Introduction to Neuroscience
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PT 535
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Systems of Neuroscience
sensory systems
motor systems
cranial nerves
interactions between systems
higher functions of the nervous system
clinical applications (developing diagnostic clinical reasoning and pattern recognition)
pattern recognition
accurate diagnosis, establish appropriate goals, and optimize your interventions
divisions of the nervous system
central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system
central nervous system
“brain” & brainstem
spinal cord
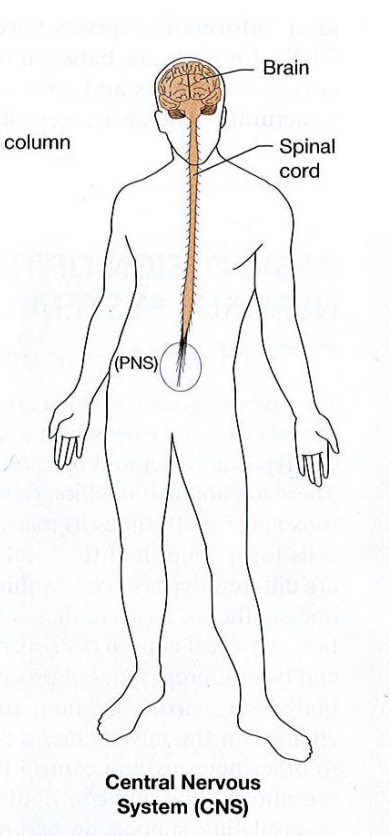
Peripheral nervous system
located outside of CNS, “anything that sticks out”
spinal nerves
cranial nerves (12 pairs)
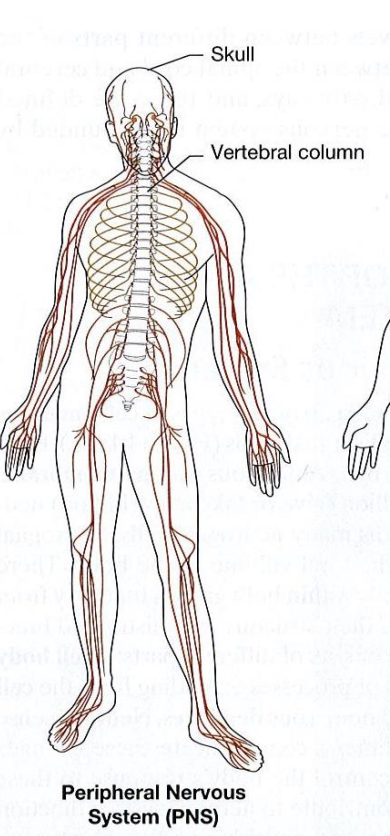
autonomic nervous system
functional subdivision with components within both the CNS and PNS
sympathetic (fight or flight)
parasympathetic (rest & digest)
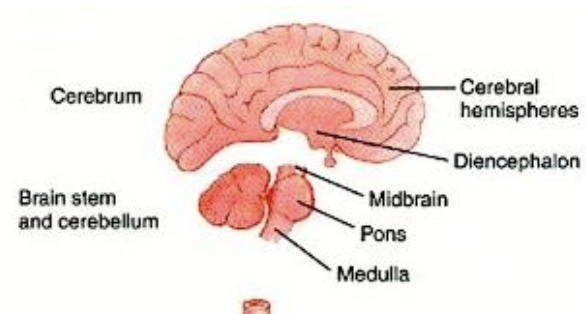
“Brain”
cerebrum
cerebral hemispheres
diencephalon
brainstem
