TELEHEALTH
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KITANE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Teleheath
saw a surge in adoption during
the pandemic, offering convenient and
accessible care.
VIRTUAL
HEALTHCARE
Virtual care solutions, including
remote consultations and digital
health platforms, have become a
crucial part of healthcare delivery
Predicting risk
Optimizing Healthcare
LEVERAGING AI AND DATA ANALYTICS
FOR PREDICTIVE HEALTH CARE
Predicting Risk
Al analyzes patient data to identify
potential risks and personalize
treatment.
2. Optimizing Care
Data analytics provides insights to
improve care delivery, streamline
workflows, and reduce costs
Heart rate
Medication reminders
WEARABLE DEVICES AND REMOTE
PATIENT MONITORING
Virtual Healthcare
Healthcare solutions that involve remote consultations and digital health platforms
Predicting Risk
Utilizing algorithms and patient data to foresee potential health issues and tailor treatment plans
Optimizing Care
Using data analysis to enhance healthcare delivery, improve workflows, and decrease expenses
Wearable Devices
Devices like smartwatches that monitor vital signs such as heart rate and sleep patterns
Medication Reminders
Tools that assist patients in remembering to take their medications
Digital Literacy
Cybersecurity
UPSKILLING HEALTHCARE WORKFORCE IN
DIGITAL COMPETENCIES
Digital Literacy
The ability of healthcare professionals to effectively use telehealth platforms and analyze data
Cybersecurity
The critical practice of safeguarding patient information in the digital realm
Expanding Access to Care
The use of technology to provide healthcare access to individuals in remote locations or with mobility limitations
1 Telehealth bridges the gap for those in
remote areas or with limited mobility.
2 Digital health platforms provide access
to health information, resources, and
virtual consultations.
3 Empowering patients to actively manage
their health through self-monitoring and
digital tools
EXPANDING ACCESS TO CARE THROUGH
DIGITAL PLATFORMS
Digital Health Platforms
Platforms offering health information, resources, and virtual consultations
Empowering Patients
The concept of empowering patients to actively participate in their health management through self-monitoring and digital tools
Integrating Technology and Human-Centered Care
The overall goal of combining technology with compassionate patient care
Data-driven Insights
Leveraging data to personalize care and improve outcome
Human-centered Approach
Maintaining the importance of empathy and patient-provider relationships.
Ethical Considerations
Ensuring responsible use of technology and safeguarding patient privacy.
Clinical
Information System
is a computerized
system that organizes, stores and
double checks all your medical
information
Enhances Patient care
Improved operational Efficiency
Importance of CIS
Enhanced Patient Care
CIS enable. efficient access to patientinformation, improving care coordination,and reducing medical errors.

Improved Operational Efficiency
CIS is automate administrative tasks,streamline, workflows and optimizeresource utilizatiom.
Data mapping
Workflow optimization
System Integration
User interface design
System analysis and design
Data Mapping
is the process of matching fields from one data source tocorresponding fields in anotherdata source.
WorkflowOptimization
the process of analyzing,streamlining, and improvingworkflows to increase efficiency,reduce errors, and enhance overallperformance.
System Integration
also known as IT integration. It is theprocess of joining software andhardware modules into one cohesiveinfrastructure.
User Interface Design
the process designers use to build interfaces in software or computerized devices, focusing on looks or style. Designers aim to create interfaces which users find easy to use and pleasurable.
Software Development
System Teaching
User Acceptance testing
CIS Development and testing
Software Development
Develop the CIS according to the agreed-upon specifications.
System Testing
Perform rigorous testing to ensure functionality, security, and dataintegrity.
User Acceptance Testing
Allow end-users to validate the system and provide feedback.
Software Development
is the process of designing, creating,testing, and maintaining different software applications.
It involves the application of various principles and techniquesfrom computer science, engineering and mathematical analysis.
System Testing
Evaluates the overall functionality and performance of a completeand fully integrated software solutio
User-Acceptance Testing
Application Testing or End-User TestingA
User-Acceptance Testing
A phase of software development in which the software is testedin the real world by its intended audience
is to ensure software can handle real-world tasksand perform up to development specifications
The goal of UAT
End user
Change management
Feedback and evaluation
CIS TRAINING AND CHANGE
MANAGEMENT
END USER TRAINING
Provide comprehensive training on using the CIS effectively.
To improve efficiency, reduce errors, ensure consistent
workflows, and enhance customer service by fostering user
confidence and competence in managing the CIS.
CHANGE MANAGEMENT
Address user concerns and provide ongoing support to ensure
smooth transition.
This process aims to minimize disruptions, maintain system
integrity, and ensure compliance with organizational and regulatory
standards.
FEEDBACK EVALUATION
Gather feedback on the system's performance and make necessary
adjustments.
