (apex view)
PSAX LV at apical (apex view)
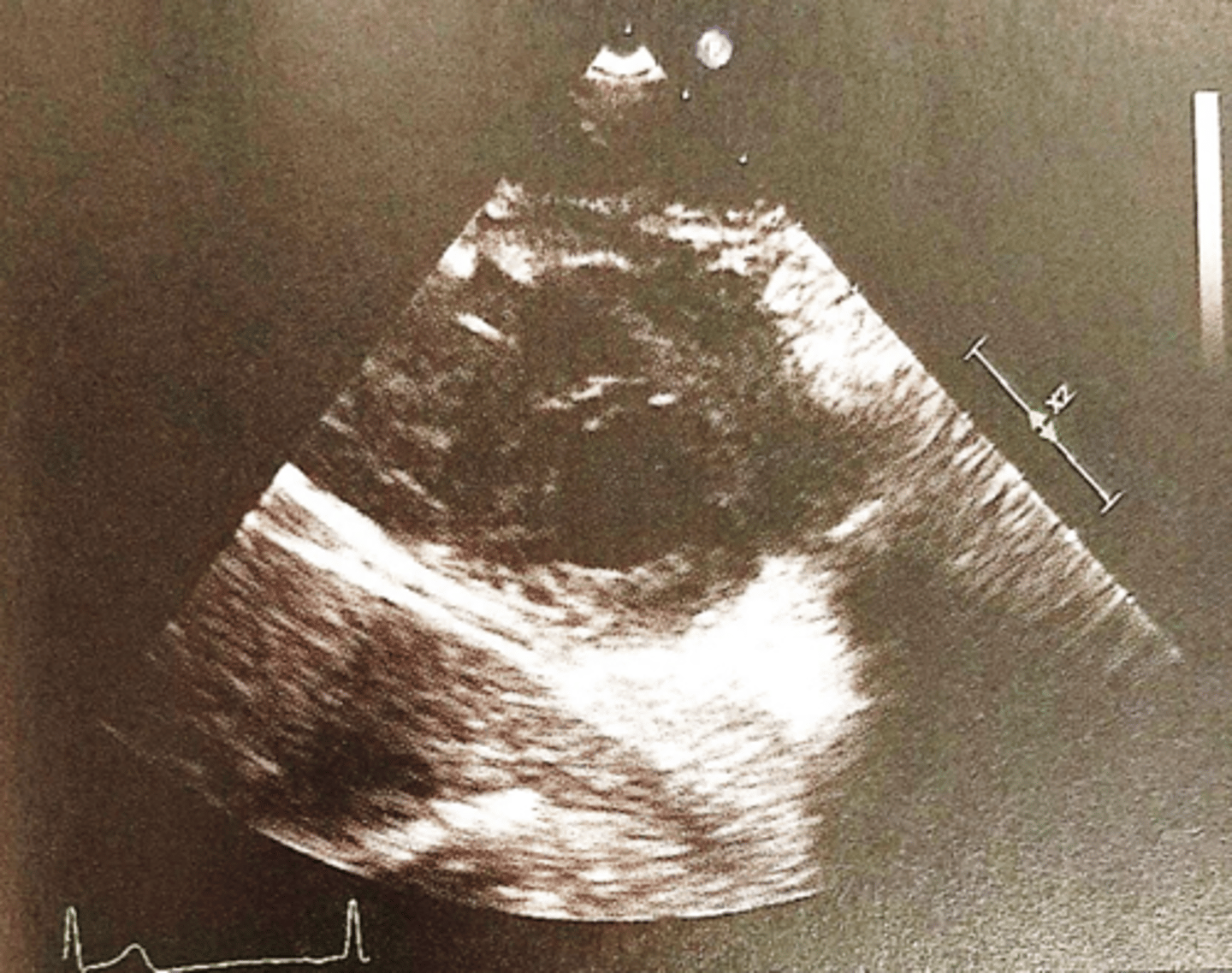
PSAX PA

PSAX AV level
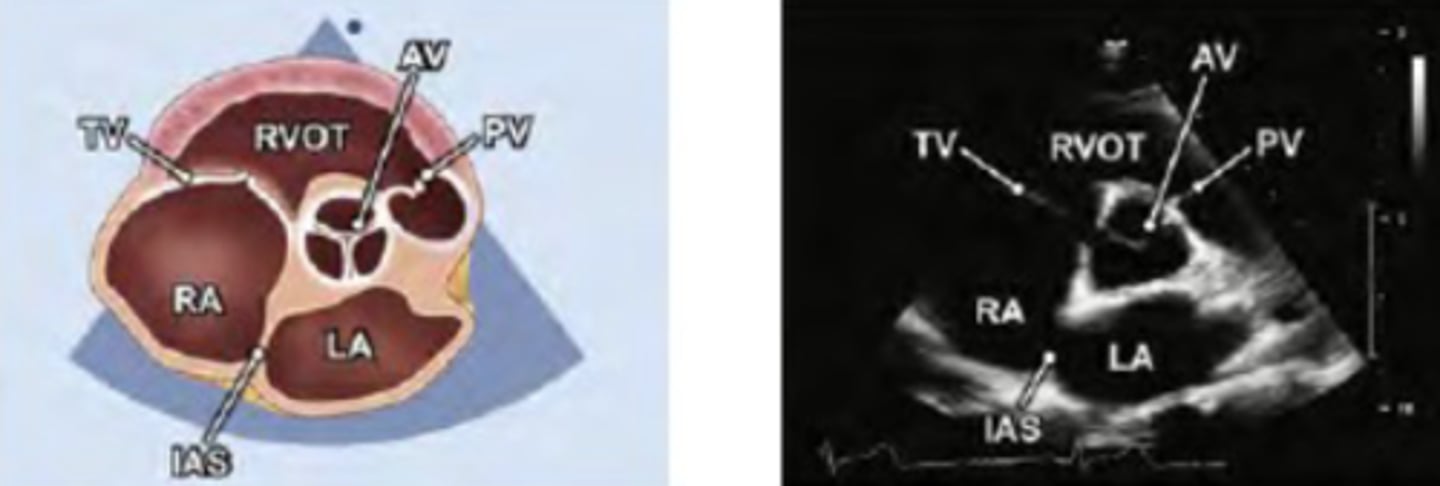

PSAX AOV level
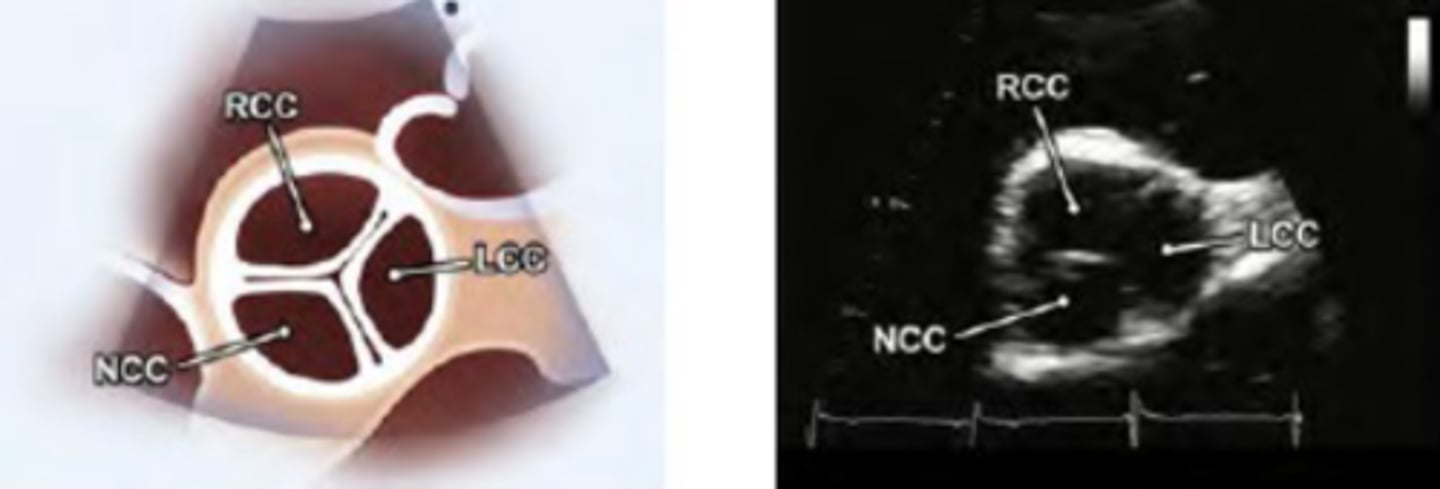