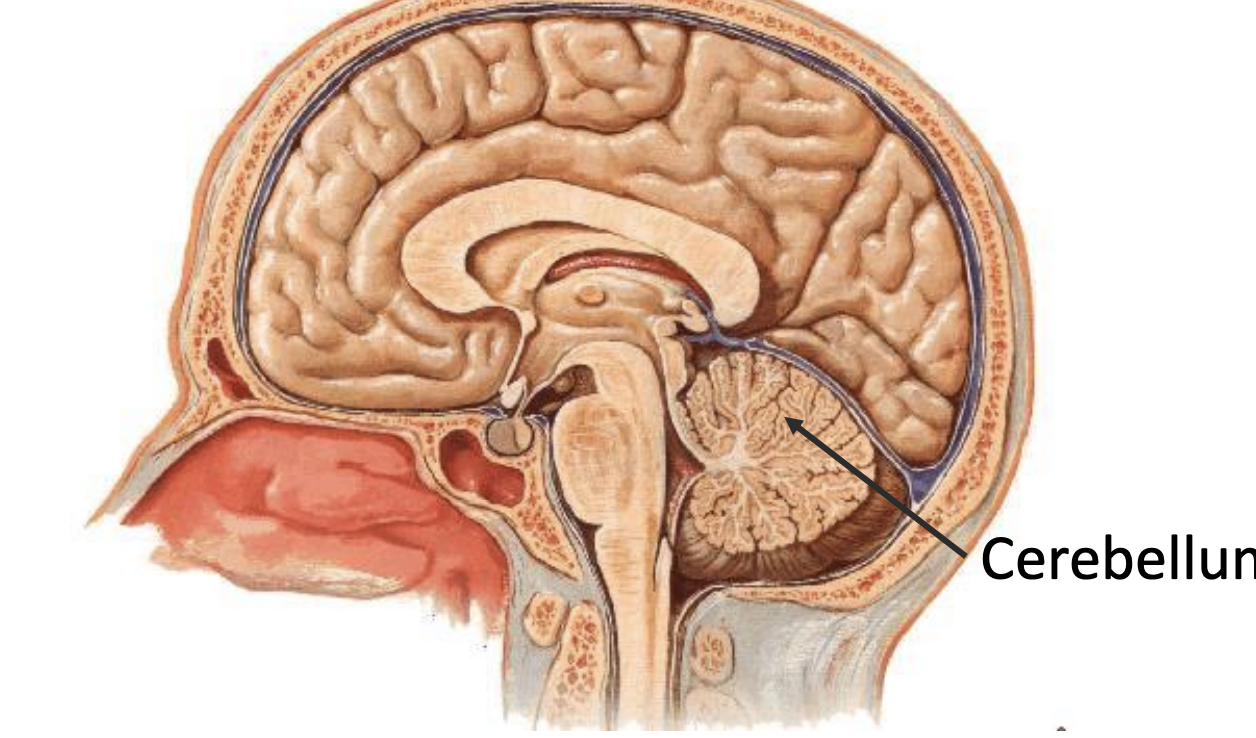
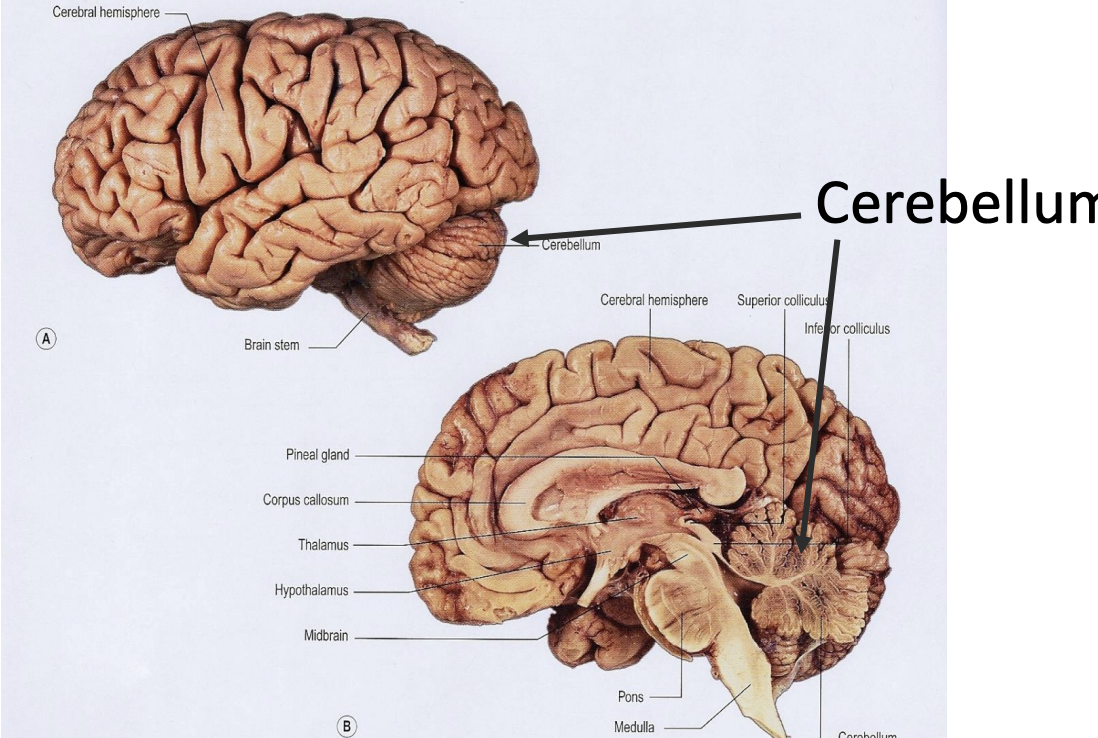
cerebellum
spinal cord
cervical region
thoracic region
lumbar region
sacral region
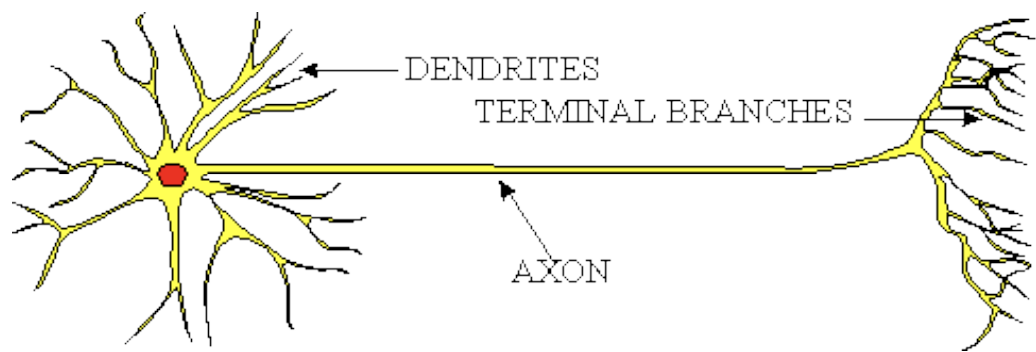
Neuron (nerve cell)
soma: cell body
axon: carries info away from cell body
dendrites: receivers of information
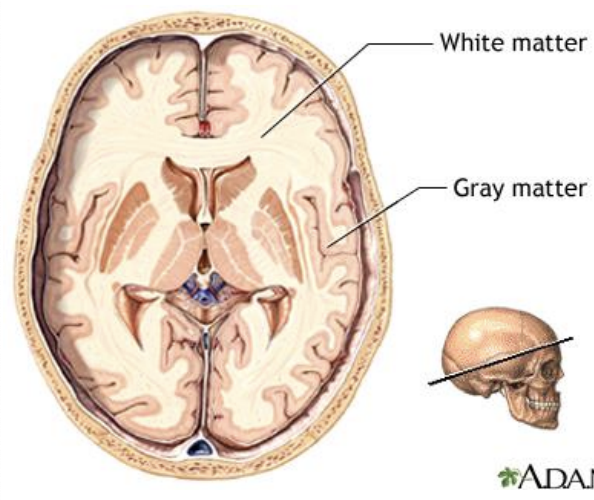
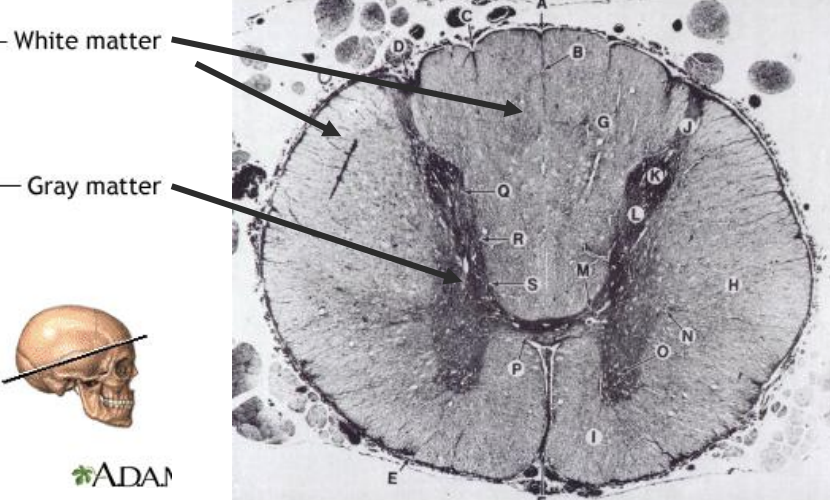
gray matter
collections of cell bodies (little myelin)
cortex of cerebrum and cerebellum
nuclei in the CNS
ganglia in PNS
white matter
