fluid therapy (treatment of shock)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
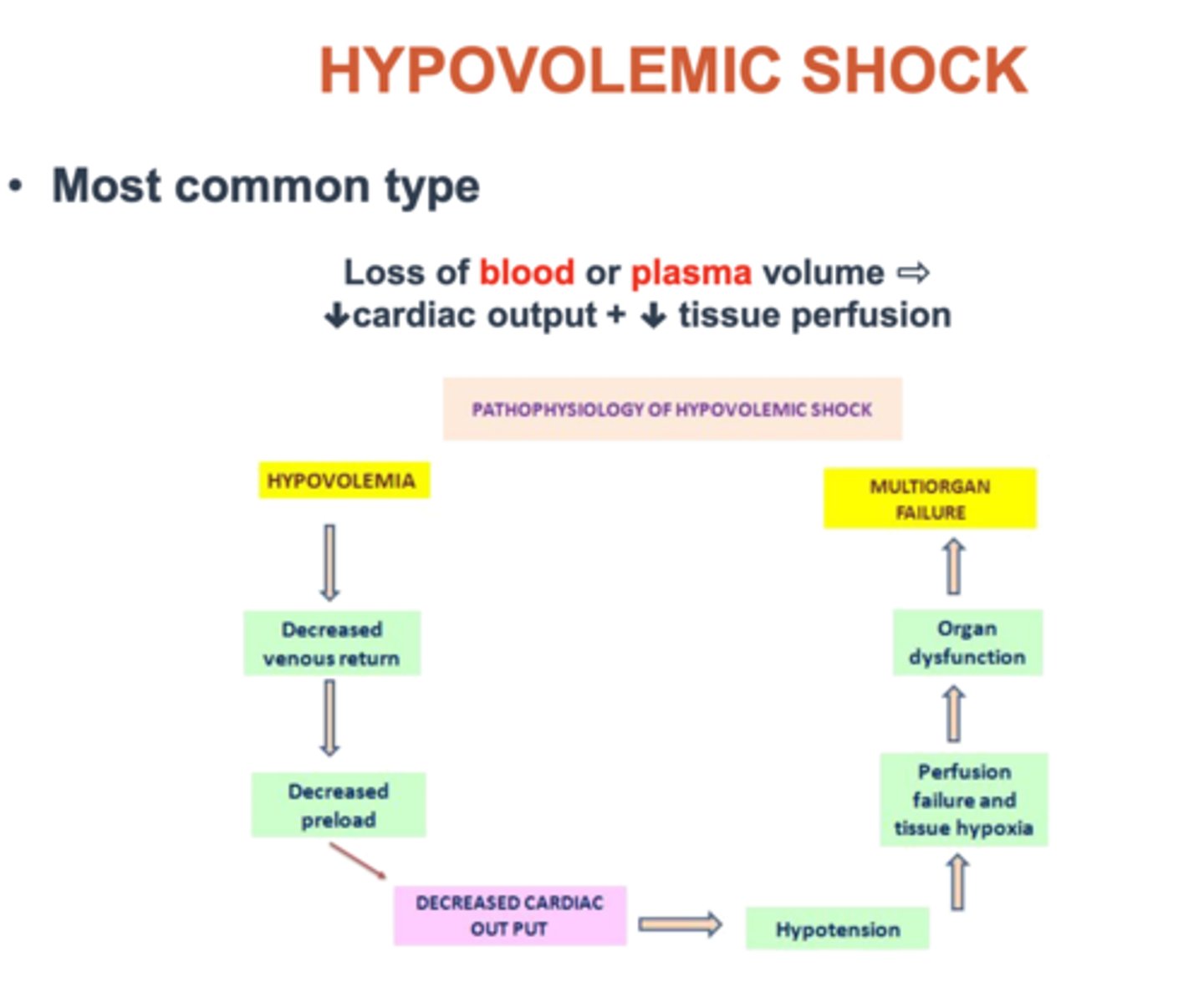
the most common type of shock is...
hypovolemic shock (due to loss of blood or plasma volume)
what can cause hypovolemic shock?
dehydration (ex-vomiting)
blood loss
spacing of fluids (edema)
what are the pathological consequences of hypovolemia?
there will be a low blood pressure, so there will be the activation of the sympathetic nervous system, causing tachycardia, peripheral vasoconstriction, and fluid retention (as compensatory mechanisms)
how does the organism try to compensate for hypovolemia?
activation of the sympathetic NS- tachycardia, vascoconstriction, fluid retention
how do we treat shock?
fluid therapy
what are the 2 types of fluids that might be used in fluid therapy?
colloids: mixture of 2 liquid (larger molecular weight molecules)
crystalloids: mixture of a solid dissolved in water (electrolyte solution)

what are crystalloids?
electrolytic solutions, containing solid+water.
there are hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic crystalloids.