PSAX AV level

PSAX PA
PSAX LV at mitral level
PSAX LV papillary muscles level
PSAX-Apex Level

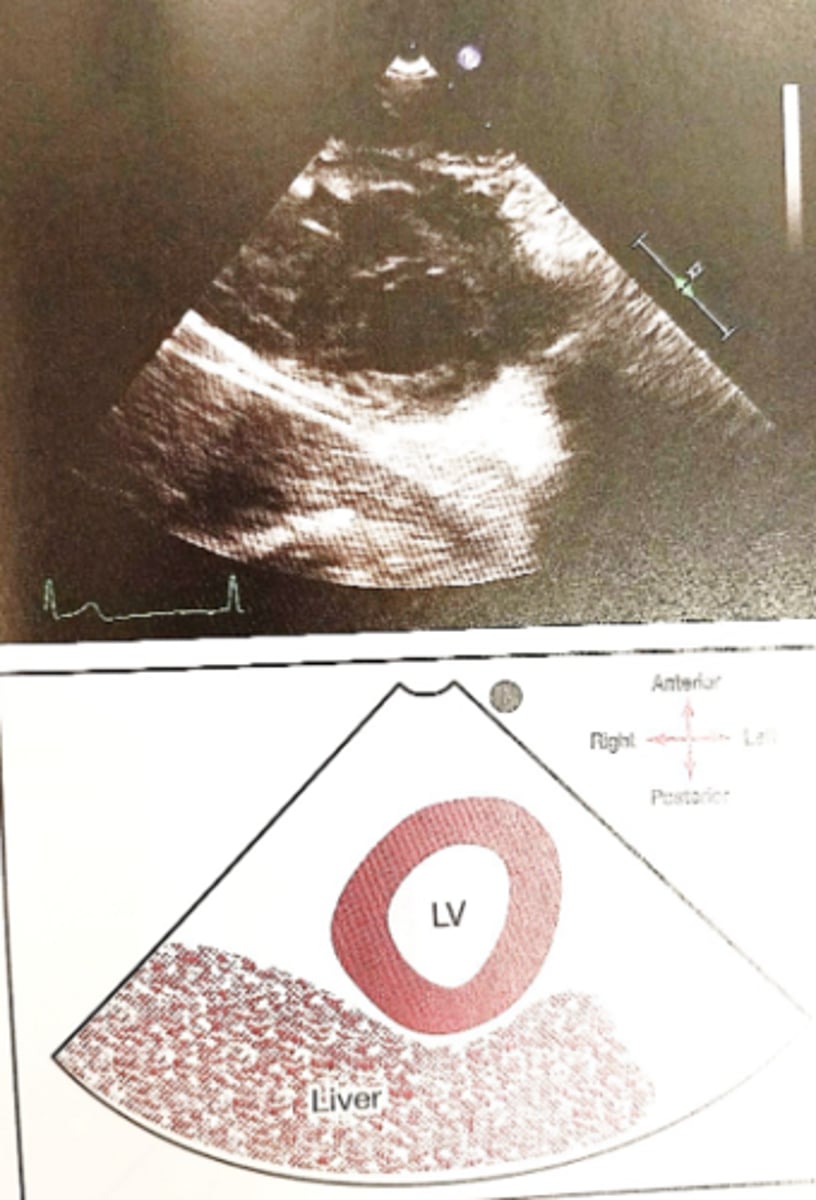
Landmark to tell if the image has a pericardial or pleural effusion