consists primarily of collections of axons (myelin appears white)
tracts, fascicles, funiculus, column, lemniscus, capsule and peduncles in the CNS and nerves
Nerve root and rami in the PNS
cerebrum gray and white matter
spinal cord gray and white matter
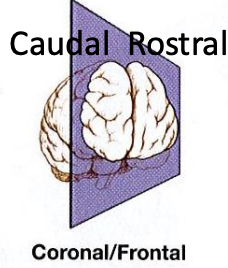
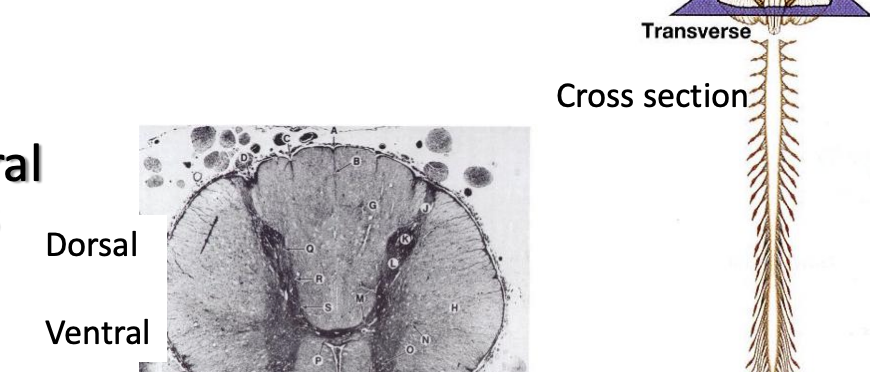
Coronal/Frontal cross section
Transverse Cross section

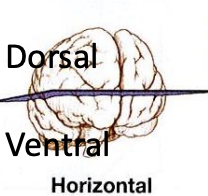
horizontal cross section
oblique cross section
vertically oriented w/brain stem
horizontally oriented w/brain