CHALLENGES & BEST PRACTICES
FOR CIS UPGRADES
Data Migration: Plan for seamless migration of data from old to new systems.
System Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing hardware, software, andother systems.
User Adoption: Encourage user engagement and address potential resistance to change.
Interoperability
Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange across various healthcare systema and settings
Interoperability
the ability of different healthcare
systems, devices, and applications to
exchange, access, and use data
a. Data access - Different systems can access
data from each other
b. Data transmission - Data can be exchanged
between systems
c. Cross-organizational collaboration -
Organizations can work together more easily
d. Data analysis - Data can be combined and
analyzed more easily
e. Data-driven improvements - Organizations can
study data trends and make improvements in
patient care
What does interoperability enable
Makes it easier to study data trends
Makes it easier to analyze data
Allows organizations to make data-driven improvements in patient care
Benefits of interoperability
Data Analysis
process of examining, organizing, transforming, and interpreting data to extract meaningful insights and facilitate informed decisionmaking.
1. Identify trends in patient outcomes.
2.Evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
3.Monitor healthcare quality indicators.
4. Support evidence-based practices.
5.Inform policy development.
By systematically analyzing patient data,
healthcare professionals can
Enumerative
Refers to a system where all possible terms or
phrases are listed, often pre-combined into clinical
phrases
Combinatorial
Enable the creation of new expressions by
combining existing terms, offering enhanced
precision and expressiveness. It allows users to
construct complex concepts dynamically.
Improved data quality
Enhanced patient safety
Efficient workflow
Benefits of Standardized Nursing terminologies
IMPROVED DATA
QUALITY
Consistent data collection and analysis
lead to better insights for research,
quality improvement, and public health
surveillance.
• Consistency Across setting
• Accurate Reporting
• Error Reduction
• Support for Data Analytics
• Regulatory Compliance
ENHANCED PATIENT
SAFETY
Accurate records support patientcentered
treatment. It improves decisionmaking
and early error detection. It
ensures continuity of care and reduces
safety risks.
• Informed Decision-making
• Early error Detection
• Continuity of Care
• Risk Management
• Patient Centered Care
EFFICIENT WORKFLOW
It saves time, simplifies communication, and
enhances collaboration. Integration with EHR
systems improves workflow efficiency and
data retrieval for research. It also streamlines
training, ensuring consistency across
healthcare teams.
• Time Saving
• Integration with technology
• Data Retrieval For Research
• Training and Education
The North American Nursing Diagnosis Association
What is NANDA
Patient Assessment
Care Planning Made Easy
Promoting Holistic Care
Empowering Nurses
ADVANTAGE
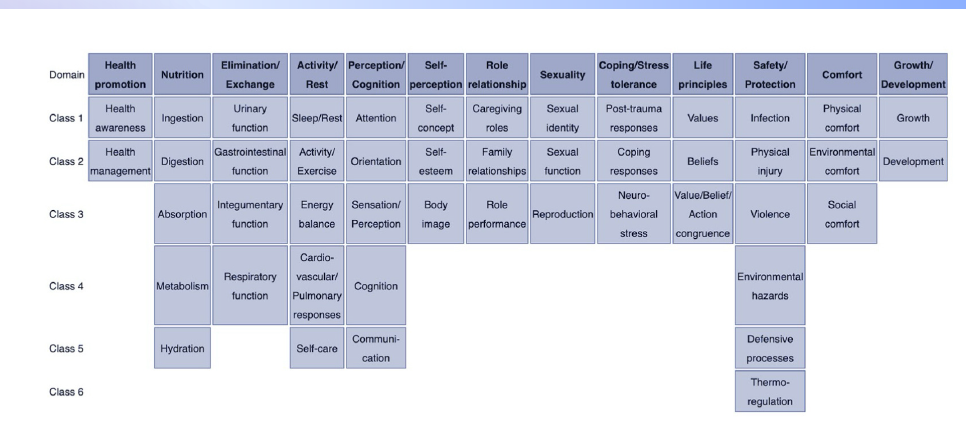
The comprehensive list of nursing diagnoses
adopted by NANDA contains thirteen (13) domains
that represents a critical aspect of health, and six
(6) classes which provides specific focus areas
within those domains.
The comprehensive list of nursing diagnoses
adopted by NANDA contains __________ domains
that represents a critical aspect of health, and _______________ classes which provides specific focus areas
within those domains.
Electronic Health Record
is an electronic
version of a patients medical history, that is
maintained by the provider over time, and may
include all of the key administrative clinical data
relevant to that persons care under a particular
provider
Standardized documentation ensures
consistency in data collection, which leads to more accurate
analysis and identification of trends.
Enhanced Coordination
Consistent terminology selection
enhances coordination of care and patient outcomes by providing a
common language for healthcare providers.
Evidence-Based Practice
Recognized terminologies support
evidence-based nursing practice by providing a framework for
nurses to make informed decisions.