Descending aorta
PLAX optimized: If you see the MV leaflets, going backwards into the LA
You went to high
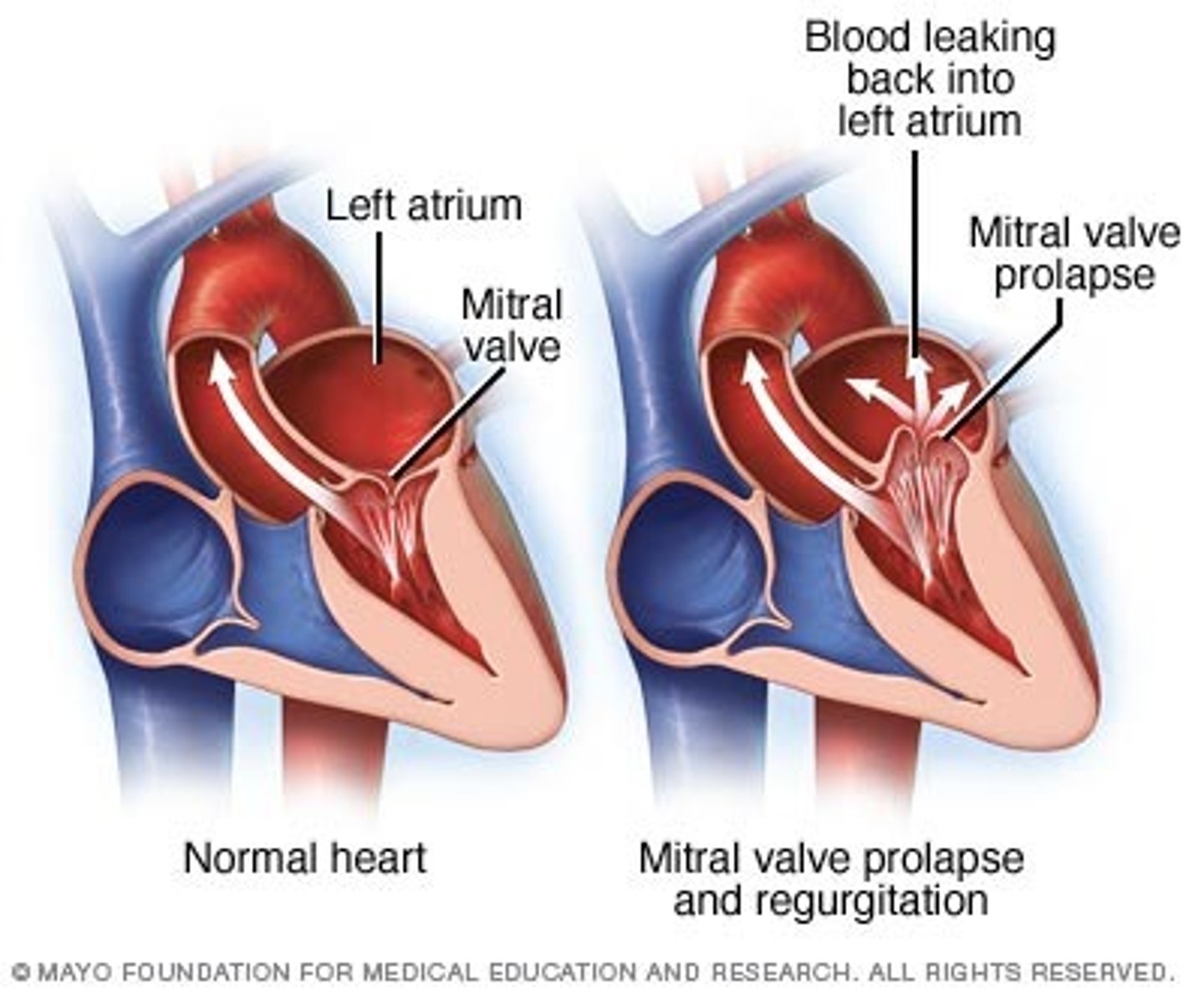
MVP (mitral valve prolapse)