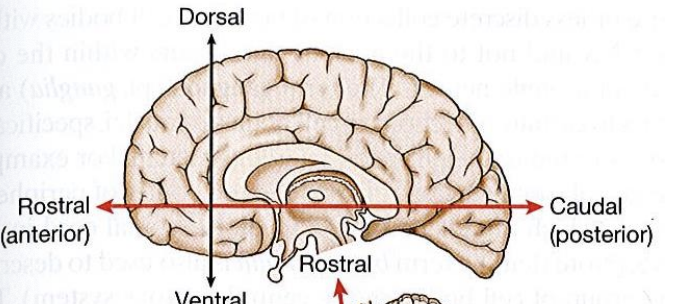
Midsagittal orientation
cuts brain into two equal right and left halves
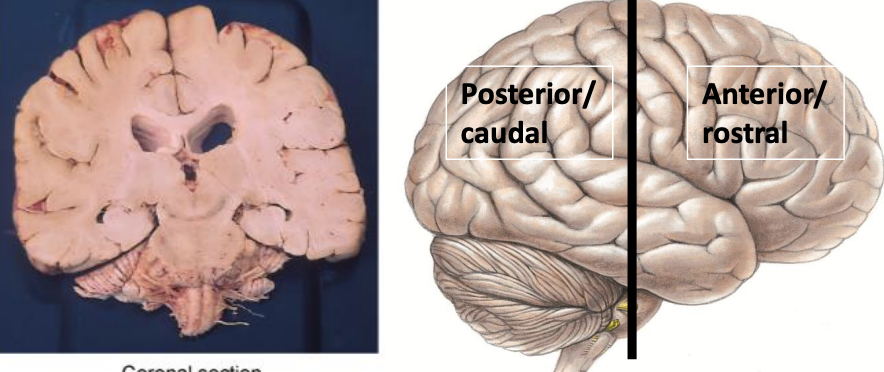
coronal orientation
cuts brain into anterior and posterior sections
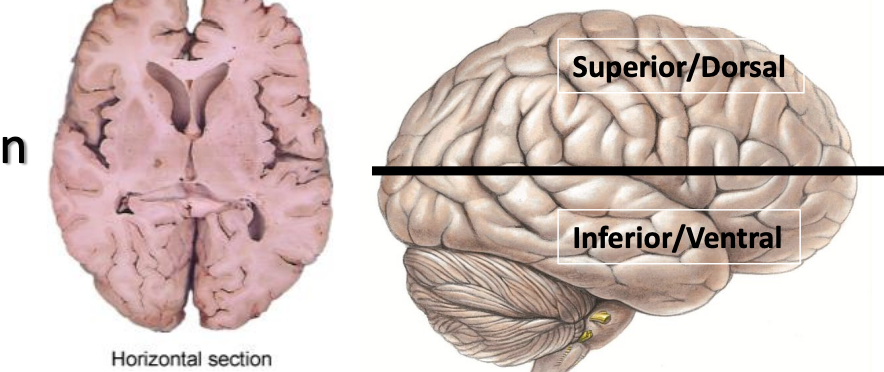
horizontal orientation
cuts brain into superior/dorsal and inferior/ventral sections
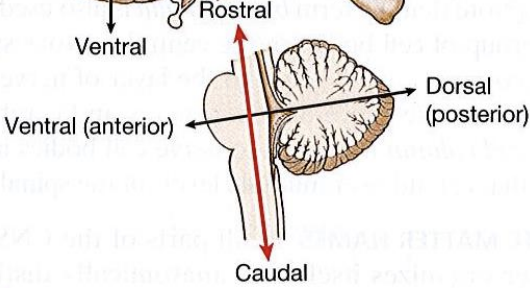
cross section
cuts spinal cord and brainstem into rostal and caudal sections
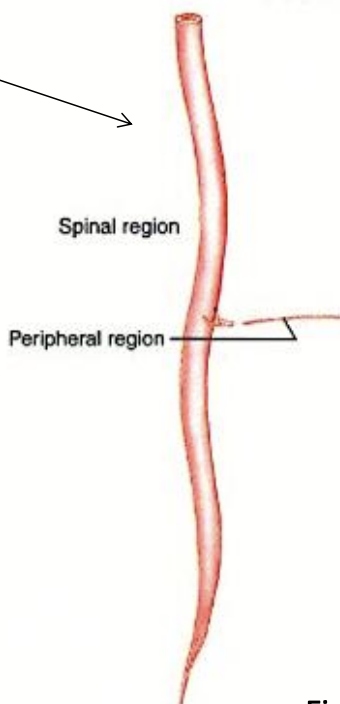
Regions of the Nervous System