Systems ensure clear
communication about
patient conditions,
interventions, and
outcomes.
WHAT IS A STANDARDIZED
NURSING TERMINOLOGIES?
ANDA (North American Nursing
Diagnosis Association) for
nursing diagnoses.
NOC (Nursing Outcomes
Classification) for patient
outcomes.
NIC (Nursing Interventions
Classification) for nursing
interventions.
EXAMPLES
DATA ANALYSIS
AI algorithms are used in nursing data
analysis to find patterns and trends in standardized nursing terminologies (SNTs).
Deeper comprehension
Increase decision-making
Enhanced patient care
PREDICTIVE MODELING
AI in nursing improves predictive modeling
by enabling t enhances real-time monitoring, reduces
errors, streamlines documentation, and
fosters better communication and training,
ultimately leading to more efficient,
effective patient care. of health risks,
personalizing care, optimizing resources,
and predicting patient outcomes
PREDICTIVE MODELING
it enhances real-time monitoring, reduces
errors, streamlines documentation, and
fosters better communication and training,
ultimately leading to more efficient,
effective patient care.
PERSONALIZED CARE
it enables us to access and interpret a patient's
unique medical history, allowing nurses to
provide more targeted and customized care
based on their specific needs.
electronic health records
data analysis
clinical decision support systems
Personalized care is the ability to tailor
healthcare treatment plans for individual
patients by utilizing:(SNOMED CT)
SNOMED CT
is a standardized, multilingual
vocabulary of clinical terminology that
is used by physicians and other
healthcare providers for the electronic
exchange of health information.
SYSTEMATIZED NOMENCLATURE
OF MEDICINE
(SNOMED CT)
CHARACTERISTICS
OF
SNOMED CT
MULTI-AXIAL STRUCTURE
SNOMED CT uses______________________. Concepts can have
multiple categories that they can
belong to—so they can have multiple
parent concepts that represent
different aspects of the concept’s
meaning.
EXTENSION COVERAGE
The extensive coverage of SNOMED
CT in the application in clinical
settings includes various concepts
ranging from anatomy, diseases,
procedures, and medications
GLOBAL ADAPTION
Provides a common language for describing
medical concepts, SNOMED CT improves data
quality and interoperability, leading to more
accurate diagnoses, more effective
treatments, and a deeper understanding of
global health trends. This international
collaboration enhances patient safety and
drives advancements in healthcare
worldwide
SIMPLE SUMMARY OF SNOMED CT
GLOBAL ADOPTION
It helps doctors and hospitals in different countries understand each other.
It improves the quality of patient care.
It helps researchers learn more about health worldwide
Electronic Health Records
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
Wearable Technology
Evolving Role of Technology
in Nursing
Electronic
Health
Records
EHRs streamline documentation,
improve communication, and
facilitate data analysis.
Telehealth
and Remote
Monitoring
Telehealth expands access to
care, allows for remote patient
monitoring, and facilitates virtual
consultations.
Wearable
Technology
Wearable devices collect health
data, providing insights into
patient behavior and enabling
personalized interventions
Data Security
Interoperability
Digital Divide
Sociotechnical Challenges
to Digital Health Integration
Data Security
Ensuring patient privacy and data
security is paramount in the digital
health environment.
Interoperability
Seamless data exchange between
different healthcare systems is critical
for effective care coordination.
Digital Divide
Addressing disparities in digital
access and literacy is essential for
equitable healthcare delivery.
Training and Education
Digital Literacy
Access to Technology
Lack of Digital Skills and Access for Nurses
Training and
Education
Nurses require comprehensive
training in using digital tools
effectively.
Digital
Literacy
Bridging the gap in digital literacy
among nurses is essential for
successful implementation of
technology.
Access to Technology
Ensuring access to reliable
technology and internet
connectivity for nurses is critical.
Data breaches can
compromise
sensitive patient
information.Strong cybersecurity
measures and data
encryption protocols
are essential.Transparency
and patient
consent are
crucial for
safeguarding
privacy.
Patient Privacy and Data Security Concerns
Fear of the Unknown
Lack of Support
Focus on User-
Friendliness
Resistance to Change
and Adapting to New
Technologies
Improved
Patient
OutcomesEnhanced
EfficiencyInnovation and
Collaboration
Enhancing Patient Care and
Nursing Innovation
Improved
Patient Outcome
Technology empowers
nurses to deliver more
effective and
personalized care.
Enhanced
Efficiency
Digital tools streamline
workflows and improve
operational efficiency.
Innovation and
Collaboration
Technology fosters innovation and
collaboration among nurses and
other healthcare professionals.
Ethical
ConsiderationsData Integrity
and BiasHuman-Centered
Approach
Balancing Risks and Rewards
of Emerging Technologies