condition in which the leaflets of the mitral valve prolapse into the left atrium during systole, resulting in incomplete closure and backflow of blood
RVIT
PSAX LV mitral valve level
PSAX LV aortic valve level
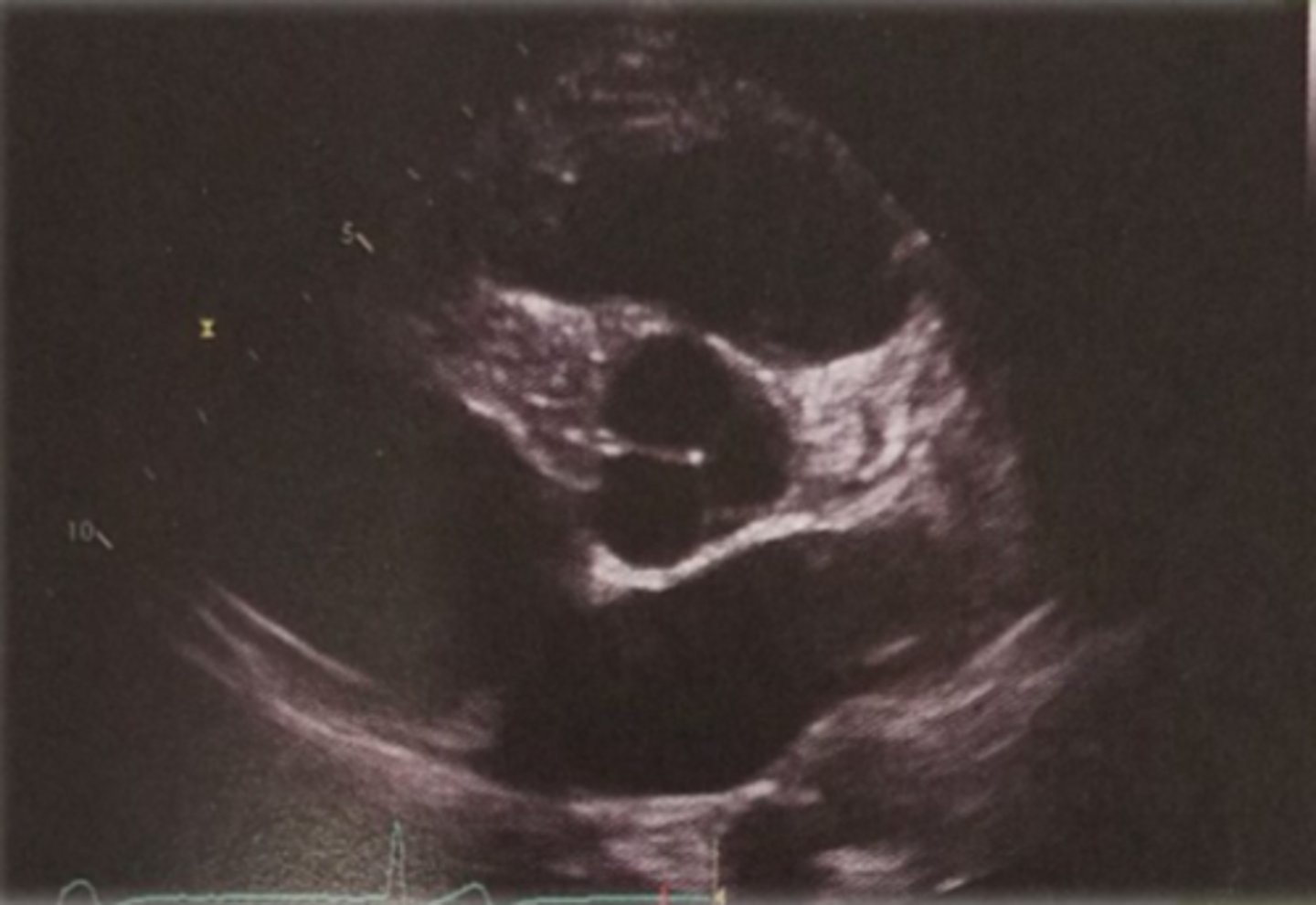
PSAX Left ventricular papillary muscle level
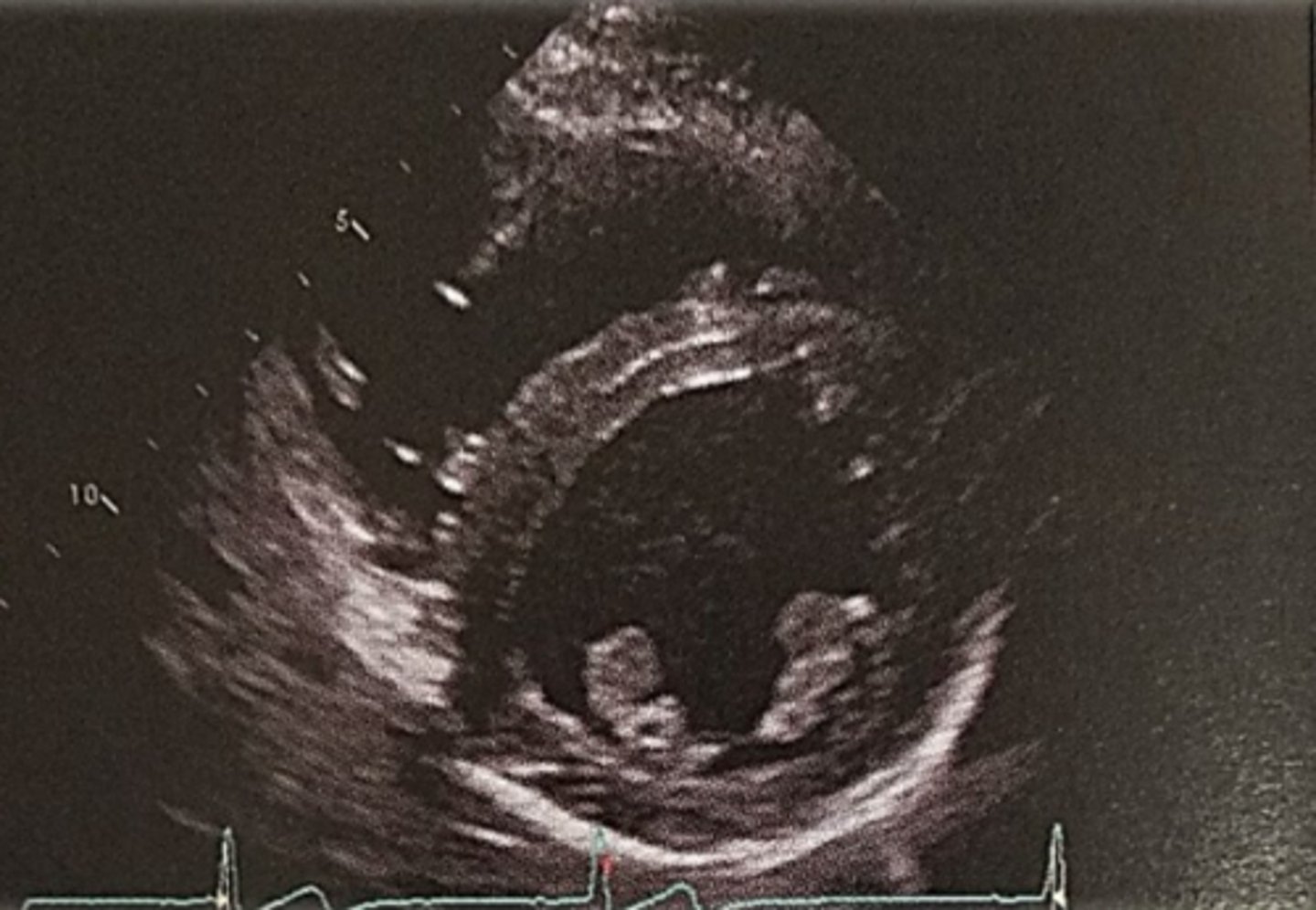
PSAX Pulmonary artery bifurcation level
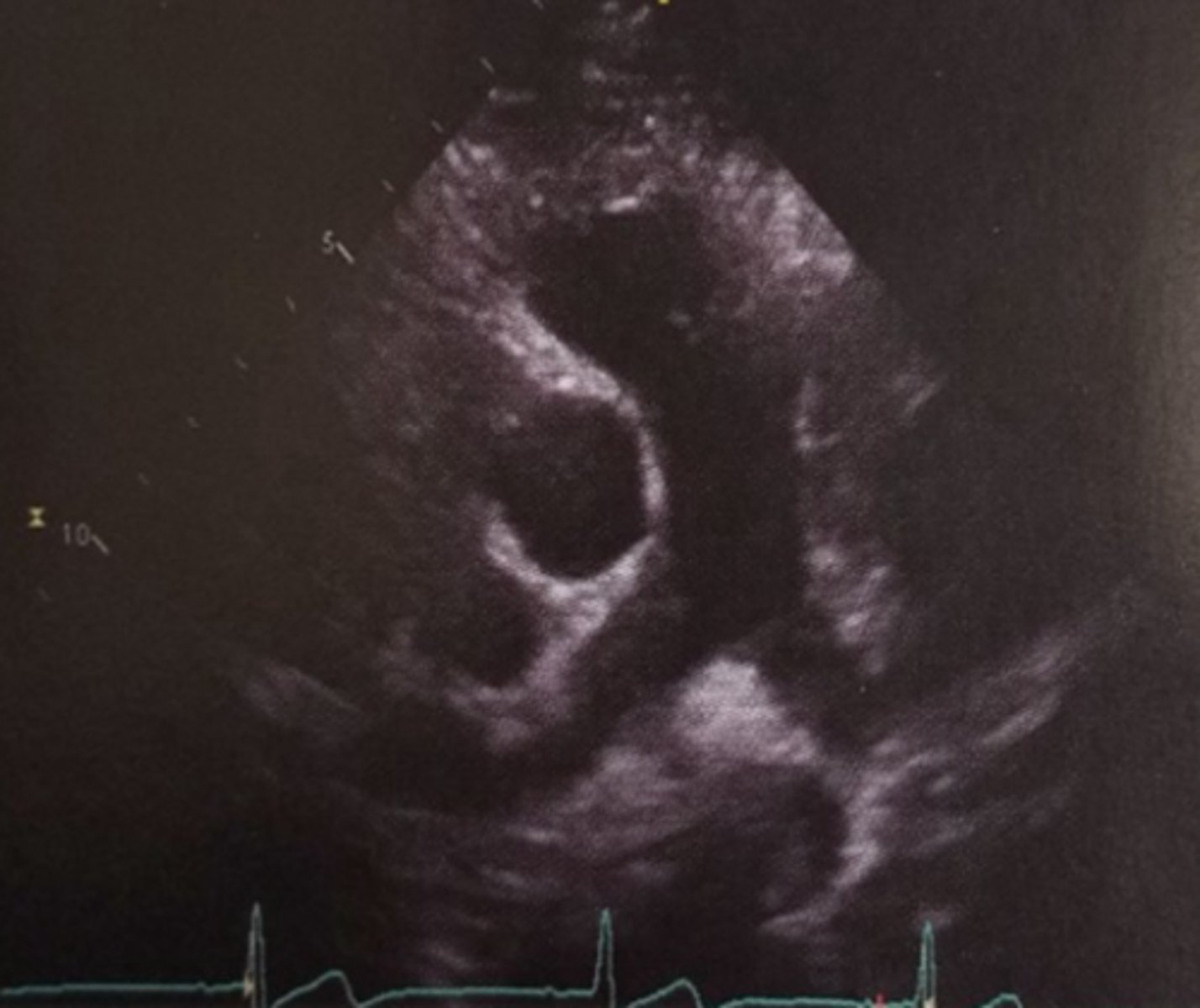