peripheral region
spinal region (CNS)
“brain” (CNS)
brainstem
cerebellum
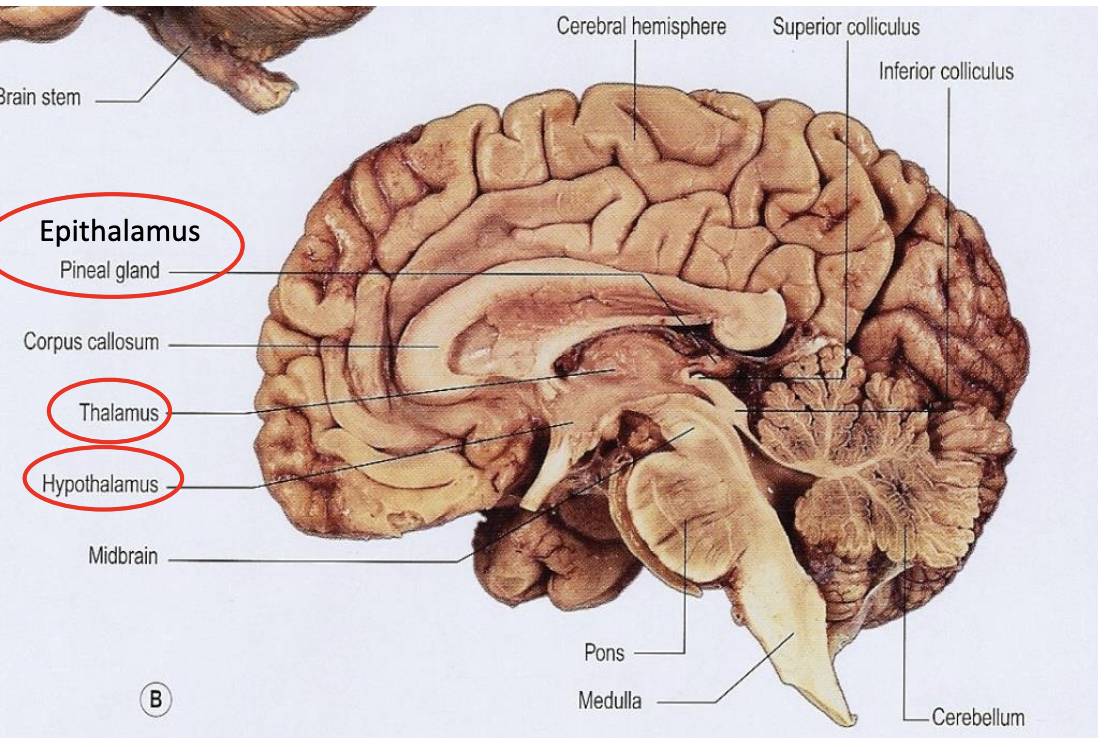
diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus)
cerebrum
peripheral region
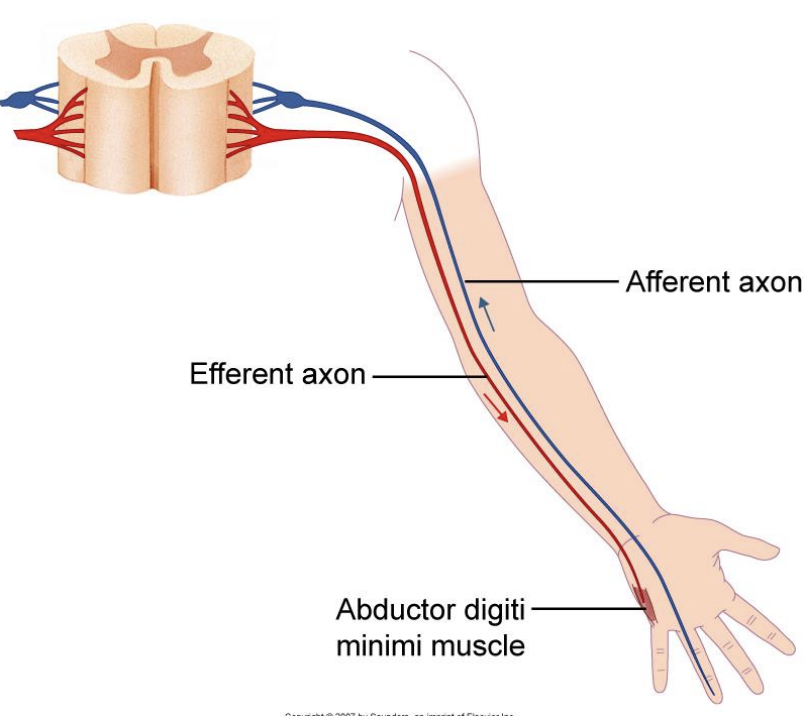
af
ef
afferent axon
efferent axon
af
toward a reference point
ef
away from a reference point
afferent axon
sensory axon
efferent axon
motor axon
spinal region/spinal cord
general functions:
conducts information between the periphery and the “brain”
involved in processing information