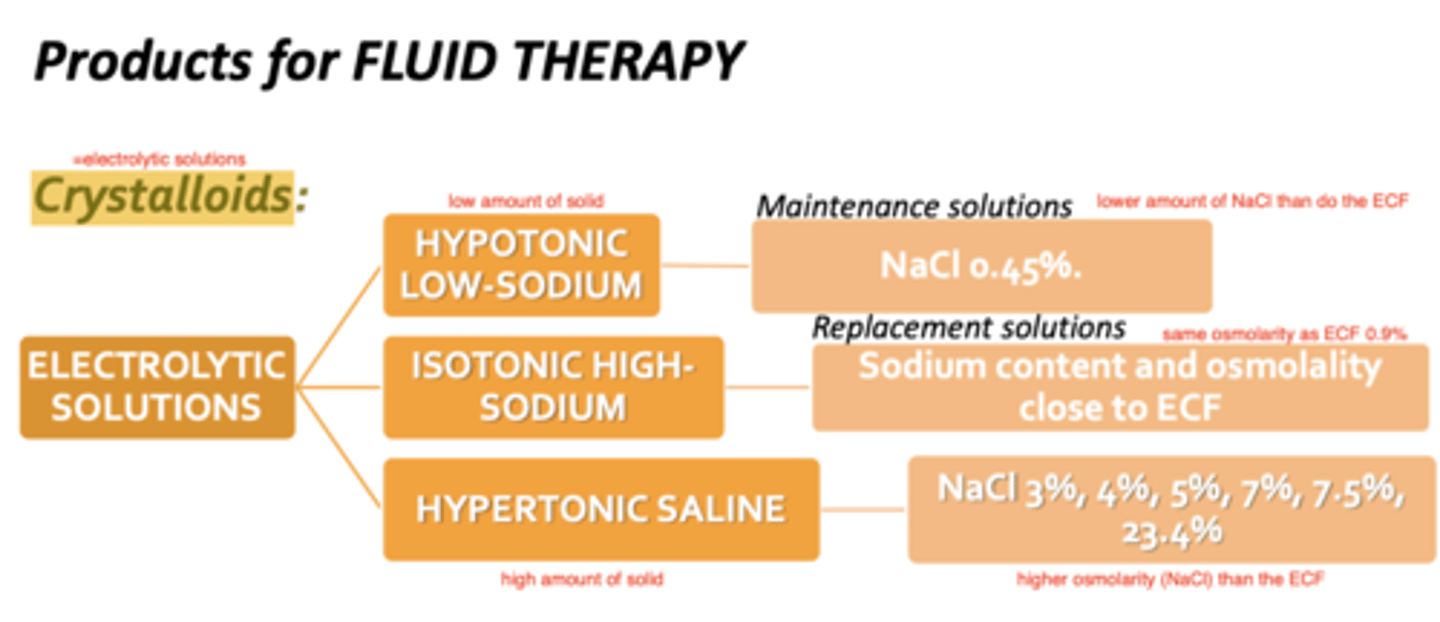
hypotonic crystalloids are known as ______ solutions. what is the main one we use?
maintenance
NaCl 0.45%
what type of solution is NaCl 0.45%?
a hypotonic crystalloid.
it has a lower amount of NaCl than the ECF.
what type of solution is NaCl 0.9%?
an isotonic crystalloid
it has the same osmolarity as ECF
isotonic crystalloids are known as ______ solutions. what is the main one we use?
replacement; NaCl 0.9%
hypertonic saline is composed of.......
NaCl 3%, 4%, 5%, 7%, 7.5%, or 23.4%
what are the uses of isotonic crystalloids?
shock
vomiting
diarrhea
we should be careful when using isotonic crystalloids in what patients?
patients that may have problems with sodium retention (heart or renal disease)
what is the use of hypotonic crystalloids?
to treat hypernatremia, shock, vomiting, or diarrhea in patients that might have a problem with sodium retention.
if a patient has severe diarrhea or vomiting or shock but we are worried they might have a problem with sodium retention, what type of crystalloid might we choose?
hypotonic crystalloids
which crystalloid- isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic, would we use to treat a patient with hypernatremia?
hypotonic crystalloids
which fluid is the best for treating hypovolemic shock rapidly?
hypertonic saline solutions (it causes fluid to move out of the intracellular/interstitial space and into the intravascular space)
what is the clinical use of hypertonic saline solutions?
hypovolemic shock
intracranial edema
which fluid should we use to treat intracranial edema?
hypertonic saline solution
what is the problem with the usage of hypertonic saline?