Tall thin patients PLAX window usually is
vertical and low
Short obese patients PLAX window usually is
vertical and high
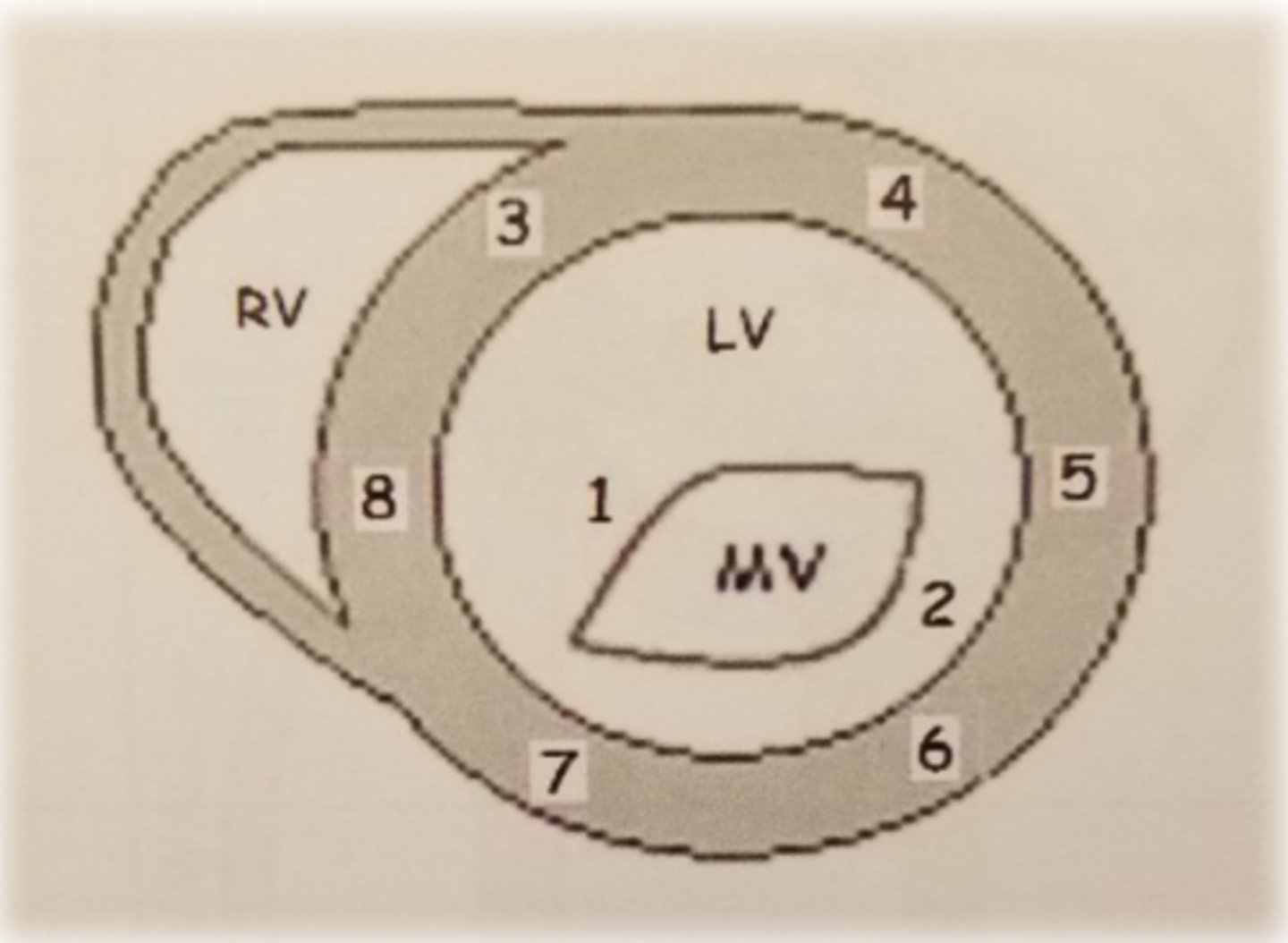
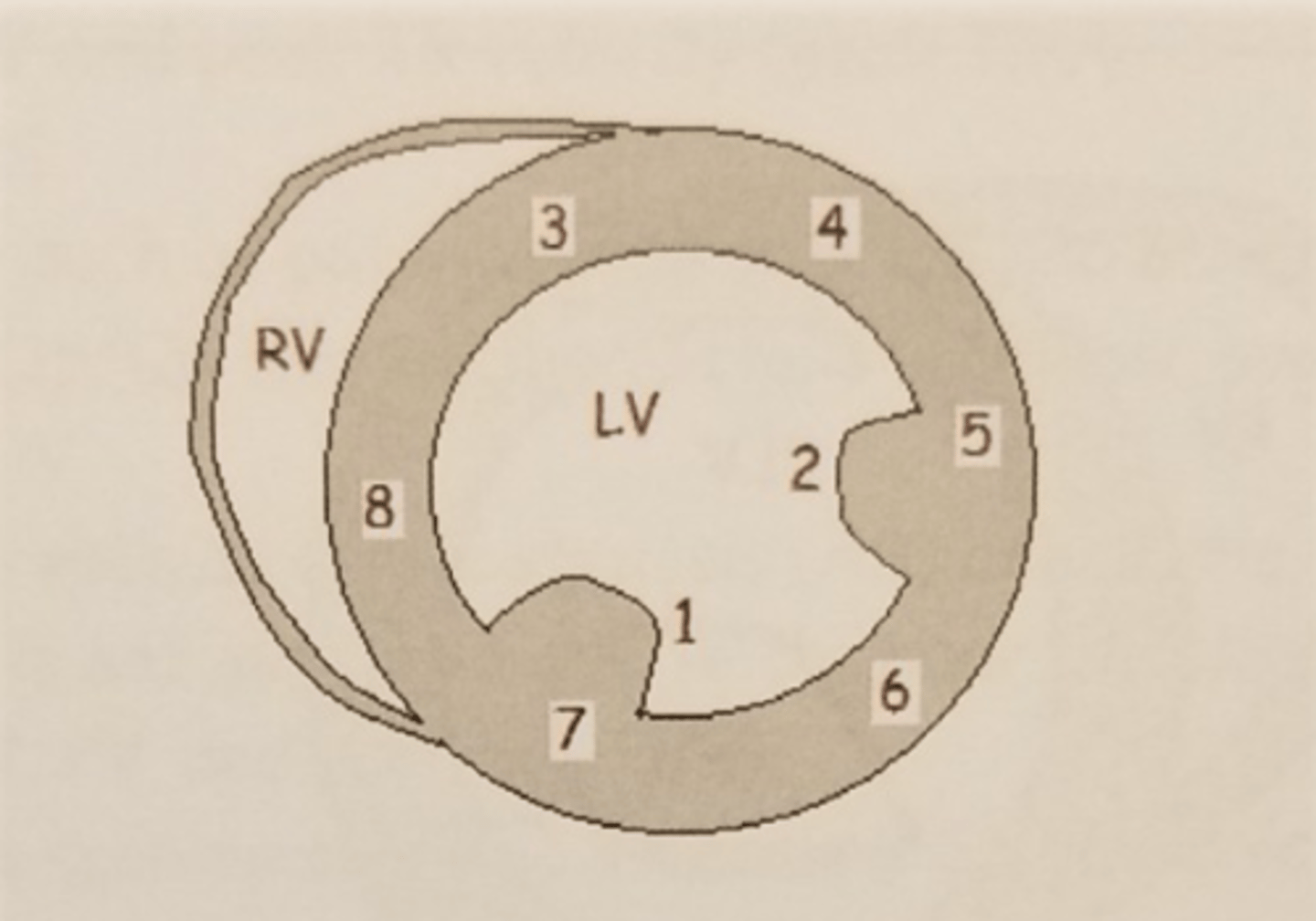