example: withdraw fingers from painful stimulus (spinal reflex)
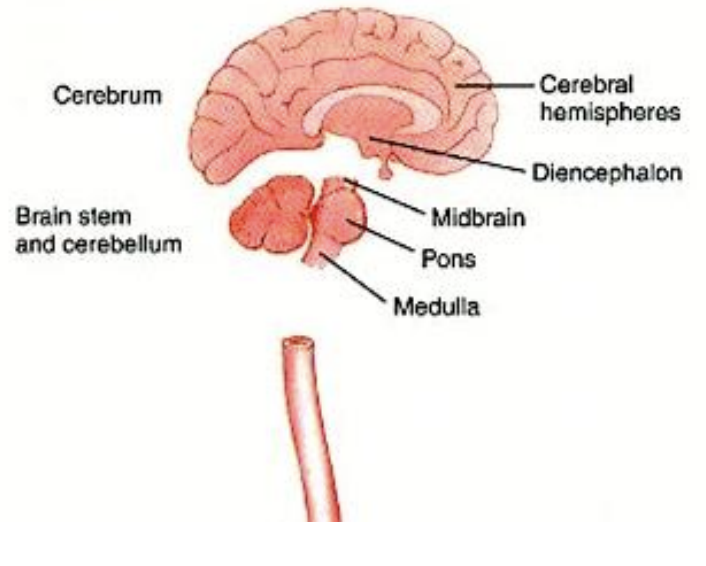
Four Major Subdivisions of the “Brain”
cerebral hemispheres
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
cerebellum
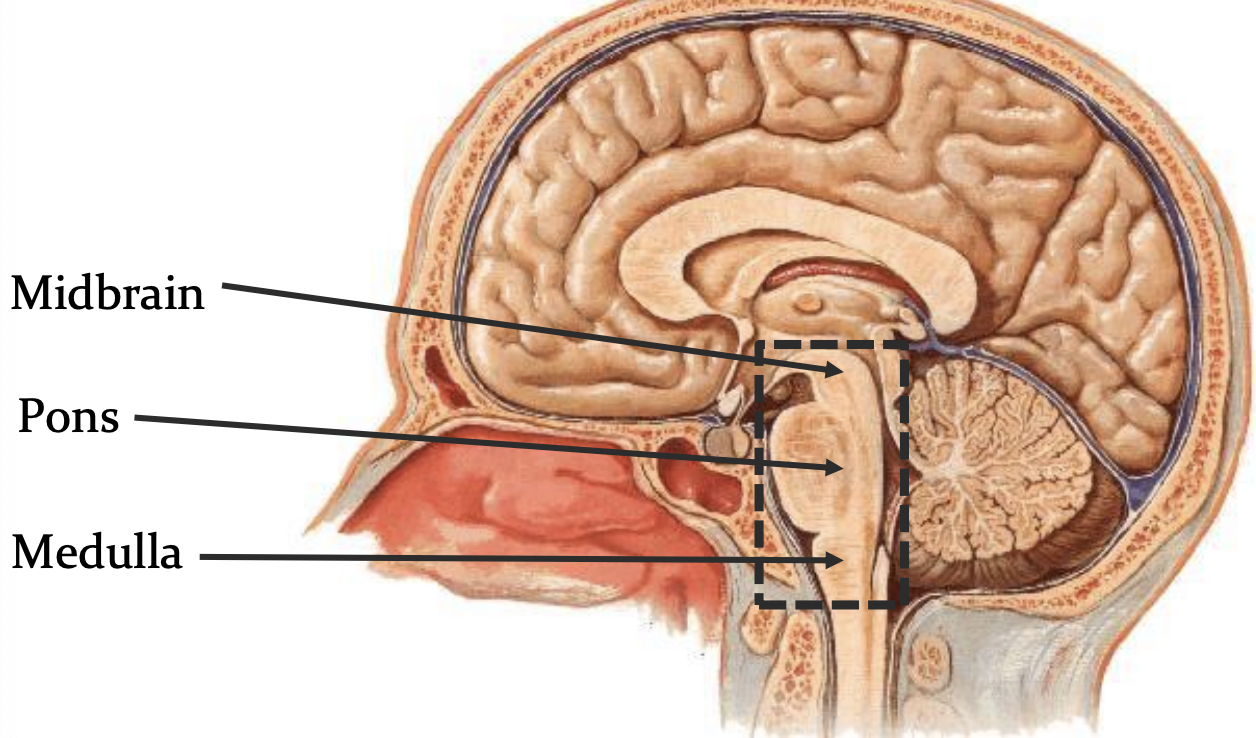
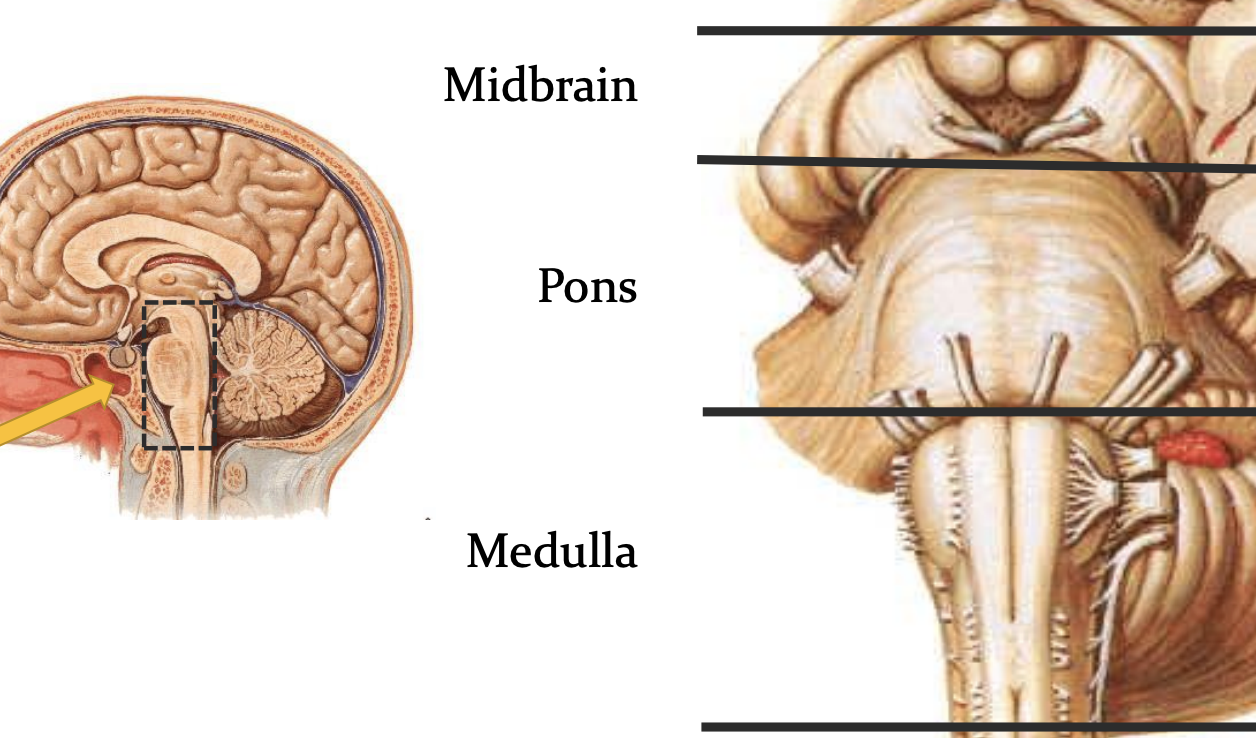
brainstem
midbrain
pons
medulla
cerebrum
includes cerebral hemispheres, basal ganglia, and diencephalon
brainstem
midbrain
pons
medulla
brainstem ventral view
Cerebellum
cerebellum midsagital cut
diencephalon