-the rapid administration may result in bradycardia and arrythmias
-cannot be used if the patient is dehydrated or has marked electrolyte disturbances
we should not use hypertonic saline solutions if the patient:
is dehydrated or has marked electrolyte disturbances
what are colloid solutions?
water + ions + large molecular weight molecules
they are composed of suspended particles of high PM (polysaccharides or synthetic proteins) that are unable to cross cell membranes, so they hold fluid in the vascular space and draw fluid from the interstitial space into the vascular space to expand the plasma volume
which type of solution is called a "plasma expander"?
colloid solutions.
this is because they are composed of suspended particles of high PM (polysaccharides or synthetic proteins) that are unable to cross cell membranes, so they hold fluid in the vascular space and draw fluid from the interstitial space into the vascular space to expand the plasma volume
do colloid solutions have a slow or rapid onset of action?
rapid, and long lasting
what are the uses of colloid solutions?
hypovolemia (not due to dehydration)
septic shock
hypoalbuminemia
what type of solution is used to treat hypoalbuminemia?
colloid
when would we choose to use a natural colloid? when would we choose to use a synthetic colloid?
natural- when the animal requires RBCs,
clotting factors, antithrombin
III, or albumin
synthetic- when the initial goal is to rapidly
improve perfusion in an animal with adequate RBCs
if an animal needs RBCs, clotting factors, albumin, or antithrombin III, what colloid (natural or synthetic) do we choose?
natural
if we want to rapidly improve perfusion in an animal with adequate RBCs, do we choose a natural or synthetic colloid?
synthetic
what are natural colloids?
blood products, obtained from species-specific donor animals (RBCs, plasma, platelets, albumin).
the most commonly used natural colloid solution is...
albumin
what type of solution is exogenous albumin?
natural colloid
what is important to do to albumin before administering it to the patient?
it is obtained from human plasma, so we must put it through an inactivation process to prevent the transmission of diseases
______ provides over 75% of the oncotic pressure of plasma
albumin
what is the natural function of albumin within the body?
maintaining intravascular colloid osmotic pressure
what colloids are plasma expanders of polysaccharide nature?
Dextran 70
Hydroxyethyl starch/ hetastarch
what is Dextran 70? what are its clinical uses?
a synthetic colloid (plasma expander) with osmotic effects similar to albumin.
it is used for thrombosis and pulmonary embolism (to expand the plasma and unblock the vessels), hypovolemia, and in cardiovascular surgery
what solution is used in cardiovascular surgery to temporarily maintain the colloidosmotic pressure?
Dextran 70
what is hydroxyethyl starch (HES) or hetastarch?
a plasma expander of polysaccharide nature, used to expand the plasma for a long period (12-36 hours).
it has few side effects and is used in hypovolemia and hypoproteinemia.
it is highly unstable in plasma, so is metabolized in the plasma by alpha-amylases
transforms the starch into glucose, so can increase the blood-glucose levels
Dextran 70 and hydroxyethal starch are both contraindicated in patients with...
coagulopathies
what adverse reactions are seen with use of hydroxyethyl starch?
although side effects are rare, it can produce anaphylactic reactions and hypervolemia
it also is not recommended in patients with coagulation disorders because it can cause a coagulation cascade
which, dextran 70 or hydroxyethyl starch has longer lasting effects?
hydroxyethyl starch (it lasts 12-36 hours, while Dextran 70 only lasts 4-8)
how is dextran 70 available?
6% solution in saline
6% solution in dextrose
which solution can be used to unblock vessels and expand plasma in thrombosis and pulmonary embolism?
Dextran 70
which is the plasma expander of protein nature that we can use in vet med?
gelatin
what is gelatin used for?
hypovolaemia and shock of various causes (haemorrhagic,
traumatic, septic)
which colloid is safe for patients with coagulation disorders?
gelatin
how do we administer gelatin?
IV
is gelatin rapidly or slowly eliminated?
rapidly, by the kidneys
does gelatin interfere with coagulation mechanisms?
no, but it can affect RBC aggregation and sedimentation rate
gelatin is obtained by..
hydrolysis of bovine collagen