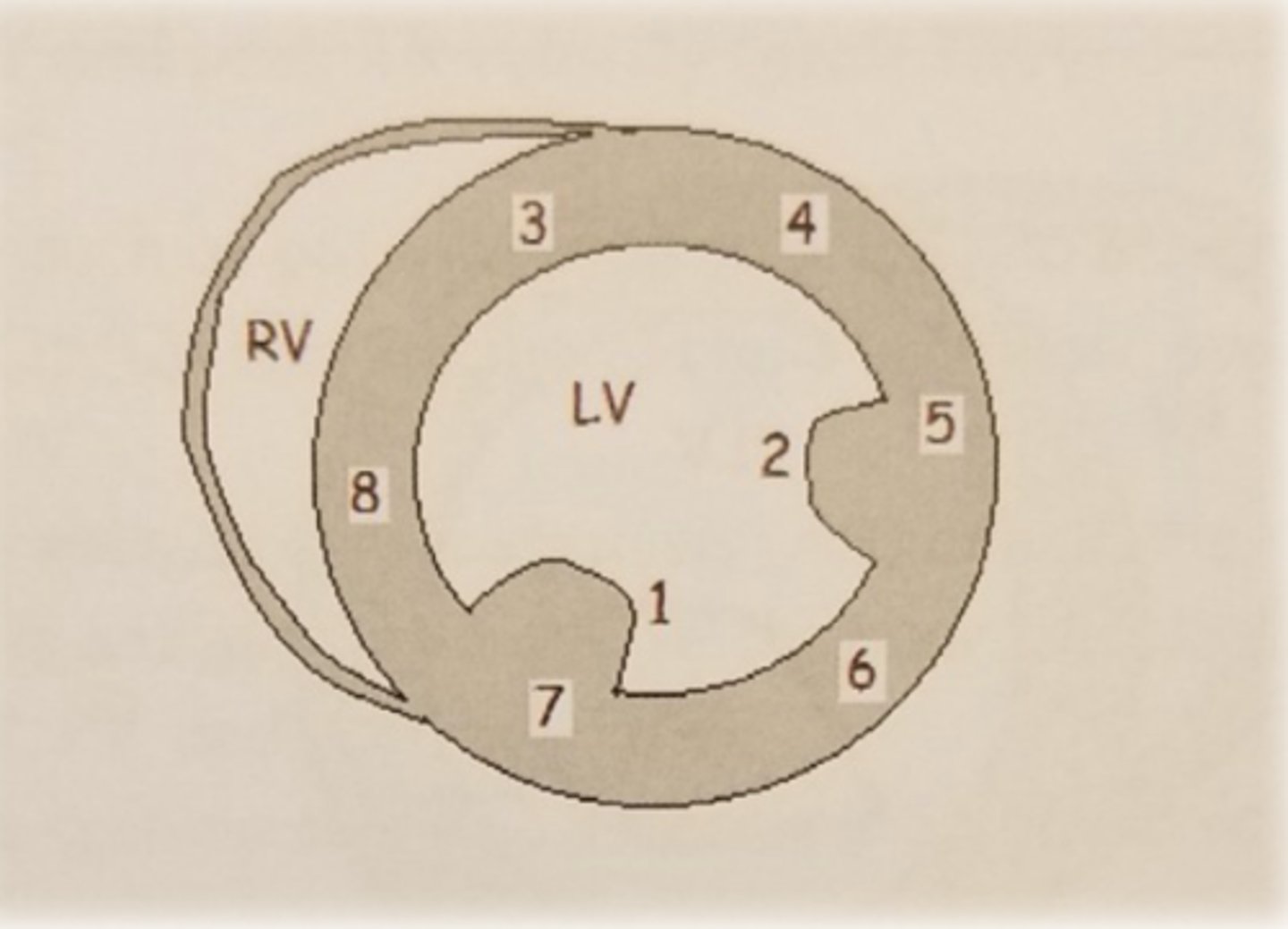
PSAX ML level: LV wall 8
inferoseptal wall
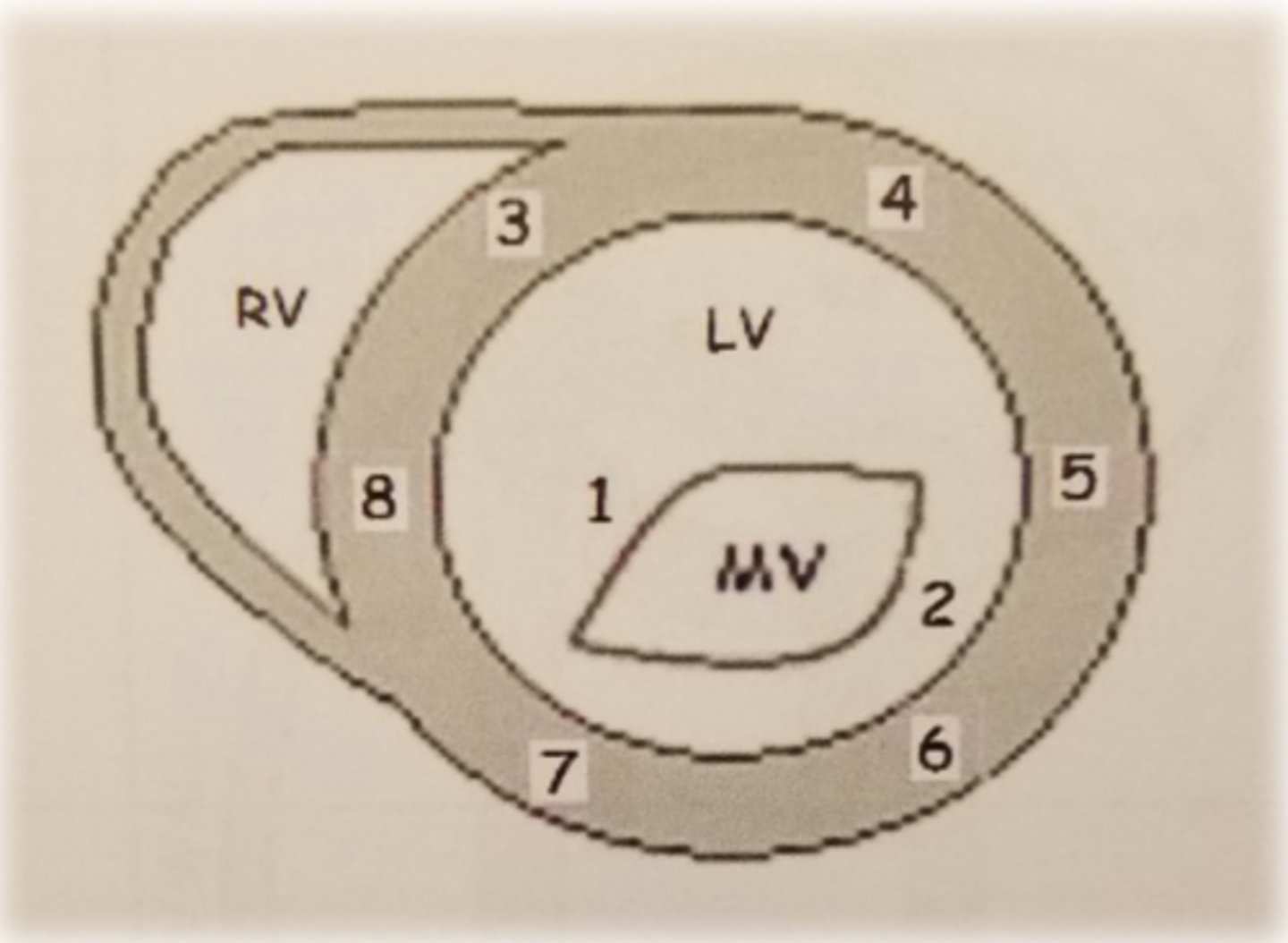
PSAX ML level: LV wall 3
anteroseptal wall
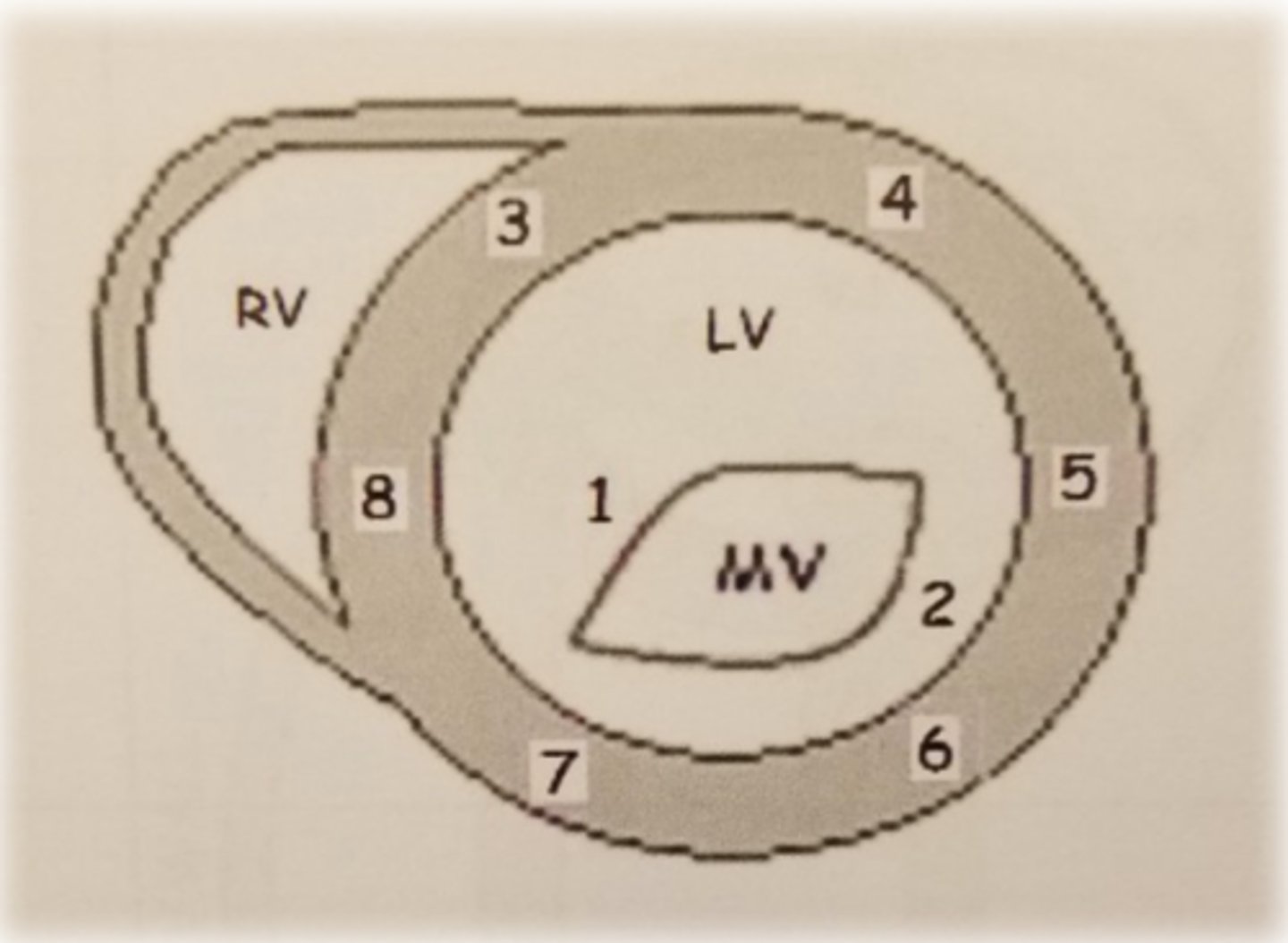