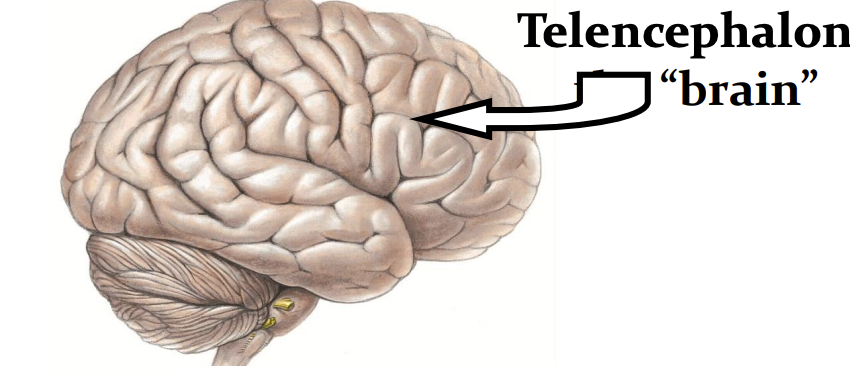
brain “telencephalon”
cerebral cortex
cortex
cortical region
two cerebral hemispheres
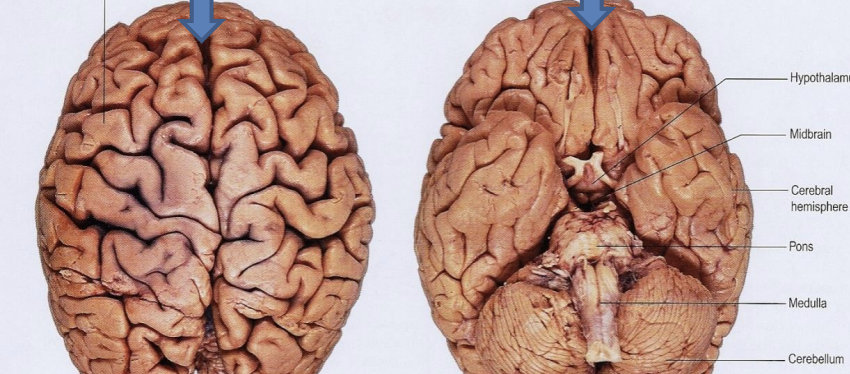
great longitudinal fissue
cerebral cortex
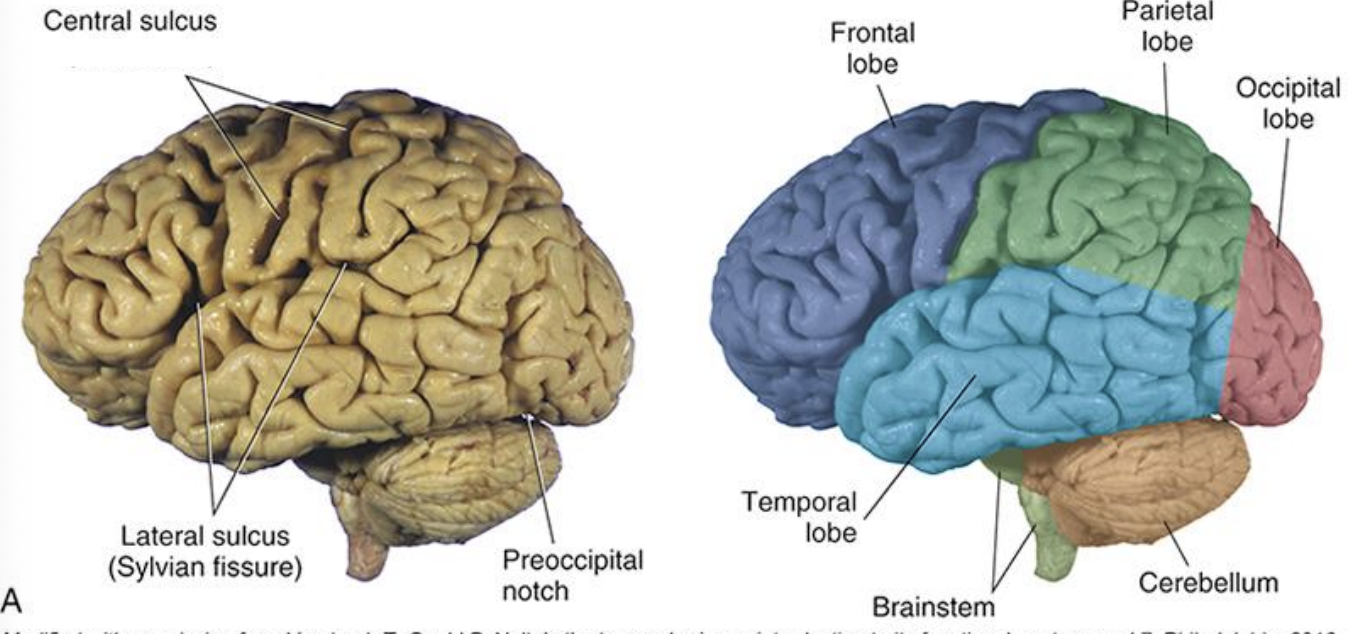
divisible into lobes
frontal (motor, planning, higher order functional)
parietal (sensory)
temporal (auditory, memory, and learning)
occipital (vision)
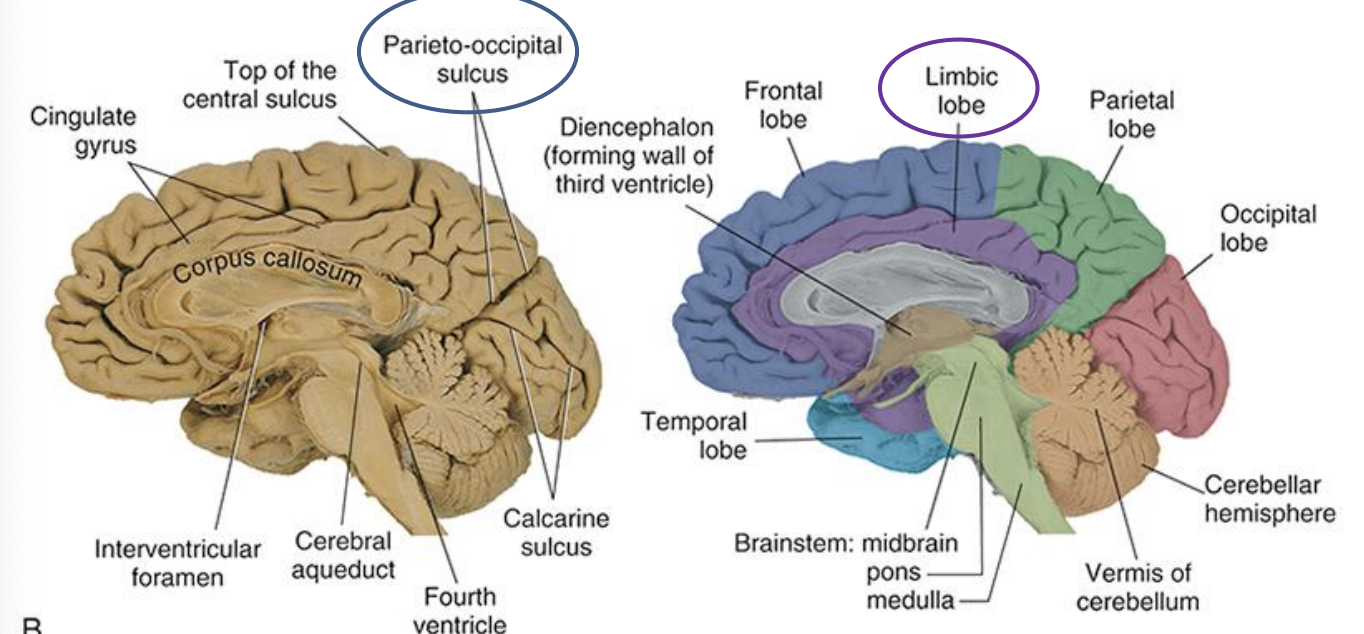
limbic (functional lobe)
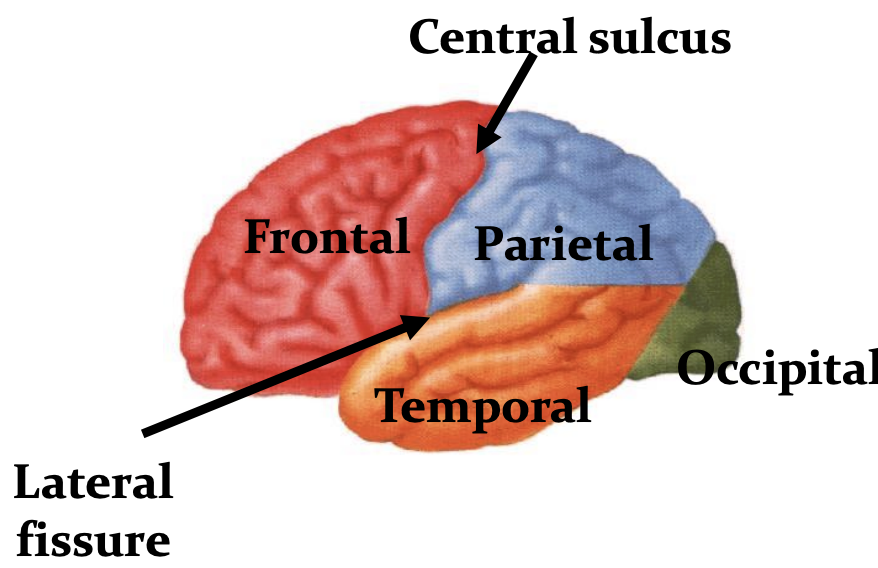
central sulcus (lateral view)
midsagittal view