PSAX ML level: LV wall 4
anterior wall
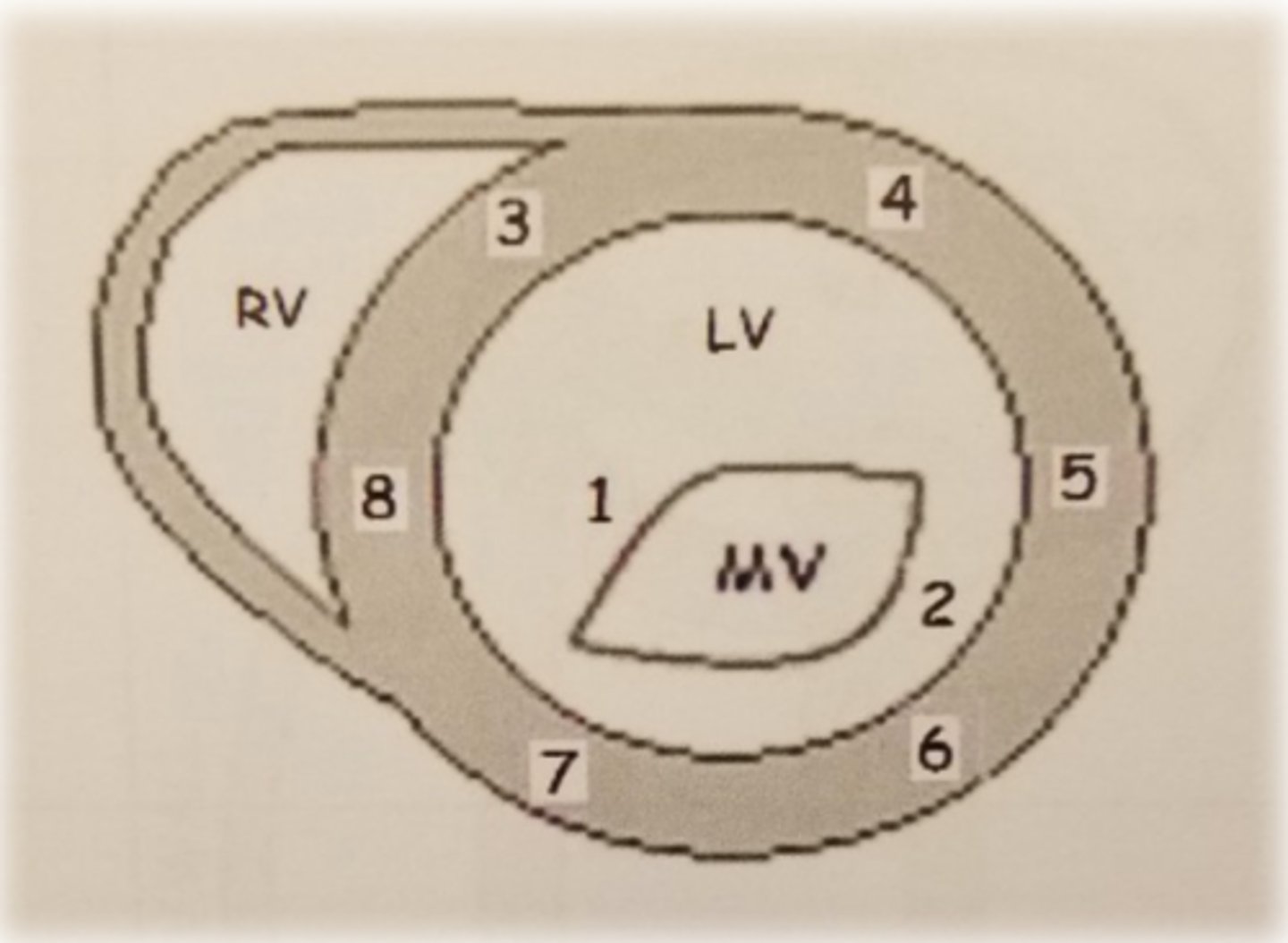
PSAX ML level: LV wall 5
anterolateral wall
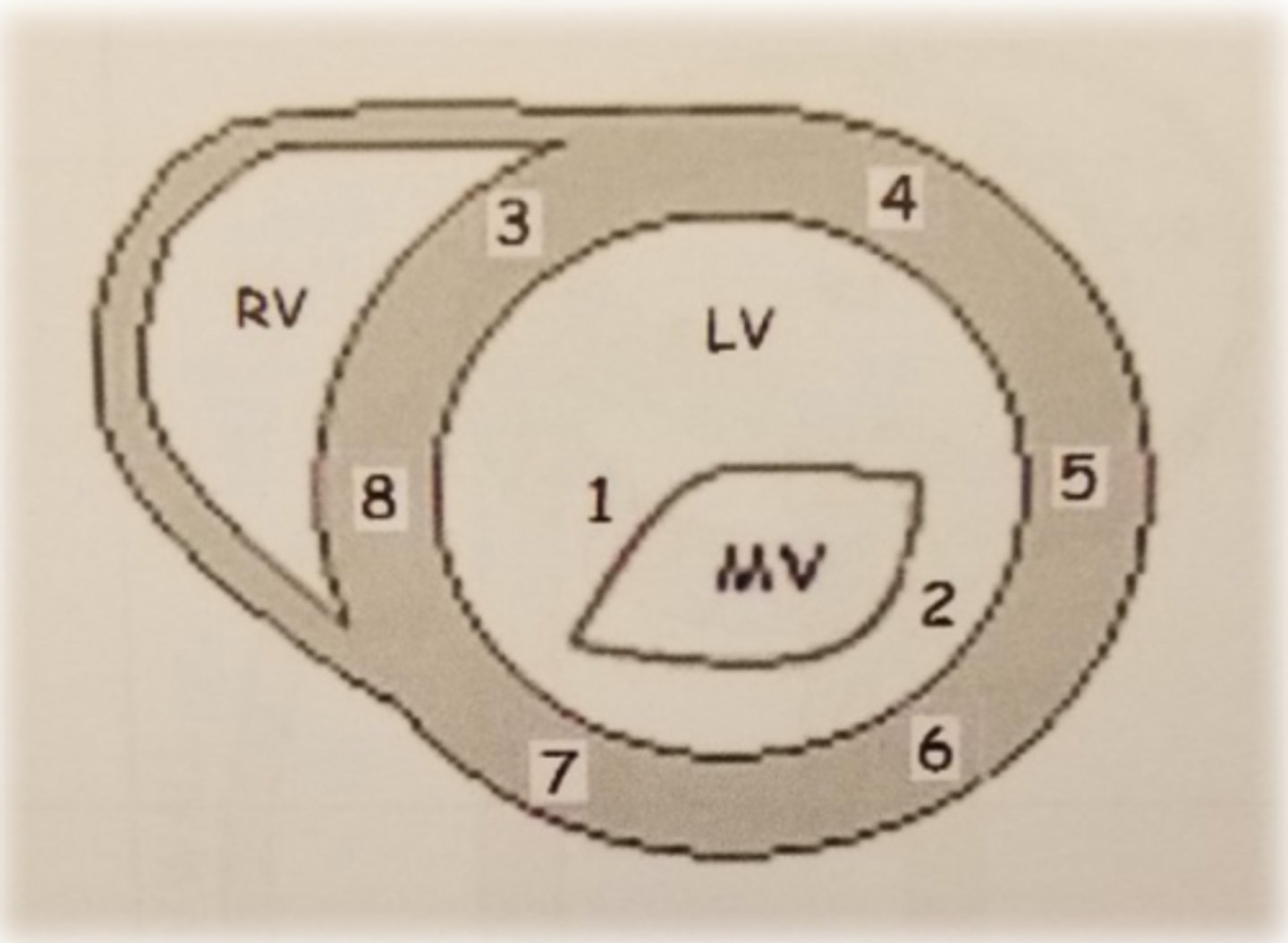
PSAX ML level: LV wall 6
inferolateral wall